Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 viewsFish Cookery
Fish Cookery
Uploaded by
shagay.sheppy0106Fish are classified into two main categories - fin fish and shellfish. Fin fish include round fish like salmon and cod with eyes on both sides, and flat fish like sole and turbot with eyes on one side. They are also classified based on fat content as white fish which are low in fat and oily fish which are high in fat. Shellfish include crustaceans like crab and shrimp, and molluscs like oysters and mussels. When selecting fish, its eyes should be bright and its flesh firm. Different cooking methods for fish include boiling, steaming, grilling, frying and baking. Fish is cut into fillets, darne, tranche and other cuts for cooking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The 800g Challenge - EC SynkowskiDocument132 pagesThe 800g Challenge - EC SynkowskiTim Riley100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood DishesDocument54 pagesLesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood DishesMaureen Latayan Agbing91% (11)
- Finfish and Shellfish CookeryDocument14 pagesFinfish and Shellfish CookeryBrianna GrahamNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Milkfish and Some Processed FishDocument7 pagesParts of A Milkfish and Some Processed FishJoseph Adrian PadrigaNo ratings yet
- Bakhtar's RecipesDocument4 pagesBakhtar's RecipesskittlesrharaamNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Write Directions Using Signal WordsDocument16 pagesEnglish: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Write Directions Using Signal WordsMark Allen Labasan67% (3)
- Find Latest Hospitality Resources atDocument7 pagesFind Latest Hospitality Resources atpiyushNo ratings yet
- Cookery Quarter 2 Week 1-3Document9 pagesCookery Quarter 2 Week 1-3jan roiNo ratings yet
- Fish CookeryDocument6 pagesFish Cookerygauravkrishana28No ratings yet
- Fish - Grade 9Document3 pagesFish - Grade 9lil sister and cousinNo ratings yet
- Fish NewDocument6 pagesFish NewUP TO DATE VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- Fish NewDocument6 pagesFish NewUP TO DATE VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- FNH Part 4Document15 pagesFNH Part 4JessicaNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument16 pagesClassification of FishfelixrajasNo ratings yet
- Cooking Your Catch - A Handy Guide to Cleaning, Scaling, Gutting, Dressing, Curing, Smoking, Kippering and Drying - Including Some Serving SuggestionsFrom EverandCooking Your Catch - A Handy Guide to Cleaning, Scaling, Gutting, Dressing, Curing, Smoking, Kippering and Drying - Including Some Serving SuggestionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Fish MongeryDocument10 pagesChapter - 2 Fish MongeryKrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Quality of FishDocument90 pagesQuality of FishMario MelrickNo ratings yet
- Fish and ShellfishDocument117 pagesFish and Shellfishshanley cyra aboNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument10 pagesClassification of FishDebjyoti BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- TLE ReviewerDocument10 pagesTLE ReviewerAndrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Prepare Seafood DishesDocument36 pagesPrepare Seafood DishesRuby Esmeralda AndayaNo ratings yet
- FISH and SHELLFISHDocument61 pagesFISH and SHELLFISHMaricel Sanchez - Costillas71% (7)
- Classification of FishDocument16 pagesClassification of FishBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Handling and Storage of FishDocument14 pagesHandling and Storage of Fishelara diorNo ratings yet
- Fish and Sea FoodDocument9 pagesFish and Sea Fooditzmeaneesh50% (2)
- Rainbow Trout CultureDocument6 pagesRainbow Trout Cultureluis ruperto floresNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE7 Cookery G10-Rosales-NHSDocument9 pagesQ2 MODULE7 Cookery G10-Rosales-NHSfishguadagraceNo ratings yet
- Q2 Mod6Document26 pagesQ2 Mod6Jermaine Francel TalampasNo ratings yet
