Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 3.2
Unit 3.2
Uploaded by
luciagarper1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 3.2
Unit 3.2
Uploaded by
luciagarper1Copyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 3.
Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
U3.
HUMAN BODY
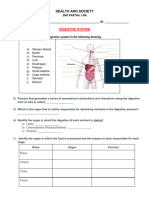
1. COMPLETE.
READ the description of the functions of each body system, IDENTIFY the system and
LABEL each.
Circulatory System Endocrine System Muscular System
Urinary System Respiratory System Reproductive System
Skeletal System Digestive System Lymphatic System
Nervous System Skin (Integumentary System
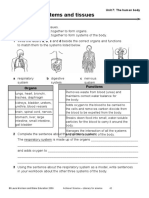
A)_RESPIRATORY SYSTEM__________________. The purpose of this system is to take in
air, filter it and take it to the tissues responsible for gas exchange. Oxygen is then transported
by the blood to all the tissues in the body. Carbon Dioxide, a waste product, is reabsorbed into
the blood and then excreted from the body.
B) _SKELETAL SYSTEM___________________. This system forms the basic framework of
the body –it supports and protects all the internal organs. Bones serve as levers
PALANCA(with the attached muscles) for movement, produce blood cells and store calcium
salts which can be absorbed into the blood when there is not enough calcium in the diet.
C) _ENDOCRINE SYSTEM____________________. The secretion of hormones which
regulate the body’s functions chemically, is the function of this system.
D) _URINARY SYSTEM_______________________. This system is also called “the
excretory system” and filters body liquids, eliminating chemicals and excess fluids from the
body.
E) __CIRCULATORY SYSTEM_______________________. This system contains an
important organ which pumps blood around the entire body. This is necessary to supply cells
with nutrients and oxygen and to transport waste products for excretion.
F)______REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM__________________. This system is essential for
reproduction and the production of hormones, sex cells (gametes) and it also enables
conception and permits the carrying and birth of babies (offspring).DESCENDENCIA
G) _DIGESTIVE SYSTEM______________________. The system which converts (changes)
food into simpler substances for the cells to use for energy also takes away (or eliminates)
waste products from the body.
H) ___SKIN/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM_____________________. This complex system
which is also thought of as an organ, protects the body from disease, helps to regulate body
temperature and acts as a sensory receptor.
I)________LINFATIC SYSTEM_________________. A system which runs parallel with the
veins throughout the body, drains fluid from the tissues and helps to defend the body against
infection and disease.
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 1
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
J)____SKELETAL SYSTEM We need this system to produce movement, both voluntary and
involuntary, and to keep our hearts beating to keep us alive.
K) _____ NERVOUS SYSTEM _____________________. This is the most complex system
in the body and its functions are to regulate all the other systems in the body, receive and
send messages and to provide us with information about our environment.
2. LISTENING
LISTEN and FILL IN the gaps.
1. ___RED BLOOD CELLS________ _____________ ____________ or
_____ERYTHROCITES___________carry__OXYGEN__________ from the lungs to every
cell in the rest of the body
2. One function of the ______KIDNEYS______ is to ___REGULATE________ the amount of
water in the body; they also __ECRETE________’urea’ (a nitrogen waste product) from the
body.
3. The_______LIVER_________ functions as both an organ of digestion and excretion.
4. The ___________HEART________ beats 80 times per minute on average.
5. The __OVARIES____________ are only found in females. They are endocrine glands which
____SECRETE______ hormones. Ovum/ Ova (OVULOS) _____ARE_____
__PRODUCED_________ here.
6. An accessory organ of digestion, which is also an endocrine gland, _SECRETES_________
insulin and is called the____PANCREAS________.
7. All the bones in the skeletal system _________FORM_______ from a fibrous connective
tissue called_________CARTILAGE_________. This tissue eventually hardens with calcium
deposits to become_BONE_________________.
