Professional Documents
Culture Documents
WAN Networking
WAN Networking
Uploaded by
gauraveesenadeera0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesA WAN is a network spread across a large geographical area like cities or countries. It uses technologies like X.25, Frame Relay, ISDN, and ATM to connect across the public internet. Switching in networks can be done through circuit switching or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path for calls but packet switching breaks messages into packets that are routed independently to their destination. Packet switching networks can provide services through datagram and virtual circuit models.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA WAN is a network spread across a large geographical area like cities or countries. It uses technologies like X.25, Frame Relay, ISDN, and ATM to connect across the public internet. Switching in networks can be done through circuit switching or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path for calls but packet switching breaks messages into packets that are routed independently to their destination. Packet switching networks can provide services through datagram and virtual circuit models.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views3 pagesWAN Networking
WAN Networking
Uploaded by
gauraveesenadeeraA WAN is a network spread across a large geographical area like cities or countries. It uses technologies like X.25, Frame Relay, ISDN, and ATM to connect across the public internet. Switching in networks can be done through circuit switching or packet switching. Circuit switching establishes a dedicated communication path for calls but packet switching breaks messages into packets that are routed independently to their destination. Packet switching networks can provide services through datagram and virtual circuit models.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
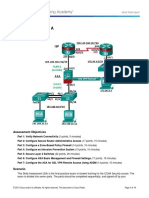
INTERNET
WIDE AREA NETWORK
CHARACTERISTICS OF WAN
• A WAN is a network in a large geographical location, maybe across cities or countries.
• Crosses the public ‘Right of way”.
• Is usually owned by a service provider.
• More expensive and complicated than a LAN.
• X.25, Frame Relay, ISDN, and ATM are some WAN technologies.
SWITCHING TECHNOLOGIES
A switched network goes through a switch instead of a router. This actually is the way most
networked are headed, towards flat switches on VLANs instead of routers. Long distance
transmission is typically done over a network of switched nodes.
CIRCUIT SWITCHING
• Originated in Public Telephone Network
• Well Suited to analog of Voice Signal
• Dedicated communication path between two stations
Three Phase
o Establish
o Transfer
o Disconnect
• Must have switching capacity and channel capacity to establish connection
• Must have intelligence to work out routing
• Developed for voice traffic (Phone)
COMMUNICATION | RIYAS RUSHARD 95
PACKET SWITCHING
• Data transmitted in small packets:
• Longer messages are split into series of
packets
• Each Packets contains a portion of user data
plus some control information (Routing
Information)
• Packets are received, stored briefly (buffered)
and passed on to the next node
ITEM CIRCUIT SWITCHING PACKET SWITCHING
Call Setup
Dedicated Physical Path
Each Packet follows the same route
Packets arrive in order
Bandwidth Available
Transparency
Charging
TYPES OF SERVICES IN PACKET SWTICH NETWORK
ISSUES DATAGRAM VIRTUAL CIRCUIT
Circuit Setup
Each packet contains full Each packet contains a
Addressing Virtual CircuitNumber (VC NO)
destination address
