Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Prefi OT-Evaluation-and-Assessment
Prefi OT-Evaluation-and-Assessment
Uploaded by
Raiza Orias (Rai)0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesThe document summarizes several assessment tools used in occupational therapy including:
- The WHO Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS 2.0) which assesses functioning across 6 domains.
- The Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) which screens for cognitive loss through tests of orientation, attention, calculation, recall, language and motor skills.
- The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) which assesses sleep quality over 1 month.
- Beck's Depression Inventory which is a 21-question self report test to measure severity of depression.
- Allen's Cognitive Level Screen which provides a quick estimate of learning and problem solving abilities through 3 visual motor tasks.
Original Description:
Original Title
prefi OT-Evaluation-and-Assessment
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes several assessment tools used in occupational therapy including:
- The WHO Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS 2.0) which assesses functioning across 6 domains.
- The Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) which screens for cognitive loss through tests of orientation, attention, calculation, recall, language and motor skills.
- The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) which assesses sleep quality over 1 month.
- Beck's Depression Inventory which is a 21-question self report test to measure severity of depression.
- Allen's Cognitive Level Screen which provides a quick estimate of learning and problem solving abilities through 3 visual motor tasks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesPrefi OT-Evaluation-and-Assessment
Prefi OT-Evaluation-and-Assessment
Uploaded by
Raiza Orias (Rai)The document summarizes several assessment tools used in occupational therapy including:
- The WHO Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS 2.0) which assesses functioning across 6 domains.
- The Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) which screens for cognitive loss through tests of orientation, attention, calculation, recall, language and motor skills.
- The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) which assesses sleep quality over 1 month.
- Beck's Depression Inventory which is a 21-question self report test to measure severity of depression.
- Allen's Cognitive Level Screen which provides a quick estimate of learning and problem solving abilities through 3 visual motor tasks.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
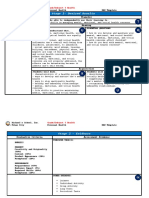
OT Evaluation and Assessment: Allen’s Cognitive Level Screen
❖ WHO Disability Assessment Schedule (WHODAS - Evidence-based, standardized screening
2.0) assessment of functional cognition developed
❖ Mini Mental Status Examination (MMSE) within the framework of the cognitive disabilities
❖ Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) model.
❖ Beck’s Depression Inventory - Provides quick estimate of an individual’s learning
❖ Allen’s Cognitive Level Screen and problem solving abilities during performance
of 3 visual motor tasks of increasing complexity.
WHODAS
- Generic assessment instrument for health and THE LPM
disability. - Tool for successful professional and personal
- Short simple and easy to administer (5-20mins) development
- Applicable in both clinical and general population
settings The Lifestyle Performance Model
- Tool to produce standardized disability levels and - Developed by Fidler and Velde
profiles - Used clinically and to measure outcomes by
- Applicable across cultures, in all adult populations Wittman and Velde
- Directly linked at the level of the concepts to the Basic Constructs:
International Classification of Functioning, • The LPM describes and examines the interacting,
Disability and Health multiple dimensions of doing and living from an
organized, holistic framework
6 Domains of Functioning: (Candy Mommy Sugar Get • Based on a philosophy of social construction (a
Lucky Please) person’s perceptions of his/her occupational
- Cognitive – understanding and communicating performance and satisfaction)
- Memory – moving and getting alone • Related to Object Relations and Wellness theories
- Self-care – hygiene, dressing, eating and staying • Performance and quality of life are essential
alone constructs
- Getting along – interacting with other people • Useful for Occupational Science and Occupational
- Life activities – domestic responsibilities, leisure Therapy
and work, school • A Top-Down Approach
- Participation – joining in community activities • Meets the four criteria for successful practice
(client-centered, occupation-based, evidence-
Mini Mental Status Examination incorporated, and outcomes-oriented)
- Offers a quick and simple way to quantify
cognitive function and screen for cognitive loss Lifestyle
- Tests the individual’s orientation, attention, - A configuration of activity patterns
calculation, recall, language and motor skills - Patterns of doing, of being engaged, emerge
- Each section of test involves a related series of through the interplay of a person’s intrinsic needs,
questions and command desires, and capacities and unique expectation of
- To give the examination, seat the individual in a the environmental contest of the person’s living
quiet, well-lit room. Ask him/her listen carefully
and to answer each question as accurately as Quality of Life
he/she can. - Integrally relate to LPM as a phenomenological
construct
Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index - Can be evaluated within each domain and overall
- Assesses sleep quality over a 1-month time
interval The Assessment Process
- Measure consists of individual items, creating 7 • The Lifestyle Performance Inventory (LPI) is used
components that produce one global score, and to gather data from the client or significant
takes 5-10 minutes to complete other(s)
- Intended to be standardized sleep questionnaire • A semi-structured interview (questions with
for clinician and researches to use with ease and is probes)
used for multiple populations.