- Seafood DishesDocument10 pagesSeafood DishesArmie LandritoNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet 5 Fish and Shellfish - Villanueva - Jonaver - C - Btvted - 2 - J - FSM - BDocument62 pagesTask Sheet 5 Fish and Shellfish - Villanueva - Jonaver - C - Btvted - 2 - J - FSM - BjohnpoulcebuNo ratings yet
- Fish and ShellfishDocument60 pagesFish and ShellfishTristhan Carl SolosaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fish and Sea Foods According Their KindDocument6 pagesClassification of Fish and Sea Foods According Their KindDedan GideonNo ratings yet
- Fishandshellfish 161118031244 1Document25 pagesFishandshellfish 161118031244 1Lily GoNo ratings yet
- Bouillabaisse (Seafood Stew) Recipe: Stew Fish Crab Squid LobsterDocument2 pagesBouillabaisse (Seafood Stew) Recipe: Stew Fish Crab Squid Lobsterjanica246No ratings yet
- Tle 10-Q4 L4 Preparation of Fish and Shellfish ProductsDocument83 pagesTle 10-Q4 L4 Preparation of Fish and Shellfish ProductsAdoree Ramos100% (1)
- Unit - 4 Le Poisson (Fish) PDFDocument12 pagesUnit - 4 Le Poisson (Fish) PDFDevil 4uNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDDocument52 pagesQ2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDKim Russel AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Cookery ReviewerDocument8 pagesCookery ReviewerolmoguezmarcelleneNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Seafood Recipes: by Dominica YangDocument19 pagesSustainable Seafood Recipes: by Dominica YangDinh PhamNo ratings yet
- nguyên lý nấu nướng khối lượng lớnDocument6 pagesnguyên lý nấu nướng khối lượng lớnNgọc HồngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2Jardine BeneroNo ratings yet
- Salmon Recipe Cookbook: Simple & Delicious Salmon Recipes Book for BeginnersFrom EverandSalmon Recipe Cookbook: Simple & Delicious Salmon Recipes Book for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Lesson 1Document39 pagesGrade 8 Lesson 1Kyle Daphne SumpayNo ratings yet
- Sucker CookbookDocument21 pagesSucker CookbookCoup Cree100% (1)
- COOKERY LAS Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesCOOKERY LAS Q4 Week 3Noel MaticNo ratings yet
- Seafood DishesDocument52 pagesSeafood DishesVhel ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Checking The Freshness of The FishDocument38 pagesChecking The Freshness of The Fishnelmae100% (1)
- Marseille Recipe Leaflet - Selection of Great RecipesDocument8 pagesMarseille Recipe Leaflet - Selection of Great RecipesLe Creuset IrelandNo ratings yet
- How To - Lobster FSC PaperDocument2 pagesHow To - Lobster FSC Papercerps_oneNo ratings yet
- Food Commodities 2a (Saltwater Fish)Document19 pagesFood Commodities 2a (Saltwater Fish)abisaptadinataNo ratings yet
- CrustaceansDocument32 pagesCrustaceanspremsyeolNo ratings yet
- Basic Fish Cooking Methods: A No Frills Guide to Preparing Fresh FishFrom EverandBasic Fish Cooking Methods: A No Frills Guide to Preparing Fresh FishNo ratings yet
- Hlibut EssayDocument6 pagesHlibut Essaymackenzie.brett2389No ratings yet
- Honey-Cured Smoked SalmonDocument6 pagesHoney-Cured Smoked SalmonIrma ManarinNo ratings yet
- Fish Curing Is An Old Industry in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesFish Curing Is An Old Industry in The PhilippinesMeliza AbellaNo ratings yet
- Cook Fish and ShellfishDocument25 pagesCook Fish and ShellfishCarla Grace Tobias-Samoy RocNo ratings yet
- Let's: Fish!Document58 pagesLet's: Fish!raphaelNo ratings yet
- Cooking with Jasmine; Fish Recipes: Cooking With Series, #3From EverandCooking with Jasmine; Fish Recipes: Cooking With Series, #3No ratings yet
- Preparing Fish & Seafood DishesDocument59 pagesPreparing Fish & Seafood DishesSan Isidro Agnes0% (1)
- SeafoodsDocument25 pagesSeafoodschristine mae calanzaNo ratings yet
- FishDocument42 pagesFishRanjit KarkiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument13 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisFuadNo ratings yet
- 3what Has A HeadDocument60 pages3what Has A HeadNguyễn PhươngNo ratings yet