8. Both the spinal cord and the brain ___ARE________ _COMPOSED__________ of
nerve cells.
9. Cells ________REPRODUCE_________ by _________DIVISION________ , a process
called mitosis.
10. The skin which ______COVERS________________________ the outside of the human body
______CONTAINS_______________ cells, sweat glands, oil-producing glands, blood
vessels and nerve endings.
11. The heart and lungs ___ARE SITUATED_______ ___________ in the thoracic cavity.
12. A zygote is formed at the time of _____CONCEPTION_______________________- it is the
union of the female and male sex cells or ___GAMETES___________.
3. STRUCTURE
'to be made up of' is used for a detailed breakdown of a part or a structure.
e.g. The joints (or articulations) are made up of bones, cartilage and ligaments.
‘consists of' is used in a general way when all the main parts of a structure are named
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 2
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
e.g. The respiratory tract consists of the pharynx, trachea, lungs, bronchi, bronchioles and
alveoli.
'to be composed of' is used when the materials or substances from which the structure
is formed.
e.g. Both the brain and the spinal cord are composed of nerve cells and fibres.
form from: del material del que está hecho
NAME OF SYSTEM STRUCTURE
1. skeletal system cartilage ligaments
bones, a) _________,
2. muscular system smooth
skeletal, cardiac and b)___________muscles,
tendons
3. circulatory system vessels
heart and blood c)_____________(arteries,
veins
d)____________and capillaries)
4. respiratory system nose (nostrils)
lungs and air passages. Nasal passages, e)_______,
trachea
pharynx, larynx, f)______________, bronchi,
bronchioles, alveoli.
5. nervous system brain
g)_____________, spinal cord and nerves
digestive
6. system tongue
mouth (teeth, h)________________and salivary
oesophagus ( sin O es US)
glands), epiglottis, I)_______________, stomach,
intestines accessory organs: liver,
j)________________,
galobladdler (vesícula biliar)pancreas. Parts of this system
are sometimes referred to as ‘the gut’.visceras
7. urinary/excretor system urethra, anus
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, k)_______________.
vejiga
8. reproductive system testicles duct/seminal vesicles, Prostate
Male: l)__________,
(testes)
gland, Penis.
uterus (womb)
Female: ovaries, Fallopian tubes or m)____________,
uterus, vagina, breasts.
9. endocrine system thymus
Glands: Pituitary, Pineal, n)___________and
thyroid
Parathyroid, o)________________, Adrenal,
Pancreas, Ovaries and Testes.
amígdalas
10. lymphatic system tonsils and adenoids), lymph
Lymph nodes (p)__________
spleen (splint: entablillar,
vessels, valves, the q)____________. sling:
bazo
cabestrillo)
11.skin/integumentary Epidermis, dermis, sebaceous or oil-producing glands
system sweat
glands, sudoriferous or r)_________________ glands.
4. VOCABULARY. Complete the table.
NOUN VERB
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 3
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
absorption 1- absorb
consumption 2- consume
contraction 3- contract
conversion 4- convert
detoxification 5- detoxify
elimination 6- eliminate
expansion 7- expand
ingestion 8- ingest/take in
secretion 9- secrete
stimulation 10- simulate
Now, complete the sentences with the correct form of words from the previous
task. DO NO FORGET agreement.
stimulate glands to produce saliva.
1. The sight, smell and taste of food __________
elimination of waste from the
2. A major role of the digestion process is the ___________
body.
ingested
3. Food is _________________ through the mouth.
secretion
4. The pancreas is involved in the __________________ of enzymes that
breakdown food molecules.
converts
5. Nutrition is when the body _______________ food substances into energy.
6. The digestive system breaks down food and transports it for
absorption
_________________________ and defecation.
contractions
7. The muscles in the oesophagus make wave-like ______________________
which push the food along.
consumption
8. Too much __________________________ of certain foods can overload the
digestive system.
expand
9. The stomach can ________________ as it fills with undigested food.
detoxifies
10. Digested products travel to the liver, which _______________ blood of harmful
substances.