• Combined with other information (from chart,
other evaluations: ROM, Sensory Profile, Burns,
Beck’s Depression Inventory
Depression Scale, etc.) to form a Lifestyle
- Created by Aaron Beck
• Performance Profile (LPP)
- 21-question multiple choice self report inventory
- One of the most widely used psychometric tests
Importance of the Environment
for measuring severity of depression
• Physical – personal space, natural and man-made
- Depression described in psychodynamic term as
• Societal – legal, political, economic
“inverted hostility against self”
- By contrast, the BDI was developed in a novel way • Interpersonal – self and significant others,
for its time; by collating px’s verbatim descriptions objects, home
of their symptoms and then using these to • Temporal – personal or inner time, mechanical
structure a scale which could reflect the intensity time, natural and social time
or severity of a given symptom. • Virtual – digitally created world (space and time)
Four Domains:
Intrinsic Gratification
- Personally referenced pleasure, engagement for
the joy of it, activity repertoire regarding fun,
personal interests
Reciprocal Interpersonal Relatedness
- Developing reciprocal relationships, sustaining
reciprocal relationships, mutually satisfying, all
aspects of living, friendships, intimacy, peer
affiliations, family
Societal Contribution
- Contributing to the fulfillment and welfare of
others, productive member of society, filling
societal roles, reciprocity is not expected
Self-care/Self Maintenance
- Expression of self, self-reliance, dressing,
grooming, maintenance of living spaces, eating,
cooking, etc. (ADLs and IADLs)
You might also like
- English SBADocument7 pagesEnglish SBAnaseeb60% (169)
- Leonard Baskin & Ted HughesDocument16 pagesLeonard Baskin & Ted Hughesmgter100% (1)
- Scholastic Number Tales 6Document19 pagesScholastic Number Tales 6Nguyen Duy100% (3)
- 1 BAFPE HandoutDocument9 pages1 BAFPE HandoutLila BandahalaNo ratings yet
- 04 Functional-Assessment NCM214LecDocument8 pages04 Functional-Assessment NCM214LecSVPSNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Summary (Chapter 3 - 4)Document15 pagesAbnormal Psychology Summary (Chapter 3 - 4)Louise Alenah LabragueNo ratings yet
- Sister Callista RoyDocument2 pagesSister Callista RoyZaldivar PenuliarNo ratings yet
- 3.analyze Aaplication of Icf-1Document32 pages3.analyze Aaplication of Icf-1AswathiNo ratings yet
- CH-1 Psychology Class 12 NotesDocument36 pagesCH-1 Psychology Class 12 NotesitsmisthyrastogiNo ratings yet
- Adaptation Modes: Physical Self - Body Sensation and Body Image Personal Self - Self Consistency, Self-IdeaDocument2 pagesAdaptation Modes: Physical Self - Body Sensation and Body Image Personal Self - Self Consistency, Self-IdeaAnna LaritaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing PracticeDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Nursing PracticemeowzartNo ratings yet
- CALISTADocument1 pageCALISTAShahina ShayneNo ratings yet
- Abpsy - Prelim ReviewerDocument31 pagesAbpsy - Prelim Reviewerdharl sandiegoNo ratings yet
