Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic No 2 & 3 Scop, Micro Macro Eco
Topic No 2 & 3 Scop, Micro Macro Eco
Uploaded by
fahad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesEconomics can be divided into microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines individual and industry economic behavior and interactions, and covers topics like elasticity, production theory, and different market structures. Macroeconomics takes a top-down view of the overall economy, studying things like economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation/deflation to understand a country's economic status.
Original Description:
ECONOMICS ADP
Original Title
Topic no 2 & 3 scop ,micro macro eco
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentEconomics can be divided into microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines individual and industry economic behavior and interactions, and covers topics like elasticity, production theory, and different market structures. Macroeconomics takes a top-down view of the overall economy, studying things like economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation/deflation to understand a country's economic status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesTopic No 2 & 3 Scop, Micro Macro Eco
Topic No 2 & 3 Scop, Micro Macro Eco
Uploaded by
fahadEconomics can be divided into microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics examines individual and industry economic behavior and interactions, and covers topics like elasticity, production theory, and different market structures. Macroeconomics takes a top-down view of the overall economy, studying things like economic growth, the business cycle, unemployment, and inflation/deflation to understand a country's economic status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Topic no.
2 & 3
Scope of Economics
Economists use different economic theories to solve various economic
problems in society. Its applicability is very vast. From a small organization to
a multinational firm, economic laws come into play. The scope of economics
can be understood under two subheads: Microeconomics and
Macroeconomics. Let’s discuss these in detail:
Microeconomics
Microeconomics examines individual economic activity, industries, and their
interaction. It has the following characteristics:
Elasticity: It determines the ratio of change in the proportion of one
variable to another variable. For example- the income elasticity of
demand, the price elasticity of demand, the price elasticity of supply,
etc.
Theory of Production: It involves an efficient conversion of input
into output. For example- packaging, shipping, storing, and
manufacturing.
Cost of Production: With the help of this theory, the object price is
evaluated by the price of resources.
Monopoly: Under this theory, the dominance of a single entity is
studied in a particular field.
Oligopoly: It corresponds to the dominance of small entities in a
market.
Macroeconomics
It is the study of an economy as a whole. It explains broad aggregates and their
interactions “top down.” Macroeconomics has the following characteristics:
Growth: It studies the factors which explain economic growth such
as the increase in output per capita of a country over a long period of
time.
Business Cycle: This theory emerged after the Great Depression of
the 1930s. It advocates the involvement of the central bank and the
government to formulate monetary and fiscal policies to monitor the
output over the business cycle.
Unemployment: It is measured by the unemployment rate. It is
caused by various factors like rising in wages, a shortfall in
vacancies, and more.
Inflation and Deflation: Inflation corresponds to an increase in the
price of a commodity, while deflation corresponds to a decrease in
the price of a commodity. These indicators are valuable to evaluate
the status of the economy of a country.
You might also like
- Chapter OneDocument9 pagesChapter OneNoorshikha NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Economics Including PDFDocument277 pagesEconomics Including PDFSushil Khadka ChettriNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To MicroeconomicsDe Leon100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Microeconomics PDFDocument16 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Microeconomics PDFMicko Capinpin100% (1)
- Definition Of: Cost BenefitDocument16 pagesDefinition Of: Cost BenefitHAFIZ ARSALAN ALINo ratings yet
- Microeconomics-Unit 1&2 PDFDocument59 pagesMicroeconomics-Unit 1&2 PDFKruti AdhiyaNo ratings yet
- Economics: MicroeconomicsDocument3 pagesEconomics: MicroeconomicsTERENo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document30 pagesUnit 1FakeNo ratings yet
- SM 2022 23 35Document18 pagesSM 2022 23 35ironnheartttNo ratings yet
- Macro Economic Variables by VikashDocument17 pagesMacro Economic Variables by VikashVikash kumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macroeconomics: 1st Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Macroeconomics: 1st Tutorial QuestionsBISHAASH বিশ্বাসNo ratings yet
- L1 - Academic ScriptDocument9 pagesL1 - Academic ScriptNaomi SaldanhaNo ratings yet
- What Is EconomicsDocument4 pagesWhat Is EconomicsAMANULLAH SHOHAGNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics Analysis Unit I: National Income AccountingDocument263 pagesMacro Economics Analysis Unit I: National Income AccountingMasroor ahmed bhatNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Introduction To MicroeconomicsAbenir Aaron PaulNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Meaning of MacroDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Meaning of Macroअभिषेक रेग्मीNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Micro Economics and Macro EconomicsDocument10 pagesDifference Between Micro Economics and Macro EconomicsHassan Tahir Sial50% (2)
