Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q # 2 February 2020
Q # 2 February 2020
Uploaded by
nimra muzaffar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe three main parameters of cone beam imaging are voxel size, field of view, and slice thickness/measurement accuracy. Voxel size refers to the cuboidal 3D elements that make up the scanned volume. Field of view is the anatomical area included in the scan, ranging from a dental arch to the entire head, and depends on factors like the diagnostic task and patient type. Slice thickness and measurement accuracy can be as thin as 0.075mm, improving visualization of dental anomalies, root morphology, and canal structures in all three anatomical planes.
Original Description:
Original Title
q # 2 February 2020
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe three main parameters of cone beam imaging are voxel size, field of view, and slice thickness/measurement accuracy. Voxel size refers to the cuboidal 3D elements that make up the scanned volume. Field of view is the anatomical area included in the scan, ranging from a dental arch to the entire head, and depends on factors like the diagnostic task and patient type. Slice thickness and measurement accuracy can be as thin as 0.075mm, improving visualization of dental anomalies, root morphology, and canal structures in all three anatomical planes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesQ # 2 February 2020
Q # 2 February 2020
Uploaded by
nimra muzaffarThe three main parameters of cone beam imaging are voxel size, field of view, and slice thickness/measurement accuracy. Voxel size refers to the cuboidal 3D elements that make up the scanned volume. Field of view is the anatomical area included in the scan, ranging from a dental arch to the entire head, and depends on factors like the diagnostic task and patient type. Slice thickness and measurement accuracy can be as thin as 0.075mm, improving visualization of dental anomalies, root morphology, and canal structures in all three anatomical planes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
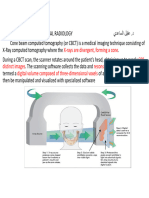
Q # 2,FEBRUARY 2020, PART II
Q:
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT PARAMETERS OF CONE BEAM IMAGING ?
ANSWER :
THREE IMPORTANT PARAMETERS OF CONE BEAM IMAGING ARE
• Voxel size
• Field of view (fov)
• Slice thickness/measurement accuracy
1. VOXEL SIZE
Voxels are cuboidal elements that constitute a 3D volume, unlike
pixels, which are 2D.
Data are acquired and represented in three dimensions using voxels,
Unlike with medical computed tomography (MDCT).
cone beam units acquire x-ray information using low kV and low mA
exposure parameters in a single pass from 180 to 360 degrees of
rotation around the anatomy of interest.
2. FIELD OF VIEW (FOV)
FOV refers to the anatomical area that will be included in the data
volume ,or the area of the patient that will be irradiated .
The field of view (FOV) ranges from as small as a portion of a dental
arch to an area as large as the entire head.
The selection of the FOV depends on several factors ,Among the most
important are the following:
Diagnostic task
Type of patient
Spatial resolution requirements
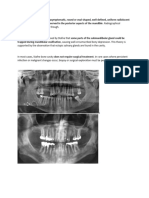
3. SLICE THICKNESS/MEASUREMENT ACCURACY
The precise location and visualization of dental anomalies, root morphology,
and canal anatomy are vastly improved with CBCT data. Root curvature,
additional roots, and anomalies within the canals themselves (e.g.,
obstructions, narrowing, bifurcation) are made more apparent when all three
anatomic planes of section are available for review,
especially with the capability of narrowing the slice thickness to as little as
0.075 mm.