Each data packet is routed Route is chosen when
independetly Virtual Circuits is created
Routing
best path
QOS Diffcult Can be provided
COMMUNICATION | RIYAS RUSHARD 96
DATAGRAM VIRTUAL CIRCUIT
STRUCTURE OF PSTN
SCHEMETIC DIAGRAM OF PSTN
COMMUNICATION | RIYAS RUSHARD 97
You might also like
- Plano de Estudo - Ccie Lucas PalmaDocument26 pagesPlano de Estudo - Ccie Lucas PalmaAdilson Pedro100% (2)
- CCNASv2 SKillsAssessment-A Student TrainingDocument11 pagesCCNASv2 SKillsAssessment-A Student TrainingDeepak JanjuNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Data NetworkDocument8 pagesPublic Switched Data NetworkMichael David CaparazNo ratings yet
- Packet SwitchingDocument57 pagesPacket Switchingsimranjeet singhNo ratings yet
- HP-Lecture 01Document55 pagesHP-Lecture 01alemuNo ratings yet
- Public Switched Data NetworkDocument79 pagesPublic Switched Data NetworkMichael David CaparazNo ratings yet
- William Stalling - Slide 01 Intro NotesDocument7 pagesWilliam Stalling - Slide 01 Intro NotesLê Đắc Nhường (Dac-Nhuong Le)No ratings yet
- Data and Computer Communications: Chapter 10 - Circuit Switching and Packet SwitchingDocument39 pagesData and Computer Communications: Chapter 10 - Circuit Switching and Packet SwitchingRuchiNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and NetworkingDocument71 pagesData Communications and NetworkingWeeraphat TulathonNo ratings yet
- Main Full Forms FTTNDocument3 pagesMain Full Forms FTTNAshish ChambiyalNo ratings yet
- Publication 10 22953 27Document42 pagesPublication 10 22953 27Ayu Rosyida zainNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Part ADocument28 pagesModule 3 Part Aanusha.j-cseNo ratings yet
- Packet Switching: Charu Gupta Chinki Aggarwal Rahul Joshi Jaspreet KaurDocument20 pagesPacket Switching: Charu Gupta Chinki Aggarwal Rahul Joshi Jaspreet KaurCharu GuptaNo ratings yet
- BCENT - Basic Cisco Entry Networking Technician: Introducing Wide-Area NetworksDocument41 pagesBCENT - Basic Cisco Entry Networking Technician: Introducing Wide-Area NetworksmanuelNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation 2Document20 pagesData Presentation 2cctmasekesaNo ratings yet
- Lec 05Document31 pagesLec 05Altayeb AbdulhameedNo ratings yet
- 02 DataDocument46 pages02 DataAhmedNo ratings yet
- Communication Networks: Chapter TwoDocument37 pagesCommunication Networks: Chapter TwoAbdullahi Salad TobanleNo ratings yet
- A Receiver Initiated Low Delay MAC Protocol For Wake-Up Radio Enabled Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument12 pagesA Receiver Initiated Low Delay MAC Protocol For Wake-Up Radio Enabled Wireless Sensor NetworkspriyankaNo ratings yet
- Routing in Mobile Ad-Hoc NetworksDocument89 pagesRouting in Mobile Ad-Hoc NetworksMona AliNo ratings yet
- 04-Network Layer-02 by ApcomsDocument4 pages04-Network Layer-02 by Apcomsrsakm20019931No ratings yet
- Telecommunication SystemDocument19 pagesTelecommunication SystemHasnin shahNo ratings yet
- Ad Hoc and Wireless Sensor Networks - Ec8702: Session byDocument26 pagesAd Hoc and Wireless Sensor Networks - Ec8702: Session byRaja MadhuvanthiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Two Introduction To WAN: by Dr. Alaa I. Al-Muttairi 2020/2021Document32 pagesLecture Two Introduction To WAN: by Dr. Alaa I. Al-Muttairi 2020/2021Bashir Emad kadimNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Computer NetworksDocument39 pages1-Introduction To Computer Networkscryz123No ratings yet
- Week 3Document26 pagesWeek 3MUBEEN LIAQATNo ratings yet
