Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Construction Technology Notes
Construction Technology Notes
Uploaded by
Prashant SunagarCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Waffle Slab DesignDocument23 pagesWaffle Slab DesignMwengei Muteti100% (1)
- Application of Gis in Civil Engineering FinalDocument14 pagesApplication of Gis in Civil Engineering FinalPrashant Sunagar100% (2)
- Unit 1Document131 pagesUnit 1madhu.ammu112No ratings yet
- And Exture of Sedímentary Rocks: The ComposítíonDocument12 pagesAnd Exture of Sedímentary Rocks: The ComposítíonAngela PerillaNo ratings yet
- Butech StoneDocument4 pagesButech StonenathaliejemgalangNo ratings yet
- Research RocksDocument14 pagesResearch RocksHappy UniverseNo ratings yet
- What Types of Rocks Do Clastic Sediments Form?Document2 pagesWhat Types of Rocks Do Clastic Sediments Form?Abdullah ShahidNo ratings yet
- BT StoneDocument6 pagesBT StonePaulyn Mae RadinNo ratings yet
- Zen Kenneth A. Panaligan STEM 11-38 Igneous Rocks History of Formation Common Environment of Formation Common Texture Common Use of The Rock GraniteDocument4 pagesZen Kenneth A. Panaligan STEM 11-38 Igneous Rocks History of Formation Common Environment of Formation Common Texture Common Use of The Rock GraniteZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Diamond As Phonograph Stylus: MaterialDocument4 pagesDiamond As Phonograph Stylus: MaterialJoão SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- List of Rock Sample Type of Rock Outstanding Characteristics UsesDocument1 pageList of Rock Sample Type of Rock Outstanding Characteristics UsesSharmaine AcNo ratings yet
- Construction MaterialsDocument104 pagesConstruction MaterialsRajesh MandalNo ratings yet
- Uartz-Is A Chemical Compound: Ls/minerals/quartz - HTML 8700692.htmlDocument2 pagesUartz-Is A Chemical Compound: Ls/minerals/quartz - HTML 8700692.htmlAyesha Faye BelarminoNo ratings yet
- GRUPO N°6 ARENISCA PA1 GeoADocument8 pagesGRUPO N°6 ARENISCA PA1 GeoAJair OlivaNo ratings yet
- Quarrying: Sario, Kachel Joy S. 2018103828Document30 pagesQuarrying: Sario, Kachel Joy S. 2018103828Kachel SarioNo ratings yet
- Science IgneousDocument12 pagesScience IgneousAira GalacgacNo ratings yet
- Hwno.3 Bsa1c Saylon Efraine AndreaDocument42 pagesHwno.3 Bsa1c Saylon Efraine Andreaefraineandrea.saylonNo ratings yet
- Activityno.2-Table ResGeo MindanaoDocument16 pagesActivityno.2-Table ResGeo Mindanao22-08420No ratings yet
- 8G Rocks and WeatheringDocument12 pages8G Rocks and WeatheringRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- PETROLOGY RevisedDocument10 pagesPETROLOGY RevisedKangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.5 Sedimentary RocksDocument26 pagesChapter 3.5 Sedimentary RocksK YNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Petroleum Engineering: Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum EngineeringDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Petroleum Engineering: Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum Engineeringanes anesNo ratings yet
- Rocks LessonDocument12 pagesRocks LessonhtfcbqxstnNo ratings yet
- Effect of Weathering To Landscape in Different Rock TypeDocument17 pagesEffect of Weathering To Landscape in Different Rock TypeWan Ahmad FaizFaizalNo ratings yet
- Igneous Sedimentary MetamorphicDocument3 pagesIgneous Sedimentary MetamorphicKezel AtangenNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialDocument44 pagesBuilding MaterialMamta Maurya100% (1)
- UNIT 2 - BM StoneDocument33 pagesUNIT 2 - BM StoneMohini ChavanNo ratings yet
- EGEO4Document6 pagesEGEO4.....No ratings yet
- Materia Stone Cha 2Document6 pagesMateria Stone Cha 2Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Building Stone: I) Geological ClassificationDocument5 pagesChapter Four Building Stone: I) Geological ClassificationAbinet AlemuNo ratings yet
- Clasification Soil and Rock by VietnamDocument3 pagesClasification Soil and Rock by VietnamThach Nik ThachNo ratings yet
- CH 1 StonesDocument20 pagesCH 1 StonesNirose ChhukanNo ratings yet
- Morphology of StoneDocument9 pagesMorphology of StoneMeg CuñadoNo ratings yet
- 15. construction materials final (1)Document65 pages15. construction materials final (1)Khushi RathodNo ratings yet
- Activityno.2 TableDocument16 pagesActivityno.2 Table22-08420No ratings yet
- Chapter Iii - Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter Iii - Guide QuestionsTroyo, Keen Mae JoyNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetHarold The GreatNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument32 pagesROCKSJhellee AquinoNo ratings yet
- Articulo 3Document5 pagesArticulo 3Maria JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument6 pagesTypes of RocksAlthea Joy SalaanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Petrology in C.EDocument16 pagesImportance of Petrology in C.EERNIE TILLAMANo ratings yet
- Mud Loggers 77 Most Important Questions With AnswersDocument12 pagesMud Loggers 77 Most Important Questions With Answersfadhian_hasbiNo ratings yet
- Rocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RocksDocument3 pagesRocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RockssubhaseduNo ratings yet
