Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Temperature and Thermal Expansion Reviewer
Temperature and Thermal Expansion Reviewer
Uploaded by
kennethCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sample Formula Sheet For ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesSample Formula Sheet For Thermodynamicsmicrop_aras100% (3)
- Module 03 Solutions Thermodynamics Applications SummaryDocument14 pagesModule 03 Solutions Thermodynamics Applications SummaryVan100% (1)
- Mid Term Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMid Term Cheat Sheethalide90No ratings yet
- ChemE 132 LE 1 ReviewerDocument17 pagesChemE 132 LE 1 ReviewerClarenceMillaresNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chapters 1, 2, 3 - List of Useful EquationsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Chapters 1, 2, 3 - List of Useful EquationsyhNo ratings yet
- GASES-CHM130 by DELZYDocument15 pagesGASES-CHM130 by DELZYmisakisuki7No ratings yet
- CIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFDocument15 pagesCIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFCedricChanNo ratings yet
- CIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFDocument15 pagesCIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFCedricChanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties of FluidDocument9 pagesThermodynamic Properties of FluidZyber ColcolNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals: Steady State DiffusionDocument13 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals: Steady State DiffusionMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- Chen 3009 - Tutorial 6 2020Document22 pagesChen 3009 - Tutorial 6 2020Rosario QFNo ratings yet
- Fluids in Rigid-Body Motion: 9. 14. 2016 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Associate Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & EngineeringDocument11 pagesFluids in Rigid-Body Motion: 9. 14. 2016 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Associate Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & EngineeringKyla Marie SurattNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05, 06Document13 pagesLecture 05, 06Faiq Ali FaiqNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes 3rd MasteryDocument3 pagesChem Notes 3rd MasteryblezieNo ratings yet
- Mixed CapacitorDocument10 pagesMixed CapacitorMr SonuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FormulasDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics FormulaskennethNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4 - Heat TransferDocument20 pagesLecture-4 - Heat TransferAhmed BahaaNo ratings yet
- Formulario TermodinámicaDocument3 pagesFormulario TermodinámicaDiego AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 - Two-Dimensional KinematicsDocument48 pagesCh.4 - Two-Dimensional Kinematicsnoriegak94No ratings yet
- Ch. 03 - Kinematics in Two DimensionsDocument22 pagesCh. 03 - Kinematics in Two Dimensionssthembisosthera992No ratings yet
- 19 09 VariationalFormulationDocument12 pages19 09 VariationalFormulationatharva.betawadkarNo ratings yet
- List of EquationsDocument8 pagesList of EquationsxadoogarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics FormulaDocument3 pagesHydraulics FormulaPatrick BreadNo ratings yet
- Hormigón Simple Hormigón Reforzado Y Recu Brimien To Hormigón Simple Con Refu Erzos Helicoidal Sin Recu Brimien ToDocument1 pageHormigón Simple Hormigón Reforzado Y Recu Brimien To Hormigón Simple Con Refu Erzos Helicoidal Sin Recu Brimien ToLuis Fabian Mendoza SuárezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Web HandoutDocument2 pagesThermodynamic Web HandoutYaren ErelNo ratings yet
- Complex Reactions-1Document15 pagesComplex Reactions-1Jocelyn Grisel García GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Chbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/18/2020Document18 pagesChbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/18/2020AnnNo ratings yet
