Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-New 1puc Chemistry Annul Examination Papers
1-New 1puc Chemistry Annul Examination Papers
Uploaded by
Dhanik Adithyanath S.JOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1-New 1puc Chemistry Annul Examination Papers
1-New 1puc Chemistry Annul Examination Papers
Uploaded by
Dhanik Adithyanath S.JCopyright:
Available Formats
1
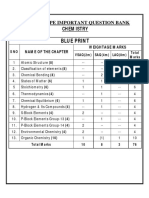
I PUC- CHEMISTRY
SPSM COLLEGE ANNUAL EXAMINATION PAPERS (UNITWISE QUESTIONS)
UNIT-1 : SOME BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
Weightage : 08 Marks [ Q.No-1: 1Mark, Q.No-11: 2 Marks & Q.No-27 : 5 Marks]
1. What is a homogeneous mixture? (March-2013)
2. 4g of NaOH are dissolved in 500ml of water. Calculate the molarity of the solution.
3. An Organic compound contains 26.66% carbon, 2.22% hydrogen and 71.12% oxygen. The molecular
mass of the compound is 90. Find its empirical formula and molecular formula.
4. Define Mole
1. Calculate the mass percentage of carbon in methane. (The molecular mass of CH4 is 16) (May-2013)
2. What is limiting reagent? How many significant figures are in 0.4500g?
3. Calculate the molecular mass of HNO3?
4. Define empirical formula. Give an example of compound whose empirical formula and molecular
formula are same.
5. Write any three basic physical quantities along with SI units.
6. State law of definite proportions?
7. What is SI unit of density?
8. Define Molarity of solution?
1. Name the SI unit of amount of substance. (March-2014)
2. Calculate the molar mass of i) Butane (C4H10) ii) Glucose (C6H12O6)
3. Define the empirical formula and molecular formula.
4. Calculate the Molarity of NaOH in the solution prepared by dissolving in 4gm in enough water to form
250mL of the solution.
1. Define Mole fraction. (May-14)
2. State law of definite proportion.
3. A compound contains 4.07% hydrogen, 24.27% carbon and 71.65% chlorine. Its molar mass is 98.96.
What are its empirical formula and molecular formula (Atomic mass of C=12, H=1.008 and Cl=35.453)
4. Define Molarity of a solution.
1. Define Molarity (Feb-2015)
2. State law of definite proportion
3. Calculate the number of grams of oxygen in 0.1mol of Na2CO3.10H2O
4. A compound contains 4.07% hydrogen, 24.27% carbon and 71.65% chlorine. Its molar mass is 98.96.
What are its empirical formula and molecular formula?
1. Name the SI unit of density. (May-2015)
2. Write the any three postulates of Dalton‟s atomic theory
3. State the law of Multiple proportions.
4. What is Homogeneous mixture? Give an example.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
2
1. What is limiting reagent? (Feb-2016)
2. Mention any two basic physical quantities?
3. a) Calcium carbonate reacts with aqueous HCl to give CaCl2 and CO2 according to the equation.
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
What mass of CaCO3 is required to react completely with 25ml of 0.75M HCl?
b) Mention any two postulates of Dalton‟s atomic theory.
1. Define atomic mass unit (May-2016)
2. Calculate the number of grams of methane required to produce 9gm of water
3. Give any three postulates of Dalton‟s atomic theory
4. Calculate the Molarity of Na2CO3 solution prepared by dissolving 5.2gm in enough water to make
500mL solution (Molecular mass of Na2CO3 = 106 gmol-1)
1. How many significant figures is present in 3 .0667g? (Feb-2017)
2. A solution is prepared by adding 4g of a substance „A‟ to 36g of water. Calculate the mass percent of
solute
3. Give any two postulates of Dalton‟s atomic theory
22
4. Calculate the number of moles in 3.01 X 10 molecules of CO2
5. What is limiting reagent?
1. What is limiting reagent ? (May-2017)
2. A solution is prepared by adding 2g of a substance „A‟ to 18g of water. Calculate the Mass percentage
of solute
3. Calculate the molarity of NaOH in the solution prepared by dissolving its 4g in enough water to form
250mL of solution.
4. What is Homogeneous mixture? Give an example.
1. State law of proportions. (Feb-2018)
2. How many significant figures are in 405?
3. Defining limiting reagent.
4. A compound contains 4.07% hydrogen, 24.37% carbon and 72.65% chlorine. Its molar mass is 98.96g.
What is its empirical and molecular formula? (Atomic mass of , C =12, H=1, Cl=35.5)
5) What is the value of Avogadro number?
1. What is Homogeneous mixture? (April-2018)
2. Calculate the molecular mass of CO2
3. What is mass number of Tritium?
4. A compound contains 4.07% hydrogen, 24.37% carbon and 72.65% chlorine. Its molar mass is 98.96g.
What is its empirical and molecular formula?
5. Write any two postulates of Dalton‟s theory
1. Give an example for a homogenous mixture? (Feb-2019)
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
3
2. Calculate the molarity of NaOH in the solution, prepared by dissolving 10g in enough water to form
500mL of the solution.( Molar mass of NaOH is 40 gmol-1)
3. The percentage composition of an organic compound found to contain 39.9% carbon, 6.7 % hydrogen
and the rest is oxygen. If the molecular mass of the compound is 60gmol-1. Determine the molecular
formula of the compound
4. State Avogadro law.
1. Define mole? (March-2019)
2. State law of definite proportions
3. A sample of a compound contains 4.07% hydrogen, 24.27% carbon and 71.65% chlorine. Its molecular
mass is 98.96g. What is its empirical and molecular formula? (Given At. Mass of C =12,H =1,Cl= 35.5)
4. What is limiting reagent?
1. Write the number of significant figures in the value 6.022 x 1023 (Feb-2020)
2. What is meant by limiting reagent? In a reaction A + B2 → AB2, identify the limiting reagent in the
mixture of 2 moles of A and 3 moles of B2.
3. A sample of a compound contains 4.07% hydrogen, 24.27% carbon and 71.65% chlorine. Its molecuar
mass is 98.96g.What is its empirical and molecular formula? (Given At.Mass of C =12, H=1,Cl=35.5)
4. Give an example each for physical property and chemical property of matter.
UNIT-2 : STRUCTURE OF ATOM
Weightage : 10 Marks [ Q.No-28 & Q.No-29 : 5 Marks Each ]
1. Write the electronic configuration of Al (Z=13) (March-2013)
2. Mention any two properties of cathode rays?
3. Give two properties of electromagnetic radiations?
4. Write all possible values of l, m and s ,when n=3 in an atom.
5. State Aufbau principle ?
6. The electron in a hydrogen atom moves with a velocity of 2.2x106 ms-1. Calculate wave length of the
electron. (Given: Mass of electron = 9.1x10-31 kg , Planck‟s constant = 6.62x10-34 JS)
7. Give two limitations of Bohr‟s model of an atom?
1. Between 4s and 3d orbital which has lowest energy? (May-2013)
2. State Heisenberg‟s uncertainty principle?
3. Write any two limitations of Bohr‟s theory?
4. For the element with atomic number (Z= 24)
i) Write electronic configuration ii) How many unpaired electrons are present in it?
5. Explain the one significance of each of four quantum numbers?
6. Atomic number (z) and Mass number (A) of element are 29 and 64. How many protons and neutrons
are present in it?
1. Write any three postulates of Bohr‟ model. (March-2014)
80
2. Calculate the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in Br35
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
4
3. Mention the significance of any three quantum numbers.
4. Give the electronic configuration of an element having atomic number i) 24 ii) 30
1. Write the four postulates of Bohr‟s model of hydrogen atom. (May-14)
2. What are isotopes?
3. For an element with atomic number Z=29 i) Write its electronic configuration
ii) How many unpaired electrons are present in it? iii) Calculate (n+l) value for 3d orbital.
4. State Pauli‟s exclusion principle.
1. Write any three observations of Rutherford nuclear model of an atom. (Feb-2015 )
2. State Heisenberg‟s uncertainty principle.
3. Write the significance of four quantum numbers
4. Give the electronic configuration of copper (Z=29).
1. Explain the significance of four quantum numbers. (May-2015)
2. State Heisenberg‟s uncertainty principle.
3. Calculate the wave number of first line in Balmer series of hydrogen spectrum. ( R =1.09677 x 107m-1)
1. a) For the element atomic number 24 i) write the electronic configuration (Feb-2016)
ii) How many unpaired electrons present in it? iii) Belongs which block in the periodic table?
b) i) Between 3d and 4s orbital, which has lower energy?
ii) Between 3p and 3s orbital, which has lower energy?
2. a) Give the significance of the following quantum numbers.
i) Principal quantum number ii) Azimuthal quantum numbers
b) Write de-Broglie equation.