- Stones Q & ADocument20 pagesStones Q & ARajha RajeswaranNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Salida de Campo Pedregal-ChosicaDocument23 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Salida de Campo Pedregal-ChosicaAnonymous GyEOgNGNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms FDocument31 pagesGlossary of Terms FVasilis LappasNo ratings yet
- GEM1207 Lab2 GroupADocument3 pagesGEM1207 Lab2 GroupADanan GentleNo ratings yet
- STONESDocument46 pagesSTONESUrmi PatelNo ratings yet
- Stones: Stones Constitute An Important Building Material Used For Various Structures. They AreDocument8 pagesStones: Stones Constitute An Important Building Material Used For Various Structures. They AreSk Suraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Stone: SEM I, F.Y. B.ArchDocument42 pagesStone: SEM I, F.Y. B.ArchRISHABH JAISWAL100% (1)
- Sedimentary RockDocument1 pageSedimentary RockTien NguyenNo ratings yet
- (For Engineer) Constructon Materials Except SoilDocument51 pages(For Engineer) Constructon Materials Except SoilMukesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks and Their Examples - 20231009 - 162754 - 0000Document2 pagesTypes of Rocks and Their Examples - 20231009 - 162754 - 0000Jhoanne Marie ColloNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Factsheet FINALDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Factsheet FINALMarta CFNo ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument2 pagesRock Cyclemrinal.lm10No ratings yet
- Handout 10 Characteristics of Placer DepositsDocument7 pagesHandout 10 Characteristics of Placer DepositsfercanzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2B RocksDocument3 pagesChapter 2B RocksJefferson YagueNo ratings yet
- NGT 49 1 001-031Document31 pagesNGT 49 1 001-031Jehezkiel SanggorNo ratings yet
- Expand: MarbleDocument5 pagesExpand: MarblederejkNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Rock PropertiesDocument5 pagesClassifications of Rock PropertiesAlwin AntonyNo ratings yet
- Rocks: The Rock CycleDocument1 pageRocks: The Rock CycleJoy Grace TablanteNo ratings yet
- Paper Template RILEmDocument3 pagesPaper Template RILEmPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Seismic Weight Calculations For EarthquakeDocument4 pagesSeismic Weight Calculations For EarthquakePrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- APPLICATONS & LIMITATIONS of Self Compacting ConcreteDocument38 pagesAPPLICATONS & LIMITATIONS of Self Compacting ConcretePrashant Sunagar100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing of ConcreteDocument5 pagesUltrasonic Testing of ConcretePrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Dams in IndiaDocument33 pagesDams in IndiaPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Properties of MortarDocument3 pagesProperties of MortarPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Application of Geotextiles inDocument17 pagesApplication of Geotextiles inPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Earthquake Resisting TechniquesDocument14 pagesAdvanced Earthquake Resisting TechniquesPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity of CementDocument3 pagesSpecific Gravity of CementPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Labor Requirement For Various Construction WorksDocument4 pagesLabor Requirement For Various Construction WorksPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Model MakingDocument2 pagesModel MakingPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Building Graphics Lab ManualDocument32 pagesBuilding Graphics Lab ManualPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Problems On C.P.M &PERT: Problem1Document17 pagesProblems On C.P.M &PERT: Problem1Kulmohan116No ratings yet
- List of Experiments (CV607L) - 1Document1 pageList of Experiments (CV607L) - 1Prashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- 2020 Exam Words:: WB GVWBK Power Vocabulary' KgwcøuDocument4 pages2020 Exam Words:: WB GVWBK Power Vocabulary' KgwcøuAll bdNo ratings yet
- Ut Austin Masters Thesis FormatDocument5 pagesUt Austin Masters Thesis Formatdnr16h8x100% (2)
- Optimized Extraction of Dimension Stone BlocksDocument14 pagesOptimized Extraction of Dimension Stone Blocksdvdcopia1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quantification of Groundwater PressureDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Quantification of Groundwater PressurekkgbkjNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: ReviewDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Science: ReviewBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- Design of The Coatzacoalcos Immersed Tunnel 3Document1 pageDesign of The Coatzacoalcos Immersed Tunnel 3Trong TranNo ratings yet
- Jurassic World Evolution Dinosaur StatsDocument9 pagesJurassic World Evolution Dinosaur StatsMatt DNo ratings yet
- The Solar System Questions KEYDocument64 pagesThe Solar System Questions KEYTel AntonNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Paper-3 - Geography: Barren Island, A&N IslandsDocument1 page2024 - Paper-3 - Geography: Barren Island, A&N IslandsVampireNo ratings yet
- Earthworks For Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesEarthworks For Civil EngineeringCristian Corso SNo ratings yet
