Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
GREEN BOXCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
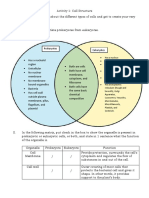
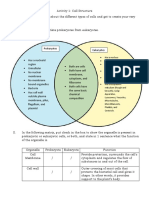
- Lab Report Bio460: Name: Siti Nur Aqilah Binti Asrul MATRIX NO.: 2020963825 Class: AS2011ADocument8 pagesLab Report Bio460: Name: Siti Nur Aqilah Binti Asrul MATRIX NO.: 2020963825 Class: AS2011ASITI NUR AQILAH ASRULNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDocument3 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name Classparesh patel67% (3)
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TransportDocument4 pagesCell Structure and TransportAena Valerie CaalimNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONDocument15 pagesBenjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONboobooNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3raja11160No ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2Document13 pages02 Handout 2Janna AngelesNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in BetweenDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in Between04Annisa PutrianeNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyMason DeidriNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- 1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIODocument25 pages1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIOedensatire21No ratings yet
- Cells VIS ChartDocument1 pageCells VIS Chartdidua08No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Document3 pagesProkaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Anime KpopNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Asa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaDocument1 pageAsa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaMary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal CellMaria AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells NotesDocument7 pagesBio Cells Notesnabita20211No ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument15 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEMaic Audolin SihombingNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument5 pagesPlant CellEster Ariza CruzadoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- Assignment Cell - ANSDocument3 pagesAssignment Cell - ANSAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cell & Binomial NomenclatureDocument6 pagesCell & Binomial NomenclatureVenice De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Topic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellDocument2 pagesTopic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellJonalyn OcampoNo ratings yet
- Act 2CDocument3 pagesAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument4 pages1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotescarlNo ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Chromosomes RibosomesDocument2 pagesCell Wall Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Chromosomes RibosomesRodtuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument7 pagesLesson 4 - Cell Parts and Functionshakuna matataNo ratings yet
- Las #6 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #6 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (ZNotes) MYPDocument65 pagesBio Notes (ZNotes) MYPkimaaya vermaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Its StucturesDocument7 pagesCell Organelles and Its StucturesHailey Eisleen LazaroNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyKent TediosNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument1 pageCell Structurekivepe9583No ratings yet
- Biology Bmat Section 2Document20 pagesBiology Bmat Section 2celiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument7 pagesCellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellAlexa MacailoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument15 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEwarod19658No ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle CardsDocument6 pagesCell Organelle CardsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellGlenda ArajaNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoNo ratings yet
- Sel Dan JaringanDocument1 pageSel Dan JaringanBakhitah Nurul100% (1)
- Eukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Document4 pagesEukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Dharyl FloresNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE Chapter 3Document18 pagesCELL STRUCTURE Chapter 3Micaela BobierNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fAinaraNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie Jaiswal100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument24 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesVassalyn Su ThatNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDocument5 pages2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNo ratings yet