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 4
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
5. PARTS OF THE BODY
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 5
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
hearing (oído)
brazo superior
costado
antebrazo
nalga
muñeca
pantorrilla
(feet: pies)
dedo gordo del pie
nostril: fosa nasal
breast o mama: pecho
ombligo
ingle
rótula
espinilla (shin bone)
planta de pie
talón
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 6
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
6. SHAPES.
Look at the following examples. Write sentences and describe the shapes of the following
organs, using the words between brackets.
The eye is shaped like a sphere.
The eye is a sphere-shaped organ.
The eye is a spherelike organ.
The eye is spherical in shape.
puño
1.The heart (fist-shaped) is fist-shaped organ
cúpula
2. The diaphragm (dome, like) is a domelike organ
3. The kidneys (beans) are shaped like beans
4. The lungs (conical) are conical in shape
5. The gallbladder (saclike) is a saclike organ
vesícula biliar
6. The oesophagus (tubular) is tubular in shape
7. The liver (pyramid) (noun) is shaped like a pyramid
pyramidal (adjective)
7. LOCATION and PREPOSITIONS
CHOOSE the best option.
1. The head is located at the bottom/ top of the body.
2. The feet are located at the bottom/ sides of the body.
3. The arms are situated at the sides/ upper limbs of the body.
extremidades superiores
4. The thorax is located among/ between the neck and abdomen.
solo usar cuando tenemos más de 2
5. The head is above/on and between the shoulders.
no xq no está en contacto
The heart directo de los hombros
The heart is a hollow, muscular organ situated in the 6) below/ front of the chest,
between the lungs. Approximately two thirds of its mass is 7) consists / situated to
the left of the median plane.
The heart is 8) followed/ surrounded by a double membrane which is called the
pericardium. It contains fluid which lubricates the heart. The heart is divided into a right
half and a left half by a wall of tissue. Each half is divided again into an upper and
lower 9) chamber / vessel, so the heart consists of four chambers.
cámaras del corazón
The upper chambers of the heart are called 10) atrium / atria and the lower chambers
aurículas
are called ventricles. The right atrium and the right ventricle are connected by a valve,
and so are the left atrium and left ventricle. Another valve is situated between the right
ventricle and pulmonary artery, and a fourth between the left ventricle and the aorta.
These are called the semi-lunar valves because they are 11) shaped like / in shape
crescent moons.
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 7
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
8. LOCATION and LOCATIVE ADJECTIVES
Remember that locative adjectives are common in medical writing. They describe situation
or place.
● right and left
● inner and outer
● upper and lower
● internal and external (especially of hollow structures)
● superficial and deep (nearer and farther from the surface of the body)
● central and peripheral (nearer and farther from the centre of the body)
● proximal and distal (especially of limbs; nearer and farther from the trunk)
● superior and inferior (higher and lower, in transverse planes)
● anterior and posterior (nearer the front, nearer the back, in coronal planes)
● medial and lateral (nearer and farther from the midline, in sagittal planes)
CHOOSE the best option.
1. The elbow is inferior/ superior to the feet.
2. The sternum is anterior/ posterior to the heart.
3. The lungs lie medial / lateral to the heart.
4. The humerous articulates at its distal / proximal end with the radius and ulna.
5. The knees are inferior / deep to the waist.
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 8
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
9. BODY SYSTEMS SUMMARY
Picture Medical Specialty, Structures Functions
specialist & Body
System
Gastroenterology mouth (teeth and tongue) Receive sensory information
Gastroenterologist salivary glands (taste)
Gastrointestinal/ oesophagus Digest food.