- First Session of NPDRRDocument359 pagesFirst Session of NPDRRHansen Thambi PremNo ratings yet
- 0 BibliografíaDocument3 pages0 BibliografíaDaniel Espinosa RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Faa Ac 150 5320-6e.2Document124 pagesFaa Ac 150 5320-6e.2troyscribdNo ratings yet
- 2 Geochemical Analysis - Gas Chromatography and GC-MSDocument12 pages2 Geochemical Analysis - Gas Chromatography and GC-MSLambok Manurung100% (1)
- NumbersDocument4 pagesNumbersClaudia Nicole Bugueño VillalonNo ratings yet
- Section 02310 Grading Rev 0Document18 pagesSection 02310 Grading Rev 0Abdul HannanNo ratings yet
- G10Q3 - Nacasabug - Sources of Evidence For EvlutionDocument16 pagesG10Q3 - Nacasabug - Sources of Evidence For EvlutionJenalyn NacasabugNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of SoilsDocument11 pagesPhysical Properties of SoilsTarpan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Sheet (3) - PermeabilityDocument4 pagesSheet (3) - PermeabilityshereenNo ratings yet
- A3 - Rock Uganda GeologyDocument1 pageA3 - Rock Uganda GeologyGeoffrey NsubugaNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement For Low Rise Buildings - Structural GuideDocument3 pagesGround Improvement For Low Rise Buildings - Structural GuideA KNo ratings yet
- Latihan ToefDocument6 pagesLatihan ToefAzri IX1No ratings yet
- GorakhpurDocument18 pagesGorakhpurDeepansha TyagiNo ratings yet
- Jurassic Sequence StratigraphyDocument22 pagesJurassic Sequence Stratigraphyعبدالعزيز عبداللهNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Site InvestigationDocument6 pagesThe Importance of Site Investigationpaul macharia100% (1)
- Ore Geology Reviews: SciencedirectDocument18 pagesOre Geology Reviews: SciencedirectLeonardo JaimesNo ratings yet
- Kyyeu-Cohocdafull (2019)Document400 pagesKyyeu-Cohocdafull (2019)thuy giang0% (1)
- What Are Lithospheric PlatesDocument4 pagesWhat Are Lithospheric PlatesCarl McDermottNo ratings yet
- Geography Ss1Document21 pagesGeography Ss1Adeniyi Israel100% (1)
- Developing A Program For The Communication of Ground Control Information in Surface and Underground MinesDocument62 pagesDeveloping A Program For The Communication of Ground Control Information in Surface and Underground MinesTúlio AbduaniNo ratings yet
Construction Technology Notes
Construction Technology Notes
Uploaded by
Prashant SunagarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Construction Technology Notes
Construction Technology Notes
Uploaded by
Prashant SunagarCopyright:
Available Formats
(9)Cut stone dressing }
The dressing in which all the projections from all the faces»of a stone block are removed by IMPORTANT POINTS ]
means of a sharp chisel, rendering the surface free of c h i s e l marks is called cut
stone dressing. This type of dressed stones used for ashlar masonry.
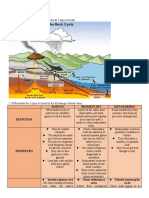
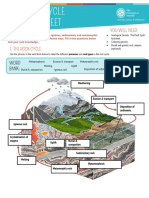
I. Sedimentary rocks are also called stratified rocks.
(10)Rubbed dressing
2. Argillaceous rocks have their main constituent as clay or a l u m i n a .
The dressing in w h i c h a perfectly smooth surface fi n i s h is obtained by grinding or rubbing a
3. The exposed surface of natural rock is used to indicate quarry and process of taking out stone
cut stone by hand or by machine is called rubbed dressing. This type of dressed stone used for
from natural rock beds is known as quarry i n g .
ashlar masonry.
4. Tools used for blastin g are D i pp er , Ju m p er , P ri m in g needle , S c r a p i n g spoon & Tamping ro d .
(11)Polished dressing
5 . L i n e of least re sis tance is the line or distance from the c e ntr e o f t h e b l ast hole to the face of
The dressing in which the rubbed stone surfaces are polished by manual labour, u s i n g sand
the ro ck exposed to air, a l ong w hich the gases g enerated durin g the e x plosion of the ch ar ge
. and water, pumice stone etc. or by means of a rubbing machine is called polished dressing.
w i ll find least resistance to escape into the a ir.
6. Forms of artificial stones are Cement concrete, Mosaic t i l e s , Terrazo.
7. Examples for I gneous rock : B asalt , G ra nite , D olerite .
8. Examples for Sedimentary rocks are: Chalk, Kankar, Li m e stone, S a n d stone.
9. EK%ipiss rorierorphic rocks: Gneiss, Laterite. Marble. Murrum, Quartzite, Slate
10. Most commonly used preservatives are Coal tar, L inseed o i l , Paint, Paraffin, S olution of alum
and soap & S olution of baryta.
[Review a u E s r o v s ]
Fill up the blanks with appropriate word/words
I. Rocks formed due to coolin g of magma at a considerable depth from earth's surface are ca ll e d ·
rocks.
-----
2. The rocks w hich are fo rmed by the deposition of products of weatherin g on the p re-e x isting
rocks is known as _
3. The process of taking out stones from natural rock beds is known as _
4. A good building stone is one which does not absorb more than o · 6 / o f its weight of
water after one day of immersion.
- 5 . o [ c o n ? c_ @ { \ formed due to pouring of magma at earth's surface.
6. In siliceous rock, the predominates.
7. To quarry the hard stone and compact rocks method is used.
8. For docks and other marine structures the best choice of stone is _
9. rocks are formed by g ra dual deposition.
