Professional Documents
Culture Documents
List Components 50 Definition
List Components 50 Definition
Uploaded by
aOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
List Components 50 Definition
List Components 50 Definition
Uploaded by
aCopyright:
Available Formats
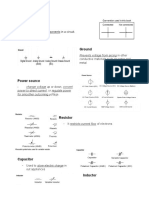
Resistor - Limits the flow of electric current
Capacitor - Stores and releases electrical energy
Inductor - Stores energy in a magnetic field
Diode - Allows current to flow in one direction only
Transistor - Amplifies or switches electronic signals
Integrated Circuit (IC) - Contains multiple electronic components on a single chip
Light Emitting Diode (LED) - Emits light when current passes through it
Voltage Regulator - Maintains a constant voltage level
Transformer - Changes voltage levels in AC circuits
Potentiometer - Variable resistor to adjust voltage or current
Relay - Electromechanical switch controlled by an electrical signal
Fuse - Protects circuits from overcurrent by melting when current exceeds a certain level
Battery - Stores electrical energy for portable devices
Thermistor - Temperature-sensitive resistor
Photodiode - Converts light into electrical current
Solar Cell - Converts sunlight into electrical energy
Crystal Oscillator - Generates precise frequency signals
Voltage Divider - Divides a voltage into smaller parts
Thermocouple - Measures temperature based on voltage produced by two different metals
Piezoelectric Transducer - Converts mechanical stress into electrical energy or vice versa
Relay - Electromagnetic switch activated by a current
Zener Diode - Regulates voltage by maintaining a constant output voltage
Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) - Amplifies voltage difference between its inputs
NAND Gate - Logic gate with output low only when all inputs are high
NOR Gate - Logic gate with output high only when all inputs are low
XOR Gate - Exclusive OR logic gate
AND Gate - Logic gate with output high only when all inputs are high
OR Gate - Logic gate with output high when any input is high
Triac - Semiconductor device for AC power control
Thyristor - Semiconductor device for controlling large amounts of power
Optocoupler - Isolates two circuits by using light to transmit signals
Varistor - Voltage-dependent resistor used for transient voltage suppression
Hall Effect Sensor - Detects magnetic fields
Microcontroller - Integrated circuit that contains a CPU, memory, and I/O peripherals
Voltage Comparator - Compares two voltages and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger
Current Transformer - Steps down high current to a measurable level
Magnetic Reed Switch - Switch activated by a magnetic field
Voltage Reference - Provides a stable voltage output for use in precision circuits
MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) - Small mechanical and electromechanical systems
integrated with electronics
RFID Tag - Radio frequency identification device for wireless data transmission
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) - Provides mechanical support and electrical connections for electronic
components
RF Antenna - Transmits and receives radio frequency signals
Hall Effect Sensor - Measures magnetic field strength
Schottky Diode - Fast-switching diode with low forward voltage drop
Reed Relay - Relay operated by a magnetic field using a reed switch
Linear Voltage Regulator - Maintains a constant output voltage regardless of input voltage changes
Switch Mode Power Supply - Converts and regulates electrical power efficiently
Flyback Diode - Used to protect circuits from voltage spikes when switching off inductive loads
Heat Sink - Dissipates heat from electronic components
Speaker - Converts electrical signals into sound waves.
You might also like
- Electronic Components - Functions& SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectronic Components - Functions& SymbolsGil Nacario91% (58)
- ESP32 Development Using The Arduino IDEDocument162 pagesESP32 Development Using The Arduino IDEGOMEZ100% (2)
- Electrical ComponentsDocument5 pagesElectrical ComponentsJohn Damever BalanquitNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component - Wikipedia PDFDocument48 pagesElectronic Component - Wikipedia PDFNivas.B100% (1)
- Electronics SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectronics SymbolsStudy SharyNo ratings yet
- Electro 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesElectro 2 ReviewerNull NullNo ratings yet
- Symbol SNI Elektronik Dan ListrikDocument7 pagesSymbol SNI Elektronik Dan ListrikInyomanKrishnaNo ratings yet
- Jacob Hergert - Basic Electronics Components and Circuits 1Document19 pagesJacob Hergert - Basic Electronics Components and Circuits 1api-534579056No ratings yet