1. What are the observations made in Rutherford‟s α-particle scattering experiment. (Feb-2017)
2. State Heisenberg‟s uncertainty principle and write its mathematical form?
3. Using s,p,d notations, describe the orbital with the following quantum numbers
i) n=1, l=0 ii) n=3, l=1 iii) n=4, l=2
4. Explain Hund‟s rule of maximum multiplicity?
1. Using s,p,d and f notations, mention the orbital with the following quantum numbers (May-2017)
a) n=2, l=1 b) n=4, l=0 c) n=5, l=3 d) n=3, l=2
2. Write Rydberg‟s equation
3. Calculate the energy of one mole of photon of radiation whose frequency is 5x1014 Hz.
4. State Hund‟s rule of maximum multiplicity.
1. Give any three postulates of Bohr‟s theory of atomic model. (Feb-2018)
2. Write Rydberg‟s equation? Explain the terms.
3. For the element with atomic number Z=29 i) Write the electronic configuration
ii) Write the value of „n‟ and „l‟ for its electrons in the valence shell
4. Give any two the difference between orbit and orbital
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
5
1. Write the characteristics of anode rays (canal rays) (April-2018)
2. What are Isotopes? Give an example.
3. State Hund‟s rule of Maximum multiplicity
4. What is wavelength of light emitted when the electron in a hydrogen atom undergoes transition from an
energy level with n=4 to an energy level with n=2 ( Given R =1.09677 x 107m-1)
1. Give any three postulate of Bohr‟s theory of atomic model (Feb-2019)
2. State Hund‟s rule of maximum multiplicity.
3. Name the four quantum numbers and mention what they indicate?
4. What is node?
1. Give any three postulates of Bohr‟s theory of atomic model of an atom (March-2019)
2. Give de-Broglie equation.
3. Name the orbital when n=3 and l=2
4. Explain the significance of four quantum numbers.
5. State Pauli‟s exclusion principle.
1. Write any three postulates of Rutherford‟s nuclear model of atom. (Feb-2020)
2. Calculate the energy of one mole of photon of radiation whose frequency is 5 x 10-34 Hz.
( Given : h = 6.626 x 10-34JS & NA = 6.022 x 1023 mol-1)
3. For an element with atomic number Z=29, i) Write its electronic configuration
ii) How many unpaired electrons are present in it? iii) Calculate (n+l) value for 3d orbital in it.
4. State Pauli‟s exclusion principle.
UNIT-5 : STATES OF MATTER (GASES AND LIQUIDS)
Weightage : 09 Marks [ Q.No-2: 1Mark, Q.No-12: 2 Marks & Q.No-30 : 5 Marks ]
1. State Boyle‟s law? (March-2013)
2. Write the postulates of Kinetic theory of gases?
3. Give two reasons for deviation of real gases from ideal behaviour?
4. Derive the ideal gas equation by combining Boyle‟s law, Charle‟s law and Avogadro‟s law?
1. What type of Vander Waal‟s force exists between HCl molecules? (May-2013)
2. Write Vander Waal‟s equation for „n‟ moles of gas and name any two terms in it?
3. Mention three postulates of kinetic theory of gases?
4. Derive ideal gas equation using gas laws?
5. State Boyle‟s law?
6. Calculate the pressure exerted by 4 moles of a gas occupying a volume of 1.5dm3 at 300K.
(Given R= 8.314 JK-1mol-1 )
7. Write an expression of compressibility factor (z) for one mole of a gas.
1. What are intermolecular forces? (March-2014)
2. State Boyle‟s law. Express it mathematically.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
6
3. Write the five important postulates of Kinetic theory of gases.
1. What are Vander Waals forces? (May-14)
2. Calculate the value of gas constant „R‟ in SI unit
3. Write any four postulates of kinetic molecular theory of gases.
4. Give the relation between molecular mass and density of a gas.
1. Between CO and CO2 which one diffuse faster ? (Feb-2015)
2. Give any two differences between ideal and non-ideal gases.
3. Mention any four postulates of Kinetic theory of gases.
4. Write Vander Waal‟s equation for „n‟ number of molecules?
1. State Boyle‟s law. (May-15)
2. Name two types of forces which determine the physical state of substances.
3. Define ideal gas. Derive ideal gas equation using gas laws.
4. Name two factors on which the magnitude of the surface tension depends.
1. Write Vander Waal‟s equation for one mole of a gas. (Feb-2016)
2. Derive ideal gas equation from gas laws
3. Write any four postulates of Kinetic theory of gases
4. Mention the type of attraction that exists between non-polar molecules.
1. Give reason: Viscosity of the liquid decreases as the temperature increases. (May-2016)
2. Derive ideal gas equation using gas laws
3. Write any three postulates of Kinetic molecular theory of gases.
4. A gas occupies 600ml of volume at 250C and 760mm Hg of pressure. What will be the volume at
677mm Hg pressure and 100oC ?
1. State Dalton‟s law of partial pressure (Feb-2017)
2. Write the expression of pressure correction term and volume correction term in real gases
o -1 -1
3. Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8g CO2 at 31.1 C & 1bar pressure (Given R= 0.083 barLK mol )
4. What is Boyle temperature?
5. Falling liquid drops are spherical in shape. Why?
1. Define an ideal gas. (May-2017)
2. State Dalton‟s law of partial pressure. Write its mathematical expression.
3. Write any three postulates of kinetic theory of gases.
4. Why real gases deviate from ideal behavior.
1. What is the compressibility factor (z) value in ideal gas? (Feb-2018)
2. What are the causes for the deviation of real gases from ideal behavior?
3. Derive ideal gas equation
4. Write the Vander Waal‟s equation for „n‟moles.
5. What is the SI unit of surface tension?
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
7
1. State Charle‟s law. (April-2018)
2. Write the SI unit of the following a) Universal constant b) Co-efficient of viscocity.
3. Write the postulates of kinetic molecular theory of gases.
4. Write the differences between ideal gas and real gas.
1. Write the ideal gas equation for „n‟ moles of a gas (Feb-2019)
2. Give any two differences between ideal and non-ideal gas
3. Write the important postulates of Kinetic theory of gases.
4. What is Boyle‟s temperature?
5. Falling liquid droplets are spherical. Give reason.
1. Write the ideal gas equation for „n‟ moles of gas. (March-2019)
2. Give the expression for a) Vander Waal‟s equation for „n‟ moles of gas b) Compressibility factor (z)
3. Write any three postulates of Kinetic theory of gases.
4. Mass of 200 mL gas at 1 atmospheric pressure and 27oC is 0.2g. Calculate the molar mass of the gas.
(Given R = 0.0821L atm K-1 mol-1)
1. State Charle‟s law. (Feb-2020)
2. Real gases deviation from ideal behavior at low temperature and high pressure. Give two reasons
3. Write any four postulates of Kinetic molecular theory of gases.
4. Give the SI unit of surface tension.
UNIT-6 : THERMODYNAMICS
Weightage : 10 Marks [ Q.No-31 & Q.No-32: 5 Marks Each]
1. Give an example for extensive property? (March-2013)
2. What is a spontaneous process? Give an example.
3. The enthalpies of combustion of carbon, hydrogen and ethane are -393.5kJ, -285.8kJ and -1410kJ
respectively. Calculate enthalpy of formation of ethane?
4. What is an isolated system?
5. One mole of an ideal gas at 270C undergoes isothermal expansion reversibly from a volume of 10dm3
to a volume of 20dm3. Calculate work done on the gas?
1. Define enthalpy of combustion? (May-2013)
2. Calculate the enthalpy of formation of Benzene (C6H6) given enthalpy of formation of CO2(g) and
H2O(l) are -393.5kJ and -286kJ. The enthalpy of combustion of benzene is -3267kJ.
3. State Hess‟s law of constant heat summation.
4. Derive the relationship between Cp and Cv for an ideal gas.
5. Give an example for the reaction ∆H=∆U.
1. Define the following thermodynamic terms. (March-2014)
i) Open system ii) Closed system iii) Isolated system.
2. i) State first law of thermodynamics. ii) Give an example for ∆H=∆U.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
8
3. State Hess‟s law of constant heat summation.
4. Calculate the enthalpy of formation of liquid Benzene (C6H6), given that
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ∆H = -393.5kJ
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ∆H = -285.8kJ
C6H6(l) + 15/2 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g ) + 3H2O(l) ∆H = -3267 kJ.
1. Give the statement of first law of thermodynamics. (May-14)
2. Calculate work done in an isothermal reversible expansion of one mole of an ideal gas from a volume
of 2 L to 20 L at 300K. (R= 8.314 JK-1mol-1)
3. i) What is an open system ? ii) what is adiabatic process ?
4. Define : i) Standard enthalpy of formation ii) Thermochemical equation
iii) Standard enthalpy of combustion.
5. The Equilibrium constant of a reaction is 10. Calculate the value of standard free energy change.
(Given R= 8.314 JK-1mol-1 and T = 300K)
1. Write the Gibb‟s equation and explain the terms in it. (Feb-2015)
2. Calculate the standard free energy change for a reaction at 298K. The equilibrium constant for the
reaction is 50.
3. What is exothermic reaction? Give an example.
4. State Hess‟s law and illustrate with an example.
1. Write Gibbs-Helmohltz equation. Explain terms involved in it. (May-2015)
2. What is entropy? Mention the entropy change when ice melts.
3. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of benzene. Given standard enthalpies of CO2, H2O and C6H6
are -393.5kJ, -286.2kJ and +49kJ respectively.