- Psychological Assessment Answers PDFDocument8 pagesPsychological Assessment Answers PDFvincent DavidNo ratings yet
- Health 5 1QTDocument8 pagesHealth 5 1QTMark Anthony EspañolaNo ratings yet
- Health GR 8Document7 pagesHealth GR 8Alex Xander AcayenNo ratings yet
- 1ST DevpsyDocument7 pages1ST DevpsyKEITH MORGAN OLAZONo ratings yet
- Psych Assessment Prelim ReviewerDocument12 pagesPsych Assessment Prelim ReviewerKiana De Ungria100% (1)
- Geriatric Assessment 10 08 21Document57 pagesGeriatric Assessment 10 08 21Alyssa NicoleNo ratings yet
- D Professional Development For Office Administration 2 1Document55 pagesD Professional Development For Office Administration 2 1maricardelosangeles103104No ratings yet
- Variations in Psy - AttributesDocument17 pagesVariations in Psy - AttributesVinithraNo ratings yet
- ClinPsych Ch. 7 11 ADocument37 pagesClinPsych Ch. 7 11 ADepamaylo MaylynNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Lecture1Document6 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Lecture1Kazlle Sheen MinianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document20 pagesChapter 2doha safwatNo ratings yet
- Phe Mock E-Portfolio Task 1 Specific Clarification (05 Pages Max)Document5 pagesPhe Mock E-Portfolio Task 1 Specific Clarification (05 Pages Max)Malaika Ekochu100% (1)
- Robbins & Judge: Organizational BehaviorDocument19 pagesRobbins & Judge: Organizational Behaviorahmed abdul hameedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy FlashcardsDocument70 pagesAnatomy Flashcardskori holubNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document49 pagesUnit 1Abcd EfghNo ratings yet
- Giisec Pyp Grade 5 21-22 Curriculum OverviewDocument17 pagesGiisec Pyp Grade 5 21-22 Curriculum Overviewapi-516787540No ratings yet
- Clinical and Counseling Assessment: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2013 Mcgraw-Hill Companies. All Rights ReservedDocument26 pagesClinical and Counseling Assessment: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2013 Mcgraw-Hill Companies. All Rights ReservedLarissa SuárezNo ratings yet
- 02 Indi BehDocument19 pages02 Indi BehRonyNo ratings yet
- Compensatory Cognitive TraininDocument10 pagesCompensatory Cognitive Traininkanni.40976No ratings yet
- Public Health CurriculumDocument57 pagesPublic Health CurriculumMuhamadiahNo ratings yet
- Individual Behaviou, Values Attitudes KIITDocument76 pagesIndividual Behaviou, Values Attitudes KIITPiyali MitraNo ratings yet
- Neurodevelopmental Disorders - Advanced Ab PsychDocument58 pagesNeurodevelopmental Disorders - Advanced Ab PsychKrizzia Louise B. CabreraNo ratings yet
- Domains of Activities:: Roles and Functions of Psychiatric NursesDocument3 pagesDomains of Activities:: Roles and Functions of Psychiatric NursesAfif Al BaalbakiNo ratings yet
- Geriatric AssessmentDocument51 pagesGeriatric AssessmentJustine Plaza100% (2)
- Ethics Midterm NotesDocument8 pagesEthics Midterm NotesMijuNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Indv BehaviourDocument39 pagesFoundations of Indv BehaviourLipikaNo ratings yet
