Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculus
Calculus
Uploaded by
rairajuliamae0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesThe document outlines various topics in mathematics including number systems, algebra, geometry, calculus, probability and statistics, and discrete mathematics. It defines natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. In algebra it discusses expressions, equations, inequalities, polynomials, factoring, functions, and linear equations and systems. Geometry covers Euclidean geometry, trigonometry, and coordinate geometry. Calculus defines differential and integral calculus. Probability and statistics defines those topics. Discrete mathematics outlines set theory, logic, and combinatorics.
Original Description:
NOTES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document outlines various topics in mathematics including number systems, algebra, geometry, calculus, probability and statistics, and discrete mathematics. It defines natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. In algebra it discusses expressions, equations, inequalities, polynomials, factoring, functions, and linear equations and systems. Geometry covers Euclidean geometry, trigonometry, and coordinate geometry. Calculus defines differential and integral calculus. Probability and statistics defines those topics. Discrete mathematics outlines set theory, logic, and combinatorics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCalculus
Calculus
Uploaded by
rairajuliamaeThe document outlines various topics in mathematics including number systems, algebra, geometry, calculus, probability and statistics, and discrete mathematics. It defines natural numbers, whole numbers, integers, rational numbers, irrational numbers, and real numbers. In algebra it discusses expressions, equations, inequalities, polynomials, factoring, functions, and linear equations and systems. Geometry covers Euclidean geometry, trigonometry, and coordinate geometry. Calculus defines differential and integral calculus. Probability and statistics defines those topics. Discrete mathematics outlines set theory, logic, and combinatorics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
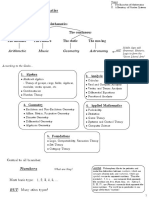
Number System:
1. Natural Numbers ( �N):
Counting numbers: 1, 2, 3, ...
2. Whole Numbers (�W):
Natural numbers and zero: 0, 1, 2, 3, ...
3. Integers (�Z):
Positive and negative whole numbers, including zero: ..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...
4. Rational Numbers (�Q):
Fractions, where numerator and denominator are integers, and the denominator
is not zero.
5. Irrational Numbers:
Numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction, e.g., 22.
6. Real Numbers ( �R):
All rational and irrational numbers.
Algebra:
1. Expressions:
Mathematical phrases involving numbers and/or variables.
2. Equations:
Statements that two expressions are equal.
3. Inequalities:
Statements that one expression is greater or less than another.
4. Polynomials:
Expressions with one or more terms, each having a non-negative integer
exponent.
5. Factoring:
Breaking down expressions into product forms.
6. Functions:
A relation between a set of inputs (domain) and a set of possible outputs
(codomain) such that each input is related to exactly one output.
7. Linear Equations and Systems:
Equations of the form ��+�=0ax+b=0 and systems involving multiple
equations.
Geometry:
1. Euclidean Geometry:
Study of shapes, sizes, properties, and dimensions of space based on Euclid's
postulates.
2. Trigonometry:
Study of the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles.
3. Coordinate Geometry:
Using algebra to study geometric concepts, introducing coordinates and graphs.
Calculus:
1. Differential Calculus:
Concerned with rates of change and slopes of curves.
2. Integral Calculus:
Concerned with the accumulation of quantities and the area under curves.
Probability and Statistics:
1. Probability:
Study of uncertainty and likelihood.
2. Statistics:
Collection, analysis, interpretation, presentation, and organization of data.
Discrete Mathematics:
1. Set Theory:
Study of sets, which are collections of objects.
2. Logic:
Study of reasoning and argumentation.
3. Combinatorics:
Counting and arranging objects.