4. What is molar heat capacity ? Write the relation between Cp and Cv
1. What is entropy? Give its SI unit. (Feb-2016)
2. Calculate the enthalpy of formation of benzene. Given that enthalpies of combustion of benzene,
carbon and hydrogen are -3267kJ,-393.5kJ and -286kJ respectively.
3. What is an intensive property? Pick out the intensive property from i) Mass ii) Density and
iii) Internal energy
4. Write the Gibb‟s equation using ∆G, how you predict whether a reaction at a given temperature is
spontaneous or non-spontaneous?
1. Explain the measurement of ∆H by calorimetry method (May-2016)
2. Give an example each for i) Isolated system ii) External property iii) Intensive property
3. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of methane from following data
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ∆H = -393.5 kJmol-1
H2 (g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ∆H = -285.83kJmol-1
C(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4(s) ∆H = -75.16 kJmol-1
4. What is entropy? Write Gibbs equation.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
9
1. What is an intensive property? Give an example. (Feb-2017)
2. Derive the relationship between Cp and Cv for an ideal gas.
3. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CH3OH (l). If standard enthalpy of combustion of
methanol, carbon and hydrogen are -726kJmol-1, -393kJmol-1 and -286kJmol-11 respectively.
4. What is the effect of entropy for a reaction, H2(g) → 2H (g)
1. State First law of thermodynamics. (May-2017)
2. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of benzene. Given that the enthalpies of combustion of
carbon, hydrogen and benzene are --393.5kJmol-1, -285.83 kJmol-1 and -3267
3267 kJmol-1 respectively.
3. What is an extensive property? Give an example.
4. State Hess‟s law of constant heat sum
mmation
5. Write Gibb‟s free energy equation
1. What is extensive property ? Give one example. (Feb-2018)
2. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CH3OH form the following data.
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ∆H= -285.83KJmol-1
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ∆H = -393.5 KJmol-1
CH3OH(l) + 3/2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ∆H= -726.0 KJmol-1
3. State first law of thermodynamics. Write its mathematical form.
4. What is entropy? What happens to entropy when ice melts?
5. Write the relation between enthalpy change and internal energy change.
1. Define entropy. (April-2018)
2. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of methyl alcohol (CH3OH) from the given data :
3. Define the enthalpy of solution with an example.
4. State First law of thermodynamics.
5. What is Spontaneous reaction ?
1. Calculate the enthalpy of formation of Benzene from the following data : (Feb-2019)
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ∆H = -393.5kJ
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ∆H = -285.9kJ
C6H6(l) + 15/2 O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) ∆H = -3264 kJ
2. What is entropy?
3. Calculate the total work done when one mole of a gas expands isothermally and reversibly from an
intial volume of 10dm3 to a final volume of 20dm3 at 298K
4. What is an intensive property? Give an example.
1. State Hess‟s law of constant heat sum
mmation. (March-2019)
2. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of CH3OH(l) from the data.
CH3OH(l) + 3 ∕2 O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ∆H = -726 KJmol-1
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ∆H = -396 KJmol-1
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ∆H = -286 KJmol-1
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
10
3. Define entropy? What happens to the entropy when liquid water changes to vapour state?
4. What is isolated system? Give an example
5. What is an intensive property?
1. What is an extensive property? Give an example. (Feb-2020)
2. Calculate the standard enthalpy of formation of benzene from the following data.
C6H6(l) + 15/2 O2(g) → 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) ∆H = -3267 kJmol-1.
C(graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g) ∆H= -393.5 kJ mol-1.
H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(l) ∆H= -285.8 kJ mol-1.
3. State First law of thermodynamics.
4. Define entropy.
5. Calculate ∆Go for the conversion of oxygen to Ozone O →O at 298K, if K for this conversion
2(g) 3(g) p
-29 -1 -1
is 2.47x 10 . (Given R = 8.314JK mol )
UNIT-7 : EQUILIBRIUM
Weightage : 11 Marks [ Q.No-3: 1 Mark, Q.No-33 & Q.No-34: 5 Marks Each]
1. Write the conjugate base of ? (March-2013)
2. What is Homogeneous equilibrium? Give an example?
3. State Lechatelier‟s principle?
4. A solution of CH3COONa is basic. Explain?
5. What is a Bronsted acid? Give an example.
6. Define ionic product of water?
7. Mention three characteristics of chemical equilibrium?
8. The [H+] in an aqueous solution is 2.0 x10-3M. What is its PH?
10
9. The values of Kp for a reaction at 300K is 4x10 .Calculate standard free energy change?
1. The value of ionic product of water at 298K is 1x10-14M. What is its [H+]? (May-2013)
2. State Lechatelier‟s principle?
3. For equilibrium BaCO3(s) ↔ BaO(s) + CO2 (g) i) Write the expression for Kp
ii) What is the effect of increase pressure on the above equation?
4. What is the effect of catalyst on equilibrium of reversible reactions?
5. Calculate the PH of solution whose hydrogen ion concentration is 2.5x10-4M.
6. What is homogeneous equilibria? Write Kp and Kc for the reaction PCl5(g) ↔ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g)
7. What is meant by Buffer solution?
1. Express Kc for the following equation. H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) (March-2014)
2. State Lechatelier‟s principle.
3. Explain common ion effect with an example.
4. Show that PH + POH = 14
5. The concentration of hydrogen ion in a sample of soft drink is 3.8 x 10-3. What is PH and POH
6. Define Lewis concept of acids and bases.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
11
1. Write the relationship between Kp and Kc (May-2014)
2. Write any three applications of equilibrium constant.
3. State Lechatelier‟s principle.
4. Define Bronsted-Lowry concept of acids and bases. Illustrate with an equation.
5. Give two examples for strong electrolytes.
1. What is chemical equilibrium? (Feb-2015)
2. Write any four applications of equilibrium constants Kc or Kp
3. What do you mean by a reversible process?
4. What is common ion effect? Give an example.
5. What are conjugate acid-base pairs? Explain with an example.
6. Define buffer action?
1. What is Heterogeneous equilibrium? (May-2015)
2. Write any three characteristics of equilibrium constants Kc or Kp.
3. Explain Lewis concept of acid and base with an example.
4. State Le-Chatlier‟s principle. What is the effect of change of temperature?
H
5. What happens to the P of water when solid NH4Cl is dissolved in it and why?
1. Aqueous solution of ammonium chloride is acidic or basic? (Feb-2016)
2. What is Homogenius equilibrium? Give an example
3. State Le-chatlier‟s principle
4. Write Kc for the reaction N2 + 3H2 ↔ 2NH3
5. What is common ion effect? Give an example
6. Give an example for acidic buffer
7. Write the relationship between solubility and solubility product for AB2type salt.
8. The PH of boiling water is 6.90. Is the boiling water acidic or neutral?
1. Mention the conjugate acid for H2O (Feb-2017)
2. Write the expression for the equilibrium constant (Kc) for the reaction Ni(s) +4CO(g) ↔ Ni(CO)4(g)
3. How do you predict the direction of reaction in terms of equilibrium constant (Kc) and the reaction
quotient (Qc)
4. Explain the effect of pressure on the equilibrium CO(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ CH4(g) + H2O(g)
5. Assuming complete dissociation, calculate the PH value of 0.005M NaOH
6. What is common ion effect? Give an example.
7. Write Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for acidic buffer
1. Give an example for liquid-vapour equilibrium (May-2017)
2. PCl5, PCl3 and Cl2 are at equilibrium at 500K and having concentration 1.59M PCl3, 1.59M Cl2 and
1.41M PCl5, Calculate the Kc for the reaction.
3. State Le-chatleir‟s principle.
4. What is Conjugte acid-base pair? Give one example.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
12
H OH Kw
5. Show that p + p =p = 14
6. Give the relation between solubility and solubility product of A2B type salt.
1. Write the value of ionic product of water at 298K (Feb-2018)
2. What are Buffer solutions? Give one example for an acidic buffer.
3. State Le-Chatelier‟s principle
4. Write the expression of equilibrium constant Kp for the gaseous reaction aA+bB → cC+dD
5. What is common ion effect? Give an example.
6. Explain Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases.
7. When does reaction quotient is equal to equilibrium constant.
1. Give an example for solid-liquid equilibrium. (April-2018)
2. Prove that PH + POH =
3. What is the heterogenius equilibrium? Give an example.
4. Write the relation between Kp and Kc for H2(g)+ I2(g) → 2HI(g)
5. Define acid and base according to Bronsted –Lowry concept.
6. Calculate the PH of 0.001M HCl
7. What is buffer solution?
1. What is hydronium ion? (Feb-2019)
-3 0
2. For the hydrolysis of sucrose the equilibrium constant KC is 2 x 10 at 300K. Calculate ∆G at 300K.
OH
3. Calculate the P of a solution obtained when 0.05 mol NH4Cl is added and dissolved in 0.025M
ammonia solution (Given Kb for ammonia = 1.77 X 10-5)
4. What is solubility product?
5. Derive Henderson-Hasserbalch equation for acidic buffer.
1) What is the PH of 1M NaOH? (March-2019)
2) State Lechatlier‟s principle. What is the effect of temperature on the equilibrium when the forward
reaction is exothermic.
3) Relate the Kp and Kc for the equilibrium H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g)
4) What is common ion effect? Explain with an example.