- MT 21006 TP Unit 3 Lec 3 and 4 06 and 09 Oct 2023 CombinedDocument19 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 3 Lec 3 and 4 06 and 09 Oct 2023 CombinedRasika MalodeNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7Solutions - Entropy 2nd LawDocument8 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7Solutions - Entropy 2nd Lawgrandw9524No ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument1 pageDiesel CycleGladys Ruth PaypaNo ratings yet
- CE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsDocument18 pagesCE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsJeric GeronaNo ratings yet
- Taller 1 Materiales: Hacemos Uso Del Teorema de LamyDocument3 pagesTaller 1 Materiales: Hacemos Uso Del Teorema de LamyMAURY SEBASTIAN MACIAS SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Solutions MTEN 204 604 PDFDocument50 pagesBehavior of Solutions MTEN 204 604 PDFVincentNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument2 pagesThermoSalvador Monroy GalvánNo ratings yet
- EMT Short Questions For MSCDocument38 pagesEMT Short Questions For MSCJunaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pipe NetworkDocument9 pagesPipe NetworkSilverlandNo ratings yet
- Tablas W Q Du DH DSDocument3 pagesTablas W Q Du DH DSMarisol CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Aimstutorial Aimstutorial: Physics-1 Physics-1Document38 pagesAimstutorial Aimstutorial: Physics-1 Physics-1hariNo ratings yet
- 2022 - SynthèseDocument9 pages2022 - SynthèseThéo MélotteNo ratings yet
- NEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Thermodynamics S7 209Document79 pagesNEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Thermodynamics S7 209anantveersinghbrarNo ratings yet
- Wave-Particle Duality Is A Central Concept in Quantum Mechanics That Describes The Behavior ofDocument5 pagesWave-Particle Duality Is A Central Concept in Quantum Mechanics That Describes The Behavior oftboyaffliateNo ratings yet
- Biomentors Classes Online, MumbaiDocument2 pagesBiomentors Classes Online, MumbaiSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Chen 3009 - Tutorial 1-2021Document31 pagesChen 3009 - Tutorial 1-2021Rosario QFNo ratings yet
- HE Lecture 19Document9 pagesHE Lecture 19presidentisc nit-rourkelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction ConductionDocument20 pagesIntroduction ConductionJuan ArangoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 PDFDocument18 pagesLecture 4 PDFdeepakNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic ModelsDocument14 pagesThermodynamic ModelsMaarifa KidogeNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 7 AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesLesson - 7 AC CircuitsMohamed Munseeth NMNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Due To Unifiromly Chared Plane SheetDocument2 pagesElectric Field Due To Unifiromly Chared Plane Sheetprinceprem369xNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document15 pagesLecture 12Shardul BhopeNo ratings yet
- Lahams 2Document10 pagesLahams 2Anthony MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Invariant DerivativeDocument1 pageInvariant DerivativeClint AustinNo ratings yet
- Stresses Composite Bars: Bibin ChidambaranathanDocument28 pagesStresses Composite Bars: Bibin ChidambaranathanDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- 09 WaveguidesDocument27 pages09 WaveguidesRounak MandalNo ratings yet
- Applications of DEDocument4 pagesApplications of DEPatrick LaurinaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Equation Sheet: K A H ADocument31 pagesHeat Transfer Equation Sheet: K A H ABeydaNo ratings yet
Temperature and Thermal Expansion Reviewer
Temperature and Thermal Expansion Reviewer
Uploaded by
kennethOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Temperature and Thermal Expansion Reviewer
Temperature and Thermal Expansion Reviewer
Uploaded by
kennethCopyright:
Available Formats
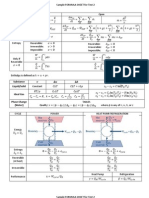
“If A and B are separately in thermal equilibrium with C, then
Zeroth Law
A and B are also in thermal equilibrium with one another.”
