Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Session 2 - Supply Chain 0 Process Strategy
Session 2 - Supply Chain 0 Process Strategy
Uploaded by
ramsurendran_3909140Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Session 2 - Supply Chain 0 Process Strategy
Session 2 - Supply Chain 0 Process Strategy
Uploaded by
ramsurendran_3909140Copyright:
Available Formats
MMZG533
Manufacturing Planning & Control
BITS Pilani Venkatesh PS/ Pavan Potdar
Pilani Campus
BITS Pilani
Pilani Campus
<MM ZG533, Manufacturing Planning & Control
Lecture No. 2
Defining Business strategy
Business Strategy
• Organization’s positioning in terms of the following dimensions of competence
Quality Time
• Performance • Delivery speed
• Consistent Quality • Development speed
• Reliability • Delivery Reliability
Flexibility Cost
• Product mix • Labour
• Mix of volume/ packaging • Materials
• Engineering
• Quality-related
• Servicing
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Role of Supply Chain strategy
Business
Strategy
Supply Chain
Strategy
Supply Chain
Capabilities
Supply Chain
Performance
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Defining Business strategy
Conflicting Dimensions
High Quality
Low Cost Short delivery
time
High Flexibility
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
From Business to Supply chain Strategy
High Quality
Efficient Responsive
Low Cost Short delivery
time
Supply Chain Supply Chain
High Flexibility
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Supply Chain Strategy to
Supply Chain Capabilities
Business Strategy
Supply Chain Strategy
Efficiency Reponsiveness
Logistical Facilities Inventory Transportation
Cross-functional Information Sourcing Pricing
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Physically Efficient vs Market
Responsive
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Supply chain strategy and product
characteristics
Functional Innovative
Products Products
Supply Chain
Efficient
Match Mismatch
Supply Chain
Responsive
Mismatch Match
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Relevant issues
MULTIPLE products
• Separate SC
• Tailored SC
Product LIFECYCLE
• SC moves towards efficiency
• Innovative products become functional
products
Product Customization/
Standardization
• Move from customized to standardized
• SC moves from flexibility/ high cost to
consistent quality and cost
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Supply Chain strategy vs Uncertainty
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Market characteristics
Lean vs Agile
Lean Agile
• Efficient reaction to • Speedy reaction to a
stable market dynamic/ unpredictable
market
Low Variability High
High
Agile
Variety
Lean
Low
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Supply vs Demand characteristics
Leagile
• Lean for base,
Lean Leagile predictable demand
Supply Characteristics
Long • Plan and • Postponement • Agile for surge
Leadtime Execute demand
• Upstream Lean =
efficiency/ cost
• Responsive, agile
Lean Agile downstream
Short
leadtime • Continuous • Quick response
Replenishment
Predictable Unpredictable
Demand Characteristics
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Make vs Buy
Cost of making Cost of Buying
• Production • Product Purchase price
• Extra labour • Taxes
• Monitoring • Shipping
• Storage • Inventory holding
• Waste product disposal • Ordering
• Risk of unutilized capacity • Supplier flexibility and reliability
• Investment in capacity • Leadtimes
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Reliability vs Speed
Production leadtimes
% of production
Cumulative
No of days orders completed
%
in
0 0 0
1 25% 25%
2 25% 50%
3 15% 65%
4 20% 85%
5 5% 90%
6 3% 93%
7 3% 96%
8 2% 98%
9 1% 99%
10 1% 100%
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Made to Order vs Made to
Stock
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
MTO vs MTS – SC impact
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
In most industries, MTO and
MTS co-exist
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Manufacturing/ Process Strategy
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Process options - 1
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Process options - 2
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Process options - 3
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Process options - 4
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Process Characteristics
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Resource Flexibility
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Service Process Design Matrix
Mass Services Professional Services
• Retailers • Law firms
• Wholesalers • Accounting firms
Degree of Labour Intensity
• Online schools • Doctors’ offices
High
• Railroads • Graphic designers
• Tutors
Service Factories Service Shops
• Airlines • Hospitals
• E-tailers • Gourmet restaurants
Low • Hotels • Auto Repair shops
• Mail/ Cheque processing
firms
Low High
Degree of Customization vs Customer interaction
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Service Blueprint
(Hotel service)
Physical Key components of the service blueprint
distinguishes between onstage and backstage employee activities which are represented with its key
Evidence/ components.
Deliverable Customer actions: central to the creation of the service blueprint, lay it out first. includes the steps,
actions, choices, and interactions the customer performs while evaluating, purchasing or using the
service delivery process. Chronological, left to right.