5) What is buffer solution? Give an example for acidic buffer.
6) Write the conjugate acid for
1) Give an example for a reaction for which Kp = Kc (Feb-2020)
2) Write the expression for Kp and Kc for the reaction N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g)
3) State Lechatelier‟s principle.
4) If the equilibrium constant for the reaction H2(g) + I2(g) ↔ 2HI(g) is 100. What is the equilibrium
constant for the reaction 2HI(g) ↔ H2(g) I2(g)?
5) Define acid and base on the basis of Bronsted-Lowry concept.Give the conjugate base of H2O.
6) Calculate the PH of 0.001M HCl, assuming complete ionization.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
13
UNIT-3 : CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS ANDPERIODICITY IN PROPERTIES
Weightage : 04 Marks [ Q.No-4: 1 Mark, Q.No-19 : 3 Marks]
1. Write the IUPAC name of an element with Z=108. (March-2013)
2. State the law of triads. Give an example of a triad?
3. Define atomic radius. How does it vary along a period and down a group?
1. State Modern periodic law. (May-2013)
2. Define ionization enthalpy? What is the variation of ionic radius on going down the group?
3. What are isoelectronic species? Select isoelectronic pair among the following. Na+, Cl+, F- , Li+
1. Name the element having highest value of electronegativity in the halogen. (March-14)
2. Give the general electronic configuration of S-block elements.
3. Size of Na+ ion is smaller than Na. Give reason.
4. What are isoelectronic species?
1. State Modern periodic law. (May-14)
2. Define ionization enthalpy. How it varies down the group in the periodic table.
3. Give the IUPAC name of an element with atomic number 112.
1. How do you differ isoelectronic ions from simple ions? (Feb-2015)
2. Define atomic radius. Give the variation of covalent radius along the period and down a group.
1. In which period does the Lanthanides appear? (May-2015)
2. State modern periodic law. Why the size of anion is always greater than the parent ion ?
1. Name the element which is having highest electronegativity in the periodic table. (Feb-2016)
2. What is Ionisation enthalpy? How does it varies along a period and down a group
1. How does Ionisation enthalpy vary along a period? Give reason (May-2016)
2. Define electron gain enthalpy.
3. Name the most electronegative element in the periodic table
1. What is ionization enthalpy? How does it vary down a group in the periodic table? (Feb-2017)
2. Give the increasing order of their metallic character for the elements B,Al, Mg and K.
3. Which group of elements are called „Chalcogens‟?
1. Write the IUPAC name of an element with atomic number 108. (May-2017)
2. Define electron gain enthalpy. How it varies along a period and down the group.
1. What are isoelectronic species? (Feb-2018)
2. Define ionization enthalpy. How does it vary along a period and down the group in the periodic table?
1. Define electron gain enthalpy. (April-2018)
2. Explain why cations are smaller and anions are larger than their parent atoms.
3. Nitrogen has higher enthalpy of ionization than that of oxygen. Give reason.
1. Write the IUPAC name of an element with atomic number 107. (Feb-2019)
2. Define electron gain enthalpy .How does it varies along a period and down the group?
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
14
1. State Modern periodic law (March-2019)
2. What is ionization enthalpy? How does it vary in group?
3. What is isoelectronic species?
1. Which quantum number corresponds to the period number in the modern periodic table? (Feb-2020)
2. What is the electron gain enthalpy? How does it generally vary across the period and down the group ?
UNIT-4 : CHEMICAL BONDING AND MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
Weightage : 11 Marks [ Q.No-13 : 2 Marks, Q.No-20, 21 & 22 : 3 Marks Each]
1. Define bond length? (March-2013)
2. Define hydrogen bond? Name a compound having intra molecular H-bond?
3. Mention the bond angle in water?
4. Write the postulates of Molecular orbital theory?
5. Explain sp hybridization in ethyne?
6. Mention the Molecular geometry in PCl5?
7. Sketch s-p overlaps of atomic orbitals?
8. Write the electronic configuration of Li2 molecule and calculate its bond order?
9. Write the Lewis symbol for N?
1. Distinguish between sigma (σ) and pi (π) bond. (May-2013)
2. Explain the shape of ammonia molecule using VSEPR theory?
3. Distinguish between sigma (σ) and pi (π) bond.
4. Mention any three postulates of Molecular orbital theory?
5. Write the electronic configuration of Lithium molecule on the basis of molecular orbital theory.
Calculate the bond order.
6. Define the following term i) Bond length ii) Bond angle iii) Bond enthalpy
1. The dipole moment of BeF2 is zero. Give reason. (March-2014)
2. Explain sp2 hybridization of BeCl2
3. Draw energy level diagram for Helium molecule and calculate its Bond order.
4. Define Hydrogen bond. Mention the types of H-bond.
5. What is meant by dipole moment? Why dipole moment of BF3 is zero?
1. Write the electronic configuration of lithium molecule. What is its bond order. (May-14)
2. Write any three postulates of VSEPR theory.
3. Explain sp2 hybridization with Boron tri chloride as an example.
4. Mention the type of hydrogen bond in the following compounds? i) Water ii) Ortho-nitro phenol?
1. Write the state of hybridization in BF3. (Feb-2015)
2. Mention two conditions for the formation of covalent bond.
3. Explain sp2 hybridization in the formation of BCl3 molecule?
4. What is VSEPR theory? Explain taking water as an example.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
15
5. Explain the monoatomic property of Helium on the basis of MOT (Molecular orbital theory)
1) Define bond order. Write electronic configuration of Lithium molecule. (May-2015)
2) Write any three important features of valence bond theory.
3) What is covalent bond? Explain the formation of covalent bond in Hydrogen chloride.
4) Explain the structure of ammonia molecule on the basis of VSEPR theory.
1) What is sigma bond? Why sigma bond is stronger than pi-bond? (Feb-2016)
2) Define bond order. Calculate the bond order in Hydrogen molecule
3) Explain sp3 hybridization in methane molecule
4) Write any three postulates of molecular orbital theory
1) Mention the hybridization of carbon in diamond. (May-2016)
2) Define dipole moment. Write the name of the unit
3) Write any three postulates of VSEPR theory
2
4) Explain sp hybridization taking BCl3 as an example
5) Write the electronic configuration of Lithium molecule. Predict its stability and magnetic property.
1) Give any two limitations of octet rule. (Feb-2017)
2) Write any two postulates of VSEPR theory
3) Define dipole moment
2
4) Explain sp hybridization in BCl3
5) Based on MOT give the electronic configuration, bond order & magnetic property of Lithium molecule.
1) What is the hybridization of carbon in graphite? (May-2017)
2) Write the Lewis dot structure of i) Cl2 ii) CO2
3) Explain sp-hybridization by taking ethyne as example.
4) Write the electronic configuration of Lithium molecule. Calculate its bond order and mention its
magnetic property.
5) What is ionic bond?
6) Mention any two conditions for the formation of covalent bond.
1) Draw the Lewis symbol for CCl4 (Feb-2018)
2) What is the shape of NH3 molecule according to VSEPR theory
3) What is meant by hydrogen bonding? Sketch the hydrogen bonding in HF.
4) Define bond length.
5) Write the molecular electronic configuration, bond order and magnetic property of Lithium molecule.
6) Define dipole moment. What is its unit?
7) State Octet rule.
8) Mention the hybridized state of carbon in fullerene
1) What is ionic bond? Give an example for ionic compound. (April-2018)
2) Write the postulates of VSEPR thory.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
16
3) How is sigma bond and pi-bond formed?
4) Define formal charge.
5) Draw the energy level diagram for hydrogen molecule, write its electronic configuration and bond order.
1) Mention any two conditions for the combination of atomic orbitals. (Feb-2019)
2) Define the terms a) Bond angle b) Bond order c) Co-valent radius
3) Give any three important postulates of VSEPR theory
4) Explain bonding in H2 molecule based on the basis of Molecular orbital theory.
1. Define : a) Lattice enthalpy b) Covalent radius c) Bond enthalpy (March-2019)
2. What is hydrogen bonding? Mention the types of hydrogen bonding involved in O-nitrophenol
3. Write the molecular orbital electronic configuration of oxygen molecule and calculate the bond order.
4. Mention the type of hybridization, geometry and bond angle in BCl3molecule
1. Write Lewis dot symbols for CH4 molecule and Cl2 molecule. (Feb-2020)
2. Give any three postulates of VSEPR theory
3. Explain the formation of BCl3 using the concept of hybridization.
4. Write the molecular orbital electronic configuration for the carbon molecule. Calculate the bond order
and comment on magnetic property
UNIT
UNIT-8 : REDOX REACTIONS
Weightage : 04 Marks [ Q.No-5 : 1 Mark, Q.No-23 : 3 Marks ]
1. What is the oxidation number of S in NaHSO4? (March-2013)
2. Balance the following redox equation by oxidation number method.
3. What is the oxidation number of oxygen in peroxides?
1. What is the oxidation number of S in H2S2O7? (May-2013)
2. Balance the following chemical equation by oxidation number method in acidic medium
1. What is the oxidation number of Mn in MnO2 ? (March-2014)
2. Balance the following equation using oxidation number method in acidic medium.
1. Define oxidation number? (May-14)
2. Balance the following chemical equation by oxidation number method in acidic medium
1. Give oxidation number is terms of electronic concepts. (Feb-2015)
2. Balance the chemical equation by oxidation number method ( in acidic medium)
Fe+2 + MnO4- → Fe+3 + Mn2+
1. Mention the oxidation number of Mn in KMno4 (May-2015)
2. Balance the redox equation by oxidation number method in acidic medium.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
17
1. Calculate the oxidation number of oxygen in Na2O2 (Feb-2016)
2. Consider the element Na , F and I
i) Identify the element that exhibits only negative oxidation states
ii) Identify the element that exhibits only positive oxidation state
iii) Identify the element that exhibits both positive and negative oxidation state.