Celsius to Fahrenheit (and vice-versa) ℉ = 1.8°𝐶 + 32
Celsius to Kelvin (and vice-versa) 𝐾 = ℃ + 273.15
Rankine to Fahrenheit (and vice-versa) °𝑅 = ℉ + 460
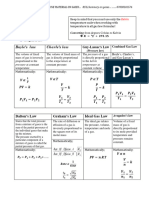
Boyle’s Law 𝑝𝑉 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 when 𝑇 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
𝑉
Charles’ Law = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡 when 𝑃 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
𝑇
𝑝𝑉
= 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
𝑇
Combined Gas Law
𝑝
= 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
𝜌𝑇
𝑉 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
Isochoric
𝑝 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
Isobaric
𝑇 = 𝑐𝑜𝑛𝑠𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑡
Isothermal
𝑄=0
Adiabatic
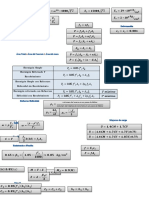
∆𝐿 = 𝛼𝐿0 ∆𝑇
Linear Expansion of Solids 𝐿 − 𝐿0 = 𝛼𝐿0 ∆𝑇
𝐿 = 𝐿0 (1 + 𝛼∆𝑇)
Area Expansion of Solids ∆𝐴 = 2𝛼𝐴0 ∆𝑇
∆𝑉 = 3𝛼𝑉0 ∆𝑇
Volume Expansion of Solids
𝑉 = 𝑉0 (1 + 3𝛼∆𝑇)
∆𝑉 = 𝛽𝑉0 ∆𝑇
Volume Expansion of Fluids
wherein 𝛽 = 3𝛼
You might also like
- Sample Formula Sheet For ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesSample Formula Sheet For Thermodynamicsmicrop_aras100% (3)
- Module 03 Solutions Thermodynamics Applications SummaryDocument14 pagesModule 03 Solutions Thermodynamics Applications SummaryVan100% (1)
- Mid Term Cheat SheetDocument1 pageMid Term Cheat Sheethalide90No ratings yet
- ChemE 132 LE 1 ReviewerDocument17 pagesChemE 132 LE 1 ReviewerClarenceMillaresNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Chapters 1, 2, 3 - List of Useful EquationsDocument3 pagesThermodynamics Chapters 1, 2, 3 - List of Useful EquationsyhNo ratings yet
- GASES-CHM130 by DELZYDocument15 pagesGASES-CHM130 by DELZYmisakisuki7No ratings yet
- CIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFDocument15 pagesCIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFCedricChanNo ratings yet
- CIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFDocument15 pagesCIVL311 - Module 1 - One - Dimensinal - Consolidation - September 8 - Lecture - 2 PDFCedricChanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties of FluidDocument9 pagesThermodynamic Properties of FluidZyber ColcolNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer Fundamentals: Steady State DiffusionDocument13 pagesMass Transfer Fundamentals: Steady State DiffusionMuhammad JawadNo ratings yet
- Chen 3009 - Tutorial 6 2020Document22 pagesChen 3009 - Tutorial 6 2020Rosario QFNo ratings yet
- Fluids in Rigid-Body Motion: 9. 14. 2016 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Associate Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & EngineeringDocument11 pagesFluids in Rigid-Body Motion: 9. 14. 2016 Hyunse Yoon, Ph.D. Associate Research Scientist IIHR-Hydroscience & EngineeringKyla Marie SurattNo ratings yet
- Lecture 05, 06Document13 pagesLecture 05, 06Faiq Ali FaiqNo ratings yet
- Chem Notes 3rd MasteryDocument3 pagesChem Notes 3rd MasteryblezieNo ratings yet
- Mixed CapacitorDocument10 pagesMixed CapacitorMr SonuNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FormulasDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics FormulaskennethNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4 - Heat TransferDocument20 pagesLecture-4 - Heat TransferAhmed BahaaNo ratings yet
- Formulario TermodinámicaDocument3 pagesFormulario TermodinámicaDiego AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 - Two-Dimensional KinematicsDocument48 pagesCh.4 - Two-Dimensional Kinematicsnoriegak94No ratings yet
- Ch. 03 - Kinematics in Two DimensionsDocument22 pagesCh. 03 - Kinematics in Two Dimensionssthembisosthera992No ratings yet
- 19 09 VariationalFormulationDocument12 pages19 09 VariationalFormulationatharva.betawadkarNo ratings yet
- List of EquationsDocument8 pagesList of EquationsxadoogarNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics FormulaDocument3 pagesHydraulics FormulaPatrick BreadNo ratings yet
