Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae
Uploaded by
Park SunghoonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae
Uploaded by
Park SunghoonCopyright:
Available Formats
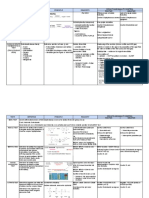
ENTEROBACTERIACEAE o Negative = colorless
- Often referred to as enterics 3. Hektoen Enteric Agar (HEA)
- Gram negative (-) - Inhibits normal flora coliforms
- Non-spore-forming - Differentiates LFs from NLFs
- Facultative anaerobe bacilli ➢ Bile salts – inhibit gram positive (+) bacteria
- All are oxidase negative (-) ➢ Carbohydrate source: lactose, sucrose,
o Except for: Plesiomonas (oxidase salicin
positive +) ➢ Indicator: Bromthymol blue
- All are catalase positive (+) ➢ Sulfur source: Sodium thiosulfate
- All are glucose fermenters (+) ➢ Detect H2S Production: Ferric ammonium
- All are motile (+) citrate
o Except for: SKY (Shigella, Klebsiella, o Blackening in the media
Yersinia) - Most non-pathogens ferment lactose and
o Klebsiella and Enterobacter – exhibits sucrose
mucoid colonies on plated media o Shows orange color (low pH)
o Proteus – swarming motility on o Green to orange – non-pathogenic
plated media - Pathogens (Salmonella and Shigella)
- EMBL MAC, HEA, XLD – media for o Green to blue green color with H2S
presumptive identification gas creating a black precipitate (no
fermentation)
SELECTIVE MEDIA FOR PRESUMPTIVE
IDENTIFICATION 4. Xylose-Lysine-Desoxycholate (XLD) Agar
- Selects for stool pathogens
1. MacConkey Agar - Differentiates xylose fermenters (yellow)
- Selects gram negative (-) bacteria from non-xylose fermenters (red)
- Differentiates lactose fermenters (LF) and - Selective for Salmonella and Shigella from
non-lactose fermenters (NLF) stool specimens
➢ Bile salts and crystal violet – inhibit gram ➢ Sodium deoxycholate – inhibit gram positive
positive (+) bacteria (+) cocci, gram negative (-) coliforms,
➢ Carbohydrate source: lactose swarming of Proteus
➢ Indicator: neutral red ➢ Detect decarboxylation – Lysine
➢ Lactose fermentation ➢ Carbohydrate source: Xylose
o Positive = pink ➢ Indicator: Phenol red
o Negative = colorless ➢ Sulfur source: Sodium thiosulfate
➢ Detect H2S: Ferric ammonium citrate
2. Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMB)
- Selects gram-negative bacteria 5. Salmonella-Shigella Agar
- Differentiates LFs from NLFs - Selects for stool pathogens
➢ Eosin and methylene blue – inhibit gram - Differentiates LFs (pink-red) from NLFs (clear)
positive (+) bacteria ➢ Bile salts and brilliant green agar – inhibit
➢ Differentiation on Fermentation – lactose geam positive (+), gram negative (-) coliforms
and sucrose ➢ Carbohydrate source: lactose
➢ Lactose fermentation ➢ Indicator: neutral red
o Positive = violet colonies ➢ Detect H2S: Ferric ammonium citrate
▪ E.coli = metallic green sheen
MAC EMB HEA XLD S-S
Inhibit gram (+) Bile salts and Eosin and Bile salts Sodium Bile salts and
bacteria crystal violet methylene blue deoxycholate brilliant green
agar
Carbohydrate Lactose Lactose Lactose Xylose Lactose
source Sucrose Sucrose
Salicin
Indicator Neutral red Bromthymol Phenol red Neutral red
blue
Detect Lysine
decarboxylation
Lactose (+) = pink (+) = violet Non-
fermentation (-) = colorless ❖ E. coli = pathogenic:
metallic Orange (low
green sheen pH)
(-) = colorless Green to
orange
Pathogenic
(Salmonella &
Shigella):
Green to blue
green
Sulfur source Sodium Sodium Sodium
thiosulfate thiosulfate thiosulfate
Detect H2S Ferric Ferric Ferric
Production ammonium ammonium ammonium
citrate citrate citrate
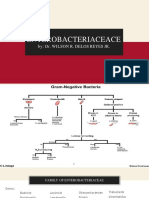