- Notes For Industrial ElectronicsDocument2 pagesNotes For Industrial ElectronicsMiko F. RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument23 pagesElectronic ComponentsUma Venkata SumanthNo ratings yet
- 50 SemiconductorsDocument5 pages50 SemiconductorsRB Ionic SilverioNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical SymbolsDocument4 pagesBasic Electrical SymbolsMichelle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument13 pagesElectronic ComponentmcmusbixNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component: Discrete Device or Physical Entity in AnDocument14 pagesElectronic Component: Discrete Device or Physical Entity in AnyirzebamleNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical & Electronic Symbolsecruz_yhwhNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components Functions Amp Symbols PDFDocument3 pagesElectronic Components Functions Amp Symbols PDFCrichelleMaeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Wire: Table of Electrical SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical Wire: Table of Electrical SymbolsMoneth Aquino BrionNo ratings yet
- RX TX and Power SupplyDocument10 pagesRX TX and Power SupplyPrashant LochamNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument11 pagesElectronic ComponentVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Terms and SymbolsDocument7 pagesGlossary of Terms and SymbolsDavid MendozaNo ratings yet
- Sprelolpil S: P Re LDocument8 pagesSprelolpil S: P Re LgoodNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical SymbolsZativa AlyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic CompoentsDocument13 pagesBasic Electronic CompoentsMurali Krishna VelavetiNo ratings yet
- Wiring SymbolsDocument13 pagesWiring SymbolsStalin TagoreNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsJeric Gader BriosoNo ratings yet
- Sana Makapasa Sa RoboticsDocument15 pagesSana Makapasa Sa RoboticsAshley CarandangNo ratings yet
- Electrical Term - Bu2Document14 pagesElectrical Term - Bu2BRIAN DIQUIATCONo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Training Module SAN REMO 2024Document15 pagesBasic Electronics Training Module SAN REMO 2024Mac Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components in AutomotiveDocument11 pagesBasic Electronic Components in Automotivedray09No ratings yet
- July 05, 2017 CEIT-05-902E MH 3:30-4:30P EngrDocument34 pagesJuly 05, 2017 CEIT-05-902E MH 3:30-4:30P EngrDiana Ross CustodioNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering SymbolDocument8 pagesElectrical Engineering SymbolAnupam BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic Symbolsmksamy2021No ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsSilviu IlNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument3 pagesElectrical SymbolsPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Elizabeth Lynch - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument20 pagesElizabeth Lynch - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525692684No ratings yet
- Table of Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesTable of Electrical SymbolsArgo Arjieanto0% (1)
- Sensors & ActuatorsDocument67 pagesSensors & Actuatorsmahendra naik100% (2)
- Table of Electrical SymbolsDocument4 pagesTable of Electrical SymbolsRhea Daluddung SanchezNo ratings yet
- Jared Duran - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument19 pagesJared Duran - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525646997No ratings yet
- Reverse Voltage Drop (Diode)Document4 pagesReverse Voltage Drop (Diode)frozhen aniviaNo ratings yet
- SimbolDocument26 pagesSimboldrion67No ratings yet
- Electronic Component: Adding Citations To Reliable SourcesDocument26 pagesElectronic Component: Adding Citations To Reliable SourcesShimadzu SPMINo ratings yet
- 200 Basic Electronic Terms FinalDocument8 pages200 Basic Electronic Terms FinalShairyl Ü TablanteNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics NotesDocument5 pagesBasic Electronics NotesRolando Carlos FloresNo ratings yet
- Paraskevi Hofioni - Basic Electronics Components and CircuitsDocument20 pagesParaskevi Hofioni - Basic Electronics Components and Circuitsapi-525648840No ratings yet
- Gibilisco (Summary)Document16 pagesGibilisco (Summary)Emmanuel RapadaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDocument34 pagesIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- Electrical SystemDocument16 pagesElectrical SystemCjoy MañiboNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 ElectricalDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 ElectricalUsamaNo ratings yet
- Power ElexDocument38 pagesPower ElexTin PelingonNo ratings yet
- Basic Elec & Electronic Engineering Lab: Vom/MultimeterDocument5 pagesBasic Elec & Electronic Engineering Lab: Vom/MultimeterKienth MatibagNo ratings yet