Visual obstruction from anatomic features such as buccal bone and the malar
process over the apices of maxillary roots simply will “disappear” when you
can scroll through the slices of the bone from facial to palatal in 0.076 mm
sections while also changing axial orientations
REFRENCE
PATHWAYS OF THE PULP 12TH EDITION CHAPTER 2,
RADIOGRAPHIC INTERPRETATION
You might also like
- CBCT in EndodonticsDocument133 pagesCBCT in EndodonticsAnciya Nazar100% (6)
- Review Articles Annals and Essences of DentistryDocument4 pagesReview Articles Annals and Essences of DentistryHitesh ChopraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 3 - Imaging Anatomy of The Jaw and Dentition With Cone Beam Computed Tomography - Febby Sitti NurDocument11 pagesJurnal 3 - Imaging Anatomy of The Jaw and Dentition With Cone Beam Computed Tomography - Febby Sitti NurFEBBY SITTINo ratings yet
- CBCT in Endodontics: Presented By: DR - Saloni PG Student Dept. of Cons and EndoDocument83 pagesCBCT in Endodontics: Presented By: DR - Saloni PG Student Dept. of Cons and Endosaloni singhNo ratings yet
- Basic of CBCT ImagingDocument7 pagesBasic of CBCT ImagingIndah VitasariNo ratings yet
- Cone Beam Technology: A Brief Technical: History of CAT and CBCTDocument9 pagesCone Beam Technology: A Brief Technical: History of CAT and CBCTHugo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cone Beamed Computerized Dental Tomography in DentistryDocument5 pagesCone Beamed Computerized Dental Tomography in DentistryMeris JugadorNo ratings yet
- Use of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in EndodonticsDocument67 pagesUse of Cone Beam Computed Tomography in EndodonticsDr.O.R.GANESAMURTHINo ratings yet
- CBCT in Endodontics: Divya Anil S Final Year Part IiDocument33 pagesCBCT in Endodontics: Divya Anil S Final Year Part IiAmal A100% (1)
- Dental Radiology LectureDocument20 pagesDental Radiology LectureAbdullahayad farouqNo ratings yet
- Role of Radiographs in Pdl. DiseaseDocument71 pagesRole of Radiographs in Pdl. DiseaseDrKrishna Das0% (1)
- CBCT in OrthodonticsDocument73 pagesCBCT in OrthodonticsdrgreeshmahariniNo ratings yet
- SER Plagiarism Report - 4Document2 pagesSER Plagiarism Report - 4Black Hack HakerNo ratings yet
- Stafne's Bone Cyst (SBC)Document8 pagesStafne's Bone Cyst (SBC)Mehmed KiossovNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Detection of Artificially CDocument9 pagesRadiographic Detection of Artificially ClukaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of CT and CBCT - 717-18-19Document59 pagesBasic Principles of CT and CBCT - 717-18-19Sara Moustafa100% (1)
- How To Read CBCTDocument17 pagesHow To Read CBCTRazvan UngureanuNo ratings yet
- IndicationDocument70 pagesIndicationPKS 1988No ratings yet
- Instrument Profile 2011 Issue 1Document4 pagesInstrument Profile 2011 Issue 1Diah MahareniNo ratings yet
- Implications of CBCT in Pediatric Dentistry-A ReviewDocument8 pagesImplications of CBCT in Pediatric Dentistry-A ReviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Aids in The Diagnosis of Periodontal Diseases: Presented By: DR: Abdullah AliDocument27 pagesRadiographic Aids in The Diagnosis of Periodontal Diseases: Presented By: DR: Abdullah AliMugahed Abdo Al-gahdariNo ratings yet
- Advancedtechniques Fordetectinglesions Inbone: Elisabetta CottiDocument21 pagesAdvancedtechniques Fordetectinglesions Inbone: Elisabetta CottiAbdul Rahman AlmishhdanyNo ratings yet
- CBCTDocument6 pagesCBCTPZNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Diagnostic AidsDocument59 pagesRecent Advances in Diagnostic AidsShubham NagrathNo ratings yet
- The Role of CBCT in The Evaluation of Periodontal DiseasesDocument5 pagesThe Role of CBCT in The Evaluation of Periodontal DiseasesMeris JugadorNo ratings yet
- CBCT EndoDocument21 pagesCBCT Endopooja muleyNo ratings yet
- Conebeam Paper 2Document6 pagesConebeam Paper 2dominiqueNo ratings yet
- Cone-Beam Computed Tomography and The DentistDocument6 pagesCone-Beam Computed Tomography and The DentistDr. Marica Ramona ElenaNo ratings yet
- Max Illo Facial SurgeryDocument92 pagesMax Illo Facial Surgerychueychuan100% (1)
- Lithoskop High Precision in Lithotripsy 00005352Document3 pagesLithoskop High Precision in Lithotripsy 00005352Mohammed Hamid Rasheed100% (1)
- Diagnosis Goes Digital: Techno BytesDocument4 pagesDiagnosis Goes Digital: Techno Bytesmentacity10No ratings yet
- Clinical: Clinical Applications of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Dental PracticeDocument6 pagesClinical: Clinical Applications of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Dental PracticeNaro HassanNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Differential Diagnosis of StafneDocument5 pagesInvestigation and Differential Diagnosis of StafneswayampradeepmohapatraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Radiographic Techniques PDFDocument21 pagesAdvanced Radiographic Techniques PDFelokfaiqNo ratings yet
