Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 viewsComparison Animalplant and Bacterial Cell
Comparison Animalplant and Bacterial Cell
Uploaded by
Janna AspacioThe document compares and contrasts plant, animal, and bacterial cells. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts, while animal cells lack these features. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic and lack organelles like nuclei. Key differences include plant cells being primarily autotrophic through photosynthesis using chloroplasts, while animal and bacterial cells are heterotrophic. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria, but plant cells have larger vacuoles and ribosomes compared to animal cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesSahar Bakrey91% (47)
- Chap No 4 DifferencesDocument10 pagesChap No 4 DifferencesWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Organsims Are Made Up of Cells - Grade 9Document17 pagesLesson 2.1 Organsims Are Made Up of Cells - Grade 9SAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- Cell Was Discovered by A British ScientistDocument6 pagesCell Was Discovered by A British Scientisttejaramjat409No ratings yet
- Differences Between Animal Cell and Plant Cell: Cell Wall Shape VacuoleDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Animal Cell and Plant Cell: Cell Wall Shape VacuoleAminTuhameNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells Vs Plant CellsDocument6 pagesAnimal Cells Vs Plant CellsEszterNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellshaji1234554No ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDocument2 pagesPlant Cell and Animal CellgunaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument15 pagesThe CellSoft BoiNo ratings yet
- Week 4a Science 7 LasDocument9 pagesWeek 4a Science 7 LasJonah Labine Jabulin-RadazaNo ratings yet
- Dom 2Document2 pagesDom 2jenrosemNo ratings yet
- Cells NotesDocument7 pagesCells Notesshinde.sampada1923No ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotes EukaryotesSayyeda SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesCells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cellgafir1230No ratings yet
- 7 - Cell ModelDocument6 pages7 - Cell ModelshailaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifetsudheraNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Are Plant & Animal Cells The Same or Different?Document18 pagesAre Plant & Animal Cells The Same or Different?Josa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Chimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Cell - Gen BioDocument2 pagesCell - Gen BioMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- Biologicalscience 150717091659 Lva1 App6892Document19 pagesBiologicalscience 150717091659 Lva1 App6892jessiNo ratings yet
- 00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallDocument4 pages00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallJeremy TanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells PDFDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells PDFFalah HabibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1ozmanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio SLDocument103 pagesCell Bio SLkrhimkrNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal CellMuhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- 00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallDocument4 pages00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallJeremy TanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDocument133 pagesIGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDIO yesNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Animal Cell & Plant Cell and Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell Using Venn Diagram.Document1 pageCompare and Contrast Animal Cell & Plant Cell and Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell Using Venn Diagram.Blair Skyreiz NymphNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Vs Plant Cell: Comparison Chart: SimilaritiesDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell Vs Plant Cell: Comparison Chart: SimilaritiesJashaswini RoyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?: ProkaryotesDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Cell?: ProkaryotesJairhiz AnnNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyshubhamkr91234No ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesLevels of OrganizationSwayangdipta TalapatraNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology NotesDocument49 pagesIgcse Biology NotesEminem RomNo ratings yet
- Terms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesTerms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsSlay SacedaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Document33 pagesScience 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Welfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Organelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)Document6 pagesOrganelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Class XI, Chp4-Animal Kingdom-1Document5 pagesClass XI, Chp4-Animal Kingdom-1anirudhgupta5050No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesSandra AtefNo ratings yet
- ELS ReviewerDocument9 pagesELS ReviewerMia TorettoNo ratings yet
- Ximon Sagucio General Biology 3rd Quarter Output.Document6 pagesXimon Sagucio General Biology 3rd Quarter Output.Grim ReaperNo ratings yet