I0. rocks are g enera ll y used for road metals .
I I. Cement concrete is an example of stone.
-12. is the ma i n p redominant in argillaceous rock.
C l o-
13. rocks formed due to cooling of magma at relatively shallow depth.
-----
4. The comp"e";"",sength of stone found out by ..test
45. T a mo p i v a is ~tool made fb d 20. State the properties and uses of marbles. u-
-" ' . g upot ronze use to ram the blasting material during the process
- of charging the hole. . 's e US
21. Name two metamorphic rocks & give their engineering S u i t a b i l i t y .
I6.The crushing strength of good building stone should not be less than _L 9 0 9_ . A @ t e a? 22. Explain the procedure generally adopted for making an artificial stone.
Answers '-' ! s / Ce .
23. How do you determine hardness of stone?
I. Plutonic rocks 24. What is texture of a rock ? what are its different forms.
2. S edimentar y rocks
3. Quarryin g 25. What are the qualities and uses of granite and sand stone.
4. 0.60%
5. Volcanic rocks
6. Silica 26. Brifely explain more common l y used explosives for blasting.
7. B l as tin g 27. What are the minerals found in the Igneous rocks? Explain briefly Hornblende and Quartz
8. Granite
9. Se dimentary rocks 28. List any two types of stones available in Karnataka and write th e i r p r o p e r t i e s .
10. B as alt
l 1. Artificial 29. What are advantages of a r t i f i c i a l stone? •
1 2 Clay
13. Hypabyssal 30. Name and e x p l a i n stone destroying agents.
14. Crushing
15. Tamping bar 3I. Explain the characteristics of good building stone.
16. l000
32. Factors to be considered while making a selection for quarry site.
Descriptive Type Questions
33. Define quarrying: Exptain the process of blasting w i th a neat sketch.
I. Lis t the methods of quarrying. .
34. Explain briefly the geological classification of rocks with examples.
2. How are "cast stones" prepared.-
35. Explain briefly deterioration of stones.
3. Distinguish between quarrying and quarry.v-
36. Explain briefly the chemical classification of rocks with examples.
4. List the precautions to be taken in the blasting operation.
37. Explain briefly the physical classification of rocks with examples.
5. State the uses of stones as an engineerin g material. I
6. List tests on stone.
7. Define natural bed of stone and give its importance.
8. Explain 'Line of least resistance ' with a sketch.
9. Mention the rock forming minerals.--
10. Expl ai n briefly different forms of art i fic i al stones.
I
. ,
11. Explain chemical classification of rocks.
12. What is meant by preservation of stones? List the commonly used preservatives.
13. What are the qualities of an i d e al preservative?
14. Expalin the following rock fo r ming minerals.
I
t
i) felspar
i
ii) quartz ;
t
15. Give sketches of tools used for blasting. !
I6. Distinguish between the Granite and marble.
17. Distinguish between natural stone and artificial s t o n e . <
I
18. Write the objects of acid test on stone. °
19. write short note on artificial stone. "
STORAGE OF T I M B E R
IMPORTANT POINTS I
The converted tim b e r s should be properly stored.
For the pu rp ose of sto rag e , sui tab le stack s of t im b er
I. The timber which is sawn and - c u t into suitable commercial sizes is known as converted
pie ces are for med. The ti m b er pi e c es are arranged in
timber.
%
layers and the lay e r s are separated by wooden spacers.
j 9 The inner annual ring surrounding pith constitute the heart wood & it imparts strength to timber.
The stock is protected from d ir ect sun , dry wind and
3. The defects occurring in the timber are grouped into fi v e categories viz., defect due to fungi
rain. The fo l l o w i n g precautions should be taken while
insects, seasoning, nat ural forces & conversion.
storing:
Correct way of stacking
4. The tern rot is used to indicate decay or disease of timber.
I. In each layer, an air space of about 25mm should ti m be r. always with st r i p s on
be maintained between adjacent members. top of each other 5. The shakes are cracks w hich p a rtly or com p l etely separate the fibres of wood.
2. The spacers should be sound, straight and uniform 6. The various method of artificial seasoning are Boiling.Chemical seasoning, Electrica
3.
th ick n ess .
The longer pieces should be placed i n bottom layers
����------
��m::-�
-_--=:.m��:
-------- _-Ji--.,-,
·
seasoning, K i l n seasoning and Water seasoning.
7. The various market forms of tim b er are Ba tte n, Ba u lk, Board, Deal, End, Log. Plank, Pole
S c a nt l in g, etc. .
and the shorter pieces sh o ul d be placed in top layers. f....:.___
___. ®j
....__ ��
-
4. The ends of all members should be coated Yiji.Jl. - _ m;. .. . . '8. The timber which is prepared scientifically in a factory is termed as the industrial timber
1
suitable materials to prevent end-cracking. E Example: Veneers, Plywoods, Fibre boards, Impreg timbers, Compreg timbers, etc.