- Year 3 Grammar and Punctuation Test 4Document12 pagesYear 3 Grammar and Punctuation Test 4Amalia Maria ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Best Ever Chocolate Brownies Recipe - BBC Good FoodDocument3 pagesBest Ever Chocolate Brownies Recipe - BBC Good Foodsimon100% (1)
- Nutrition Final Research PaperDocument7 pagesNutrition Final Research PaperMatthew PalagyiNo ratings yet
- Tacos Baja Recipe - Carnival Cruise LineDocument2 pagesTacos Baja Recipe - Carnival Cruise Linevietqueen928427No ratings yet
- Souk Menu 2022Document8 pagesSouk Menu 2022Soham DattaNo ratings yet
- Green FridayDocument77 pagesGreen FridayHosam HasanNo ratings yet
- FIZAN MOHAMMED 4E - WS-Chapter 8-Malala Yousafzai's Speech at The United NationsDocument4 pagesFIZAN MOHAMMED 4E - WS-Chapter 8-Malala Yousafzai's Speech at The United NationsShabana ferozNo ratings yet
- Female Foodie San Francisco Bucket ListDocument8 pagesFemale Foodie San Francisco Bucket Listarnoldlee1No ratings yet
- Factors For Consideration in Presenting Egg DishesDocument7 pagesFactors For Consideration in Presenting Egg DishesMARY JOY VILLARUELNo ratings yet
- The Otterbein Cook BookDocument170 pagesThe Otterbein Cook BookBianca PradoNo ratings yet
- New Round Up 3Document176 pagesNew Round Up 3jonathan collinsNo ratings yet
- Grandpa, Did Miss Amelia Really Crash Into The Atlantic Like Teacher Said She Did?Document3 pagesGrandpa, Did Miss Amelia Really Crash Into The Atlantic Like Teacher Said She Did?Benjamin Newland100% (1)
- Marketing Plan - Final RevDocument28 pagesMarketing Plan - Final RevDanni QuinnNo ratings yet
- C - B L M: Ompetency Ased Earning AterialsDocument45 pagesC - B L M: Ompetency Ased Earning AterialsKent HufanoNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns - Personal Care Products - Basic IIIDocument17 pagesCountable and Uncountable Nouns - Personal Care Products - Basic IIIPaola Forero SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Table of Appointments BrochureDocument2 pagesTable of Appointments BrochureArlene NavarroNo ratings yet
- (2g Net Carb!) Gluten Free & Keto Tortillas - Gnom-GnomDocument2 pages(2g Net Carb!) Gluten Free & Keto Tortillas - Gnom-GnomCiupi TikNo ratings yet
- Panasonic SD 257 Bread Maker User ManualDocument40 pagesPanasonic SD 257 Bread Maker User ManualJulie Tran75% (4)
- Oferta Bite Sandwiches 2019Document2 pagesOferta Bite Sandwiches 2019K. TibiNo ratings yet
- FB A1.1 Beginners Tests KeysDocument10 pagesFB A1.1 Beginners Tests Keyseugene hojkoNo ratings yet
- Preparation IV NoteDocument63 pagesPreparation IV Notetebebe solomonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)Document19 pagesLesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)BERNARDO VIZARRANo ratings yet
- To Go MenuDocument2 pagesTo Go Menuprofess828No ratings yet
- The 3 Ts - Tonicity: HighlightDocument2 pagesThe 3 Ts - Tonicity: HighlightAfrodithaGoldenNo ratings yet
- Minireview Cracker "Keropok": A Review On Factors Influencing ExpansionDocument12 pagesMinireview Cracker "Keropok": A Review On Factors Influencing ExpansionAmin AkasyafNo ratings yet
Fish Cookery
Fish Cookery
Uploaded by
shagay.sheppy01060 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views12 pagesFish are classified into two main categories - fin fish and shellfish. Fin fish include round fish like salmon and cod with eyes on both sides, and flat fish like sole and turbot with eyes on one side. They are also classified based on fat content as white fish which are low in fat and oily fish which are high in fat. Shellfish include crustaceans like crab and shrimp, and molluscs like oysters and mussels. When selecting fish, its eyes should be bright and its flesh firm. Different cooking methods for fish include boiling, steaming, grilling, frying and baking. Fish is cut into fillets, darne, tranche and other cuts for cooking.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFish are classified into two main categories - fin fish and shellfish. Fin fish include round fish like salmon and cod with eyes on both sides, and flat fish like sole and turbot with eyes on one side. They are also classified based on fat content as white fish which are low in fat and oily fish which are high in fat. Shellfish include crustaceans like crab and shrimp, and molluscs like oysters and mussels. When selecting fish, its eyes should be bright and its flesh firm. Different cooking methods for fish include boiling, steaming, grilling, frying and baking. Fish is cut into fillets, darne, tranche and other cuts for cooking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