- Class9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesDocument7 pagesClass9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesabhishekNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 2 Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument2 pagesBiology Chapter 2 Cell Structure and OrganizationKen Wei OngNo ratings yet
- 08 Nov Ar SirDocument16 pages08 Nov Ar SirL fNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of BacteriaDocument12 pages1.structure of BacteriaDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellridabatool151214No ratings yet
- Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument55 pagesEukaryotes and ProkaryotesNavya NarangNo ratings yet
- Cell Organization and Structure (Option C)Document4 pagesCell Organization and Structure (Option C)-Sabiraaa -No ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument33 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAyellah Bless MejiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory 1Document45 pagesCell Theory 1Reylyn SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Cell - Study NotesDocument16 pagesCell - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Notes: Unit 1: Characteristics of LivingDocument50 pagesIgcse Biology Notes: Unit 1: Characteristics of LivingMa XóNo ratings yet
- Cell Part 2Document8 pagesCell Part 2Harshit Mishra 09 2865No ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sri Ananda AnjaneyamDocument18 pagesSri Ananda AnjaneyamSailee RNo ratings yet
- The Way of Chanting and Knowing KrsnaDocument16 pagesThe Way of Chanting and Knowing Krsnamaggie_cbdNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1Document52 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1My WritingsNo ratings yet
- Suction Pump FAZZINI F-30 - Service ManualDocument10 pagesSuction Pump FAZZINI F-30 - Service ManualAnonymous qmNwOUtUd100% (1)
- Đề Cương - PPGD Ngữ Liệu Ngôn NgữDocument5 pagesĐề Cương - PPGD Ngữ Liệu Ngôn NgữHòa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument62 pagesLaboratory Manualتبارك موسى كريم علوانNo ratings yet
- VO FinalDocument140 pagesVO Finalsudhasesh2000No ratings yet
- Prosec Ii+ ManualDocument1 pageProsec Ii+ ManualBachtiar WidyantoroNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ReportDocument17 pagesUcsp ReportChrystleen MondeloNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (Suleman)Document4 pagesCurriculum Vitae (Suleman)Muhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Instant Coffee With Natural Aroma by Spray-Drying.: January 1993Document8 pagesInstant Coffee With Natural Aroma by Spray-Drying.: January 1993Nhan NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus CDocument16 pagesAP Calculus CSNNo ratings yet
- VSM TrainingDocument90 pagesVSM Trainingjoaoalcada100% (1)
- LIMITSMains PDFDocument18 pagesLIMITSMains PDFBhavadip VamjaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyDocument8 pagesThe Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyPaul HorriganNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics Solved MCQsDocument8 pagesDiscrete Mathematics Solved MCQsamna_shifaNo ratings yet
- ReadiGASS Bro 1709Document4 pagesReadiGASS Bro 1709arunkumar277041No ratings yet
- ResearchDocument125 pagesResearchchittynagamaniNo ratings yet
- Android Developer: About Me ExperienceDocument1 pageAndroid Developer: About Me ExperienceDeby Aprilucia FarahdeviraNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Ied 126 Charmedimsure Designbriefand RubricDocument4 pagesGroup 2 Ied 126 Charmedimsure Designbriefand Rubricapi-551027316No ratings yet
- Ccie Lab k8Document2 pagesCcie Lab k8sosapabec0% (1)
- Prague Wednesday AM - AcquirerDocument85 pagesPrague Wednesday AM - AcquirerbenNo ratings yet
- Amit Power PresentDocument17 pagesAmit Power PresentClassic AddaNo ratings yet
- IC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - SequenceDocument4 pagesIC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - Sequencematerial didacticoNo ratings yet
- National Geographic 2022.05Document142 pagesNational Geographic 2022.05yingying ZhengNo ratings yet
- Kyland Opal5 Datasheet ENDocument4 pagesKyland Opal5 Datasheet ENseb.rogardNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs UniversityDocument5 pagesDifference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs Universitytapar.dashNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods of Diaphragm Walls Design: SustainabilityDocument13 pagesModern Methods of Diaphragm Walls Design: SustainabilitymattNo ratings yet
- MODEL 248 Multiple Arbitrary Function Generator User Manual REV 2.0Document17 pagesMODEL 248 Multiple Arbitrary Function Generator User Manual REV 2.0Nordlys OfficialNo ratings yet
Comparison Animalplant and Bacterial Cell
Comparison Animalplant and Bacterial Cell
Uploaded by
Janna Aspacio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesThe document compares and contrasts plant, animal, and bacterial cells. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts, while animal cells lack these features. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic and lack organelles like nuclei. Key differences include plant cells being primarily autotrophic through photosynthesis using chloroplasts, while animal and bacterial cells are heterotrophic. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria, but plant cells have larger vacuoles and ribosomes compared to animal cells.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document compares and contrasts plant, animal, and bacterial cells. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts, while animal cells lack these features. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic and lack organelles like nuclei. Key differences include plant cells being primarily autotrophic through photosynthesis using chloroplasts, while animal and bacterial cells are heterotrophic. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria, but plant cells have larger vacuoles and ribosomes compared to animal cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views6 pagesComparison Animalplant and Bacterial Cell