Customer Onstage/ visible contact employee actions: appears after customer actions, separated by the line of
actions/ interaction. Actions include what frontline contact employees do when they encounter customers face-
interaction to-face.
Backstage/ invisible contact employee actions: Backstage/ behind the scene actions taken by contact
employees, not visible to the customer. Non-visible interactions with the customer - telephone calls and
Onstage other activities backstage contact employees carry out to support the onstage activities.
Support processes: Includes all actions, interactions, internal services carried out by individuals or units
Employee (not contact employees) within the company to support contact employees deliver the service. They are
actions not visible to the customers.
Physical evidence: this comes at the top of the diagram and represents the physical evidence of the
service. They are typically listed above each point of contact. For example, the physical evidence of a
Backstage face-to-face meeting can be listed as office decor.
Employee Lines: Each component of the service blueprint is separated by a line. First is the line of interaction -
direct interaction between customer & organization
actions Line of visibility. All components that come above this line are visible to the customer while the ones
that come below it are invisible.
Internal line of interaction. This separates contact employee activities from other service support
Support activities and people. Vertical lines cutting across the line of internal interaction represent internal
service encounters.
processes Arrows: These represent the relationships/ dependencies. A single arrow indicates a one-way exchange,
and a double arrow indicates the need for agreement from both parties or codependence.
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Service Blueprint – Homework
(Hotel service) - Solution
Evidence
Bill
Physical
Desk
Hotel Cart for Bags Elevators Cart for Bags Delivery Tray Room Lobby
Paperwork
Ad Website Exterior Employee Hallway Employee Menu Food Food Amenities Hotel
Lobby
Parking Dress Room Dress Appearance Bathroom Exterior
Key
Parking
Customer
Actions
Receive
Make Arrive at Give bags to Call Room Sleep Check out &
Check in Go to room Receive bags food/ sign/ Eat
Reservation hotel bell person Service Shower leave
tip
Line of interaction
Employee
Onstage
Actions
Greet & take Process Process
Deliver bags Deliver food
bags Registration Check out
Line of visibility
Backstage
Employee
Actions
Make
Take bags to Take food
Reservation
room order
for Guest
Line of internal interaction
Processes
Support
Reservation Registration Registration
Process food
system system system
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Location Strategy
Operating
expenses
Risk and Revenue
Profits driver
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Factors affecting location
decisions
Exchange
Labour
Rates and Costs
Productivity
Currency Risk
Political Risk,
Proximity to Proximity to
Values,
markets suppliers
Culture
Proximity to
Competitors
(Clustering)
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Layout strategies
(a) Fixed (c) Process
(b) Process (d) Product/
Position (Work cell)
Layout Line Layout
Layout layout
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Layout strategies - application
Offices Retail Stores Manufacturing
Warehouses Service areas Sales offices
Dealerships/
Distribution
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Location strategy example –
SmartBank India - Homework
SmartBank India, a new entrant in the banking sector, aims to cater specifically to the middle-income category of the population.
The bank focuses on providing innovative financial services, seamless digital banking, and personalized customer experiences.
Choosing the right locations for branches is crucial for SmartBank's success in serving its target market.
a) Define the concept of location strategy in the context of SmartBank India's expansion. Discuss the factors that SmartBank should
consider when selecting branch locations to effectively reach the middle-income population. Provide examples to illustrate the
importance of location strategy.
b) SmartBank is considering opening branches in two potential locations: a busy commercial district and a residential area with high
footfall. Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of each location in terms of customer accessibility, visibility, and operational costs.
Recommend a location based on your analysis.
c) The middle-income population is increasingly tech-savvy. Suggest two alternative location strategies that SmartBank could consider
to complement its physical branch network and enhance digital accessibility for customers. Discuss the benefits and potential
challenges associated with each strategy.
d) SmartBank plans to offer special promotions for middle-income customers during the launch phase. Propose a location strategy that
maximizes visibility and foot traffic to attract potential customers to take advantage of these promotions. Explain how this strategy
aligns with SmartBank's target market.
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Layout strategy example –
Govt run shipyard - Homework
You work for a Government-run shipyard that manufactures small boats for the coast
guard (made of fiber-reinforced plastic) in bulk. Now, the government has decided to
also manufacture large war ships in the same shipyard (largely made of steel). You are
called upon to design the process layout for this large value order. Explain the choice of
layout, the associated factors leading to the choice, alternative strategies to address
some of the issues associated with the layout.