ENTEROBACTERIACEAE
H2S (+) UREASE (+) INDOLE (+) MR (-) VP (+) PD (+) MAN (-)
Edwardsielleae Citrobacteriaceae Escherichieae Klebsiellae Klebsiellae Proteeae Edwardsielleae
Citrobacteriaceae Klebsiellae Edwardsielleae
Salmonelleae Proteeae Citrobacteriaceae
Proteeae Yersiniae Proteeae
Yersiniae
You might also like
- Microbio Lab 8Document4 pagesMicrobio Lab 8api-3743217100% (5)
- Gram Negative Bacill1Document6 pagesGram Negative Bacill1IAN GABRIELLE MERCADO CUYNONo ratings yet
- Medically Important Bacteria Gram Negative - PPTX Filename UTF-8 Medically.Document104 pagesMedically Important Bacteria Gram Negative - PPTX Filename UTF-8 Medically.jethreel diosoNo ratings yet
- 12 EnterobacteriaciaeDocument29 pages12 EnterobacteriaciaeASECO LISH50% (2)
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument28 pagesEnterobacteriaceaewimarshana gamage100% (1)
- Agars & TestsDocument73 pagesAgars & Testssana khanNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae Handout (Lec & Lab)Document15 pagesEnterobacteriaceae Handout (Lec & Lab)Lucille MarieNo ratings yet
- Practical Bacteriology Laboratory Manual: Prepared byDocument37 pagesPractical Bacteriology Laboratory Manual: Prepared bysalamon2tNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative EntericDocument30 pagesGram Negative EntericJohn Emmanuel TayagNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Practical Explanation: Gastroenterohepatology System 2014Document63 pagesMicrobiology Practical Explanation: Gastroenterohepatology System 2014ZackychunNo ratings yet
- (Microbio) Enterobacteriaceae-Dr. Natividad (Mulan)Document11 pages(Microbio) Enterobacteriaceae-Dr. Natividad (Mulan)Lee Delos Santos100% (4)
- Salmonella and Listeria 2Document11 pagesSalmonella and Listeria 2Gurpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- 16 Chapter19 Enterobacteriaceae 121004141132 Phpapp01Document105 pages16 Chapter19 Enterobacteriaceae 121004141132 Phpapp01Yelsin Denis Fabian AmbrosioNo ratings yet
- E. Coli and K. PneumoniaDocument26 pagesE. Coli and K. PneumoniamryamNo ratings yet
- Hektoen Enteric Agar (HEA) : S Indicator: Ferric Ammonium Citrate (Producing Black Precipitate DueDocument3 pagesHektoen Enteric Agar (HEA) : S Indicator: Ferric Ammonium Citrate (Producing Black Precipitate Dueguerlain sagunNo ratings yet
- Bacte TestDocument10 pagesBacte TestRiondalionNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae: Biochemical ReactionsDocument20 pagesEnterobacteriaceae: Biochemical Reactionslindaprihastiwi100% (1)
- Microbiology ReviewerDocument8 pagesMicrobiology ReviewerSteph Vee100% (7)
- 11.1 Enterobacteriaceae Quick NotesDocument5 pages11.1 Enterobacteriaceae Quick Notescolleges660No ratings yet
- Enterics Reviewer For MicrobiologyDocument8 pagesEnterics Reviewer For MicrobiologyGea MarieNo ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument81 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAEAyessa VillacorteNo ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument6 pagesCulture MediaAlanah JaneNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lab 8Document4 pagesMicrobio Lab 8Amrit KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Bacte MidtermDocument40 pagesBacte MidtermTrangia, SharmaineNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Identification of Enteric OrganismsDocument7 pagesIsolation and Identification of Enteric OrganismsCzarina Charmaine DiwaNo ratings yet
- Lezon 4Document3 pagesLezon 4Idk UlitNo ratings yet