- Hormigón Simple Hormigón Reforzado Y Recu Brimien To Hormigón Simple Con Refu Erzos Helicoidal Sin Recu Brimien ToDocument1 pageHormigón Simple Hormigón Reforzado Y Recu Brimien To Hormigón Simple Con Refu Erzos Helicoidal Sin Recu Brimien ToLuis Fabian Mendoza SuárezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Web HandoutDocument2 pagesThermodynamic Web HandoutYaren ErelNo ratings yet
- Complex Reactions-1Document15 pagesComplex Reactions-1Jocelyn Grisel García GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Chbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/18/2020Document18 pagesChbe 6300 Graduate Kinetics and Reactor Design: Carsten Sievers 8/18/2020AnnNo ratings yet
- MT 21006 TP Unit 3 Lec 3 and 4 06 and 09 Oct 2023 CombinedDocument19 pagesMT 21006 TP Unit 3 Lec 3 and 4 06 and 09 Oct 2023 CombinedRasika MalodeNo ratings yet
- MMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7Solutions - Entropy 2nd LawDocument8 pagesMMAN2700ThermoProblemSheet7Solutions - Entropy 2nd Lawgrandw9524No ratings yet
- Diesel CycleDocument1 pageDiesel CycleGladys Ruth PaypaNo ratings yet
- CE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsDocument18 pagesCE 108 - Lecture 1 - Introducton To FluidsJeric GeronaNo ratings yet
- Taller 1 Materiales: Hacemos Uso Del Teorema de LamyDocument3 pagesTaller 1 Materiales: Hacemos Uso Del Teorema de LamyMAURY SEBASTIAN MACIAS SANCHEZNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Solutions MTEN 204 604 PDFDocument50 pagesBehavior of Solutions MTEN 204 604 PDFVincentNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument2 pagesThermoSalvador Monroy GalvánNo ratings yet
- EMT Short Questions For MSCDocument38 pagesEMT Short Questions For MSCJunaid AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pipe NetworkDocument9 pagesPipe NetworkSilverlandNo ratings yet
- Tablas W Q Du DH DSDocument3 pagesTablas W Q Du DH DSMarisol CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Aimstutorial Aimstutorial: Physics-1 Physics-1Document38 pagesAimstutorial Aimstutorial: Physics-1 Physics-1hariNo ratings yet
- 2022 - SynthèseDocument9 pages2022 - SynthèseThéo MélotteNo ratings yet
- NEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Thermodynamics S7 209Document79 pagesNEO JEE 11 P1 PHY H Thermodynamics S7 209anantveersinghbrarNo ratings yet
- Wave-Particle Duality Is A Central Concept in Quantum Mechanics That Describes The Behavior ofDocument5 pagesWave-Particle Duality Is A Central Concept in Quantum Mechanics That Describes The Behavior oftboyaffliateNo ratings yet
- Biomentors Classes Online, MumbaiDocument2 pagesBiomentors Classes Online, MumbaiSmit PatelNo ratings yet
- Chen 3009 - Tutorial 1-2021Document31 pagesChen 3009 - Tutorial 1-2021Rosario QFNo ratings yet
- HE Lecture 19Document9 pagesHE Lecture 19presidentisc nit-rourkelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction ConductionDocument20 pagesIntroduction ConductionJuan ArangoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 PDFDocument18 pagesLecture 4 PDFdeepakNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic ModelsDocument14 pagesThermodynamic ModelsMaarifa KidogeNo ratings yet
- Lesson - 7 AC CircuitsDocument15 pagesLesson - 7 AC CircuitsMohamed Munseeth NMNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Due To Unifiromly Chared Plane SheetDocument2 pagesElectric Field Due To Unifiromly Chared Plane Sheetprinceprem369xNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document15 pagesLecture 12Shardul BhopeNo ratings yet
- Lahams 2Document10 pagesLahams 2Anthony MacalindongNo ratings yet
- Invariant DerivativeDocument1 pageInvariant DerivativeClint AustinNo ratings yet
- Stresses Composite Bars: Bibin ChidambaranathanDocument28 pagesStresses Composite Bars: Bibin ChidambaranathanDr. BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- 09 WaveguidesDocument27 pages09 WaveguidesRounak MandalNo ratings yet
- Applications of DEDocument4 pagesApplications of DEPatrick LaurinaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Equation Sheet: K A H ADocument31 pagesHeat Transfer Equation Sheet: K A H ABeydaNo ratings yet