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Post-reads for session 2
T1 Chapters 7, 8 and 9
Go through the examples and problems therein
Articles
• T1 Case study on D-Mart (Chapter 8) titled “D-Mart emerged as top retailer”
– read through and summarize the advantages and D-Mart faces because
of its choice of location/ layout/ market-facing strategies
• Why investing in company location still matters - McKinsey Quarterly
• In banking, location is everything again—for now – McKinsey Quarterly
• Other articles on SC/ Process strategies
• Complete Guide on Safe Design of a New Production/Manufacturing Plant |
LinkedIn
• Plant Layout (hse.gov.uk)
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
Thank you
BITS Pilani, Pilani Campus
You might also like
- 1 - SAP - S4HANA Fashion Vertical Business Master DataDocument28 pages1 - SAP - S4HANA Fashion Vertical Business Master DataIndraNo ratings yet
- Advanced Lean Training ManualDocument50 pagesAdvanced Lean Training ManualJunjie Chen100% (2)
- TFC Supply Chain ManagementDocument37 pagesTFC Supply Chain ManagementSalahdineNo ratings yet
- SCM Network OptimizationDocument64 pagesSCM Network OptimizationHEMA NNo ratings yet
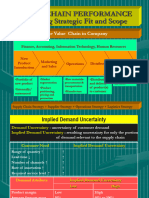
- Achieving Strategic Fit and ScopeDocument15 pagesAchieving Strategic Fit and ScopeAman SanatanNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Lecture-2 28 July 2018, SaturdayDocument25 pagesSupply Chain Management: Lecture-2 28 July 2018, Saturdaysap6370No ratings yet
- ch2 SCMDocument40 pagesch2 SCMTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- OM Session 3Document38 pagesOM Session 3mayra salirrosasNo ratings yet
- SCM-02 Performance of Supply ChainDocument16 pagesSCM-02 Performance of Supply Chainshivani radhu100% (1)
- Supply Chain MGMTDocument22 pagesSupply Chain MGMThimanshu111992No ratings yet
- Session 9, Supply Network StrategyDocument16 pagesSession 9, Supply Network StrategyShaivy TyagiNo ratings yet
- Bài thuyết trình1Document26 pagesBài thuyết trình1Hằng LêNo ratings yet
- Strategy: Achieving The FitDocument167 pagesStrategy: Achieving The FitNaveen K. JindalNo ratings yet
- S1-18-Ba ZG621 Mba ZG621 MM ZG621-L3Document34 pagesS1-18-Ba ZG621 Mba ZG621 MM ZG621-L3sap6370No ratings yet
- Supply Chain Performance: Achieving Strategic Fit and Scope: 1 DR S K Sharma, BITS PialniDocument32 pagesSupply Chain Performance: Achieving Strategic Fit and Scope: 1 DR S K Sharma, BITS PialniNISHANT SHAHNo ratings yet
- Module 2 PPTsDocument31 pagesModule 2 PPTsAlex BorellNo ratings yet
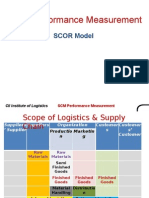
- SCM PerformanceDocument48 pagesSCM PerformancemaddyrockzNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Noman NasirDocument26 pagesSupply Chain Management: Noman NasirwasianwerNo ratings yet
- Basics of Supply Chain ManagementDocument19 pagesBasics of Supply Chain Managementparab_bhushan100% (1)
- Session 15-16 Supply Chain ManagementDocument30 pagesSession 15-16 Supply Chain ManagementWilliam MatthewNo ratings yet
- Apple Global Supply Chain S2 Teknik IndustriDocument23 pagesApple Global Supply Chain S2 Teknik IndustriRuth Dame Pricilia0% (1)
- Quality Control Assurance & Reliability: BITS PilaniDocument62 pagesQuality Control Assurance & Reliability: BITS Pilanithasarathanr1993_939No ratings yet
- Quality Control: BITS Pilani BITS PilaniDocument51 pagesQuality Control: BITS Pilani BITS PilaniRevant Kumar100% (1)
- Supply Chain Drivers and Metrics: 1 DR S K Sharma, BITS PilaniDocument45 pagesSupply Chain Drivers and Metrics: 1 DR S K Sharma, BITS PilaniNISHANT SHAHNo ratings yet
- Supplier Selection Process Imran A AbbasiDocument35 pagesSupplier Selection Process Imran A AbbasiHaroon AhmedNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument277 pagesOperations ManagementdanigeletaNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document115 pagesCH 11Vedagya SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Sesi#1 - Design of Goods & ServicesDocument9 pagesSesi#1 - Design of Goods & ServicesDhea nurfaNo ratings yet