You might also like
- New General Mathematics For Secondary Schools 3 TG Full PDFDocument73 pagesNew General Mathematics For Secondary Schools 3 TG Full PDFmoola67% (42)
- Math Class NotesDocument1 pageMath Class Notesainur.seidullaNo ratings yet
- Supporting MaterialDocument184 pagesSupporting MaterialAayush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Afrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsDocument37 pagesAfrin Sadia Rumana Lecturer Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsJHNo ratings yet
- Course Intro I. The Branches of MathematicsDocument5 pagesCourse Intro I. The Branches of MathematicsAbhimanyu SharmaNo ratings yet
- 11 Math Eng 2018Document231 pages11 Math Eng 2018Karuna SuriNo ratings yet
- Hne 104 Het 104 NotesDocument86 pagesHne 104 Het 104 NotesPriviledge ChipfumbuNo ratings yet
- 7-Mathematics Foundations SLMDocument100 pages7-Mathematics Foundations SLMva.vitekaramitNo ratings yet
- ModuleDocument205 pagesModuleNoel PhillipNo ratings yet
- 11 SM 2017 Math Eng-1Document222 pages11 SM 2017 Math Eng-1nehabehlNo ratings yet
- Cumt101 NotesDocument90 pagesCumt101 Notesangelzengwe8No ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusSECRET ButterflyNo ratings yet
- Compulsory Mathematics Booklet 2023 - 2024 FinalDocument106 pagesCompulsory Mathematics Booklet 2023 - 2024 Finalainaakhan01No ratings yet
- Mathematics Class 10 Syllabus: Course StructureDocument11 pagesMathematics Class 10 Syllabus: Course StructureBangaru BabuNo ratings yet
- Class 9 10 Curriculum 2016 2017 MathsDocument12 pagesClass 9 10 Curriculum 2016 2017 MathsAbhishek PatraNo ratings yet
- Eco 228 Mathematics For EconomistsDocument176 pagesEco 228 Mathematics For EconomistsBenjaminNo ratings yet
- Anchesofmath PDFDocument5 pagesAnchesofmath PDFRajatNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICSDocument3 pagesMATHEMATICSAljhon Matthew DizonNo ratings yet
- 38 MathematicsDocument6 pages38 MathematicsShivamNo ratings yet
- Course Structure Class Xi One Paper Three Hours Max Marks. 100Document3 pagesCourse Structure Class Xi One Paper Three Hours Max Marks. 100Faiz AhmedNo ratings yet
- What Is Mathematics PDFDocument13 pagesWhat Is Mathematics PDFLoise Hedwig Magadia100% (1)
- Mathematics Honours Syllabus of Presidency UniversityDocument14 pagesMathematics Honours Syllabus of Presidency UniversityADITI LibraryNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Mathematics - Analysis and ApproachesDocument26 pagesSyllabus Mathematics - Analysis and ApproachesCan SinanNo ratings yet
- SafariDocument73 pagesSafaribp7310746No ratings yet
- Maths TopicDocument7 pagesMaths Topicjaheimcarl16No ratings yet
- Business Mathematics and Statistics E-Sample PDFDocument36 pagesBusiness Mathematics and Statistics E-Sample PDFCaroline NdiranguNo ratings yet
- Disc MathsDocument50 pagesDisc MathsaidahusnaNo ratings yet
- Final Exam - Dela Cruz, RegelleDocument11 pagesFinal Exam - Dela Cruz, RegelleDela Cruz, Sophia Alexisse O.No ratings yet
- C Math-101Document1 pageC Math-101Athar tajNo ratings yet
- Second Semester Projects ExpandedDocument2 pagesSecond Semester Projects Expandedsobre1982No ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument1 pageDiscrete MathematicsreachudaycNo ratings yet
- Maths Syllabus JkboseDocument5 pagesMaths Syllabus JkboseNew DevideNo ratings yet
- Prog Mathematics 2024Document7 pagesProg Mathematics 2024New LifeNo ratings yet
- Prior Learning Topics: SyllabusDocument2 pagesPrior Learning Topics: Syllabusnn f dfNo ratings yet
- 2015-16 - Senior School MathematicsDocument11 pages2015-16 - Senior School MathematicsJyoti BholaNo ratings yet