- Jzusb15 1064Document8 pagesJzusb15 1064Irfan Cahya PermanaNo ratings yet
- 8.b CBCT 2023 - Compatibility ModeDocument62 pages8.b CBCT 2023 - Compatibility ModeAli AlsayedNo ratings yet
- Classification of Manfibular FractureDocument16 pagesClassification of Manfibular FractureFaheem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Imaging of The TMJ October 16 2020Document51 pagesDiagnostic Imaging of The TMJ October 16 2020AlysonNo ratings yet
- Cap 7Document31 pagesCap 7Egylany LanyNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Multislice CT: Recent TopicsDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Multislice CT: Recent TopicsAngelina ProtikNo ratings yet
- Skull Base, Orbits, TB, Cran Nerv Anatomy On MRI, MRI Clin of A 2011Document18 pagesSkull Base, Orbits, TB, Cran Nerv Anatomy On MRI, MRI Clin of A 2011Mauricio FrancoNo ratings yet
- Optimal Sites For Orthodontic Mini-Implant Placement Assessed by Cone Beam Computed TomographyDocument13 pagesOptimal Sites For Orthodontic Mini-Implant Placement Assessed by Cone Beam Computed TomographySuli M ENo ratings yet
- TAC PeñascoDocument10 pagesTAC PeñascoJose ManuelNo ratings yet
- Cone Beam in Endodontics - Bertrand Khayat and Jean-Charles MichonneauDocument5 pagesCone Beam in Endodontics - Bertrand Khayat and Jean-Charles MichonneauBadr Abdelghani MohameedNo ratings yet
- Micro Implanted Anchorage Safety Cortical Bone Thickness in IZCDocument5 pagesMicro Implanted Anchorage Safety Cortical Bone Thickness in IZCLisbethNo ratings yet
- CH 4.MDCTDocument8 pagesCH 4.MDCTKumail KhandwalaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Root Resorption Following Rapid Maxillary Expansion Using Cone-Beam Computed TomographyDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Root Resorption Following Rapid Maxillary Expansion Using Cone-Beam Computed TomographyElla GolikNo ratings yet
- A Cross-Sectional Study of Artifacts in Cone Beam Computed Tomography Images of Patients in A HospitalDocument4 pagesA Cross-Sectional Study of Artifacts in Cone Beam Computed Tomography Images of Patients in A HospitalIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Radiological Aspects of HR-CT Scan On Temporal BonDocument15 pagesRadiological Aspects of HR-CT Scan On Temporal Bonjeetchoudhary7890No ratings yet
- Internal Morphology of Mandibular Second Premolars Using Micro-Computed TomographyDocument11 pagesInternal Morphology of Mandibular Second Premolars Using Micro-Computed TomographyRenata LopesNo ratings yet
- Mandibular Posterior Anatomic Limit For MolarDocument8 pagesMandibular Posterior Anatomic Limit For MolarRommy MelgarejoNo ratings yet
- Cone BeamDocument17 pagesCone BeamViri ValdeNo ratings yet
- The Size of The Cochlea and Predictions 20170611-2684-Iv574h-With-Cover-Page-V2Document8 pagesThe Size of The Cochlea and Predictions 20170611-2684-Iv574h-With-Cover-Page-V2RizkilukumNo ratings yet
- COL042Spring2018CBCTinDiagnosis PDFDocument8 pagesCOL042Spring2018CBCTinDiagnosis PDFPaweł SieradzkiNo ratings yet
- COL042Spring2018CBCTinDiagnosis PDFDocument8 pagesCOL042Spring2018CBCTinDiagnosis PDFRuxandra GabrielaNo ratings yet
- Shouldconebeam Computedtomographybe Routinelyobtainedinimplant Planning?Document17 pagesShouldconebeam Computedtomographybe Routinelyobtainedinimplant Planning?javiers45No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Aids in OrthodonticsDocument11 pagesDiagnostic Aids in OrthodonticsSwati SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dosi Me TriaDocument10 pagesDosi Me TriafabiolaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyFrom EverandFundamentals of Oral and Maxillofacial RadiologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Q # 18 February 2020Document2 pagesQ # 18 February 2020nimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Q # 9 February 2020Document1 pageQ # 9 February 2020nimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Q # 1, October 2019, Part IiDocument1 pageQ # 1, October 2019, Part Iinimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Q # 4 February 2020 Part IiDocument2 pagesQ # 4 February 2020 Part Iinimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Q # 2, October 2019, Part IiDocument2 pagesQ # 2, October 2019, Part Iinimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Q # 3, October 2019, Part IiDocument2 pagesQ # 3, October 2019, Part Iinimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2021 48 643-650Document7 pagesDent Update 2021 48 643-650nimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2021 48 620-631Document11 pagesDent Update 2021 48 620-631nimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2021 48 707-709Document3 pagesDent Update 2021 48 707-709nimra muzaffarNo ratings yet
- Dent Update 2021 48 671-678Document8 pagesDent Update 2021 48 671-678nimra muzaffarNo ratings yet