Digestive system spleen Absorb nutrients into the blood
liver Excrete undigested waste.
stomach
bile duct
gallbladder
pancreas
duodenum
kidneys
small intestine
large intestine (colon)
appendix
bladder
rectum
anus
Pulmonology nose Inhale (breathe in) oxygen
Pulmonologist tonsils exhale (breathe out) carbon
Respiratory System pharynx (throat) dioxide
larynx: glottis, thyroid, exchange gases in the alveoli
voice box and vocal cords)
trachea (windpipe)
bronchial tubes
bronchi (pl.)
bronchioles
alveoli (in the lungs)
right/left lobes of the lungs
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 9
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
Cardiology heart: jugular vein, aorta, Circulate blood throughout the
Cardiologist pulmonary artery, body.
Cardiovascular pulmonary vein, left
system auricle, left ventricle, wall,
septum
blood vessels (arteries,
veins, capillaries)
Haematology Blood cells: Transport oxygen and nutrients to
Haematologist erythrocytes (red cells) the cells
Blood thrombocytes (platelets), Transport carbon dioxide to the
leucocytes (white cells) lungs and wastes to the kidneys
plasma
Immunology lymphatic vessels, lymph Recognise and destroy disease-
Immunologist nodes, and lymph fluid causing organisms and abnormal
Blood, Lymphatic spleen cells
System thymus
white blood cells
Dermatology Skin Receive sensory information
Dermatologist Hair (pain, touch, temperature)
Integumentary Nails Protect internal organs
System Sweat glands Regulate body temperature by
oil glands sweating
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 10
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
Orthopaedics bones: Support the body
Orthopaedist cranium (skull) Protect viscera
Skeletal System clavicle (collar bone) Contribute and allows movement
scapula (shoulder blade) Store mineral substances
sternum (breast bone) Take part in blood cell formation
vertebrae
backbone cola
ribs, ribcage
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Carpals
Metacarpals
Phalanges
Ilium (hip)
Sacrum
Coccyx
Greater trochanter
Femur (thigh bone)
Patella (thigh bone)
Tibia (shin bone)
Fibula (calf bone)
Tarsals
Metatarsals
cartilage
ligaments
articulations (Joints)
Orthopaedics Muscles Produce movement of the body
Orthopaedist Tendons
Muscular System
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 11
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
Neurology Brain Receive, relay, and interpret
Neurologist Cranial nerves sensory information (vision,
Nervous System Spinal cord hearing, smell, taste) and
spinal nerves sensations (pain, touch,
cerebrospinal fluid temperature, body position,
neurons balance)
Coordinate movement
Store and interpret memory and
emotion
Urology kidneys Filter out waste products from the
Urologist ureters blood and excrete them in the
Urinary system bladder(waterworks) urine
urethra
nephrons
Male Reproductive scrotum secrete male hormones
Medicine testes (pl.) develop male secondary sexual
A reproductive epididymides characteristics
specialist vas deferens produce and release sperm
Male genital and seminal vesicles
Reproductive prostate gland
system urethra
penis
anal sphincter
anus
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 12
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
Gynaecology and breasts secrete female hormones
Obstetrics ovaries develop female secondary sexual
gynaecologist, uterine/Fallopian tubes characteristics
obstetrician ova (pl.) produce ova
Female Genital and uterus (womb) menstruate
reproductive cervix (neck of womb) conceive and bear children
system vagina produce milk to nourish children
external genital
Endocrinology pituitary gland secrete hormones into the blood
Endocrinologist pineal gland direct the activities of the body
Endocrine system thyroid gland
parathyroid glands
thymus
pancreas
adrenal glands
ovaries
testes
Ophthalmology eyes receive sensory information
ophthalmologists (cornea, pupil, iris, lens, (vision)
Eyes vitreous humour, retina,
macula)
Otolaryngology ears receive sensory information
otolaryngologist nose, nostrils (hearing, balance, smell)
Ears, Nose and sinuses (pl.) produce speech
Throat (ENT) pharynx (throat)
System larynx (voice box)
There are structures and systems responsible for fetching information coming from outside the body and
the environment. These systems are normally known as senses. The senses include sight (vision), hearing,
touch (also called sensation or feeling), smell and taste.