29 views12 pagesFish Cookery
Fish Cookery
Uploaded by
shagay.sheppy0106Fish are classified into two main categories - fin fish and shellfish. Fin fish include round fish like salmon and cod with eyes on both sides, and flat fish like sole and turbot with eyes on one side. They are also classified based on fat content as white fish which are low in fat and oily fish which are high in fat. Shellfish include crustaceans like crab and shrimp, and molluscs like oysters and mussels. When selecting fish, its eyes should be bright and its flesh firm. Different cooking methods for fish include boiling, steaming, grilling, frying and baking. Fish is cut into fillets, darne, tranche and other cuts for cooking.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 12
Fish are vertebrates and have skin and
scales, which cover the body and they
move with the help of fines. Fish is very
much of a food of the nineties, the
epitome of modern cooking and eating
styles – low in fat, high in protein, rich in
minerals and vitamins, quick and easy to
prepare and cook, versatile enough to be
adapted to suit any occasion.
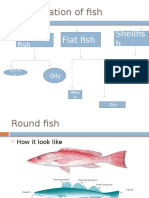
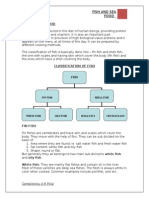
Classification :
Fishes are broadly classified into 2
categories :
Fin Fish
On the basis of shape
Round fish: These are the fish that have
eyes on both sides of their body. They are
found swimming near the surface of the
water. E.g. cod, hake, haddock, whiting,
eel, mackerel,salmon, trout.
Flat fish: These are the fish, which have
eyes on the same side of their body. They
are found at great depths at the bottom of
the sea.E.g. Halibut, lemon sole, plaice,
sole, turbot.
On the basis of thier fat content
White fish: These are the fish that are low
in fat content e.g. cod, hake, haddock,
whiting, halibut, lemon sole, turbot.
Oily fish: These are the fish that are high
in their fat content. E.g. eel, mackerel,
salmon trout.
On the basis of their habitat
River fish: River fish are More nourishing
than seawater fish e.g. eel, lamprey, etc
and are also more flavorful.
Sea fish: Less nourishing than fresh water
fish.
ShellFish
Crustacea: Crab, crawfish, crayfish,
lobster, prawns and shrimps.
Mollousca: Cockles, mussels,
oysters, scallops
Cephalopods: They include octopus and
squids.
Octopus: octopus is firmly textured and
has a marine flavour. It is generally sold
fresh and free of its ink and beak. They
are used in number of dishes including
chowders and salads.
Squids:
It is one of the most widely available
forms of seafood. They are suited to most
of the cooking methods but the most
popular are fried rings served in spicy
sauces or stuffed.
How to select fin fish?
The following points must be looked at the
time of selecting fish-
1. Eyes should be bright.
2. Grills should be red.
3. The tail should be the stick.
4. The flesh should be firm and not
floppy.
5. The whole body should be covered by
full scales.
How to select shellfish:
They should be bought in a season as far
as possible. They should medium-sized
and of good weight. It is best to buy them
alive, particularly oyster, crabs, and
lobsters.
If they have died the following precautions
should be taken-
The claws of crabs should be springy and
not hanging down.
The eyes should be bright.
The tail of lobsters should spring back
when stretched out.
Shrimp and prawns must be crisp
Oyster shells should be tightly closed.
Storing Fish
Fresh fish should be stored for as short a
time as possible after purchase. Fish that
has been freshly caught is the best for
cooking.