- Lect For PCKTDocument29 pagesLect For PCKTHammad WaseemNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Telemetry Tracking ControlDocument29 pages3.2 Telemetry Tracking ControlarzshNo ratings yet
- ViaSat LinkStar S2a 1Document4 pagesViaSat LinkStar S2a 1Eliander J. P CorderoNo ratings yet
- Network Layer: Design IssuesDocument12 pagesNetwork Layer: Design IssuessridharfbookNo ratings yet
- Network Layer Design IssuesDocument12 pagesNetwork Layer Design IssuesaakashNo ratings yet
- 388 Wireless TechnologyDocument44 pages388 Wireless TechnologySyed Ali Irfan JaffriNo ratings yet
- Lec4 Switching TechniquesDocument24 pagesLec4 Switching TechniquesVibhav ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Wimax: R.Manikarnika 2018610011Document69 pagesWimax: R.Manikarnika 2018610011185534 ktr.ece.14No ratings yet
- Routing Protocols: Ad Hoc Wireless NetworksDocument78 pagesRouting Protocols: Ad Hoc Wireless NetworksmakNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Networking For Digital Substations: 2019 Texas A&M Protective Relaying ConferenceDocument20 pagesTutorial On Networking For Digital Substations: 2019 Texas A&M Protective Relaying ConferenceInayat HathiariNo ratings yet
- Notes3 WANDocument40 pagesNotes3 WANsamitha deshanNo ratings yet
- Chapter-04 Network LayerDocument208 pagesChapter-04 Network LayerPratik ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document15 pagesModule 2ARUNNo ratings yet
- VSATDocument24 pagesVSATVikalp ThukralNo ratings yet
- PSDN and IsdnDocument32 pagesPSDN and IsdnLYNN JANE JANIERNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Network LayerDocument154 pagesComputer Network Network LayerPurushotham Prasad K100% (1)
- Asynchronous Transfer Mode (Atm) and Frame RelaysDocument15 pagesAsynchronous Transfer Mode (Atm) and Frame RelaysOmar CaabiNo ratings yet
- DS 8605 Smart Router 74C0029Document2 pagesDS 8605 Smart Router 74C0029Walisan turiNo ratings yet
- ContentDocument39 pagesContentZain Alabeeden AlarejiNo ratings yet
- Unit IiDocument45 pagesUnit IiVENU VNo ratings yet
- Network Architecture: Rakesh Kumar Naik Madhav Institute of Technology and Science GwaliorDocument32 pagesNetwork Architecture: Rakesh Kumar Naik Madhav Institute of Technology and Science GwaliorUnknown SurvivorNo ratings yet
- Wireless ATM: Nipurba KonarDocument16 pagesWireless ATM: Nipurba KonarNipurba KonarNo ratings yet
- Switching: Switched NetworksDocument33 pagesSwitching: Switched NetworksdavdamiteshNo ratings yet
- Cdma 2000 PDFDocument29 pagesCdma 2000 PDFswaroop raneNo ratings yet
- Lec 02Document46 pagesLec 02Emad KhanNo ratings yet
- William Stallings Data and Computer Communications: Packet SwitchingDocument59 pagesWilliam Stallings Data and Computer Communications: Packet SwitchingSocaciu VioricaNo ratings yet
- Data Communications and Networking: Circuit Switching and Packet SwitchingDocument22 pagesData Communications and Networking: Circuit Switching and Packet SwitchingPratibhaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document34 pagesUnit 3vishalnishad5238No ratings yet
- Switched Network:: Data Communication and Computer Networks Chapter 6: Packet SwitchingDocument7 pagesSwitched Network:: Data Communication and Computer Networks Chapter 6: Packet SwitchingMr. GyamzoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document162 pagesUnit 3Manish NagarNo ratings yet
- 07 - Mobile Ad Hoc Wireless NetworksDocument21 pages07 - Mobile Ad Hoc Wireless NetworksCastridah NachibingaNo ratings yet
- SCADA Communications: Author: Birinder Singh H.O.D. Projects RBH Solutions Private LimitedDocument61 pagesSCADA Communications: Author: Birinder Singh H.O.D. Projects RBH Solutions Private LimitedBirinder SinghNo ratings yet