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 13
UNIT 3. Human Body LECTURES 2023 2024
E.U.E. Dr. Dacio Crespo 2nd year. NURSING ENGLISH MODULE 14
You might also like
- Anaphy 100 Lab Practice Review Sheet 1 and 2Document6 pagesAnaphy 100 Lab Practice Review Sheet 1 and 2Mariam GamosNo ratings yet
- Human Body Test Study Guide Answer KeyDocument6 pagesHuman Body Test Study Guide Answer KeyAhmad WirawanNo ratings yet
- Science F1 - Cell As A Unit of LifeDocument8 pagesScience F1 - Cell As A Unit of LifeamyryuzainiNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure and Function - General ReviewDocument3 pagesTissue Structure and Function - General Reviewapi-295869261No ratings yet
- Semester A Final Exam ReviewDocument46 pagesSemester A Final Exam ReviewMadison MauckNo ratings yet
- Total Soccer Fitness Juniors PDFDocument133 pagesTotal Soccer Fitness Juniors PDFAmelRahmanović100% (4)
- 20230118-Biol-1190-Lecture-1-Notes 2Document18 pages20230118-Biol-1190-Lecture-1-Notes 2camillejbtqNo ratings yet
- Body Systems: G1352 Inglés Ruth Alonso & Rosa RumayorDocument1 pageBody Systems: G1352 Inglés Ruth Alonso & Rosa RumayorLuni VampNo ratings yet
- REVIEW 2nd PARTIALDocument10 pagesREVIEW 2nd PARTIALruywero08No ratings yet
- Body Systems WorksheetDocument5 pagesBody Systems WorksheetManimtim Salisi Jasper100% (1)
- 2 Organ SystemsDocument5 pages2 Organ SystemsBeaNo ratings yet
- Level - 1 I. Fill in The BlanksDocument5 pagesLevel - 1 I. Fill in The BlanksKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- 8HW Body Organisation ws1Document2 pages8HW Body Organisation ws1noddy_noddyNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lab ManualDocument9 pagesAnaphy Lab ManualKen KanekiNo ratings yet
- Body Systems 6-11Document2 pagesBody Systems 6-11Yelizaveta BondarenkoNo ratings yet
- Body Systems 6-11Document2 pagesBody Systems 6-11Yelizaveta BondarenkoNo ratings yet
- Natural Sciences Exam - Unit 4 "Our Systems" NameDocument3 pagesNatural Sciences Exam - Unit 4 "Our Systems" NameSilvia IzquierdoNo ratings yet
- Name: - Grade & Section: - Date: - Topic: Introduction To Life Science Learning CompetenciesDocument7 pagesName: - Grade & Section: - Date: - Topic: Introduction To Life Science Learning Competenciesjanice alquizarNo ratings yet
- Human Body ActivitiesDocument2 pagesHuman Body ActivitiesLoren DamásioNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5 Mita Sem 6Document7 pagesLESSON 5 Mita Sem 6MitaNo ratings yet
- Simple Present Other Verbs MedicineDocument8 pagesSimple Present Other Verbs MedicineFernanda VigilNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document36 pagesScience 9Lovely ManaloNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Body SystemsDocument3 pagesStudy Guide Body SystemsMatthew BrennanNo ratings yet
- Human Body AdventureDocument5 pagesHuman Body Adventurebonz2008100% (1)
- Human Body WorkbookDocument25 pagesHuman Body Workbookjk centralNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Vertebrate Organ Systems: Biology 18 Spring 2008Document43 pagesLab 9 - Vertebrate Organ Systems: Biology 18 Spring 2008JulsNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory Manual Fetal Pig Version Update 10th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full Human Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory Manual Fetal Pig Version Update 10th Edition Marieb Solutions Manual PDFpeiwenhlmel100% (13)