5. The platform of stack should be made at least I5cm wrong way, staggering the 9. The thin sheets of wood are known as veneers & the boards prepared by. gluing under pressur
higher than gro u n d . p ositi o ns of strips induces three or more veneers is kn o w n as ply wood. .
bending
Fig. 2 . 1 7 : Stacking of Timber
REVIEW QUESTIONS]
Fill up the blanks with appropriate word/words
I. The tim b er which is prepared scien t i fi ca ll y in a ctory
fa and possess desired shape, strengtl
appearance, etc, is termed as
2. Timber which is mostly used for engineering purposes are _trees.
3. The process of removing s ap from timber is known as
-----
4. Timber which is o bta i ned after felling a tree is _
5. The thin radial fibres extending from pith to cambium layer are known as _
6. Conifers are also known as _trees.
7. The innermost central portion of timb er is called
8. An irregular growth c a used by the fibres on wo und left after the branch e s h av e cut off
9. Decay of t i mber due to alternate w ettin g and dry i ng is called _
10.
trees grow inward by depositing each fresh layer internally instead of on tl
exterior.
H. Deciduous trees are known as _trees.
2. Dry rot defect is caused by
13. Trees growing outwards are known.as _
26. Differentiate between lmpreg timber and Compreg timber.
14. The inner layer covering the cambium layer is known as _
27. Mention five varieties of industrial timber.
15. Thin sheets or slices of wood of superior quality called as _
28. Give the classification of trees according to their mode of growth.
Answers
29. Name the five d i v i s i o n s of defects occurring in the timber.
I. Industrial timber 2. Exogenous 3. S easoning
4. Rough ti m be r 30. Enumerate the comparison between natural seasoning and k i l n seasoning.
5. Medullary rays 6. Ever-green
5
Pith 3 1. What is meant by decay and seasoning of timber?
7.
8. Ringza" 9. wet rot
10. Endogenous 32. What are the causes of decay in timber?
1 1. Bro ad - leaf trees 12. fungi
13. Exogenous trees 2 33. Name the various methods of artificial seasoning.
1 4. I nner bark 15. Veneers z
�
34. Write note on c h e m i c a l seasoning.
Descriptive Type Questions
35. write short note on Prevention of wet rot.
1. What is meant by rough timber and converted timber.
36. Give the names and dimensions of the various fo rms of timber sold i n the market.
2. With e xa m pl e compare soft wood and hard wood.
37. What are the three objects of preservation of timber?
3. With an neat sketch, explain the transverse section of the trunk of an exogenous tree.
38. Differentiate between cup shake and star shake.
4. Differentiate between cup sha kes and heart shaes.
39. State the various market forms of timber.
···································
5 Write a note on water seasoning method.
40. Give sketch for horizontal s t a c k for air seasoning.
6. Expla i n the charring method of preservation of timber.
4 1. Define: veneers, Knots.
7. Write a brief note on cl a s sifi c a tion of trees.
4 42. Ex plain brie fl y Termites & F o x iness.
8. List the methods of seasoning. Ex p l ain the k i l n sea so nin g.
6 43. W hat are the advantages and disadvantages of natural seasoning.
9. List the variet i es of ind u s t r i al timber.
5 44. Define: Timber, softwood, pith, medullary rays.
10. What are the uses of timber?
4 45. Describe the defects caused in timber due to fu ng i .
11. W h a t are the advantages of plyw ood s?
6 45. D istinguish between:
12. Write a note on preservation of timber s.
5 i) Plywood & fibre board.
13. What is meant by season i n g of t i mber?
ii) Plywood & veneers.
14. List the defects i n t i m be r.
iii ) Natural seasoning & Art i fi c i a l seasoning.
15. Write short note on ind u s trial timber.
46. Men tion the four varieties of timber.
16. What are Plywood's? Give its uses.
4 7. How trees are clas sified?
17. Name the various market forms of timb e r.
48. What are k nots? How are they cl assified?
18. Draw a neat cross-section of an exogenous tree and s h o w its v arious co mponents .
1 9. E x p l a in natu ra l se a soni n g of timber.
20. What are the defects caused due to s ea son i ng ?
2 1 . Name the types of preservatives c om m on ly used fo r timber.
2
2. Write a note on the storage of timber.
23. Differentiate between exogenous and endogenous trees.
2 4. Exp lain brie fly with s k etch , Tangential s a w i ng of t i m b e r.
2 5. State the objects of seasonin g .
Descriptive Type Questions
. ' ..
IMPORTANT P O I N T S ]
I. Name the standard tests conducted on bricks & mention the standard values, if any.
2. Write short note on clay bricks.
1. A good brick clay contains 20 to 30% of alumina, 50 to 60% s i l i c a and the remaining
3. What are the qualities of a good brick?
constituents are lime, magnesia, sodium, potassium, manganese and iron oxide.
_A
Defferentiate between header and stretcher.
2. The excess of silica in the clay makes the brick brittle and weak.
5. Explain the construction and working of the intermittent upright kiln with neat sketch. u
3. The standard size of brick are 19cm x 9cm x 9cm.
4. Process of manufacturing of bricks consists of Preparation of brick clay, Moulding bricks, 6. What are the raw materials required for manufacture of bricks? Mention their percentage and
functions..
Drying of bricks and Burning of bricks.
7. Differentiate between plastic clay machines and dry clay machines. •.
5. Moulding of bricks may be hand moulding or machine moulding.
8. What are the harmful ingredients of brick earth? In what way are they harmful?
6. Harmful constituents of brick earth are Lime, Iron pyrites, Alkalies, Pebbles & Vegetation
and organic matter. 9. What is meant by pu g ging ? '-
7. The burning of dry bricks is done either in clamp or in a kiln. 10. Ex plain with a neat sketch, the process of bu rn in g of bricks by a cl a m p .