1. What is oxidation in terms of electron transfer? (May-2016)
2. Balance the following redox reaction by oxidation number method
(Acidic medium)
1. Assign the oxidation number of oxygen in O2F2 (Feb-2017)
2. Balance the following redox reactions using oxidation number method.
Mn + → MnO2 + Br ( in acidic medium)
1. What is the oxidation state of Nitrogen in nitric acid (HNO3)
2. Balance the redox reaction using oxidation number.
(Acidic medium)
1. Give the oxidation state of Calcium in CaO2. (Feb-2018)
2. Balance the following redox reaction by oxidation number method
MnO2 + Br-→ Mn+2 + Br2 + H2O (acid medium)
1. Give an example for decomposition reaction. (April-2018)
2. Balance the following redox reactions by oxidation number method
(Acidic medium)
1. Identify the element in the compound K2Cr2O7 showing negative oxidation number. (Feb-2019)
2. What is the oxidation number of Cl in KClO3?
3. Write the separate equations for the oxidation and reduction reactions occurring in the given redox
reaction. 2Fe + HCl →FeCl2 + H2
1. Calculate the oxidation number of Mn in MnO4-. (March-2019)
2. Balance the following redox reaction by using oxidation number method in acidic medium
Mn + → MnO2 + Br
1. Mention the oxidation number of Mn in MnO4- ion. (Feb-2020)
2. Balance the following red ox reaction by oxidation number method.(acid medium)
UNIT-9 : HYDROGEN
Weightage : 03 Marks [ Q.No-24 : 3 Marks ]
1. How is hydrogen gas prepared in the laboratory ? (March-2013)
2. What is hard water? Mention any one method of removing temporary hardness of water?
3. Give two uses of hydrogen peroxide?
1. What is the role of heavy water in nuclear reactor? (May-2013)
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
18
2. What are the causes for temporary and permanent hardness of water?
3. What is the composition of water gas(or) synthesis gas?
4. What volume of O2 produced by 1lire 10 volume of H2O2 at STP
1. Mention the three uses of Dihydrogen. (March-2014)
2. Name the isotope of Hydrogen containing two neutrons?
1. Write any two similarities between hydrogen and alkali metals. (May-14)
2. Give an example for an ionic hydride.
1. CO + H2 is the composition of which gas? (Feb-2015)
2. Explain softening of permanent hardness of water by Calgon‟s process.
1. Explain the preparation of H2O2 from BaO2. (May-2015)
2. Write the composition of water gas.
1. Complete the given equation: a) PbS + 4 H2O2 → ---- + 4H2O (Feb-2016)
b) CO + H2O → ---- + ----
c) H2 + 2Na → ----
1. Give the laboratory method of preparation of dihydrogen. Write the equation (May-2016)
2. What is Soft water?
1. What causes the temporary and permanent hardness of water? (Feb-2017)
2. Give one example for ionic hydride
1. Write the composition of producer gas (May-2017)
2. How Hydrogen peroxide is prepared from Barium peroxide.
3. Give an example for electron precise hydride.
1. Name the radioactive isotope of hydrogen. (Feb-2018)
2. What is water gas?
3. Temporary hardness of water is due to what?
1. What is dry ice? (Aril-2018)
2. Giver the differences between temporary hard water and permanent hard water.
1. Give the composition of water gas? (Feb-2019)
2. Explain the process of softening of temporary hardness by Clark‟s method.
1. Complete the following reaction : i) Zn + 2NaOH → (March-2019)
ii) PbS + 4H2O2 →
2. What is the molecular formula for heavy water ?
1. Explain the process of softening of temporary hardness by Clark‟s method. (Feb-2019)
2. Name the radioactive isotope of hydrogen.
1. What happens when i) hydrogen peroxide is treated with lead sulphide ? (Feb-2020)
ii) Zinc on treating with dilute hydrochloric acid.
2.Write the reaction of dihydrogen with halogen
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
19
UNIT-10 : S-BLOCK ELEMENTS
Weightage : 06 Marks [ Q.No-06 : 1 Mark, Q.No-14 : 2 Marks & Q.No-25 : 3 Marks]
1. Give two uses of Ca(OH)2? (March-2013)
2. How is sodium chloride obtained from sea water?
1. Name the alkali metal which is radioactive? (May-2013)
2. Mention one biological importance of each Na and K.
3. Write any three points of similarity of Li and Mg.
4. What happens when : i) Sodium metal is dropped into water. ii) Potassium burns in air ?
1. Give the general electronic configuration of s-block elements. (March-14)
2. How quicklime is commercially prepared ?
3. Write any three points of similarities between lithium and magnesium.
1. How is sodium hydroxide prepared commercially by castner-kelllner cell? (May-14)
2. Name the most abundant metal in the earth crust.
3. Aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is alkaline. Give reason.
1. Why are alkali metals are soft? (Feb-2015)
2. What are alkali metals? Give any two general properties?
3. What is dead burnt plaster (Plaster of paris). How it is obtained from Gypsum ?
1. How is ionization enthalpy varies in alkali metals? (May-2015)
2. Explain the factors responsible for the anamolous properties of second period elements.
3. How is sodium hydroxide (Caustic soda) is manufactured by Castner-Kellner cell method?
4. What is Gypsum? Mention its role in cement.
1. Write the molecular formula for washing soda. (Feb-2016)
2. What happens when i) Sodium metal dropped in water? ii) Sodium is heated in free supply of air?
3. Boric acid is protic acid (or) non-protic acid.
4. Aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is alkaline. Give reason.
1. Write the general electronic configuration of alkaline earth metals. (May-2016)
2. Lithium shows anomalous properties. Give reasons
3. How is calcium oxide prepared on commercial scale? Write equation
4. What is milk of lime?
1. Write the reaction taking place at cathode and anode in the preparation of caustic soda using Castner-
Kellner cell. (Feb-2017)
2. Why compounds of alkaline earth metals are more extensively hydrated than those of alkali metals.
3. Complete the following equation : i) 2Ca(OH)2 + 2Cl2 → ii) CaCO3 +H2SO4→
4.Beryllium shows diagonal relationship with aluminium. Give reason.
1. Write the composition of caustic soda and Baking soda . (May-2017)
2. Give the chemical formula for i) Plaster of paris ii) Lime stone
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
20
3. Why compounds of alkaline earth metals are more extensively hydrated than those of alkali metals ?
1. Which alkali metal gives golden yellow colour to the flame ? (Feb-2018)
2. Write the chemical composition for the following a) Baking Soda b) Plaster of paris
3. Name the gas liberated when alkaline earth metals react with acids.
4. Complete the following: a) 2Na + O2 → ------ b) CaCO3 →-------------+ CO2
1. Alkali metals are stored in kerosene, why? (April-2018)
2. Give the diagonal relationship between beryllium and aluminium (any two)
3. How is sodium bicarbonate prepared?
4. Write the chemical formula of caustic soda.
1. Complete the following equations . i) 4Li + O2 → ---- ii) 2Na + O2 → -----. (Feb-2019)
2. Name the gas liberated when a piece of sodium metal is added into the water.
3. Give the composition of Plaster of paris and mention one use of it.
4. Write any one biological importance of magnesium.
1. Name the alkali metal has maximum hydration enthalpy (energy) and why ? (March-2019)
2. Explain the manufacture of sodium carbonate by Solvay‟s process
3. Which alkali metal is the strongest reducing agent and Why ?
1. How does ionization enthalpy vary in alkali metals? (Feb-2020)
2. With conditions, give the equation for the reaction between H2 and N2
3. In the commercial preparation of sodium hydroxide by Castner-Kellner process, write
i) anodic reaction ii) cathodic reaction iii) electrolyte used.
UNIT-11 : SOME P-BLOCK ELEMENTS
Weightage : 07 Marks [ Q.No-7 & 8 : 1 Mark Each, Q.No-15 : 2 Marks & Q.No-26 : 3 Marks]
1. What is the shape of Buckminster Fullerene? (March-2013)
2. Explain the reactions taking place when i) Boric acid is added to water. ii) H3BO3 is heated?
3. Why is carbon monoxide poisonous?
1. Write the composition of Borax? (May-2013)
2. Explain the differences in properties of diamond and graphite on the basis of their structure?
3. Write any two uses of each Boron and Aluminium?
4. Explain the effect of heat on Orthoboric acid. Give equation.
1. Give three differences between diamond and graphite (March-14)
2. Write the formula for dry ice ?
3. Name the gas which forms complex carboxy haemoglobin.
4. What is producer gas ? How it is prepared ?
1 .Give any two reasons for anoamalous behavior of carbon? (May-14)
2. Explain the structure of diborane.
3. Which is the repeating unit of organosilicon polymers?
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
21
1. CO +H2 is composition of which gas ? (Feb-2015)
2. Write the state of hybridization in BF3.
3. Draw the shapes of a) SiF4 b) SiF6-2
4. Give reasons: i) Concentrated nitric acid transferred in aluminium container
ii) Diamond is a hard and shiny substance
iii) Silicon forms p-type semi-conductor.