- PART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesDocument11 pagesPART 1 Health Assessment Lec Prelim TransesLoLiNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric 2 Nursing-LectureDocument183 pagesPsychiatric 2 Nursing-LectureHarley Justiniani Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Emotional InteligenceDocument32 pagesEmotional InteligenceDinesh Chugh100% (1)
- Lara Abou Houssa Organizatinal BehaviorDocument11 pagesLara Abou Houssa Organizatinal BehaviorRanda Abo HoussaNo ratings yet
- Dev Psych - Intro ReviewerDocument14 pagesDev Psych - Intro ReviewerALEXANDRA SAN PEDRONo ratings yet
- OB FundamentalsDocument32 pagesOB Fundamentalsbaya.hadjsaid0903No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Foundations of Individual BehaviorDocument22 pagesChapter 2: Foundations of Individual BehaviorAbeeraKhanGhaznaviNo ratings yet
- Psy 306 NotesDocument3 pagesPsy 306 Notesacz50838No ratings yet
- PSW Psychosocial Assessment MainDocument4 pagesPSW Psychosocial Assessment MaintintuNo ratings yet
- MethodsDocument2 pagesMethodsrenjun792No ratings yet
- 7 May PresentationDocument24 pages7 May PresentationAishwarya PatilNo ratings yet
- GCrevDocument10 pagesGCrevjunnelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Fundementals of OBDocument33 pagesChapter 1 Fundementals of OBbeka negewo100% (2)
- VinelandDocument35 pagesVinelandHajra KhanNo ratings yet
- Psychology: CLASS 12thDocument17 pagesPsychology: CLASS 12thARYAN SAININo ratings yet
- Psy 119 Lec 3Document2 pagesPsy 119 Lec 3Angelo SumaoyNo ratings yet
- Full Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) (AUCS) Understanding The Person Life Transitions 92326 Custom Fo All ChapterDocument43 pagesFull Download PDF of (Ebook PDF) (AUCS) Understanding The Person Life Transitions 92326 Custom Fo All Chaptertazawakiyool100% (9)
- Clegg 6e 02Document24 pagesClegg 6e 02Haseeb AliNo ratings yet
- CAFS YR 11 Syllabus Study CardsDocument12 pagesCAFS YR 11 Syllabus Study Cardseliza.corcoranNo ratings yet
- Hbo Midterm ReviewerDocument13 pagesHbo Midterm Reviewerhakdog ka baNo ratings yet
- Mental Status Examination Mse 1Document19 pagesMental Status Examination Mse 1Karl Kiw-isNo ratings yet
- Positive Health': A New, Dynamic Concept of HealthDocument47 pagesPositive Health': A New, Dynamic Concept of Healthmert05No ratings yet
- Asm Psychology 215317Document11 pagesAsm Psychology 215317Vivaan BattishNo ratings yet
- Not Just Any Usul: Semai in Pre-Nineteenth-Century Performance Practice Mehmet Uğur EkinciDocument16 pagesNot Just Any Usul: Semai in Pre-Nineteenth-Century Performance Practice Mehmet Uğur Ekinciroxy_crestfallenNo ratings yet
- Valuations - DamodaranDocument308 pagesValuations - DamodaranharleeniitrNo ratings yet
- IFB FinancingDocument175 pagesIFB Financingtahirfeyo105No ratings yet
- Contracting From East To West Bridging The CulturalDocument8 pagesContracting From East To West Bridging The CulturalNiketa JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 90.FT. Salvatierra v. Garlitos, 103 Phil. 757 (1958)Document3 pages90.FT. Salvatierra v. Garlitos, 103 Phil. 757 (1958)IamIvy Donna PondocNo ratings yet