The ideal temperature for storage of fresh
fish is 0ºC. Ideal temperature for a fish
walk-in refrigerator is (-2) ºC– 0ºC.
Whole fish will keep fresh for a longer
time if it is gutted (removing the
intestines) as enzymes present in the
stomach accelerate decay.
Fish should be stored tightly wrapped in a
cling film and covered with ice.
Cut fish should never come in contact
directly with ice as it discolors the flesh
and draws out the juices.
Preparing fish for cooking:-
Scaling and cleaning:
1. To scale the bland side of the knife,
holding the fish by the tail, scraps finely
from the tail towards the head, wash well
and removed any lose of scale.
2. Remove the fins and tail.
3. In case of flatfish cut away the grills
and make a small opening in the belly.
The cooking of fish:
Boiling– Fish generally boiled in a
courtbollion”. The method is suitable for
the whole fish; thick cuts of fish could
also be boiled. Whole fish clean would be
put in courtboilion liquid and boil. The fish
is put into a pen, fill with courtboilion then
boiled. If the fish is cooked, then a stewer
will easily place in the flesh of fish.
Approximate time of boiling of fish is 10-
15 min. /500gm. of fish.
Steaming:- Place the fish in a steamer
and sprinkle with salt and pepper, then
the water in the steamer must be fast
broiling with the fire and the fish is
cooked.
Grilling:- It is a suitable method for
various cuts and types of fish are cooked
on top of the grill bar use of butter or oil.
The grill should be greased so that the
flesh does not sticky and then garnish
with lemon, fine fresh parsley chop,
accompaniment with suitable sauce and
time of grilling of fish is 5-7 minutes.
Frying:- Small fish can be fried whole or
out into steaks or fillet or pieces of fish in
huge amount of oil. The cooking time of
frying is about 5 minutes.
Baking:- Round white fish is suitable for
baking. The fish should be cleaned and
belly is staff with forcemeat (bread
crumbs, chop onion, nutmeg, lemon juice,
egg yolk, and high seasoning and
flavoring), butter is applied to the fish and
then it is baked in a baking tray. Baking
time is 10min. /500gm. of fish.
Court-bouillon:
To preserve and enhance the delicate
flavor of fish, the liquid in which they are
poached, those are prepared with care.
The poaching liquid is called court-
bouillon. Traditional uses include
poaching fish and seafood, but it is also
used for poaching vegetables, eggs,
sweetbreads, cockscombs, and delicate
meats.
Ingredients for court-bouillon:
SL.
Ingredient Quanti
NO
s ty
.
01 Water 1 lit.
02 Salt 15gm.
03 Carrot 60gm.
Slice
04 60gm.
lemon
05 Vinegar 75mil.
Parsley
06 3 sprig
stalk
Peppercor
07 6 No.
ns
1-2
08 Bay leaf
No.
Simmering all the ingredients for 30-40
minutes and then strain and used as
liquor.
Strain and used as liquor.
Different types of court-bouillon are-
1. White court-bouillon (sliced onion, bay
leaf, parsley, peppercorn, lemon juice,
salt, milk, and water).
2. Ordinary court-bouillon (vinegar,
water, peppercorn, slice onion, carrots,
salt, parsley, thyme, and bay leaf).
3. White wine court-bouillon (white wine,
water, minced onion, banquet gurney, salt,
peppercorn, few drops of vinegar, carrots).
4. Red wine court-bouillon (Red wine,
vinegar, water, minced onion, bouquet
gurney, parsley, salt, peppercorn, carrots.
Popular fish dishes:
1. Prom fret- Pagodas
2. Prom frets with M.D.H.
3. Prom frets with Portuguese sauce.
4. Tandoori prom fret.
5. Amritsar- machchi (Indian).
Cuts of fish:
1. Fillet or filla:- A cut fish free from the
bone without skin. A round fish have two
number of fillet and the flatfish have four
number of fillet.
2. Darne: – A piece or slice of cut across
and through the bone of large whole round
fish. Example – Salmon, cord.
3. Trancon:– A slice of flat fishs cut on
the bone. It is a section of a large flat fish
such as Turbot or Brill after being split
down the backbone, approximately 45 mm
thick.