- Organelle With Solution 2022-23Document1 pageOrganelle With Solution 2022-23LuLaMejorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their Functionsllena llenaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Careers PosterDocument1 pageCareers PosterGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Preamble of The ConstitutionDocument1 pagePreamble of The ConstitutionGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Acids Acid Strength and ConcentrationDocument1 pageA Guide To Acids Acid Strength and ConcentrationGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- HUMAN ANATOMY Single FrameDocument1 pageHUMAN ANATOMY Single FrameGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Kindle 3Document1 pageKindle 3GREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- A Brief Guide To Atmospheric PollutantsDocument1 pageA Brief Guide To Atmospheric PollutantsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Biodegradable PlasticsDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Biodegradable PlasticsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- SymmetryDocument1 pageSymmetryGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Notes Solid Geometry 2 PDFDocument1 pageNotes Solid Geometry 2 PDFGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- PostersDocument1 pagePostersGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Xyz Trifold Brochure FinalDocument2 pagesXyz Trifold Brochure FinalGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Poultry HousingDocument13 pagesPoultry HousingGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Sangam DairyDocument2 pagesSangam DairyGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Constants in PhysicsDocument9 pagesConstants in PhysicsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- English Plant NurseryDocument106 pagesEnglish Plant NurseryGREEN BOX100% (1)
- Form 2 Homework Chapter 1 Note1.-1Document3 pagesForm 2 Homework Chapter 1 Note1.-1jasmine tNo ratings yet
- 1 - BIO-Identify The Components of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument3 pages1 - BIO-Identify The Components of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsCarlo ThornappleNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis For Behavior ResourcesDocument34 pagesBiological Basis For Behavior ResourcesTimothy PettineNo ratings yet
- Bioteknologi Farmasi PendahuluanDocument65 pagesBioteknologi Farmasi PendahuluanNadhifa MukarommNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatic CoursesDocument2 pagesBioinformatic Coursesdenilw100% (1)
- Module 7 RationaleDocument2 pagesModule 7 RationaleG INo ratings yet
- Treatment of Localized Aggressive Periodontitis With Platelet-Rich Plasma and Bone Allograft. Clinical Case ReportDocument8 pagesTreatment of Localized Aggressive Periodontitis With Platelet-Rich Plasma and Bone Allograft. Clinical Case ReportLori SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Zoology Science Course at NIMS University JaipurDocument5 pagesPh.D. Zoology Science Course at NIMS University JaipurstepincollegeNo ratings yet
- Gerald Huether - Neurobiological Preconditions ForDocument7 pagesGerald Huether - Neurobiological Preconditions ForAcademixNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker: Authorized/approved VaccinesDocument8 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Tracker: Authorized/approved VaccinestucchaNo ratings yet
- HES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-3Document1 pageHES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-3bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Ap - Breed ChickenDocument20 pagesAp - Breed ChickenWynnie RondonNo ratings yet
- PHP2018Document25 pagesPHP2018radu nicolaeNo ratings yet
- The Fetal Period: by DR - Abdallah GreeballahDocument55 pagesThe Fetal Period: by DR - Abdallah GreeballahrawanNo ratings yet
- Marker TDS-MW-1700-10Document2 pagesMarker TDS-MW-1700-10Anny LovibNo ratings yet
- BGIDocument7 pagesBGIGuneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- Worksheets: Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesWorksheets: Digestive SystemAbigailBarrionGutierrezNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & LeavesDocument38 pagesPhotosynthesis & LeavesSanthoshNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.2 Karyogram PracticeDocument2 pagesTopic 3.2 Karyogram PracticeAleksandra LukanovskaNo ratings yet
- h24 Dstrainingguide Usen Rev03Document5 pagesh24 Dstrainingguide Usen Rev03Elisan BrasilNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Pharmacy YearSession 2022-2023-MAY-FINAL REGULAR Term 2 Term ReportDocument2 pagesDiploma in Pharmacy YearSession 2022-2023-MAY-FINAL REGULAR Term 2 Term Report2506sanjaydwivediNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Industrial BiotechnologyDocument29 pagesB.Sc. Industrial BiotechnologyDawnNo ratings yet
- MRNA Assay Development Summit BrochureDocument9 pagesMRNA Assay Development Summit BrochureAbhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Characteristics of Human Population: by Group 4Document9 pagesNature and Characteristics of Human Population: by Group 4Michelle Gutierrez SibayanNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Beta OxidationDocument59 pagesFatty Acid Beta OxidationEve YapNo ratings yet
- Science6 - q2 - CLAS6 - Interactions Among Living Things and Nonliving Things - v6 - Liezl ArosioDocument11 pagesScience6 - q2 - CLAS6 - Interactions Among Living Things and Nonliving Things - v6 - Liezl ArosioJeffrey VigonteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Modern Biology, Characteristics of LifeDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Modern Biology, Characteristics of LifeAizabelle FerrerasNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in Marrow Reading ICH PDFDocument16 pagesGuidelines in Marrow Reading ICH PDFsidNo ratings yet
Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
GREEN BOXOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
GREEN BOXCopyright:
Available Formats
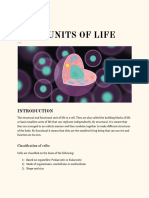
Cells - The Basic Units of Life
NANDAN INFOGRAPHICS
The cell is the basic building block of all living
organisms. It is the smallest unit of an organism that
can carry out the functions of life. Robert Hooke was
one of the first people to observe cells using his own
compound microscope in 1663.
Some cells are single, bacteria self-sustaining organisms
such as amoebas and bacteria; others cells are part of
multicellular organisms and cannot survive alone.