- Nature of Operations Strategy: Different Competitive Factors Imply Different Performance ObjectivesDocument4 pagesNature of Operations Strategy: Different Competitive Factors Imply Different Performance ObjectivesAnggini PangestuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document8 pagesAssignment 2Shubham RathiNo ratings yet
- Webinar-Translating Business Drivers Into Technology RequirementsDocument17 pagesWebinar-Translating Business Drivers Into Technology RequirementsdtzanakNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document31 pagesCH 10Vedagya SaraswatNo ratings yet
- MC Inventory Day 1 - Block 3 Inventory Management Framework - 20180613Document28 pagesMC Inventory Day 1 - Block 3 Inventory Management Framework - 20180613samah sNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument74 pagesSupply Chain ManagementAisyah RamliNo ratings yet
- 01 Strategy 1Document21 pages01 Strategy 1SJNo ratings yet
- EWM 2020 L1 Presentation 20200403Document54 pagesEWM 2020 L1 Presentation 20200403satyamulagala1236No ratings yet
- Apics Cpim Pt+1 Mod+1 SecaDocument23 pagesApics Cpim Pt+1 Mod+1 SecaHisham Ahmed FouadNo ratings yet
- 7 - Valuation of InventoriesDocument14 pages7 - Valuation of InventoriesSamar GuptaNo ratings yet
- SCM Session 1 - Introduction z0J4XaMCylDocument16 pagesSCM Session 1 - Introduction z0J4XaMCylapoorva vedpathakNo ratings yet
- CH 6 Value of Information & SCMDocument26 pagesCH 6 Value of Information & SCMahsanzia62No ratings yet
- At Kenerey Purchasing Chess BoardDocument20 pagesAt Kenerey Purchasing Chess BoardAhsan Ahmad100% (2)
- QM ZG526-L1Document17 pagesQM ZG526-L1baluNo ratings yet
- Basics of Supply Chain Management: Live HD Cricket+Tv Free at atDocument44 pagesBasics of Supply Chain Management: Live HD Cricket+Tv Free at atMuhammad Faisal RashidNo ratings yet
- Aml CS 4 PRVDocument42 pagesAml CS 4 PRVved prakashNo ratings yet
- Lecture - Sourcing & Procurement SCM. 05.10Document16 pagesLecture - Sourcing & Procurement SCM. 05.10Chad Freeman100% (1)
- Supply Chain Management (SCM)Document58 pagesSupply Chain Management (SCM)Yusril KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Supply Chain Management: Syed Tabish Hussain Iqra UniversityDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Supply Chain Management: Syed Tabish Hussain Iqra UniversityfarahsayaniNo ratings yet
- Advanced LeanDocument50 pagesAdvanced LeanMuhammad RehmanNo ratings yet
- T1S1-Supply Chain ExcellenceDocument28 pagesT1S1-Supply Chain ExcellenceGabriel Benson Leung100% (1)
- A Project On Supply Chain Management'Document23 pagesA Project On Supply Chain Management'anish_ani777No ratings yet
- ch4 SCMDocument60 pagesch4 SCMSHAABAN KARIMNo ratings yet
- Bringing The Voice of The Consumer Into The Consumer Into Your Supply ChainDocument28 pagesBringing The Voice of The Consumer Into The Consumer Into Your Supply ChaingreedyvenomNo ratings yet
- Agile Supply ChainDocument22 pagesAgile Supply ChainSubbarayan Pulamadan SekarNo ratings yet
- Overview of LSCM Part IDocument14 pagesOverview of LSCM Part IAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management: Noman JafriDocument32 pagesSupply Chain Management: Noman Jafrisukhpreet singhNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of SCMDocument23 pagesFundamentals of SCMSYED MURTAZA ABIDINo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering LECTURE 1Document42 pagesReliability Engineering LECTURE 1Krishna PrasathNo ratings yet
- Week 02 - Fundamentals of Supply Chain ManagementDocument36 pagesWeek 02 - Fundamentals of Supply Chain ManagementMUHAMMAD FAYZAN TAYYABNo ratings yet
- Sectionb Module 1Document60 pagesSectionb Module 1OSAMANo ratings yet
- IT Success!: Towards a New Model for Information TechnologyFrom EverandIT Success!: Towards a New Model for Information TechnologyRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- 01 The QuizDocument7 pages01 The QuizJabriellaSanMiguel100% (1)