- Subject Duration Maximum Marks 1. English 2 Hours 100 2. General Knowledge 2 Hours 100 3. Elementary Mathematics 2 Hours 100Document1 pageSubject Duration Maximum Marks 1. English 2 Hours 100 2. General Knowledge 2 Hours 100 3. Elementary Mathematics 2 Hours 100apandey_358373No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Complex Number, Quadratic Equations and Linear InequalitiesDocument10 pagesMathematics: Complex Number, Quadratic Equations and Linear InequalitiesSenpai KorouNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (CODE NO. 041) : Course Structure Class IXDocument6 pagesMathematics (CODE NO. 041) : Course Structure Class IXSudhakar RNo ratings yet
- Maths Sec 2022-23Document10 pagesMaths Sec 2022-23Vaibhav SBNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (Ix-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2022-23: ObjectivesDocument10 pagesMathematics (Ix-X) (CODE NO. 041) Session 2022-23: ObjectivesShivaniNo ratings yet
- Course Structure CLASS XI (2018-19) : Unit-I: Sets and FunctionsDocument5 pagesCourse Structure CLASS XI (2018-19) : Unit-I: Sets and Functionsjaya prasannaNo ratings yet
- CA-3 Assignment-Term Paper Title: Combinatorics and Its Applications School of Chemical Engineering and Physical SciencesDocument12 pagesCA-3 Assignment-Term Paper Title: Combinatorics and Its Applications School of Chemical Engineering and Physical SciencesAaditya DhakaNo ratings yet
- Class 9 Mathematics Syllabus 2020-21Document6 pagesClass 9 Mathematics Syllabus 2020-21Channappa C SNo ratings yet
- 9 Math Eng 2024 25Document3 pages9 Math Eng 2024 25Birendra RayNo ratings yet
- PMAEE - PNPAEE Mathematics Modules and ReadingsDocument142 pagesPMAEE - PNPAEE Mathematics Modules and ReadingsSarah Estalane100% (1)
- Reduced Syllabus: Class-IX: Mathematics: 80 Marks: 2020-2021 Deleted Portion of SyllabusDocument7 pagesReduced Syllabus: Class-IX: Mathematics: 80 Marks: 2020-2021 Deleted Portion of Syllabusamar sarkarNo ratings yet
- Neet PreparationDocument3 pagesNeet PreparationManojNo ratings yet
- Teacher's Manual (For Online Teaching)Document15 pagesTeacher's Manual (For Online Teaching)rgoodzstraight777No ratings yet
- Skripta Inf - Mat - Fiz - TehDocument99 pagesSkripta Inf - Mat - Fiz - TehPaola KrpanNo ratings yet
- AsimplemathdictionaryDocument31 pagesAsimplemathdictionaryapi-111747034No ratings yet
- Term - Wise Syllabus Session - 2019-20 Class-IX Subject: Mathematics (Code: 041)Document5 pagesTerm - Wise Syllabus Session - 2019-20 Class-IX Subject: Mathematics (Code: 041)Shreya JhaNo ratings yet
- AlgebraDocument183 pagesAlgebraMcrenji Abarai100% (1)
- 01 The Nature of MathematicsDocument96 pages01 The Nature of MathematicsOnechoNo ratings yet
- Maths PDFDocument3 pagesMaths PDFGaganpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- 9 Maths EMDocument4 pages9 Maths EMSai VermaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Linear Algebra and TensorsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Linear Algebra and TensorsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Calculus OverviewDocument2 pagesCalculus OverviewrairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- History 9Document1 pageHistory 9rairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- History 11Document1 pageHistory 11rairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- English Notes 6Document2 pagesEnglish Notes 6rairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- Math Assessment 4Document2 pagesMath Assessment 4rairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- English NotesDocument2 pagesEnglish NotesrairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- Research PaperDocument2 pagesResearch PaperrairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- English Notes 5Document2 pagesEnglish Notes 5rairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 1Document2 pagesEarth Science 1rairajuliamaeNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryrairajuliamaeNo ratings yet