Ribosomes Bacteria Amoeba Paramecium
Cell wall
Bacteria are the most abundant organisms on Earth. They thrive in diverse
DNA conditions and places, including our bodies. Bacteria are single celled
organisms. They are considered prokaryotes, since their DNA is in the
Cell membrane cytoplasm and not within a nucleus.
Bacteria
Animal Cell Nucleus is the control center of the
cell. It houses the nucleolus and the
Nuclear pores allow materials to
pass in and out of the nucleus.
The structures within the cell genetic material (chromatin). Nucleolus is the site where
are known as organelles which ribosomes are made.
carry out specific functions.
Nuclear envelope is a
membrane which surrounds
Chromatin contains the genetic and protects the nucleus.
material that is used for
directing the cell functions. Endoplasmic reticulum is a
transport system of tubes
Cytoplasm is a gel-like substance and channels connecting
containing the organelles. organelles in the cell.
Golgi bodies are organelles that Ribosomes are the factories
direct different materials made in that produce proteins
the cell to where they need to go. needed by the cell.
Lysosome contains chemicals Mitochondrion is a rod like
(enzymes) that break down and structure that converts the
recycle harmful materials. energy in food molecules to a
form that the cell can use.
Cell membrane is the gate keeper of
the cell that controls the passage of
materials into and out of the cell.
Inside Cell
Glycoprotein
Plant Cell
Vacuoles are sacs that
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll
contain water and store
which captures energy from the
nutrients and waste
Sun and uses it to produce food
Lipid b products.
ilayer for the plant in a process known
as photosynthesis.
Outside Cell Protein
Cell wall is a rigid outer
layer of plant cells that
provides support.
Specialized Cells
The human body consists of trillions of cells, including some
200 different cell types that vary greatly in size, shape, and
function. Sperm cells are the tiniest human cells, a few
micrometers wide (1/12,000 of an inch); whereas the longest
cells, the neurons that run from the tip of the big toe to the
spinal cord, can be as long as several feet in an average adult!
Skin cells Nerve cell Blood cells
(neuron)
You might also like
- Lab Report Bio460: Name: Siti Nur Aqilah Binti Asrul MATRIX NO.: 2020963825 Class: AS2011ADocument8 pagesLab Report Bio460: Name: Siti Nur Aqilah Binti Asrul MATRIX NO.: 2020963825 Class: AS2011ASITI NUR AQILAH ASRULNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDocument3 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name Classparesh patel67% (3)
- Organelle Present/Absent Description FunctionDocument5 pagesOrganelle Present/Absent Description FunctionTania BacsinNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and TransportDocument4 pagesCell Structure and TransportAena Valerie CaalimNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer 2Document3 pagesAnaphy Reviewer 2Christopher Valle ArgelNo ratings yet
- Benjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONDocument15 pagesBenjamin Watson - Summer PiXL Gateway Biology - Cells TRANSITIONboobooNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Activity 1Document4 pagesActivity 1sharksiedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document22 pagesLecture 3raja11160No ratings yet
- Premidterms NotesDocument4 pagesPremidterms NotesRenee Andrei Concepcion MozarNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Module 3Document7 pagesGen Bio Module 3Jann Ranniel PanlilioNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2Document13 pages02 Handout 2Janna AngelesNo ratings yet
- Basic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismDocument2 pagesBasic Building Blocks of Life Smallest Living Unit of An OrganismkikomagsaysayNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in BetweenDocument1 pageAnimal Cell Structure: The Cell Membrane, Nucleus, Cytoplasm, and Everything in Between04Annisa PutrianeNo ratings yet
- What Are Cell OrganellesDocument19 pagesWhat Are Cell OrganellesMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyMason DeidriNo ratings yet
- Lesso N 2: Organe LlesDocument19 pagesLesso N 2: Organe LlesMicha E.No ratings yet
- 1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIODocument25 pages1.2 The Two Types of Cells 12BIOedensatire21No ratings yet
- Cells VIS ChartDocument1 pageCells VIS Chartdidua08No ratings yet
- Prokaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Document3 pagesProkaryotes: "Good or True Nuclei."Anime KpopNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Gen BioDocument3 pagesModule 2 Gen BioZirah Lee ValledorNo ratings yet