- Is Yom Haatzmaut Worth A Hallel?: Rabbi Yitzchak TwerskyDocument4 pagesIs Yom Haatzmaut Worth A Hallel?: Rabbi Yitzchak Twerskyoutdash2No ratings yet
- Mizzima Counseling A Trauma SocietyDocument4 pagesMizzima Counseling A Trauma SocietyJoshua ConwayNo ratings yet
- A Uniform Change For The Better: MembersDocument12 pagesA Uniform Change For The Better: MembersAko Si Vern ÖNo ratings yet
- 32 Vaporization TNDocument4 pages32 Vaporization TNAjeng FadillahNo ratings yet
- Science of The Total Environment: Steven G. Brown, Shelly Eberly, Pentti Paatero, Gary A. NorrisDocument10 pagesScience of The Total Environment: Steven G. Brown, Shelly Eberly, Pentti Paatero, Gary A. NorrisJuana CalderonNo ratings yet
- Bound by DesireDocument5 pagesBound by DesireHannaNo ratings yet
- Verse (82:1) - Word by Word: Quranic Arabic CorpusDocument12 pagesVerse (82:1) - Word by Word: Quranic Arabic CorpusaminchatNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN IN General Physics 1 CO1Document8 pagesLESSON PLAN IN General Physics 1 CO1jmym0902No ratings yet
- Tafseer Kalimatu-Tawheed - An Explanation of Tawheed - by Shaikh Dr. Rabee' Bin HadeeDocument21 pagesTafseer Kalimatu-Tawheed - An Explanation of Tawheed - by Shaikh Dr. Rabee' Bin HadeeMountainofknowledgeNo ratings yet
- Memo of 2015 Aspbi & Sict - Signed 0301Document6 pagesMemo of 2015 Aspbi & Sict - Signed 0301tiyatiyaNo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar University: Collage of Economics and Business Depatermment of Logistic and Supply Chain ManagementDocument5 pagesBahir Dar University: Collage of Economics and Business Depatermment of Logistic and Supply Chain ManagementBiruktayit BelewNo ratings yet
- ℏ d dx V ψ=Eψ ℏ d dx ψ + (E−V) ψ =0 d dx ψ+ ℏ E−V) ψ =0 d dx ψ+k ψ=0Document8 pagesℏ d dx V ψ=Eψ ℏ d dx ψ + (E−V) ψ =0 d dx ψ+ ℏ E−V) ψ =0 d dx ψ+k ψ=0Indah pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Hurricane Harvey: Michael ShrimptonDocument5 pagesHurricane Harvey: Michael ShrimptonAnonymous m6yoprE9zNo ratings yet
- Icf College Syllabus 2022-2023 TTL2Document5 pagesIcf College Syllabus 2022-2023 TTL2Skill Plus Review Center PaniquiNo ratings yet
- Jeeweon Moon Research PaperDocument11 pagesJeeweon Moon Research PaperJeeweon MoonNo ratings yet
- Tsukumojuuku - Maijo OtaroDocument400 pagesTsukumojuuku - Maijo OtaroBailey FensomNo ratings yet
- (BATCH-2018-20) : Chetan Dattaji Gaikwad Institude of Management Studies, PuneDocument8 pages(BATCH-2018-20) : Chetan Dattaji Gaikwad Institude of Management Studies, PuneRubina MansooriNo ratings yet
- De Thi Tieng Anh Lop 3 Hoc Ky 2 Nam 2019 2020Document5 pagesDe Thi Tieng Anh Lop 3 Hoc Ky 2 Nam 2019 2020tran van hoaNo ratings yet
- Danfoss 103 Easy User GuideDocument2 pagesDanfoss 103 Easy User GuidePaul JonesNo ratings yet
- Labor Organization (LO) Legitimate Labor Organization (LLO)Document10 pagesLabor Organization (LO) Legitimate Labor Organization (LLO)Aster Beane AranetaNo ratings yet
- 1) Politics - Gilles Deleuze & Claire ParnetDocument2 pages1) Politics - Gilles Deleuze & Claire Parnetrayrod614No ratings yet
- UMC Social Phobia Inventory SPINDocument1 pageUMC Social Phobia Inventory SPINVũ Trần Hữu TuấnNo ratings yet