4. Goujon:- This term is applied to fillet
of fishs cut into strips format.
Approximate size of gorgons is 3” X ¼”.
5. Goujonette: – As well as gorgons but
smaller. Approximate size of
gougonnettes is 2” X ¼”.
6. Paupiette:- A rolled and stuffed fillet,
usually of flat fishs. The stuffing would
generally be a fine fish farce.
7. Supreme: A portioned piece – cut on
the slant from the fillet of a large round or
flat fishs.
You might also like
- The 800g Challenge - EC SynkowskiDocument132 pagesThe 800g Challenge - EC SynkowskiTim Riley100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood DishesDocument54 pagesLesson 2 Prepare and Cook Seafood DishesMaureen Latayan Agbing91% (11)
- Finfish and Shellfish CookeryDocument14 pagesFinfish and Shellfish CookeryBrianna GrahamNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Milkfish and Some Processed FishDocument7 pagesParts of A Milkfish and Some Processed FishJoseph Adrian PadrigaNo ratings yet
- Bakhtar's RecipesDocument4 pagesBakhtar's RecipesskittlesrharaamNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Write Directions Using Signal WordsDocument16 pagesEnglish: Quarter 3 - Module 2: Write Directions Using Signal WordsMark Allen Labasan67% (3)
- Find Latest Hospitality Resources atDocument7 pagesFind Latest Hospitality Resources atpiyushNo ratings yet
- Cookery Quarter 2 Week 1-3Document9 pagesCookery Quarter 2 Week 1-3jan roiNo ratings yet
- Fish CookeryDocument6 pagesFish Cookerygauravkrishana28No ratings yet
- Fish - Grade 9Document3 pagesFish - Grade 9lil sister and cousinNo ratings yet
- Fish NewDocument6 pagesFish NewUP TO DATE VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- Fish NewDocument6 pagesFish NewUP TO DATE VIDEOSNo ratings yet
- FNH Part 4Document15 pagesFNH Part 4JessicaNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument16 pagesClassification of FishfelixrajasNo ratings yet
- Cooking Your Catch - A Handy Guide to Cleaning, Scaling, Gutting, Dressing, Curing, Smoking, Kippering and Drying - Including Some Serving SuggestionsFrom EverandCooking Your Catch - A Handy Guide to Cleaning, Scaling, Gutting, Dressing, Curing, Smoking, Kippering and Drying - Including Some Serving SuggestionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 Fish MongeryDocument10 pagesChapter - 2 Fish MongeryKrishna ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Quality of FishDocument90 pagesQuality of FishMario MelrickNo ratings yet
- Fish and ShellfishDocument117 pagesFish and Shellfishshanley cyra aboNo ratings yet
- Classification of FishDocument10 pagesClassification of FishDebjyoti BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- TLE ReviewerDocument10 pagesTLE ReviewerAndrea JimenezNo ratings yet
- Prepare Seafood DishesDocument36 pagesPrepare Seafood DishesRuby Esmeralda AndayaNo ratings yet
- FISH and SHELLFISHDocument61 pagesFISH and SHELLFISHMaricel Sanchez - Costillas71% (7)
- Classification of FishDocument16 pagesClassification of FishBharat NailwalNo ratings yet
- Handling and Storage of FishDocument14 pagesHandling and Storage of Fishelara diorNo ratings yet
- Fish and Sea FoodDocument9 pagesFish and Sea Fooditzmeaneesh50% (2)
- Rainbow Trout CultureDocument6 pagesRainbow Trout Cultureluis ruperto floresNo ratings yet
- Q2 MODULE7 Cookery G10-Rosales-NHSDocument9 pagesQ2 MODULE7 Cookery G10-Rosales-NHSfishguadagraceNo ratings yet
- Q2 Mod6Document26 pagesQ2 Mod6Jermaine Francel TalampasNo ratings yet