- Tests For Identification of Bacteria ASSDocument4 pagesTests For Identification of Bacteria ASSkrisNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Identification of Gram (-) Bacteria: I. Carbohydrate UtilizationDocument4 pagesBiochemical Identification of Gram (-) Bacteria: I. Carbohydrate UtilizationprincessNo ratings yet
- Lab Group Disc Suzea and ErikaDocument14 pagesLab Group Disc Suzea and ErikaJaneNo ratings yet
- Pseudomonaceae, Vibrionaceae, AeromonadaceaezDocument39 pagesPseudomonaceae, Vibrionaceae, AeromonadaceaezMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Bacte Lab Final PracticalDocument24 pagesBacte Lab Final PracticalJenelle Jane QuilanetaNo ratings yet
- Proteus SPDocument3 pagesProteus SPImelda HamdiniNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative BacilliDocument1 pageGram Negative BacilliDe Guzman E AldrinNo ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceace Part 1Document48 pagesEnterobacteriaceace Part 1Krenz CatiboNo ratings yet
- Non-Fermenting and Miscellaneous Gram Negative BacilliDocument33 pagesNon-Fermenting and Miscellaneous Gram Negative BacilliLin Sison Vitug100% (1)
- Bacterial Indentification (Micro)Document19 pagesBacterial Indentification (Micro)Aryaman MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Vibrionaceae: 1. V. CholoraeDocument7 pagesVibrionaceae: 1. V. CholoraeKLIPPNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests Enterobacteria IdentificationDocument10 pagesBiochemical Tests Enterobacteria IdentificationArleen MatincaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab (Midterms) : November 2015 Dr. Mark CalbanDocument3 pagesMicrobiology Lab (Midterms) : November 2015 Dr. Mark Calbanrichmarkconag1No ratings yet
- Enterobacteriaceae Si Teste BiochimiceDocument83 pagesEnterobacteriaceae Si Teste BiochimiceAlle BedereagNo ratings yet
- 18.1-FAMILY ENTEROBACTERIACEAE and TESTSDocument2 pages18.1-FAMILY ENTEROBACTERIACEAE and TESTSJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- FrenchFries MmemonicsDocument5 pagesFrenchFries MmemonicsromeroroakylarNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Bacteria: EnterobacteriaceaeDocument55 pagesGram Negative Bacteria: EnterobacteriaceaeMaria Camille GasparNo ratings yet
- SS AgarDocument2 pagesSS AgaroktaNo ratings yet
- LAB 8 - Salmonella & ShigellaDocument25 pagesLAB 8 - Salmonella & Shigellasajad abasNo ratings yet
- Glucose Broth With Durham TubesDocument7 pagesGlucose Broth With Durham TubesJAN CAMILLE OLIVARESNo ratings yet
- Test Media Purpose Components Reagents Expected Result Quality Control Gram StainDocument7 pagesTest Media Purpose Components Reagents Expected Result Quality Control Gram StainAngelNo ratings yet
- Microbio Lab 7 (Leigh)Document8 pagesMicrobio Lab 7 (Leigh)api-3743217100% (6)
- CulturenewDocument78 pagesCulturenewsillythings300No ratings yet
- Culture MediaDocument2 pagesCulture MediaJobelleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleDocument23 pagesLesson 3 Quality Control Sterilization and Disinfection ModuleTinNo ratings yet
- EnterobakteriaDocument41 pagesEnterobakteriaMuhammad MirzaNo ratings yet
- Bacte Methods Part II of Part IIDocument3 pagesBacte Methods Part II of Part IILea Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument8 pagesEnterobacteriaceaeWansun MaglangitNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY NO. 6-Color Reactions of ProteinsDocument12 pagesACTIVITY NO. 6-Color Reactions of ProteinsReano Zendrix Perez AndresNo ratings yet