8. Refractory bricks are Acid bricks, Basic bricks and Neutral bricks. IE Explain the stages i n v o l v e d in preparation of clay for brick manufacturing. ...
._Explain briefly the constituents of good brick earth.
13. B rie fly describe the w orking of B u ll ' s trench kiln , with neat sketch for the b u r n i n g of b ricks.
REVIEW QUESTIONS I
14. What are the uses of bricks? «
I5. Explain briefly 'absorption test' on bricks.
Fill up the blanks with appropriate word/words
l6.
Mention the standard dimensions of bricks as per IS.
[. Hollow bricks are also known as ' s p y bricks
17. Explain the stages involved in preparation of clay for brick manufacturing.
2. 9 s i n imparts yellow tint to bricks.
_I8 W r i t e short note on wire cut bricks.
3. Brickearth possesses the property of plasticity due to presence of
19. Draw a neat sketch of a pug mill & explain it.
The bricks prepared by dipping mould in water every time is known a s 7 ' ii
20. Write a short note on Fl y -ash bricks.
/ 5. The process of grinding clay with water and making it plastic is known a s. ' _ 1 ' 2 y ; ;
21. What are fire bricks? Mention their varities.
6. A good brick should not absorb more than ' ' '· o f its dry weight of water when
22. Explain the process of hand moulding of b ri c k s . .
immersed in water for 24 hours.
23. Give the comparison between clamp burnin g and k iln burning.
7. Brick made from fire clay are called s ± ·
24. Explain briefl y the hollow bricks.
8. Colour of good brick is [_ts¥ 5 D '
25. What are the uses of refractory bricks?
9. li,_ are the permanent structures used to burn bricks in large scale.
26. With the help of a neat s k e t c h , explain the working of Hoffman's Kiln for burning of bricks.
..,� The art of arranging the brick masonry wall is called ,-:_ ·- , , -t• :
27. Distinguish between first class bricks and second class bricks.
Answers 28. Write short note on Refractory Material.
I. Cellular or Cavity bricks 2. Magnesia
29. State the three important qualities of bricks.
3. Alumina 4. Ground moulded bricks
30. Differentiate between intermittent kiln and continuous kiln.
5. pugging 6. 20% 3 l. B rie fly explain artificial d r y in g of bricks.
7. Fire bricks 8. Copper colour 32. Write short note on hollow bricks.
9. Kilns IO. Bond 33. Give IS specification for bricks.
34. what are the different shapes of bricks?
You might also like
- Waffle Slab DesignDocument23 pagesWaffle Slab DesignMwengei Muteti100% (1)
- Application of Gis in Civil Engineering FinalDocument14 pagesApplication of Gis in Civil Engineering FinalPrashant Sunagar100% (2)
- Unit 1Document131 pagesUnit 1madhu.ammu112No ratings yet
- And Exture of Sedímentary Rocks: The ComposítíonDocument12 pagesAnd Exture of Sedímentary Rocks: The ComposítíonAngela PerillaNo ratings yet
- Butech StoneDocument4 pagesButech StonenathaliejemgalangNo ratings yet
- Research RocksDocument14 pagesResearch RocksHappy UniverseNo ratings yet
- What Types of Rocks Do Clastic Sediments Form?Document2 pagesWhat Types of Rocks Do Clastic Sediments Form?Abdullah ShahidNo ratings yet
- BT StoneDocument6 pagesBT StonePaulyn Mae RadinNo ratings yet
- Zen Kenneth A. Panaligan STEM 11-38 Igneous Rocks History of Formation Common Environment of Formation Common Texture Common Use of The Rock GraniteDocument4 pagesZen Kenneth A. Panaligan STEM 11-38 Igneous Rocks History of Formation Common Environment of Formation Common Texture Common Use of The Rock GraniteZen Kenneth A. PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Diamond As Phonograph Stylus: MaterialDocument4 pagesDiamond As Phonograph Stylus: MaterialJoão SiqueiraNo ratings yet
- List of Rock Sample Type of Rock Outstanding Characteristics UsesDocument1 pageList of Rock Sample Type of Rock Outstanding Characteristics UsesSharmaine AcNo ratings yet
- Construction MaterialsDocument104 pagesConstruction MaterialsRajesh MandalNo ratings yet
- Uartz-Is A Chemical Compound: Ls/minerals/quartz - HTML 8700692.htmlDocument2 pagesUartz-Is A Chemical Compound: Ls/minerals/quartz - HTML 8700692.htmlAyesha Faye BelarminoNo ratings yet
- GRUPO N°6 ARENISCA PA1 GeoADocument8 pagesGRUPO N°6 ARENISCA PA1 GeoAJair OlivaNo ratings yet
- Quarrying: Sario, Kachel Joy S. 2018103828Document30 pagesQuarrying: Sario, Kachel Joy S. 2018103828Kachel SarioNo ratings yet
- Science IgneousDocument12 pagesScience IgneousAira GalacgacNo ratings yet
- Hwno.3 Bsa1c Saylon Efraine AndreaDocument42 pagesHwno.3 Bsa1c Saylon Efraine Andreaefraineandrea.saylonNo ratings yet
- Activityno.2-Table ResGeo MindanaoDocument16 pagesActivityno.2-Table ResGeo Mindanao22-08420No ratings yet
- 8G Rocks and WeatheringDocument12 pages8G Rocks and WeatheringRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- PETROLOGY RevisedDocument10 pagesPETROLOGY RevisedKangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.5 Sedimentary RocksDocument26 pagesChapter 3.5 Sedimentary RocksK YNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Petroleum Engineering: Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum EngineeringDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Petroleum Engineering: Faculty of Petroleum Engineering Faculty of Petroleum Engineeringanes anesNo ratings yet