1) Write any one use of diamond. (May-2015)
2) What happens when aluminium is heated with air?
3) Write any three anamolus properites of Boron
4) How do you prepare carbon dioxide in the laboratory?
1. Give reasons: a) Con.HNO3 can be transported in aluminium containers. (Feb-2016)
b) Diamond is used as abrasive c) Graphite is used as lubricant.
2. Write the molecular formula of inorganic benzene.
3. Write the basic structural unit in silicates
4.Boric acid is protic acid (or) non-protic acid.
5.What is catenation ?
6. Write the formula of Borax.
7. Mention the hybridization of carbon in diamond
1. Write the molecular formula of Borax.
2. Mention the hybridization of carbon in diamond
3. Explain the method of preparation of Diborane on industrial scale with equation.
4. Aqueous solution of sodium carbonate is alkaline.Give reason.
5.Explain the structure of graphite
1. What is the chemical composition of Borazine (Feb-2017)
2. Complete the following equation : H-COOH →
3. Diamond is covalent, yet it has high melting point. Why?
4. Complete the following equation : i) 2Ca (OH)2 + 2Cl2 → ii) CaCO3 + H2SO4 →
5. Explain the action of heat on Borax.
6. What are Silicones?
1. Give any three anomalous properties of Boron. (April-2017)
2. How is Bleaching powder is prepared from slaked lime.
3. Write the composition of plaster of paris.
4. Write the structure of diborane ? Mention the type of bonds present between two boron atoms.
1. Write the general electronic configuration of „P‟ block elements. (Feb-2018)
2. Solid Carbon dioxide is called -----------
3. Diamond is a bad conductor of electricity but graphite is a good conductor .Justify the statement.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
22
4. Which compound is known as “inorganic benzene”?
5. Why Boron has high melting point?
6. Mention the hybridized state of carbon in fullerene.
1. Write the general electronic configuration of P-block elements. (April-2018)
2. Write any two differences between graphite and diamond.
3. Between Boron and aluminium boron can not form trivalent but aluminium can form. Give reason.
4. How diborane is prepared form boron trifluoride ? Write the chemical equation.
1. What is zeolite? (Feb-2019)
2. What is dry ice?
3. Write the formula of basic structural unit of silicates
4. Give the composition of water gas.
5. Boron shows anamolous behavior with other elements of the same group. Give reasons.
6. Name the gas liberated when formic acid is heated with concentrated H2SO4.
1. Write the partial structure of silicone polymer. (March-2019)
2. What is the state of hybridization of carbon atom in diamond
3. Give any two reasons for the anomalous behavior of boron.
4. How diborane is prepared from Boron trifluoride?
5. What is inorganic benzene?
1. Name the neutral oxide of carbon. (Feb-2020)
2. Which element of group-13 has unusual high melting point?
3. Write the molecular formula of inorganic benzene.
4 Concentrated nitiric acid renders aluminium passive. Why?
5. Give two differences between diamond and graphite with respect to hybridization of carbon and
electrical conductivity.
6. Mention any one man made silicate.
UNIT-12 : SOME BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
Weightage : 11 Marks [ Q.No-09 : 1 Mark, Q.No-35 & Q.No-36 : 5 Marks Each]
1. Write the IUPAC name of (March-2013)
2. Describe the experiment to estimate the percentage of Carbon and Hydrogen in an organic compound.
3. Explain i) Sublimation method of separating organic compound in a mixture.
ii) Distilling method of separating organic compounds.
4. What is meant by inductive effect? Give an example of a group causing +I effect?
5. What is functional isomerism? Give an example
1. Write the IUPAC name of i) ii) (May-2013)
2. What are electrophiles? Give an example.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
23
3. With a neat labeled diagram describe the estimation of carbon and hydrogen in an organic compound?
4. Define functional isomerism? But-11-ene and But-2-ene exhibit which type of isomerism?
5. Write the functional group of i) Aldehyde ii) carboxylic acids?
1. Give the IUPAC name of the following : (March-2014)
2. Mention the name of any two methods of purification of organic compounds
3. Explain Homolysis and Heterolysis with an example
4. What is the functional isomerism? Explain with an example
5. Which metal is used to prepare Lasssaigne‟s extract solution?
6. Describe the detection of carbon and hydrogen.
1. Write the IUPAC names for the following. (May-14)
i) CH3-C(CH3)2CH2-CH-(CH3)2 ii) CH3-CO-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH
2. For the molecule
i) Write the bond-line formula of the compound
ii) What is the hybridization of carbon attached to bromine?
iii) How many sigma bonds are present in it
3. What is functional isomerism? Give example
4. How can halogen present in an organic compound be estimated by carius method?
5. Explain the preparation of Sodium fusion extract.
6.Which metal is used to prepare lassaigne extract solution ?
1. Is isobutene a straight chain or branched chain hydrocarbon? (Feb-2015)
2. Identify the type of isomerism exhibited by i) n-butane and isobutene ii) Propanone and propanal
3. Write the IUPAC names of i) CH3-CH2-CH (CH3)-CH2-OH ii) CH3-CH═CH
═CH-CH3
4. Give the bond line structures for But
But-1-ene
5. Define electromeric effect. Give an example.
6. Mention any two differences between inductive effect and Mesomeric effect.
7. Give one example of an atom or group which shows I-effect.
8. How is percentage of sulphur estimated in an organic compound?
9. Mention any two methods used for the purification of organic compound.
1. What is meant by homolysis of a covalent bond. (May-2015)
2. Which effect involves the displacement of electron pair under the influence of an attacking reagent?
3. How is percentage of sulphur estimated in an organic compound by Carius method?
4. Give IUPAC name of the following i) CH3-CH2-CH=CH2 ii) CH3-C(CH3)2-CH2-CH2-CH3
5. Write short notes on thin layer chromatography (TLC)
1. What is catenation? (Feb-2016)
2. Mention the best and latest technique for isolation, purification and separation of organic compound.
3. Give the IUPAC name and bondline formula for the compound. CH3-CH=CH
CH=CH-CH2-CH3
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
24
4. For the compound CH ≡ C-CH = CH
CH–CH3
i) Identify the number of sigma and pi-bond
ii) Write the bondline formula for the compound
iii) Mention the compound is saturated or unsaturated.
5. Give any two differences between inductive effect and Electromeric effect
6. Write the principle involved in the estimation of carbon and hydrogen present in the organic compound
by Liebig‟s method.
7. Explain Functional isomerism with an example.
1. Write the IUPAC name of (May-2016)
2. Describe Crystallisation
3. Expalin chain isomerism with an example
4. Describe carius method for the estimation of halogen
5. What is homologoues series?
1. Write the IUPAC name of Cl2-CH--CH2-CH2OH (Feb-2017)
2. Explain functional group isomerism with suitable example.
3. Write a bondline formula for a compound N≡C-CH(OH)-C≡N
4. What is positive resonance (+R) effect? Illustsrate with an example.
5. Describe the estimation of sulphur by Carius method.
6. Name a suitable technique of separation of the components from a mixture of aniline and water
7. Indicate the colour formed in Lassaigne
Lassaigne‟s test for the detection of nitrogen.
1. What is the functional group of alcohol? (May-2017)
2. Give the chain isomers of Butane (C4H10)
3. On complete combustion, 0.246g of an organic compound gave 0.198g of carbondioxide and 0.1014g of
water. Determine the percentage composition of carbon and hydrogen in the compound.
4. What is Electromeric effect? Which type of electromeric effect is shown by H+
5. Explain the free radical mechanism of Chlorination of Methane.
1. Mention one use of chromatorgraphy. ( Feb-2018)
2. Give any two differences between inductive effect and Electromeric effect
3. Explain the functional isomerism with an example
4. Write the IUPAC name of (CH3)2-CH
CH-CH2-CH2-OH
5. Write the principle involved in the estimation of halogen by carius method.
6. How is nitrogen detected using sodiium fusion extract?(Lassaigne‟s reagent)
1. Write the IUPAC name of (April-2018)
2. Define position isomerism with an example.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
25
3. Explain the estimation of carbon and hydrogen by Liebig‟s method. Write the calculation method.
4. Write the differences between inductive effect and mesomeric effect.
5. On complete combustion 0.246g of an organic compound gave 0.198g of carbon dioxide and 0.101g of
water. Determine the percentage composition of carbon and hydrogen in the compound.
1. Write the bond line formula for 3-chloro octane. (Feb-2019)
2. Write the principles involved in the estimation of i) Halogens ii) Sulphur present in an organic
compound by Carius method.
3. Describe the estimation of carbon and Hydrogen by Liebig‟s method
4. Name the element estimated by Kjeldhal‟s method.
5.What is cracking ?