- Asa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaDocument1 pageAsa Double-Membraned Eukaryotic Cell Organelle That Contains The Genetic Material. The Nucleus Has Two Major Functions: It Stores The Cell's Genetic Material, or DnaMary Pauline G. CamposNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal CellMaria AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Cell NotesDocument7 pagesCell NotesBrohi NadeemNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells NotesDocument7 pagesBio Cells Notesnabita20211No ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument15 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEMaic Audolin SihombingNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument5 pagesPlant CellEster Ariza CruzadoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesDocument6 pagesStructure and Functions of Cells: RibosomesShakib al molik100% (1)
- Assignment Cell - ANSDocument3 pagesAssignment Cell - ANSAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Cell & Binomial NomenclatureDocument6 pagesCell & Binomial NomenclatureVenice De los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Topic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellDocument2 pagesTopic Subtopic: Eukaryotic CellJonalyn OcampoNo ratings yet
- Act 2CDocument3 pagesAct 2CCHARLIENE FAYE ASPRERNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument4 pages1.3.1 - Differences Between Eukaryotes and ProkaryotescarlNo ratings yet
- Acp1 ActDocument6 pagesAcp1 ActAldrin VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Chromosomes RibosomesDocument2 pagesCell Wall Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus Chromosomes RibosomesRodtuNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Cell Parts and FunctionsDocument7 pagesLesson 4 - Cell Parts and Functionshakuna matataNo ratings yet
- Las #6 AttachmentDocument4 pagesLas #6 AttachmentShmaira Ghulam RejanoNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes (ZNotes) MYPDocument65 pagesBio Notes (ZNotes) MYPkimaaya vermaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Its StucturesDocument7 pagesCell Organelles and Its StucturesHailey Eisleen LazaroNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument22 pagesBiologyKent TediosNo ratings yet
- Bio Cells ReviewerDocument4 pagesBio Cells ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument6 pagesCell StructureZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument1 pageCell Structurekivepe9583No ratings yet
- Biology Bmat Section 2Document20 pagesBiology Bmat Section 2celiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyDocument7 pagesCellular Biology: Cell Structure and TaxonomyFelyn Roseann AretaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellAlexa MacailoNo ratings yet
- Detailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEDocument15 pagesDetailed Notes - Topic 1 Key Concepts in Biology - Edexcel Biology GCSEwarod19658No ratings yet
- A Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneDocument3 pagesA Specialized Structure Occurring in Most Cells and Separated From The Rest of The Cell by A Double Layer, The Nuclear MembraneGian Carlo MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelle CardsDocument6 pagesCell Organelle CardsVienne MonroidNo ratings yet
- CellDocument5 pagesCellGlenda ArajaNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganelleDocument9 pagesCell OrganelleGwencytech DomingoNo ratings yet
- Sel Dan JaringanDocument1 pageSel Dan JaringanBakhitah Nurul100% (1)
- Eukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Document4 pagesEukaryotic Cell Parts and Functions (Flores)Dharyl FloresNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE Chapter 3Document18 pagesCELL STRUCTURE Chapter 3Micaela BobierNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGYDocument5 pagesMICROBIOLOGYCia RraNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Activiities - Ainaratorres3fAinaraNo ratings yet
- Cells: by - NatalieDocument24 pagesCells: by - NatalieNatalie Jaiswal100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesDocument24 pagesChapter 2: Structure of Cells and OrganellesVassalyn Su ThatNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation of The Organism NotesDocument5 pages2 Organisation of The Organism Notesarayana sharmaNo ratings yet
- Organelle With Solution 2022-23Document1 pageOrganelle With Solution 2022-23LuLaMejorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - Cell Structures and Their Functionsllena llenaNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Careers PosterDocument1 pageCareers PosterGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Preamble of The ConstitutionDocument1 pagePreamble of The ConstitutionGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Acids Acid Strength and ConcentrationDocument1 pageA Guide To Acids Acid Strength and ConcentrationGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- HUMAN ANATOMY Single FrameDocument1 pageHUMAN ANATOMY Single FrameGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Kindle 3Document1 pageKindle 3GREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- A