Comparison Animalplant and Bacterial Cell
Uploaded by
Janna AspacioThe document compares and contrasts plant, animal, and bacterial cells. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts, while animal cells lack these features. Bacterial cells are prokaryotic and lack organelles like nuclei. Key differences include plant cells being primarily autotrophic through photosynthesis using chloroplasts, while animal and bacterial cells are heterotrophic. Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic and share organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria, but plant cells have larger vacuoles and ribosomes compared to animal cells.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Difference Between Plant, Animal and Bacterial Cells
Classification of Cells - Plant, Animal and Bacterial Cells
A Cell is the basic structural and functional unit of organisms. The word ‘cell’ is derived
from the Latin word “cella” which means “small room”. The type and number of cells in
plants and animals vary. The cells can be classified in different ways. For example, based
on the presence of a nuclear membrane, the cells are classified into two types i.e
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic. Cells may also be classified based on the number of cells an
organism is made of i.e unicellular, multicellular, and acellular.
Brief on Animal Cell
An animal cell is typically a eukaryotic type that has a well-defined nucleus and
other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum,
and Golgi apparatus. All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane or plasma
membrane which separates the inner and outer components of the cell. The cell
components are suspended in a fluid called cytoplasm.
Animals are multicellular organisms. The cells are specialized to perform various
functions. Also, they look and function differently from each other even if they belong to
the same organism.
Animal Cell Types
There are numerous types of animal cells and each of them is designed to serve specific
functions. However, some of the most common types of animal cells are as follows:
Skin Cells
Melanocytes, keratinocytes, Merkel cells and Langerhans cells
Muscle Cells
Myocyte, Myosatellite cells, Tendon cells, Cardiac muscle cells
Blood Cells
Leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelet
Nerve Cells
Schwann cell, glial cells etc
Fat Cells
Adipocytes
Animal cells need to adapt to a more active and non-sedentary lifestyle as animals
acquire their food, hence, they do not possess any of the specialized cell organelles such
as chloroplasts.
Brief on Plant Cell
A plant cell is mainly a eukaryotic cell with a true nucleus and organelles similar to an
animal cell but also consists of certain specific components such as chloroplasts which
carry out photosynthesis. Plants are multicellular and have a distinct rigid wall
surrounding the cells.
Plant Cell Functions
The plant cells are the building blocks of the plants. Since photosynthesis (the process of
preparing food by the plants, by utilizing sunlight, carbon dioxide and water) is the major
function performed by the plant cells it occurs in the chloroplasts of the plant cell.
Plant Cell Types
There are different types of plant cells some of which include the following different
types:
Collenchyma Cells
These cells are hard or rigid and play a primary role in providing support to the plants if
there is restraining growth due to the lack of hardening agents in the primary walls.
Sclerenchyma Cells
These are more rigid as compared to the collenchyma cells and it is because of the
presence of a hardening agent. They are usually found in all the plant roots and are
mainly involved in providing support to the plants.
Parenchyma Cells
The Parenchyma cells have a significant role to play in all plants. As they are the living
cells of plants, which are involved in the production of leaves, they are also involved in
the exchange of gasses, production of food, storage of organic products and cell
metabolism. The Parenchyma cells are typically more flexible because they are thinner
than other cells.
Xylem Cells
The Xylem cells are the transport cells in vascular plants. They are responsible for the
transport of water and minerals from the roots to the leaves and other parts of the plants.
Phloem Cells
These are the common type of cells and the most heard ones, the phloem cells are the
transport cells in vascular plants as they are responsible for transporting food which is
prepared by the leaves to different parts of the plants.
Brief on Bacterial Cell
A bacterial cell is a prokaryotic cell that lacks a well-defined nucleus and membrane-
bound organelles. Instead, it contains an irregular-shaped region where the genetic
material is suspended. Bacteria is a single-celled organism.