- Nucleus Anabolism Metabolism Histologist Genes: Pharynx Adipose Tissue Trachea Ureter Larynx Pleura Cartilage UrethraDocument6 pagesNucleus Anabolism Metabolism Histologist Genes: Pharynx Adipose Tissue Trachea Ureter Larynx Pleura Cartilage Urethrateemo no JutsuNo ratings yet
- KS3 Human Organ SystemDocument2 pagesKS3 Human Organ Systemejljn1No ratings yet
- Organ and Organ SystemDocument3 pagesOrgan and Organ SystemAzaan AnwarNo ratings yet
- Chloe Reviewer SCienceDocument3 pagesChloe Reviewer SCienceKim Carlo AglinaoNo ratings yet
- Human Tissue Lab Student HandoutDocument6 pagesHuman Tissue Lab Student HandoutmathandsciencesforkidsNo ratings yet
- File 1 AnaphyDocument3 pagesFile 1 Anaphyserainie maiNo ratings yet
- English Test: Digestive System - Respiratory System - Circulatory System - Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesEnglish Test: Digestive System - Respiratory System - Circulatory System - Excretory SystemMariAngel MoragaNo ratings yet
- Frog LBLDocument5 pagesFrog LBLchandumenswear3No ratings yet
- The Human Body: Name: - Date: - PeriodDocument2 pagesThe Human Body: Name: - Date: - PeriodTada86No ratings yet
- Summative Test Q2 Science2023Document2 pagesSummative Test Q2 Science2023Juliean JulianaüNo ratings yet
- Science ExamPractices 1683230064851Document4 pagesScience ExamPractices 1683230064851Manuel AzofeifaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PharmacologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To PharmacologyBEATRICE SALANo ratings yet
- Social Practice of The Language 6Document9 pagesSocial Practice of The Language 6Brenda LizarragaNo ratings yet
- 2 Summative Test 2 Quarter Name: - ScoreDocument4 pages2 Summative Test 2 Quarter Name: - ScoreannNo ratings yet
- Exam t1 5th ScienceDocument3 pagesExam t1 5th Sciencemaartiius11No ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet No. 14 Urinary SystemDocument36 pagesLab Worksheet No. 14 Urinary SystemKarylle Ezra GulifardoNo ratings yet
- TOS in Science IVDocument7 pagesTOS in Science IVPaulane NavaltaNo ratings yet
- Cell-Modification LectureDocument6 pagesCell-Modification LectureFiona LeeNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM Notes WorksheetDocument2 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM Notes WorksheetCarla MirandaNo ratings yet
- Las 21Document10 pagesLas 21Ge ccaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test Lesson 1Document1 pageSummative Test Lesson 1Pedro GenosasNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System MatchDocument2 pagesEndocrine System MatchInternational Tutoring Association100% (6)
- Science6 ST1 Q2Document4 pagesScience6 ST1 Q2Meriam LuatNo ratings yet
- Animal Systems Review 202401Document10 pagesAnimal Systems Review 202401NoelleNo ratings yet
- Pig DLab ReportDocument3 pagesPig DLab Reportiloveyou205No ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue LabDocument6 pagesEpithelial Tissue Labapi-245368774No ratings yet
- Exercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)Document7 pagesExercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)tomaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2-The Language of MedicineDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 2-The Language of Medicineeddy surielNo ratings yet
- JajaDocument2 pagesJajaSANTIAGO LAINEZ HIGUERANo ratings yet
- Jawaban - Meeting 2 Practice 2-Tk 2 d3Document12 pagesJawaban - Meeting 2 Practice 2-Tk 2 d3Salma Salsa BillaNo ratings yet
- Tds Luccile StratDocument4 pagesTds Luccile Stratsameerkhurana045No ratings yet
- Science6 Q2 Mod1 TheHumanBodySystems V4Document30 pagesScience6 Q2 Mod1 TheHumanBodySystems V4ThievesPHNo ratings yet