- Rocks LessonDocument12 pagesRocks LessonhtfcbqxstnNo ratings yet
- Effect of Weathering To Landscape in Different Rock TypeDocument17 pagesEffect of Weathering To Landscape in Different Rock TypeWan Ahmad FaizFaizalNo ratings yet
- Igneous Sedimentary MetamorphicDocument3 pagesIgneous Sedimentary MetamorphicKezel AtangenNo ratings yet
- Building MaterialDocument44 pagesBuilding MaterialMamta Maurya100% (1)
- UNIT 2 - BM StoneDocument33 pagesUNIT 2 - BM StoneMohini ChavanNo ratings yet
- EGEO4Document6 pagesEGEO4.....No ratings yet
- Materia Stone Cha 2Document6 pagesMateria Stone Cha 2Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Building Stone: I) Geological ClassificationDocument5 pagesChapter Four Building Stone: I) Geological ClassificationAbinet AlemuNo ratings yet
- Clasification Soil and Rock by VietnamDocument3 pagesClasification Soil and Rock by VietnamThach Nik ThachNo ratings yet
- CH 1 StonesDocument20 pagesCH 1 StonesNirose ChhukanNo ratings yet
- Morphology of StoneDocument9 pagesMorphology of StoneMeg CuñadoNo ratings yet
- 15. construction materials final (1)Document65 pages15. construction materials final (1)Khushi RathodNo ratings yet
- Activityno.2 TableDocument16 pagesActivityno.2 Table22-08420No ratings yet
- Chapter Iii - Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter Iii - Guide QuestionsTroyo, Keen Mae JoyNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Activity Sheet KS2 Answer SheetHarold The GreatNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument32 pagesROCKSJhellee AquinoNo ratings yet
- Articulo 3Document5 pagesArticulo 3Maria JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument6 pagesTypes of RocksAlthea Joy SalaanNo ratings yet
- Importance of Petrology in C.EDocument16 pagesImportance of Petrology in C.EERNIE TILLAMANo ratings yet
- Mud Loggers 77 Most Important Questions With AnswersDocument12 pagesMud Loggers 77 Most Important Questions With Answersfadhian_hasbiNo ratings yet
- Rocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RocksDocument3 pagesRocks (Contd.) : Note 6 Class 9 Sedimentary RockssubhaseduNo ratings yet
- Stones Q & ADocument20 pagesStones Q & ARajha RajeswaranNo ratings yet
- Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Salida de Campo Pedregal-ChosicaDocument23 pagesUniversidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos: Salida de Campo Pedregal-ChosicaAnonymous GyEOgNGNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms FDocument31 pagesGlossary of Terms FVasilis LappasNo ratings yet
- GEM1207 Lab2 GroupADocument3 pagesGEM1207 Lab2 GroupADanan GentleNo ratings yet
- STONESDocument46 pagesSTONESUrmi PatelNo ratings yet
- Stones: Stones Constitute An Important Building Material Used For Various Structures. They AreDocument8 pagesStones: Stones Constitute An Important Building Material Used For Various Structures. They AreSk Suraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Stone: SEM I, F.Y. B.ArchDocument42 pagesStone: SEM I, F.Y. B.ArchRISHABH JAISWAL100% (1)
- Sedimentary RockDocument1 pageSedimentary RockTien NguyenNo ratings yet
- (For Engineer) Constructon Materials Except SoilDocument51 pages(For Engineer) Constructon Materials Except SoilMukesh MishraNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks and Their Examples - 20231009 - 162754 - 0000Document2 pagesTypes of Rocks and Their Examples - 20231009 - 162754 - 0000Jhoanne Marie ColloNo ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Factsheet FINALDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Factsheet FINALMarta CFNo ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument2 pagesRock Cyclemrinal.lm10No ratings yet
- Handout 10 Characteristics of Placer DepositsDocument7 pagesHandout 10 Characteristics of Placer DepositsfercanzaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2B RocksDocument3 pagesChapter 2B RocksJefferson YagueNo ratings yet
- NGT 49 1 001-031Document31 pagesNGT 49 1 001-031Jehezkiel SanggorNo ratings yet
- Expand: MarbleDocument5 pagesExpand: MarblederejkNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Rock PropertiesDocument5 pagesClassifications of Rock PropertiesAlwin AntonyNo ratings yet
- Rocks: The Rock CycleDocument1 pageRocks: The Rock CycleJoy Grace TablanteNo ratings yet