- Seafood DishesDocument10 pagesSeafood DishesArmie LandritoNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet 5 Fish and Shellfish - Villanueva - Jonaver - C - Btvted - 2 - J - FSM - BDocument62 pagesTask Sheet 5 Fish and Shellfish - Villanueva - Jonaver - C - Btvted - 2 - J - FSM - BjohnpoulcebuNo ratings yet
- Fish and ShellfishDocument60 pagesFish and ShellfishTristhan Carl SolosaNo ratings yet
- Classification of Fish and Sea Foods According Their KindDocument6 pagesClassification of Fish and Sea Foods According Their KindDedan GideonNo ratings yet
- Fishandshellfish 161118031244 1Document25 pagesFishandshellfish 161118031244 1Lily GoNo ratings yet
- Bouillabaisse (Seafood Stew) Recipe: Stew Fish Crab Squid LobsterDocument2 pagesBouillabaisse (Seafood Stew) Recipe: Stew Fish Crab Squid Lobsterjanica246No ratings yet
- Tle 10-Q4 L4 Preparation of Fish and Shellfish ProductsDocument83 pagesTle 10-Q4 L4 Preparation of Fish and Shellfish ProductsAdoree Ramos100% (1)
- Unit - 4 Le Poisson (Fish) PDFDocument12 pagesUnit - 4 Le Poisson (Fish) PDFDevil 4uNo ratings yet
- Q2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDDocument52 pagesQ2 Module 6 Preparing and Cooking Seafood Dishes UPDATEDKim Russel AgpaoaNo ratings yet
- Cookery ReviewerDocument8 pagesCookery ReviewerolmoguezmarcelleneNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Seafood Recipes: by Dominica YangDocument19 pagesSustainable Seafood Recipes: by Dominica YangDinh PhamNo ratings yet
- nguyên lý nấu nướng khối lượng lớnDocument6 pagesnguyên lý nấu nướng khối lượng lớnNgọc HồngNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2Jardine BeneroNo ratings yet
- Salmon Recipe Cookbook: Simple & Delicious Salmon Recipes Book for BeginnersFrom EverandSalmon Recipe Cookbook: Simple & Delicious Salmon Recipes Book for BeginnersNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Lesson 1Document39 pagesGrade 8 Lesson 1Kyle Daphne SumpayNo ratings yet
- Sucker CookbookDocument21 pagesSucker CookbookCoup Cree100% (1)
- COOKERY LAS Q4 Week 3Document8 pagesCOOKERY LAS Q4 Week 3Noel MaticNo ratings yet
- Seafood DishesDocument52 pagesSeafood DishesVhel ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Checking The Freshness of The FishDocument38 pagesChecking The Freshness of The Fishnelmae100% (1)
- Marseille Recipe Leaflet - Selection of Great RecipesDocument8 pagesMarseille Recipe Leaflet - Selection of Great RecipesLe Creuset IrelandNo ratings yet
- How To - Lobster FSC PaperDocument2 pagesHow To - Lobster FSC Papercerps_oneNo ratings yet
- Food Commodities 2a (Saltwater Fish)Document19 pagesFood Commodities 2a (Saltwater Fish)abisaptadinataNo ratings yet
- CrustaceansDocument32 pagesCrustaceanspremsyeolNo ratings yet
- Basic Fish Cooking Methods: A No Frills Guide to Preparing Fresh FishFrom EverandBasic Fish Cooking Methods: A No Frills Guide to Preparing Fresh FishNo ratings yet
- Hlibut EssayDocument6 pagesHlibut Essaymackenzie.brett2389No ratings yet
- Honey-Cured Smoked SalmonDocument6 pagesHoney-Cured Smoked SalmonIrma ManarinNo ratings yet
- Fish Curing Is An Old Industry in The PhilippinesDocument5 pagesFish Curing Is An Old Industry in The PhilippinesMeliza AbellaNo ratings yet
- Cook Fish and ShellfishDocument25 pagesCook Fish and ShellfishCarla Grace Tobias-Samoy RocNo ratings yet
- Let's: Fish!Document58 pagesLet's: Fish!raphaelNo ratings yet
- Cooking with Jasmine; Fish Recipes: Cooking With Series, #3From EverandCooking with Jasmine; Fish Recipes: Cooking With Series, #3No ratings yet