Functions of a Bacterial Cell
The Cytoplasm or protoplasm is the part of the bacterial cells, where the functions for cell
growth, metabolism, and replication are carried out. This is a gel-like matrix that is
composed of water, enzymes, nutrients, wastes, and gasses and contains cell structures
such as ribosomes, a chromosome, and plasmids.
Types of Bacteria Cells
The Bacterial cells are classified into five groups according to their basic shapes:
Spherical (cocci)
Rod (bacilli)
Spiral (spirilla)
Comma (vibrios)
Corkscrew (spirochaetes)
These can exist as single cells, in pairs, chains or clusters.
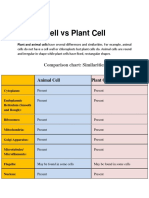
Difference Between Plant, Animal and Bacterial Cell
Plant Cell Animals Cell Bacterial Cell
Type of Cell
Eukaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells
Size of the cell
10 to 100 µm 10 to 100 µm 0.2 to 2 µm
The shape of the cell
Are of different shapes- cocci,
Rectangular shaped Round or Oval shaped
bacillus, vibrio, spirilla.
Cell Wall
Present Absent Present
Nucleus
Present Present Absent
Plasmids
Absent Absent Present
Plastids
Present Absent Absent
Mitochondria
Present Present Absent
Ribosomes
Larger 80s Ribosomes Larger 80s Ribosomes Smaller 70s Ribosomes
Centrioles
Absent Present Absent
Vacuoles
Larger vacuoles Smaller vacuoles Larger vacuoles
Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Present Present Absent
Golgi Apparatus
Present Present Absent
Lysosomes
Present but are few in
Present Absent
numbers
Cilia and Filaments
Absent Present Present
Mode of Nutrition
Both heterotrophs and
Autotrophs Heterotrophs
autotrophs
Mode of Reproduction
Sexual reproduction in higher
Both sexual and asexual Both sexual and asexual mode
animals and asexual in lower
mode of reproduction. of reproduction.
animals.
Mode of Respiration
Aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration. Both aerobic and anaerobic.
The major differences between the plant cell and animal cell are mentioned below:
Plant Cell Animal Cell
Cell Shape
Square or rectangular in shape Irregular or round in shape
Cell Wall
Present Absent
Plasma/Cell Membrane
Present Present
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Present Present
Nucleus
Present and lies on one side of the cell Present and lies in the centre of the cell
Lysosomes
Present but are very rare Present
Centrosomes
Absent Present
Golgi Apparatus
Present Present
Cytoplasm
Present Present
Ribosomes
Present Present
Plastids
Present Absent
Vacuoles
Few large or a single, centrally positioned vacuole Usually small and numerous
Cilia
Absent Present in most of the animal cells
Mitochondria
Present but fewer in number Present and are numerous
Mode of Nutrition
Primarily autotrophic Heterotrophic
Conclusion
Both plant and animal cells comprise membrane-bound organelles, such as endoplasmic
reticulum, mitochondria, the nucleus, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, lysosomes. They also have
similar membranes, such as cytoskeletal elements and cytosol. The plant cell can also be larger
than the animal cell. The normal range of the animal cell varies from about 10 – 30 micrometres
and that of plant cell range between 10 – 100 micrometres.