- After Addition of Ether/xylene Negative: Just Yellow: All Tests Must Have A ControlDocument4 pagesAfter Addition of Ether/xylene Negative: Just Yellow: All Tests Must Have A ControlgurbyfuryNo ratings yet
- D 5008 - 01 - RduwmdgDocument4 pagesD 5008 - 01 - RduwmdgHHans MSilvaNo ratings yet
- CPI PD 1 ChE Refresher Nov 2017 ExamDocument52 pagesCPI PD 1 ChE Refresher Nov 2017 ExamPaulo Emmanuele BetitaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Extraction of ElementsDocument32 pagesModule 1 Extraction of Elementsnawal2007No ratings yet
- Chapter 3.4 and 4Document65 pagesChapter 3.4 and 4Kyla Gabrielle TutoNo ratings yet
- Dehydrate Castor OilDocument1 pageDehydrate Castor OilherryNo ratings yet
- Additional Numerical BufferDocument2 pagesAdditional Numerical BufferPrahlad DasNo ratings yet
- Conductor and SuperconductorDocument12 pagesConductor and Superconductorankesh_ghoghariNo ratings yet
- Sewage Sludge Ash (SSA) PR CementDocument5 pagesSewage Sludge Ash (SSA) PR CementMAHESH A VNo ratings yet
- Chapter 07Document47 pagesChapter 07AC BañaresNo ratings yet
- DCG Recording With Red LightDocument10 pagesDCG Recording With Red LightMaximoNo ratings yet
- Chemical Resistance Selection Chart For Protective GlovesDocument2 pagesChemical Resistance Selection Chart For Protective GlovesSaad QaiserNo ratings yet
- Applied Inorganic Chemistry: Rainer Pöttgen, Thomas Jüstel, Cristian A. Strassert (Eds.)Document526 pagesApplied Inorganic Chemistry: Rainer Pöttgen, Thomas Jüstel, Cristian A. Strassert (Eds.)d1g1tal3rNo ratings yet
- Baroid Basic Mud Engineering 4Document11 pagesBaroid Basic Mud Engineering 4Alexander KlmNo ratings yet
- Magnesium Chloride HexahydrateDocument2 pagesMagnesium Chloride HexahydratekrutNo ratings yet
- Production of Carotenoids From Rhodotorula Mucilaginosa and Their Applications As Colorant Agent in Sweet CandyDocument7 pagesProduction of Carotenoids From Rhodotorula Mucilaginosa and Their Applications As Colorant Agent in Sweet CandyEspinosa Balderas GenaroNo ratings yet
- QP Biology Sample Paper Mumbai Region 2022-23Document7 pagesQP Biology Sample Paper Mumbai Region 2022-23SATYAM RASTOGINo ratings yet
- Desalination: Zhi Chien NG, Woei Jye Lau, Ahmad Fauzi IsmailDocument11 pagesDesalination: Zhi Chien NG, Woei Jye Lau, Ahmad Fauzi IsmailSK SahooNo ratings yet
- Module 2 CementDocument20 pagesModule 2 CementKamil ShairNo ratings yet
- Fantasy WritingDocument4 pagesFantasy Writingapi-636811605No ratings yet
- Choudhary Et Al 2021Document15 pagesChoudhary Et Al 2021Patrick MinusculliNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Organic ChemistryDocument52 pagesBasic Concept of Organic ChemistrySushan KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation Techniques and Their PerpectivesDocument60 pagesBioremediation Techniques and Their PerpectivesAdamNo ratings yet
- Applsci 13 08240Document17 pagesApplsci 13 08240Aris NasNo ratings yet
- Chapter5-Kesetimbangan Asam BasaDocument115 pagesChapter5-Kesetimbangan Asam BasaAnnisah MardiyyahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - Shobhit NirwanDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- PET Recycle Case StudyDocument5 pagesPET Recycle Case StudyIndustria ProyectosNo ratings yet
- PRPC Ch-6 NotesDocument23 pagesPRPC Ch-6 Noteslakshya chovatiaNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Importance of Algae: ReviewDocument11 pagesAgricultural Importance of Algae: ReviewNelson NicolasNo ratings yet
- 5070 s06 QP 1Document16 pages5070 s06 QP 1Sherlock Wesley ConanNo ratings yet
- Granlux For Green Bio-CosmeticsDocument13 pagesGranlux For Green Bio-CosmeticsKirk BorromeoNo ratings yet