- Preparing Fish & Seafood DishesDocument59 pagesPreparing Fish & Seafood DishesSan Isidro Agnes0% (1)
- SeafoodsDocument25 pagesSeafoodschristine mae calanzaNo ratings yet
- FishDocument42 pagesFishRanjit KarkiNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument13 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisFuadNo ratings yet
- 3what Has A HeadDocument60 pages3what Has A HeadNguyễn PhươngNo ratings yet
- Year 3 Grammar and Punctuation Test 4Document12 pagesYear 3 Grammar and Punctuation Test 4Amalia Maria ConstantinNo ratings yet
- Best Ever Chocolate Brownies Recipe - BBC Good FoodDocument3 pagesBest Ever Chocolate Brownies Recipe - BBC Good Foodsimon100% (1)
- Nutrition Final Research PaperDocument7 pagesNutrition Final Research PaperMatthew PalagyiNo ratings yet
- Tacos Baja Recipe - Carnival Cruise LineDocument2 pagesTacos Baja Recipe - Carnival Cruise Linevietqueen928427No ratings yet
- Souk Menu 2022Document8 pagesSouk Menu 2022Soham DattaNo ratings yet
- Green FridayDocument77 pagesGreen FridayHosam HasanNo ratings yet
- FIZAN MOHAMMED 4E - WS-Chapter 8-Malala Yousafzai's Speech at The United NationsDocument4 pagesFIZAN MOHAMMED 4E - WS-Chapter 8-Malala Yousafzai's Speech at The United NationsShabana ferozNo ratings yet
- Female Foodie San Francisco Bucket ListDocument8 pagesFemale Foodie San Francisco Bucket Listarnoldlee1No ratings yet
- Factors For Consideration in Presenting Egg DishesDocument7 pagesFactors For Consideration in Presenting Egg DishesMARY JOY VILLARUELNo ratings yet
- The Otterbein Cook BookDocument170 pagesThe Otterbein Cook BookBianca PradoNo ratings yet
- New Round Up 3Document176 pagesNew Round Up 3jonathan collinsNo ratings yet
- Grandpa, Did Miss Amelia Really Crash Into The Atlantic Like Teacher Said She Did?Document3 pagesGrandpa, Did Miss Amelia Really Crash Into The Atlantic Like Teacher Said She Did?Benjamin Newland100% (1)
- Marketing Plan - Final RevDocument28 pagesMarketing Plan - Final RevDanni QuinnNo ratings yet
- C - B L M: Ompetency Ased Earning AterialsDocument45 pagesC - B L M: Ompetency Ased Earning AterialsKent HufanoNo ratings yet
- Countable and Uncountable Nouns - Personal Care Products - Basic IIIDocument17 pagesCountable and Uncountable Nouns - Personal Care Products - Basic IIIPaola Forero SalamancaNo ratings yet
- Table of Appointments BrochureDocument2 pagesTable of Appointments BrochureArlene NavarroNo ratings yet
- (2g Net Carb!) Gluten Free & Keto Tortillas - Gnom-GnomDocument2 pages(2g Net Carb!) Gluten Free & Keto Tortillas - Gnom-GnomCiupi TikNo ratings yet
- Panasonic SD 257 Bread Maker User ManualDocument40 pagesPanasonic SD 257 Bread Maker User ManualJulie Tran75% (4)
- Oferta Bite Sandwiches 2019Document2 pagesOferta Bite Sandwiches 2019K. TibiNo ratings yet
- FB A1.1 Beginners Tests KeysDocument10 pagesFB A1.1 Beginners Tests Keyseugene hojkoNo ratings yet
- Preparation IV NoteDocument63 pagesPreparation IV Notetebebe solomonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)Document19 pagesLesson 2 Prepare Cereals and Starch: Learning Outcome 1 Perform Mise'en Place (Week 5)BERNARDO VIZARRANo ratings yet
- To Go MenuDocument2 pagesTo Go Menuprofess828No ratings yet
- The 3 Ts - Tonicity: HighlightDocument2 pagesThe 3 Ts - Tonicity: HighlightAfrodithaGoldenNo ratings yet
- Minireview Cracker "Keropok": A Review On Factors Influencing ExpansionDocument12 pagesMinireview Cracker "Keropok": A Review On Factors Influencing ExpansionAmin AkasyafNo ratings yet