- SwitchingDocument20 pagesSwitchinglimenihNo ratings yet
- Eln PPT FinalDocument25 pagesEln PPT Finalmeghashrii21No ratings yet
- Radio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSFrom EverandRadio Network Planning and Optimisation for UMTSJaana LaihoRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Virtual Machine Mobility With VMware VMotion and Cisco Data Center Interconnect TechnologiesDocument17 pagesVirtual Machine Mobility With VMware VMotion and Cisco Data Center Interconnect TechnologiescspowerNo ratings yet
- Show - CDP - Neighbors - HTML - CiscoDocument3 pagesShow - CDP - Neighbors - HTML - Ciscomobio jeanNo ratings yet
- Computer ServicingDocument32 pagesComputer ServicingJhon Keneth NamiasNo ratings yet
- Part - I SummeryDocument105 pagesPart - I Summerysalim_doddamaniNo ratings yet
- CCNA Notes Compiled by Mr. MalooDocument216 pagesCCNA Notes Compiled by Mr. MalooDarren Owen100% (1)
- 802.1x and RadiusDocument19 pages802.1x and RadiusmmarotaNo ratings yet
- ICND120SG Vol1Document372 pagesICND120SG Vol1Phuoc Trinh100% (2)
- Aruba Instant On 1830 48g 24p Class4 Poe 4sfp 370w Switch (Jl815a) DatasheetDocument4 pagesAruba Instant On 1830 48g 24p Class4 Poe 4sfp 370w Switch (Jl815a) Datasheetsekolah martabakNo ratings yet
- Internship 1Document60 pagesInternship 1Nahom Alemnew100% (1)
- Cisco Just Switch It PlaybookDocument49 pagesCisco Just Switch It PlaybooknenjamsNo ratings yet
- Ruckus ICX Switch Quick Start GuideDocument10 pagesRuckus ICX Switch Quick Start GuideAakashNo ratings yet
- Lab - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: TopologyDocument3 pagesLab - Basic Switch and End Device Configuration: Topologybriggyd rojasNo ratings yet
- HS NCM Series Guia de Insta 54014 - PDFDocument18 pagesHS NCM Series Guia de Insta 54014 - PDFyousuf fazilNo ratings yet
- NetDe - Sign - 11 - Selecting Technologies For Campus NetworkDocument19 pagesNetDe - Sign - 11 - Selecting Technologies For Campus NetworkphamthientrungNo ratings yet
- Create Dan Config GPONDocument38 pagesCreate Dan Config GPONking2No ratings yet
- QFX5120 DatasheetDocument13 pagesQFX5120 DatasheetHmaid MohamedNo ratings yet
- MACH1000 Full Gigabit Ethernet Switch 16 PortsDocument3 pagesMACH1000 Full Gigabit Ethernet Switch 16 Portsandre_tfjrNo ratings yet
- Linksys SRW224G4Document3 pagesLinksys SRW224G4outlaw666hrNo ratings yet
- Lista de Precios Meruq 20-11-2019Document29 pagesLista de Precios Meruq 20-11-2019LuiisAx'lSlimNo ratings yet
- C Node Presen3.0Document33 pagesC Node Presen3.0Ehsan RohaniNo ratings yet
- Lab 7-1 Configuring Switches For IP Telephony Support: Learning ObjectivesDocument22 pagesLab 7-1 Configuring Switches For IP Telephony Support: Learning Objectivesvishal tatwadeNo ratings yet
- Instruction For Setup of CoCoS-EDS On ME EnginesDocument3 pagesInstruction For Setup of CoCoS-EDS On ME EnginesLazar Petre-GabrielNo ratings yet
- NB 06 Cat9400 Ser Data Sheet Cte enDocument21 pagesNB 06 Cat9400 Ser Data Sheet Cte enmladen antesevicNo ratings yet
- Fortigate Ha 50 PDFDocument291 pagesFortigate Ha 50 PDFyusuframlyNo ratings yet
- IP Networking Quick Best Practice Guide-2 PDFDocument10 pagesIP Networking Quick Best Practice Guide-2 PDFArun SomashekarNo ratings yet
- Qasim Saeed: ContactDocument6 pagesQasim Saeed: ContactTanveer AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Questions and AnswersDDD50Document16 pagesQuestions and AnswersDDD50Fetsum LakewNo ratings yet
- Sungrow Data Logger 1000 - 1000B Usert ManualDocument120 pagesSungrow Data Logger 1000 - 1000B Usert ManualJoão TeixeiraNo ratings yet