- Paper Template RILEmDocument3 pagesPaper Template RILEmPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Seismic Weight Calculations For EarthquakeDocument4 pagesSeismic Weight Calculations For EarthquakePrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- APPLICATONS & LIMITATIONS of Self Compacting ConcreteDocument38 pagesAPPLICATONS & LIMITATIONS of Self Compacting ConcretePrashant Sunagar100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing of ConcreteDocument5 pagesUltrasonic Testing of ConcretePrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Dams in IndiaDocument33 pagesDams in IndiaPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Properties of MortarDocument3 pagesProperties of MortarPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Application of Geotextiles inDocument17 pagesApplication of Geotextiles inPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Earthquake Resisting TechniquesDocument14 pagesAdvanced Earthquake Resisting TechniquesPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity of CementDocument3 pagesSpecific Gravity of CementPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Labor Requirement For Various Construction WorksDocument4 pagesLabor Requirement For Various Construction WorksPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Model MakingDocument2 pagesModel MakingPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Building Graphics Lab ManualDocument32 pagesBuilding Graphics Lab ManualPrashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- Problems On C.P.M &PERT: Problem1Document17 pagesProblems On C.P.M &PERT: Problem1Kulmohan116No ratings yet
- List of Experiments (CV607L) - 1Document1 pageList of Experiments (CV607L) - 1Prashant SunagarNo ratings yet
- 2020 Exam Words:: WB GVWBK Power Vocabulary' KgwcøuDocument4 pages2020 Exam Words:: WB GVWBK Power Vocabulary' KgwcøuAll bdNo ratings yet
- Ut Austin Masters Thesis FormatDocument5 pagesUt Austin Masters Thesis Formatdnr16h8x100% (2)
- Optimized Extraction of Dimension Stone BlocksDocument14 pagesOptimized Extraction of Dimension Stone Blocksdvdcopia1No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quantification of Groundwater PressureDocument7 pagesChapter 2 Quantification of Groundwater PressurekkgbkjNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: ReviewDocument2 pagesEarth and Life Science: ReviewBobby Arguilles PaboresNo ratings yet
- Design of The Coatzacoalcos Immersed Tunnel 3Document1 pageDesign of The Coatzacoalcos Immersed Tunnel 3Trong TranNo ratings yet
- Jurassic World Evolution Dinosaur StatsDocument9 pagesJurassic World Evolution Dinosaur StatsMatt DNo ratings yet
- The Solar System Questions KEYDocument64 pagesThe Solar System Questions KEYTel AntonNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Paper-3 - Geography: Barren Island, A&N IslandsDocument1 page2024 - Paper-3 - Geography: Barren Island, A&N IslandsVampireNo ratings yet
- Earthworks For Civil EngineeringDocument20 pagesEarthworks For Civil EngineeringCristian Corso SNo ratings yet
- First Session of NPDRRDocument359 pagesFirst Session of NPDRRHansen Thambi PremNo ratings yet
- 0 BibliografíaDocument3 pages0 BibliografíaDaniel Espinosa RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Faa Ac 150 5320-6e.2Document124 pagesFaa Ac 150 5320-6e.2troyscribdNo ratings yet
- 2 Geochemical Analysis - Gas Chromatography and GC-MSDocument12 pages2 Geochemical Analysis - Gas Chromatography and GC-MSLambok Manurung100% (1)
- NumbersDocument4 pagesNumbersClaudia Nicole Bugueño VillalonNo ratings yet
- Section 02310 Grading Rev 0Document18 pagesSection 02310 Grading Rev 0Abdul HannanNo ratings yet
- G10Q3 - Nacasabug - Sources of Evidence For EvlutionDocument16 pagesG10Q3 - Nacasabug - Sources of Evidence For EvlutionJenalyn NacasabugNo ratings yet
- Physical Properties of SoilsDocument11 pagesPhysical Properties of SoilsTarpan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Sheet (3) - PermeabilityDocument4 pagesSheet (3) - PermeabilityshereenNo ratings yet
- A3 - Rock Uganda GeologyDocument1 pageA3 - Rock Uganda GeologyGeoffrey NsubugaNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement For Low Rise Buildings - Structural GuideDocument3 pagesGround Improvement For Low Rise Buildings - Structural GuideA KNo ratings yet
- Latihan ToefDocument6 pagesLatihan ToefAzri IX1No ratings yet
- GorakhpurDocument18 pagesGorakhpurDeepansha TyagiNo ratings yet
- Jurassic Sequence StratigraphyDocument22 pagesJurassic Sequence Stratigraphyعبدالعزيز عبداللهNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Site InvestigationDocument6 pagesThe Importance of Site Investigationpaul macharia100% (1)
- Ore Geology Reviews: SciencedirectDocument18 pagesOre Geology Reviews: SciencedirectLeonardo JaimesNo ratings yet
- Kyyeu-Cohocdafull (2019)Document400 pagesKyyeu-Cohocdafull (2019)thuy giang0% (1)
- What Are Lithospheric PlatesDocument4 pagesWhat Are Lithospheric PlatesCarl McDermottNo ratings yet
- Geography Ss1Document21 pagesGeography Ss1Adeniyi Israel100% (1)
- Developing A Program For The Communication of Ground Control Information in Surface and Underground MinesDocument62 pagesDeveloping A Program For The Communication of Ground Control Information in Surface and Underground MinesTúlio AbduaniNo ratings yet