- Opto - Electronic Vts Final 2-1-1Document15 pagesOpto - Electronic Vts Final 2-1-1Vincent GamliNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Controls For Fluid Power CircuitsDocument69 pagesBasic Electrical Controls For Fluid Power Circuitsloveincyber3No ratings yet
- Electronics: Basic Terminology: A/C CurrentDocument4 pagesElectronics: Basic Terminology: A/C CurrenttowsenNo ratings yet
- Automobile Electricals and ElectronicsDocument235 pagesAutomobile Electricals and ElectronicsMutaawe MMark100% (4)
- Term Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyDocument15 pagesTerm Paper On Construction of 12 Volts Power SupplyVictor ImehNo ratings yet
- Beato Bscpe3b Cedd Act3 EditedDocument2 pagesBeato Bscpe3b Cedd Act3 EditedBeato MichaelNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Tcw-Kompleto-Rereviewhin Na LangDocument78 pagesTcw-Kompleto-Rereviewhin Na LangaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in TCW MidtermDocument218 pagesReviewer in TCW MidtermaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Digital Electronics 2Document3 pagesReviewer in Digital Electronics 2aNo ratings yet
- Transmission MediaDocument5 pagesTransmission MediaaNo ratings yet
- CAPE IA U2 Activities and Rubrics 2011Document18 pagesCAPE IA U2 Activities and Rubrics 2011Donnell Francis100% (2)
- Oilhead Hall Sensors PDFDocument15 pagesOilhead Hall Sensors PDFtoby100% (1)
- Magnetic LevitationDocument7 pagesMagnetic LevitationCofetaria FragutaNo ratings yet
- 1101 931 Hall Effect ES104 RevEDocument2 pages1101 931 Hall Effect ES104 RevESalman KhanNo ratings yet
- Mock Defense Parcon 1Document19 pagesMock Defense Parcon 1Nash Gemar Braga EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 ReportDocument11 pagesLab 1 ReportangelosoutiNo ratings yet
- Mini Max User Manual ENGDocument49 pagesMini Max User Manual ENGMark StolzoffNo ratings yet
- Electric Current Measurement Using AMR Sensor ArrayDocument5 pagesElectric Current Measurement Using AMR Sensor ArrayShunfu LinNo ratings yet
- Schemat Elektryczny SPE125 - 125L - 135S - 160 - 160L - 200 - 200D - 200LDocument20 pagesSchemat Elektryczny SPE125 - 125L - 135S - 160 - 160L - 200 - 200D - 200LMarcin GostołekNo ratings yet
- Senzor Magnetic FarnellDocument5 pagesSenzor Magnetic FarnellAndrei GhitaNo ratings yet
- Wheel Chair Engineering ProjectDocument26 pagesWheel Chair Engineering ProjectswordprakashNo ratings yet
- CMOS Three Axis Hall Sensor and Joystick Application Schott3axisJoystickDocument4 pagesCMOS Three Axis Hall Sensor and Joystick Application Schott3axisJoystickbesttv046936No ratings yet
- SENSOR and Signal Processing UnitDocument57 pagesSENSOR and Signal Processing UnitRohit Ghulanavar100% (1)
- EX 2 Brushless DC Motor 1600073824807Document23 pagesEX 2 Brushless DC Motor 1600073824807kewalNo ratings yet
- BLDC Motor With Speed Control With RPM DisplayDocument16 pagesBLDC Motor With Speed Control With RPM DisplayVõ Đức HuyNo ratings yet
- Digital Control of Four Quadrant Operation of BLDC MotorDocument10 pagesDigital Control of Four Quadrant Operation of BLDC MotorMehmet KırgözoğluNo ratings yet
- Dacor Wall OvenDocument77 pagesDacor Wall OvenJim Harmke100% (2)
- MLX91209CA Datasheet PDFDocument15 pagesMLX91209CA Datasheet PDFJavierPariNo ratings yet
- Users Manual: Digital GaussmeterDocument5 pagesUsers Manual: Digital GaussmeterndsramNo ratings yet
- Speed Synchronization of Multiple BLDC MotorsDocument6 pagesSpeed Synchronization of Multiple BLDC MotorsIJIERT-International Journal of Innovations in Engineering Research and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Linear Motor For Maglev TrainDocument3 pagesLinear Motor For Maglev TrainSandeep ThakurNo ratings yet
- To Study Hall Effect and Determine The Hall Coefficient LabDocument5 pagesTo Study Hall Effect and Determine The Hall Coefficient LabWomba LukamaNo ratings yet
- N Sushma Smart Water Flow Meter For ImprovedDocument6 pagesN Sushma Smart Water Flow Meter For ImprovedXian SameonNo ratings yet
- A Low Cost Smart Energy Monitoring and Control System For Smart BuildingsDocument5 pagesA Low Cost Smart Energy Monitoring and Control System For Smart BuildingsManuel GuijarroNo ratings yet
- Speed and Position Sensors HandoutDocument16 pagesSpeed and Position Sensors HandoutJose Ramón Orenes ClementeNo ratings yet
- BLDC Motor Drive PDFDocument83 pagesBLDC Motor Drive PDFrijilpoothadi100% (1)
- The Drive Design of The STM32-based Brushless DC Motor: Song Wang, Wang Guo, Wenqiang DunDocument9 pagesThe Drive Design of The STM32-based Brushless DC Motor: Song Wang, Wang Guo, Wenqiang DunMarco LisiNo ratings yet
- Measure of Angular VelocityDocument12 pagesMeasure of Angular VelocityAshley_Rulzzzzzzz100% (2)
- Micropower, Ultra-Sensitive Hall-Ef Fect Switches: A3211 and A3212Document13 pagesMicropower, Ultra-Sensitive Hall-Ef Fect Switches: A3211 and A3212Audio TecnologiaNo ratings yet