- The Belbin Team RolesDocument10 pagesThe Belbin Team RolesMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Boyd Aiw Lesson Cover PageDocument2 pagesBoyd Aiw Lesson Cover Pageapi-244827434No ratings yet
- How Parents Influence Deviant Behavior Among Adolescents: An Analysis of Their Family Life, Their Community, and Their PeersDocument1 pageHow Parents Influence Deviant Behavior Among Adolescents: An Analysis of Their Family Life, Their Community, and Their PeersNuhaNo ratings yet
- Es ManualDocument37 pagesEs ManualSVCET SVCETNo ratings yet
- 4-SSS SAS ASA and AAS Congruence PDFDocument4 pages4-SSS SAS ASA and AAS Congruence PDFAivie Jannelle Columna BejoNo ratings yet
- Ipc 2581BDocument9 pagesIpc 2581BlaxenovNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Scientific Ways of Acquiring Knowledge and Solving ProblemsDocument22 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Scientific Ways of Acquiring Knowledge and Solving Problemsnoahzaec100% (2)
- Grade 8 Unit 9 Practice 3. HSDocument4 pagesGrade 8 Unit 9 Practice 3. HSKhôi Nguyên ĐặngNo ratings yet
- Switch POE 16 Porturi - Dahua PFS4218-16ET-240-wDocument1 pageSwitch POE 16 Porturi - Dahua PFS4218-16ET-240-wVasiliuNo ratings yet
- 6 Settlement Response of A Multi-Story BuildingDocument4 pages6 Settlement Response of A Multi-Story BuildingmazNo ratings yet
- X ZXZXDocument2 pagesX ZXZXDaniel BrownNo ratings yet
- Strain Index Scoring Sheet: Date: Task: Company: Supervisor: Dept: EvaluatorDocument1 pageStrain Index Scoring Sheet: Date: Task: Company: Supervisor: Dept: EvaluatorAngeline Henao BohorquezNo ratings yet
- The New Paliotan Pigments Time To Replace Lead Chromate-EnglishDocument18 pagesThe New Paliotan Pigments Time To Replace Lead Chromate-EnglishAli KesikogluNo ratings yet
- NARA - T733 - R3 - 48 (Records of German Field Commands Armies (Part VI) )Document102 pagesNARA - T733 - R3 - 48 (Records of German Field Commands Armies (Part VI) )V ManNo ratings yet
- Chm457 Fundamental Organic Chemistryexp 1Document7 pagesChm457 Fundamental Organic Chemistryexp 1Aida SyasyaNo ratings yet
- Maria Montessori and Her Educational Philosophy: Breaking Barriers in EducationDocument5 pagesMaria Montessori and Her Educational Philosophy: Breaking Barriers in EducationfreddyNo ratings yet
- Crawljammer - #02Document36 pagesCrawljammer - #02JosephLouisNadeau100% (1)
- Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument27 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundstechvipreshNo ratings yet
- Hygiene - Nutrition Grade 3 Term 2-2Document6 pagesHygiene - Nutrition Grade 3 Term 2-2Willy AddijahNo ratings yet
- RCC 100 Important Questions 39Document33 pagesRCC 100 Important Questions 39Engr Mehdi BugtiNo ratings yet
- Zoho Interview QustionsDocument4 pagesZoho Interview QustionsRadheshyam Nayak0% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFDocument12 pagesArtificial Intelligence The End of The Beginning PDFK Cor100% (1)
- 2040 - Cut-Off-Points - 2020 - 2021 of The Special Provision For Students Who Have Excelled in Extra Curricular Activities - New SyllabusDocument5 pages2040 - Cut-Off-Points - 2020 - 2021 of The Special Provision For Students Who Have Excelled in Extra Curricular Activities - New SyllabusGayanuka MendisNo ratings yet
- Anglo Indian DaalDocument1 pageAnglo Indian Daalna_1nanaNo ratings yet
- Precast Connections Using Grout Sleeve Coupler Systems - Concrete Article February 2018Document2 pagesPrecast Connections Using Grout Sleeve Coupler Systems - Concrete Article February 2018Nuno MiguelNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Conveying Basic PointsDocument33 pagesPneumatic Conveying Basic Pointsgchewo50% (2)
- ARMY TM 5-814-2 AIR FORCE AFM 88-11, Vol. 2Document32 pagesARMY TM 5-814-2 AIR FORCE AFM 88-11, Vol. 2MuhammadUsmanNo ratings yet
- MTCR - Missile Technology Control RegimeDocument11 pagesMTCR - Missile Technology Control Regimefernandocwrocha-1No ratings yet
- Data SufficiencyDocument7 pagesData SufficiencySaurav BhasinNo ratings yet