Brief Guide To Atmospheric PollutantsDocument1 pageA Brief Guide To Atmospheric PollutantsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Biodegradable PlasticsDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Biodegradable PlasticsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- SymmetryDocument1 pageSymmetryGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Notes Solid Geometry 2 PDFDocument1 pageNotes Solid Geometry 2 PDFGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- PostersDocument1 pagePostersGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Xyz Trifold Brochure FinalDocument2 pagesXyz Trifold Brochure FinalGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Poultry HousingDocument13 pagesPoultry HousingGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Sangam DairyDocument2 pagesSangam DairyGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- Constants in PhysicsDocument9 pagesConstants in PhysicsGREEN BOXNo ratings yet
- English Plant NurseryDocument106 pagesEnglish Plant NurseryGREEN BOX100% (1)
- Form 2 Homework Chapter 1 Note1.-1Document3 pagesForm 2 Homework Chapter 1 Note1.-1jasmine tNo ratings yet
- 1 - BIO-Identify The Components of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsDocument3 pages1 - BIO-Identify The Components of The Nervous, Endocrine, and Reproductive SystemsCarlo ThornappleNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis For Behavior ResourcesDocument34 pagesBiological Basis For Behavior ResourcesTimothy PettineNo ratings yet
- Bioteknologi Farmasi PendahuluanDocument65 pagesBioteknologi Farmasi PendahuluanNadhifa MukarommNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatic CoursesDocument2 pagesBioinformatic Coursesdenilw100% (1)
- Module 7 RationaleDocument2 pagesModule 7 RationaleG INo ratings yet
- Treatment of Localized Aggressive Periodontitis With Platelet-Rich Plasma and Bone Allograft. Clinical Case ReportDocument8 pagesTreatment of Localized Aggressive Periodontitis With Platelet-Rich Plasma and Bone Allograft. Clinical Case ReportLori SimmonsNo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Zoology Science Course at NIMS University JaipurDocument5 pagesPh.D. Zoology Science Course at NIMS University JaipurstepincollegeNo ratings yet
- Gerald Huether - Neurobiological Preconditions ForDocument7 pagesGerald Huether - Neurobiological Preconditions ForAcademixNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker: Authorized/approved VaccinesDocument8 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Tracker: Authorized/approved VaccinestucchaNo ratings yet
- HES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-3Document1 pageHES 032 - SAS 1 - Merged-3bangtanswifue -No ratings yet
- Ap - Breed ChickenDocument20 pagesAp - Breed ChickenWynnie RondonNo ratings yet
- PHP2018Document25 pagesPHP2018radu nicolaeNo ratings yet
- The Fetal Period: by DR - Abdallah GreeballahDocument55 pagesThe Fetal Period: by DR - Abdallah GreeballahrawanNo ratings yet
- Marker TDS-MW-1700-10Document2 pagesMarker TDS-MW-1700-10Anny LovibNo ratings yet
- BGIDocument7 pagesBGIGuneyden GuneydenNo ratings yet
- Worksheets: Digestive SystemDocument9 pagesWorksheets: Digestive SystemAbigailBarrionGutierrezNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & LeavesDocument38 pagesPhotosynthesis & LeavesSanthoshNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.2 Karyogram PracticeDocument2 pagesTopic 3.2 Karyogram PracticeAleksandra LukanovskaNo ratings yet
- h24 Dstrainingguide Usen Rev03Document5 pagesh24 Dstrainingguide Usen Rev03Elisan BrasilNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Pharmacy YearSession 2022-2023-MAY-FINAL REGULAR Term 2 Term ReportDocument2 pagesDiploma in Pharmacy YearSession 2022-2023-MAY-FINAL REGULAR Term 2 Term Report2506sanjaydwivediNo ratings yet
- B.Sc. Industrial BiotechnologyDocument29 pagesB.Sc. Industrial BiotechnologyDawnNo ratings yet
- MRNA Assay Development Summit BrochureDocument9 pagesMRNA Assay Development Summit BrochureAbhi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Characteristics of Human Population: by Group 4Document9 pagesNature and Characteristics of Human Population: by Group 4Michelle Gutierrez SibayanNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Beta OxidationDocument59 pagesFatty Acid Beta OxidationEve YapNo ratings yet
- Science6 - q2 - CLAS6 - Interactions Among Living Things and Nonliving Things - v6 - Liezl ArosioDocument11 pagesScience6 - q2 - CLAS6 - Interactions Among Living Things and Nonliving Things - v6 - Liezl ArosioJeffrey VigonteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Modern Biology, Characteristics of LifeDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Modern Biology, Characteristics of LifeAizabelle FerrerasNo ratings yet
- Guidelines in Marrow Reading ICH PDFDocument16 pagesGuidelines in Marrow Reading ICH PDFsidNo ratings yet