You might also like
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesSahar Bakrey91% (47)
- Chap No 4 DifferencesDocument10 pagesChap No 4 DifferencesWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 Organsims Are Made Up of Cells - Grade 9Document17 pagesLesson 2.1 Organsims Are Made Up of Cells - Grade 9SAMI DHAOUINo ratings yet
- Cell Was Discovered by A British ScientistDocument6 pagesCell Was Discovered by A British Scientisttejaramjat409No ratings yet
- Differences Between Animal Cell and Plant Cell: Cell Wall Shape VacuoleDocument3 pagesDifferences Between Animal Cell and Plant Cell: Cell Wall Shape VacuoleAminTuhameNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells Vs Plant CellsDocument6 pagesAnimal Cells Vs Plant CellsEszterNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellDocument4 pagesProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellshaji1234554No ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Animal CellDocument2 pagesPlant Cell and Animal CellgunaNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument15 pagesThe CellSoft BoiNo ratings yet
- Week 4a Science 7 LasDocument9 pagesWeek 4a Science 7 LasJonah Labine Jabulin-RadazaNo ratings yet
- Dom 2Document2 pagesDom 2jenrosemNo ratings yet
- Cells NotesDocument7 pagesCells Notesshinde.sampada1923No ratings yet
- CellDocument6 pagesCellHONEYLYN CASINGNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument3 pagesDifference Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsWareesha BatoolNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesProkaryotes EukaryotesSayyeda SumaiyahNo ratings yet
- Cells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic CellDocument3 pagesCells Are The Basic Building Blocks of All Living Things Type of Cells 1.prokaryotic Cell 2. Eukaryotic Cellgafir1230No ratings yet
- 7 - Cell ModelDocument6 pages7 - Cell ModelshailaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifeDocument6 pagesCH 1 Notes Cell Basic Unit of LifetsudheraNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCell Theory Consists of Three PrinciplesdaddysharkNo ratings yet
- Are Plant & Animal Cells The Same or Different?Document18 pagesAre Plant & Animal Cells The Same or Different?Josa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles LectureDocument54 pagesCell Organelles LectureAlthea Aubrey AgbayaniNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Document2 pagesDepartment of Education: Module in General Biology 1 Grade 12 First Quarter Week 2Chimmy ChangaNo ratings yet
- Cell - Gen BioDocument2 pagesCell - Gen BioMaraon CharitaNo ratings yet
- Biologicalscience 150717091659 Lva1 App6892Document19 pagesBiologicalscience 150717091659 Lva1 App6892jessiNo ratings yet
- 00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallDocument4 pages00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallJeremy TanNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells PDFDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells PDFFalah HabibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document13 pagesChapter 1ozmanNo ratings yet
- What Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Prokaryotic Cell?: Genetic MaterialAnkan RoyNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio SLDocument103 pagesCell Bio SLkrhimkrNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument1 pageAnimal CellMuhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- 00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallDocument4 pages00 - Cell: Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell WallJeremy TanNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDocument133 pagesIGCSE Biology Notesss YehahahaDIO yesNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast Animal Cell & Plant Cell and Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell Using Venn Diagram.Document1 pageCompare and Contrast Animal Cell & Plant Cell and Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic Cell Using Venn Diagram.Blair Skyreiz NymphNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Vs Plant Cell: Comparison Chart: SimilaritiesDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell Vs Plant Cell: Comparison Chart: SimilaritiesJashaswini RoyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Cell?: ProkaryotesDocument7 pagesWhat Is A Cell?: ProkaryotesJairhiz AnnNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument7 pagesBiologyshubhamkr91234No ratings yet
- Levels of OrganizationDocument4 pagesLevels of OrganizationSwayangdipta TalapatraNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology NotesDocument49 pagesIgcse Biology NotesEminem RomNo ratings yet
- Terms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesTerms: It Is A Polymer That Makes Up The Cell Wall of Bacteria and Is Made Up of Sugars and Amino AcidsSlay SacedaNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Document33 pagesScience 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Welfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- Organelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)Document6 pagesOrganelle-Which Means Small Part (Body Has Small Parts Called Organs) (Cells Has Small Parts Called Organelles)vscolegit shoppeNo ratings yet