1. Which is the highly stable conformation of ethane among staggered and eclipsed form (March-2019)
2. Write any two differences between inductive effect and electromeric effect
3. Explain Functional isomerism with example.
0 0 0
4. What is carbocation? Mention the stability order among 1 , 2 and 3 carbocations.
5. Name the method used to separate the liquids with small difference in boiling point
6. Write the principle and formulae of calculation for the determination of percentage of nitrogen by
Kjeldahl‟s method.
7. How do you detect sulphur using Lassaigne‟s extract?
1. Draw the bond line structure of (CH3)2CH-CH2-CH2-OH (Feb-2020)
2. What type of isomerism the following pairs of compounds exhibit?
i) Propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol ii) Pentane and 2-methyl butane.
3. Explain the principle and calculation involved in the estimation of carbon in the orgnic compound,
4. Using sodium fusion extract (Lassaigne‟s extract) how do you detect nitrogen present in the organic
compound.
5. How are free radicals formed?
UNIT-13 : HYDROCARBONS
Weightage : 10 Marks [ Q.No-10 : 1 Mark, Q.No-16 &17: 2 Marks Each , Q.No-37 : 5 Marks ]
1. Mention the catalyst in Friedel-craft‟s alkylation? (March-2013)
2. Explain the mechanism of chlorination of methane?
3. Explain nitration of benzene?
4. How is methane converted to Methanol?
5. How is ethyne prepared from calcium carbide?
6. Explain the reaction between propene and HBr.
1. Explain the mechanism of chlorination of methane with equations? (May-2013)
2. Write the general formula of alkenes.
3. Describe the mechanism of chlorination of Benzene with equations.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
26
4. State Markownikov‟s rule.
5. Draw staggered conformation of ethane?
6. Name the products formed when ethyne is passed through red hot iron tube?
7. What happens when phenol is heated with zinc dust?
1. Explain Friedel-craft‟s reaction with an example. (March-2014)
2. How do you prepare Ethyne from calcium carbide?
3. Describe the mechanism of chlorination of Benzene
4. State Markovnikoff‟s rule?
5.Give the name of the following.
1. Draw the staggered conformation of ethane? (May-14)
2. Mention the product obtained due to cyclic polymerization of ethyne?
3. State Markovnikovs rule?
4. Explain the mechanism involved in the nitration of benzene?
5. How are alkenes prepared from unsaturated hydrocarbons? Give equation.
1. Explain Wurtz reaction with an example. (Feb-2015)
2. How the ozonolysis taking place? Explain using alkene
1. Why are alkenes reactive in nature? (May-2015)
2. Explain the preparation of alkane by Kolbe‟s electrolytic method?
3. What is pyrolysis? Give example.
4. Explain the mechanism of chlorination of benzene.
5. Mention the conditions for aromaticity.
1. Give any two lists to distinguish between alkane and alkene. (Feb-2016)
2. Explain the mechanism of nitration of benzene
3. State Markownikoffs rule
4. Draw the structure of cis-isomer of 2-butene.
5. Give the IUPAC name and bond line formula for the compound
1. The simple compounds from which polymers are made are called as ------- (May-16)
2. Explain Wurtz reaction taking bromo ethane as example. Write the equation.
3. How benzene in prepared from phenol? Write the equation.
4. Explain the mechanism of Friedel craft‟s alkylation of benzene.
5. What is the product obtained by the cyclic polymerization of ethane?
1. Complete the following equation. HCOOH → (Feb-2017)
2. Draw the Newman projection for staggered conformation of ethane.
3. Explain Markownikov‟s rule with an example.
4. Explain the mechanism of nitration of benzene.
5. Write the major product formed in the following reaction
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
27
i) CH3-C≡CH + H2O→
ii) 3CH ≡ CH →
1. Name the product formed when phenol is heated with zinc dust. (May-2017)
2. State Markownikoff‟s rule with an eexample.
3. Explain the mechanism of chlorination of methane.
4. Write the Geometrical isomers of But
But-2-ene
5. How do you convert Benzene into nitrobenzene?
6. Give the three conditions for aromaticity.
1. Draw the staggered conformation of ethane. (Feb-2018)
2. What is a cis-isomer? Give an example
3. State Markownikoff‟s rule.
4. Explain the mechanism of nitration of Benzene
5. How phenol is converted to Benzene?
1. Name the reagent used in dehydro halogenation of alkyl halides. (April-2018)
2. How is benzene converted into toluene? Write the chemical equation.
3. Write the Saw horse eclipsed and staggered representation of ethane.
4. Complete the following reactions :
i) + H2 →
ii) CH4 + Cl2 → ---- + HCl
iii) CH4 + O2 →
5. What is the hybridization of carbon in alkanes and shape of alkanes?
1. What are benzenoids ? Give an example. (Feb-2019)
2. Explain the mechanism of chlorination of Methane.
3. Name the product formed when phenol vapours are passed over heated zinc dust. Write the chemical
equation.
4. Alkanes are not soluble in water. Give reason.
5. Explain Wurtz reaction with a suitable example.
1. State Markownikovs rule. (March-2019)
2. Explain the mechanism of nitration of Benzene
3. What is Wurtz reactopm? Give an example.
1. Name the metal used in Wurtz reaction. (Feb-2020)
2. Write the two geometrical isomers of but-2-ene.
3. What happens when ethyne is passed through red hot iron tube? Give equation.
4. Write the equations for the steps involved in the mechanism of chlorination of benzene.
5. Write any two conditions for the aromaticity of an organic molecule.
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
28
UNIT-14 : ENVIRONMENTAL CHEMISTRY
Weightage : 02 Marks [ Q.No-18 : 2 Marks]