- Stage 3 Lab BiologyDocument17 pagesStage 3 Lab BiologyarmandoomoralesgalindoNo ratings yet
- Intro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1From EverandIntro To Human Anatomy & Physiology: Quick Review Notes Chapter 1No ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- Managing Heat StressDocument14 pagesManaging Heat StressMuhammad Aliff100% (1)
- Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument17 pagesCommunity Acquired PneumoniaDaniel Puentes SánchezNo ratings yet
- Kidney Best FoodsDocument4 pagesKidney Best FoodsDrake SuyatNo ratings yet
- Vega - Vicente Position PaperDocument4 pagesVega - Vicente Position PapervalshkaNo ratings yet
- Major Final Output (MFO) - CIUDocument13 pagesMajor Final Output (MFO) - CIURene MollenidoNo ratings yet
- Antiparkinson DrugsDocument19 pagesAntiparkinson DrugsSV SagarNo ratings yet
- Med Surg 2 Study GuideDocument5 pagesMed Surg 2 Study GuideMichibooNo ratings yet
- Genetic Polymorphisms Personalized MedicineDocument38 pagesGenetic Polymorphisms Personalized MedicineBayu WisnuNo ratings yet
- Sprout Guide - How To Sprout Grains, Nuts and Beans - Dr. AxeDocument25 pagesSprout Guide - How To Sprout Grains, Nuts and Beans - Dr. Axearjun Singh100% (1)
- Section: of The History of MedicineDocument10 pagesSection: of The History of MedicineaceNo ratings yet
- DEEP Vein ThrombosisDocument72 pagesDEEP Vein ThrombosisLevy Garcia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Food Safety Management SystemsDocument87 pagesFood Safety Management SystemsAshish SahuNo ratings yet
- Cosmetology SynopsisDocument79 pagesCosmetology SynopsisAnonymous DgPsK0oQNo ratings yet
- NSTP Disaster Preparedness: Risk AssessmentDocument6 pagesNSTP Disaster Preparedness: Risk AssessmentkrizylNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology NotesDocument13 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology NotesJomar Tibig100% (1)
- Grisold Et Al-2009-Acta Neurologica ScandinavicaDocument16 pagesGrisold Et Al-2009-Acta Neurologica ScandinavicaJorgeNo ratings yet
- Homework Module 4-QualityDocument3 pagesHomework Module 4-QualityTamahqua Tankamochkhanna HunterHoggsirls0% (20)
- Lecture 1 - Smear Positive PTBDocument40 pagesLecture 1 - Smear Positive PTBNasibah Tuan YaacobNo ratings yet
- 7154 MsdsDocument3 pages7154 MsdslightsleeperNo ratings yet
- Travel Medicine and Infectious DiseaseDocument8 pagesTravel Medicine and Infectious Diseaseariani khikmatul mazidahNo ratings yet
- Practice Guidelines For Telemental HealthDocument51 pagesPractice Guidelines For Telemental HealthNataanatiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Chronic Renal Disease, A Staged ApproachDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Chronic Renal Disease, A Staged Approachtaner_soysurenNo ratings yet
- Polyphenols Health Benefits PDFDocument10 pagesPolyphenols Health Benefits PDFfather.mckenzie.twitterNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Aortitis: A Case Report and Literature ReviewDocument7 pagesRheumatoid Arthritis-Associated Aortitis: A Case Report and Literature ReviewMuhammad RaflirNo ratings yet
- Advanced Critical Reading - Columbian ExchangeDocument4 pagesAdvanced Critical Reading - Columbian ExchangeVahid UzunlarNo ratings yet
- Checklist of SSATDocument13 pagesChecklist of SSATJOVELYN JOY CABUELLONo ratings yet
- Drug Study DiazepamDocument2 pagesDrug Study DiazepamBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Albumin 20 Per CentDocument3 pagesAlbumin 20 Per CentidaNo ratings yet