- Class XI, Chp4-Animal Kingdom-1Document5 pagesClass XI, Chp4-Animal Kingdom-1anirudhgupta5050No ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesSandra AtefNo ratings yet
- ELS ReviewerDocument9 pagesELS ReviewerMia TorettoNo ratings yet
- Ximon Sagucio General Biology 3rd Quarter Output.Document6 pagesXimon Sagucio General Biology 3rd Quarter Output.Grim ReaperNo ratings yet
- Class9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesDocument7 pagesClass9 - The Fundamental Unit of Life Notes by Zenith ClassesabhishekNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 2 Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument2 pagesBiology Chapter 2 Cell Structure and OrganizationKen Wei OngNo ratings yet
- 08 Nov Ar SirDocument16 pages08 Nov Ar SirL fNo ratings yet
- 1.structure of BacteriaDocument12 pages1.structure of BacteriaDr P N N ReddyNo ratings yet
- CellDocument23 pagesCellridabatool151214No ratings yet
- Eukaryotes and ProkaryotesDocument55 pagesEukaryotes and ProkaryotesNavya NarangNo ratings yet
- Cell Organization and Structure (Option C)Document4 pagesCell Organization and Structure (Option C)-Sabiraaa -No ratings yet
- Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument33 pagesCell Structures and FunctionsAyellah Bless MejiaNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory 1Document45 pagesCell Theory 1Reylyn SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Cell - Study NotesDocument16 pagesCell - Study NotesrockyajeetNo ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Notes: Unit 1: Characteristics of LivingDocument50 pagesIgcse Biology Notes: Unit 1: Characteristics of LivingMa XóNo ratings yet
- Cell Part 2Document8 pagesCell Part 2Harshit Mishra 09 2865No ratings yet
- The Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Animal Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandCell Biology 7th Grade Textbook | Children's Biology BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sri Ananda AnjaneyamDocument18 pagesSri Ananda AnjaneyamSailee RNo ratings yet
- The Way of Chanting and Knowing KrsnaDocument16 pagesThe Way of Chanting and Knowing Krsnamaggie_cbdNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1Document52 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits m1My WritingsNo ratings yet
- Suction Pump FAZZINI F-30 - Service ManualDocument10 pagesSuction Pump FAZZINI F-30 - Service ManualAnonymous qmNwOUtUd100% (1)
- Đề Cương - PPGD Ngữ Liệu Ngôn NgữDocument5 pagesĐề Cương - PPGD Ngữ Liệu Ngôn NgữHòa NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Laboratory ManualDocument62 pagesLaboratory Manualتبارك موسى كريم علوانNo ratings yet
- VO FinalDocument140 pagesVO Finalsudhasesh2000No ratings yet
- Prosec Ii+ ManualDocument1 pageProsec Ii+ ManualBachtiar WidyantoroNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ReportDocument17 pagesUcsp ReportChrystleen MondeloNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae (Suleman)Document4 pagesCurriculum Vitae (Suleman)Muhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Instant Coffee With Natural Aroma by Spray-Drying.: January 1993Document8 pagesInstant Coffee With Natural Aroma by Spray-Drying.: January 1993Nhan NguyenNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus CDocument16 pagesAP Calculus CSNNo ratings yet
- VSM TrainingDocument90 pagesVSM Trainingjoaoalcada100% (1)
- LIMITSMains PDFDocument18 pagesLIMITSMains PDFBhavadip VamjaNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyDocument8 pagesThe Nature of Philosophical AnthropologyPaul HorriganNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics Solved MCQsDocument8 pagesDiscrete Mathematics Solved MCQsamna_shifaNo ratings yet
- ReadiGASS Bro 1709Document4 pagesReadiGASS Bro 1709arunkumar277041No ratings yet
- ResearchDocument125 pagesResearchchittynagamaniNo ratings yet
- Android Developer: About Me ExperienceDocument1 pageAndroid Developer: About Me ExperienceDeby Aprilucia FarahdeviraNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Ied 126 Charmedimsure Designbriefand RubricDocument4 pagesGroup 2 Ied 126 Charmedimsure Designbriefand Rubricapi-551027316No ratings yet
- Ccie Lab k8Document2 pagesCcie Lab k8sosapabec0% (1)
- Prague Wednesday AM - AcquirerDocument85 pagesPrague Wednesday AM - AcquirerbenNo ratings yet
- Amit Power PresentDocument17 pagesAmit Power PresentClassic AddaNo ratings yet
- IC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - SequenceDocument4 pagesIC5 Level Intro - Scope - and - Sequencematerial didacticoNo ratings yet
- National Geographic 2022.05Document142 pagesNational Geographic 2022.05yingying ZhengNo ratings yet
- Kyland Opal5 Datasheet ENDocument4 pagesKyland Opal5 Datasheet ENseb.rogardNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs UniversityDocument5 pagesDifference Between Institute and University - Difference Between - Institute Vs Universitytapar.dashNo ratings yet
- Modern Methods of Diaphragm Walls Design: SustainabilityDocument13 pagesModern Methods of Diaphragm Walls Design: SustainabilitymattNo ratings yet
- MODEL 248 Multiple Arbitrary Function Generator User Manual REV 2.0Document17 pagesMODEL 248 Multiple Arbitrary Function Generator User Manual REV 2.0Nordlys OfficialNo ratings yet