1. What is meant by ozone layer? Mention its use. (March-2013)
2. Give two causes for water pollution.
1. Name any two gases responsible for green house effect? (May-2013)
2. How is ozone layer is formed in the stratosphere? Name the chief chemical thus causes depletion?
3. What is acid rain? Which one of the following acids is not present in acid rain? HNO3,H2SO4& HCOOH
1. Name the gas which forms complex carboxy haemoglobin? (March-2014)
2. What is meant by Biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). Write its significance.
1. What is acid rain? Name a gas which contributes to acid rain? (May-14)
1. Write the harmful effects of hydrocarbons pollutants. (Feb-2015)
2. What is photochemical equation ?
1. Write any two harmful effects of oxide of sulphur. (May-2015)
1. Write any two common chemicals of photochemical smog. (Feb-2016)
1. Name the two gases which are responsible for greenhouse effect. (May-2016)
1. List the gases which are responsible for green house effects. (Feb-2017)
1. Mention any two components of photochemical smog. (May-2017)
1. Mention any two green house gases. (Feb-2018)
1. What do you mean by a)BOD b) Pathogens (April-2018)
1. How ozone is formed in the atmosphere? Give equations. (Feb-2019)
1. What is meant by Biological oxygen demand (BOD)? (March-2019)
2. Name the gas which is mainly responsible for global warming.
1. Mention any two gases causing global warming. (Feb-2020)
*************
MOHAN G S (GSM) SPSM PU COLLEGE DAVANGERE
You might also like
- Solution of Chapter 5 of Modern PhysicsDocument25 pagesSolution of Chapter 5 of Modern PhysicsAnonymous b6H1rBG56% (9)
- CH 3 ReviewDocument4 pagesCH 3 ReviewAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- PUC I Year CHEMISTRY Chapterwise Imp QuestionsDocument50 pagesPUC I Year CHEMISTRY Chapterwise Imp Questionsbimappaankalagi143No ratings yet
- Class 11 Chapter 1 Chemistry Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesClass 11 Chapter 1 Chemistry Important QuestionsradhavenkateshwaranNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 1 ChemDocument3 pagesChapter # 1 ChemRana Hassan TariqNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Worksheet Chpter 1 Grade 11Document6 pagesChemistry Worksheet Chpter 1 Grade 11adaladin0077No ratings yet
- I Year EM CHEMISTRY IMP QUESTIONSDocument6 pagesI Year EM CHEMISTRY IMP QUESTIONSgoritakasi3No ratings yet
- Chemistry3 96) PDocument43 pagesChemistry3 96) PShlok ParekhNo ratings yet
- JR Chemistry QUESTION BANKDocument15 pagesJR Chemistry QUESTION BANKtelukuntlasaivardhanNo ratings yet
- Hss LiveDocument3 pagesHss LiveAslam KtNo ratings yet
- 1st Pu Chapter Wise QuestionsDocument13 pages1st Pu Chapter Wise QuestionsMir RayyanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chpter 1Document6 pagesWorksheet Chpter 1Devout “Mauro Ogami” LuckNo ratings yet
- First Year Chemistry Very Important Questions Half YearlyDocument3 pagesFirst Year Chemistry Very Important Questions Half Yearlyhyper5350No ratings yet
- Plus 1 - Chemistry PYQ SCERT Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument3 pagesPlus 1 - Chemistry PYQ SCERT Some Basic Concepts of Chemistrysivaranjini S.VNo ratings yet
- Class XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Document43 pagesClass XI Chemistry Worksheet 2021Muffadal AlaviNo ratings yet
- I PUC Imp Chapterwise Questions - MidtermDocument3 pagesI PUC Imp Chapterwise Questions - Midtermdiyadiya060707No ratings yet
- 2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsDocument13 pages2022 Puc I Chem Imp QuestionsCHAKRI BABLUNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 7380Document66 pagesChemistry Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 7380Paulje PaulNo ratings yet
- (Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsDocument1 page(Basic Concepts) : How N and CO Have Same Number of Electrons, Protons and NeutronsJarar VirkNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Digital Answer SheetsDocument10 pagesWeek 3 Digital Answer SheetsKelvin Mark KaabayNo ratings yet
- Previous Yr PaperDocument3 pagesPrevious Yr Papermaryak3050No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Atomic Structure: Four (4) Marker QuestionsDocument11 pagesChapter 1-Atomic Structure: Four (4) Marker Questionsisaacvivek7093No ratings yet
- Chemistry-1st PU: 2&3 Marks Important QuestionsDocument9 pagesChemistry-1st PU: 2&3 Marks Important QuestionsDaksha SubrhamanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ModifiedDocument3 pagesChemistry ModifiedHarshith HN Harshith HNNo ratings yet
- Hsslive Xi Chem Prvs QN 1. Some Basic ConceptsDocument4 pagesHsslive Xi Chem Prvs QN 1. Some Basic Conceptsdhanish942006No ratings yet
- XI Ch1 Some Basic Concepts HssliveDocument2 pagesXI Ch1 Some Basic Concepts HssliveJoshua Chacko Ponnachan100% (2)
- Chemistry - Class 11spiral - 2020-21Document71 pagesChemistry - Class 11spiral - 2020-21NirmalaNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-Xi-Chemistry-1. Some Basic ConceptsDocument4 pagesHsslive-Xi-Chemistry-1. Some Basic Conceptsddreamboy289No ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry: One Mark QuestionsDocument9 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry: One Mark QuestionsTanvi KishoreNo ratings yet
- Keep 501Document13 pagesKeep 501Suriya ElangoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem QRT Slem Week 3Document10 pagesGen Chem QRT Slem Week 3tokyo tokyoNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Moles and StoichiometryDocument5 pagesFormative Assessment Moles and StoichiometryAli NyallNo ratings yet
- TS - JR - Chemistry - Imp - Questions 2023-24Document6 pagesTS - JR - Chemistry - Imp - Questions 2023-24chatlanagababu1986No ratings yet
- Mid TermDocument12 pagesMid TermKaran PrabaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry, Work Sheet Part-I: Define The Following TermsDocument19 pagesGeneral Chemistry, Work Sheet Part-I: Define The Following TermstesfayeNo ratings yet
- JR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesJR. CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsRocky Water0% (1)
- Previous Hse Questions From The Chapter "Some Basic Concepts"Document3 pagesPrevious Hse Questions From The Chapter "Some Basic Concepts"GKJ kalaiyagamNo ratings yet
- REVISION CLASS XI SSE 2024 ImpDocument7 pagesREVISION CLASS XI SSE 2024 Impshuklaanmol1997No ratings yet
- 1st Puc Chemistry Fix QuestionsDocument4 pages1st Puc Chemistry Fix QuestionserannakalivalNo ratings yet
- TS JR Chemistry Imp QuestionsDocument6 pagesTS JR Chemistry Imp QuestionsAmair Khan100% (1)
- First Yeat EM IMP Questions 23-24Document5 pagesFirst Yeat EM IMP Questions 23-24barevishnuvardhan2007No ratings yet
- Chem Q.bank Xi 2022Document16 pagesChem Q.bank Xi 2022rishikaa.saxenaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 - 3 Practice Test - 161Document6 pagesCH 2 - 3 Practice Test - 161Nithya RNo ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Impq ch01 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Kvs PDFDocument8 pages11 Chemistry Impq ch01 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Kvs PDFChamarthi Srinivas100% (1)
- XI-UT-1QP-JUNE-GRADE-11Chemistry - Copy-2Document3 pagesXI-UT-1QP-JUNE-GRADE-11Chemistry - Copy-2RefaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xi 2011Document134 pagesChemistry Xi 2011Mini PGNo ratings yet
- S-Cool A Level Chemistry Practice Questions and AnswersDocument28 pagesS-Cool A Level Chemistry Practice Questions and AnswersMaruf Hassan100% (1)
- Chemistry Revision 3 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDocument8 pagesChemistry Revision 3 For Test 2: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 2 Revision 1: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDocument7 pagesChemistry Test 2 Revision 1: Collision Theory and Rate of ReactionDaniel BerryNo ratings yet
- 9TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperDocument11 pages9TH Class Chemistry Guess PaperMarkpiciNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry AssignmentDocument2 pagesGeneral Chemistry AssignmentCumar MaxamuudNo ratings yet
- Junior Chemistry Smart AcademyDocument8 pagesJunior Chemistry Smart Academyaheadkhan593No ratings yet
- 2022-23 Class - 11TH Assignment of Chemistry Chapters - 1 To 4Document8 pages2022-23 Class - 11TH Assignment of Chemistry Chapters - 1 To 4carsk403No ratings yet
- Slo Review Standard 2Document3 pagesSlo Review Standard 2api-305204604No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry-AssignmentDocument3 pagesChapter-1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry-AssignmentAdithya kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- JR ImpDocument8 pagesJR ImpGovindu PrathapNo ratings yet
- 11 ChemistryDocument8 pages11 ChemistrydhanushbodybuilderNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and Moles with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Compounds, Reactions and MolesNo ratings yet
- The Atomic StructureDocument22 pagesThe Atomic StructureDeonLeo CuencaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRONMICROSCOPIODocument503 pagesELECTRONMICROSCOPIOenrique torresNo ratings yet
- CH 17 ElectricityDocument16 pagesCH 17 ElectricityErna GampalNo ratings yet
- Journal Pre-Proof: Journal of Molecular StructureDocument57 pagesJournal Pre-Proof: Journal of Molecular Structureanderson yesidNo ratings yet
- Xe F5 XF6 Complexes Engl 2005Document12 pagesXe F5 XF6 Complexes Engl 2005رضا جویاNo ratings yet
- Magnetron TechDocument10 pagesMagnetron TechramjoceNo ratings yet
- Electrical ChargeDocument18 pagesElectrical ChargeSamrat100% (1)
- Study of CRO: Submitted By-Vikram Arya M.Sc-1 Semester Department of Physics D.S.B-Campus NainitalDocument21 pagesStudy of CRO: Submitted By-Vikram Arya M.Sc-1 Semester Department of Physics D.S.B-Campus NainitalneerajNo ratings yet
- Lem Tek 57Document71 pagesLem Tek 57MohdHuzairiRusliNo ratings yet
- 4 - Density Functional Theory 1Document24 pages4 - Density Functional Theory 1AndreaAbdelLatif100% (1)
- Electrodynamics of Solids - Dressel GrunerDocument487 pagesElectrodynamics of Solids - Dressel Grunerinkognito_silver100% (3)
- Chapter 27【Current and Resistance】Document21 pagesChapter 27【Current and Resistance】陳慶銘No ratings yet
- Science9 Q2 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver.1.0Document41 pagesScience9 Q2 Weeks1to4 Binded Ver.1.0alonzomonitaroseNo ratings yet
- Physics of Atoms and MoleculesDocument7 pagesPhysics of Atoms and MoleculesKAUSTAV DUTTANo ratings yet
- Chapter 07tifDocument38 pagesChapter 07tifAthar RizwanNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom PDFDocument82 pagesStructure of Atom PDFAthipatla RahulNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam MachiningDocument25 pagesElectron Beam MachiningAbhay P John100% (2)
- HomeworkDocument6 pagesHomeworkmyalyaNo ratings yet
- G8 Science Q3 Week 5 6 Atomic Structure 1Document28 pagesG8 Science Q3 Week 5 6 Atomic Structure 1Anne DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology - Final - 1st Mid Sem - August 2020Document6 pagesNanotechnology - Final - 1st Mid Sem - August 2020chauhanjay1402100% (1)
- What Is TimeDocument74 pagesWhat Is TimeJason ReschNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Electric Field Paper 1Document14 pagesTopic 5 Electric Field Paper 1felNo ratings yet
- QSL (Yasir Iqbal IIT Madras)Document35 pagesQSL (Yasir Iqbal IIT Madras)NeerajNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Content Zinc LeadDocument61 pagesComparative Study of Content Zinc LeadAdeNo ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document54 pagesLecture 01Islam Brave HaqNo ratings yet
- Konstantin D. Stefanov Thesis: Radiation Damage Effects in CCD Sensors For Tracking Applications in High Energy PhysicsDocument110 pagesKonstantin D. Stefanov Thesis: Radiation Damage Effects in CCD Sensors For Tracking Applications in High Energy PhysicsSalah Eddine BekhoucheNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade Science ReviewDocument5 pages8th Grade Science Reviewapi-327567606No ratings yet
- NDT 2-20 Part 2 (Equipment) OkDocument37 pagesNDT 2-20 Part 2 (Equipment) OkAbdul Ahad LoneNo ratings yet