- Macro EconomicsDocument101 pagesMacro Economicsapi-3700469100% (22)
- Micro and Macro EconomicsDocument8 pagesMicro and Macro EconomicsAnuNo ratings yet
- Economic Theories Macro and Micro Economics Macro Economics May Be Defined As That Branch of Economic Analysis WhichDocument1 pageEconomic Theories Macro and Micro Economics Macro Economics May Be Defined As That Branch of Economic Analysis WhichJames WilliamNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Topic 1 LectureDocument11 pagesMacroeconomics Topic 1 LectureКатеринаNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Dde PDFDocument253 pagesMacroeconomics Dde PDFPankaj GahlautNo ratings yet
- DEFINITION OF ECONOMICS - Docx 2Document6 pagesDEFINITION OF ECONOMICS - Docx 2Bello AdoNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Introduction To Macroeconomics: Chapter OneDocument118 pages1.1. Introduction To Macroeconomics: Chapter OneBereketNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Introduction To Macroeconomics: Chapter OneDocument119 pages1.1. Introduction To Macroeconomics: Chapter OneFanuel DereseNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Macro EconomicsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Macro EconomicsRutika AttardeNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics vs. Macroeconomics Microeconomics MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesMicroeconomics vs. Macroeconomics Microeconomics MacroeconomicsruthNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument30 pagesUnit-I Introduction To Managerial Economicspinnamaraju kavyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Introduction To Micro and Macro EconomicsDocument13 pagesChapter 6 Introduction To Micro and Macro EconomicsVinay ShettyNo ratings yet
- Micro & Macro Economics UTU NotesDocument80 pagesMicro & Macro Economics UTU Notesonly_vimaljoshi83% (12)
- Combined Macro SlidesDocument263 pagesCombined Macro SlideskwamecalculusNo ratings yet
- Micro and Macro EconomicsDocument6 pagesMicro and Macro EconomicsSiva KumarNo ratings yet
- The State of Macroeconomics: Chapter OneDocument15 pagesThe State of Macroeconomics: Chapter OneLee HailuNo ratings yet
- Branches of EconomicsDocument8 pagesBranches of Economicsralph andrew marcalinasNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument19 pagesDocumentReal JoyNo ratings yet
- Economics NotesDocument13 pagesEconomics Notesbabydollhasina721No ratings yet
- SBA1201Document93 pagesSBA1201Rashi GargNo ratings yet
- MB 513 Macroeconomics Study MaterialDocument87 pagesMB 513 Macroeconomics Study Materialbojit90345No ratings yet
- GC03 - I-Economic ConceptsDocument18 pagesGC03 - I-Economic Conceptsswati chaturvediNo ratings yet
- 202004201521034435madhurima App Micro AnalysisDocument11 pages202004201521034435madhurima App Micro AnalysisGod BoyNo ratings yet
- Difference BTW Micro & Macro EconDocument5 pagesDifference BTW Micro & Macro EconshyasirNo ratings yet
- Scope and Methods of EconomicsDocument4 pagesScope and Methods of EconomicsBalasingam PrahalathanNo ratings yet
- Meaning of MacroeconomicsDocument12 pagesMeaning of Macroeconomicssushmita1999522No ratings yet
- Economics Difference BetweenDocument11 pagesEconomics Difference Between2580 Soumil SinghNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics StudentsDocument2 pagesMacroeconomics StudentsГордей ПолищукNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics - IntroductionDocument14 pagesMicroeconomics - IntroductionNahidul Islam IUNo ratings yet
- Microeconomics - Policy AnalysisDocument14 pagesMicroeconomics - Policy AnalysisGaudencio MembrereNo ratings yet
- MicroeconomicsDocument9 pagesMicroeconomicsJohnfernando Abalos JuanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicroeconomicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To MicroeconomicsVideos BankNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Fundamental TheoryDocument4 pagesMacroeconomics Fundamental TheoryDEEPA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Management AwakeningDocument34 pagesManagement AwakeningAnubhav Sony100% (1)
- Economic: By: Cleve G. Lauro To: Ms. Mary Mae FrutoDocument7 pagesEconomic: By: Cleve G. Lauro To: Ms. Mary Mae FrutoCleve LauroNo ratings yet
- Eco Chap 1 PPTDocument30 pagesEco Chap 1 PPTayushpatelap07No ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument17 pagesManagerial Economicsdushyant chaudharyNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionJnUBBABATCH-16 A-SECTIONNo ratings yet
- Economics UWUUDocument13 pagesEconomics UWUUStar Sheena GedayaNo ratings yet
- Principles of EconomicsDocument9 pagesPrinciples of EconomicsChazzy f ChazzyNo ratings yet
- Concept of MacroeconomicsDocument12 pagesConcept of MacroeconomicsYograj PandeyaNo ratings yet
- Utility FunctionDocument2 pagesUtility FunctionfahadNo ratings yet
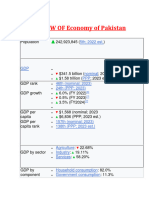
- OVER VIEW OF Economy of Pakistan 2023Document5 pagesOVER VIEW OF Economy of Pakistan 2023fahadNo ratings yet
- Price Elasticity of DemandDocument1 pagePrice Elasticity of DemandfahadNo ratings yet
- Economic Development Experience of PakistanDocument3 pagesEconomic Development Experience of PakistanfahadNo ratings yet
- Headings,,, Major Problems of Economy of PakistanDocument3 pagesHeadings,,, Major Problems of Economy of PakistanfahadNo ratings yet