Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Revivewer
Science Revivewer
Uploaded by
Vaughn Siegfried FuertezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Science Revivewer
Science Revivewer
Uploaded by
Vaughn Siegfried FuertezCopyright:
Available Formats
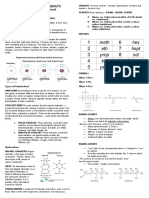
JOHN DALTON- proposed the most simple model of atom
JOHN THOMSON- proposed the plum pudding model of atom
ERNEST RUTHERFORD: proposed the nuclear model of an atom, gold foil experiment, got nothing
NEILS BOHR- he modified Rutherford’s model by including concentric circles
VALENCE ELECTRON`
– the outermost level of energy of an atom
– Comes from the latin word valentia which means capacity
IONIC FORMATION
- When neutral atom loses or gains electrons, it becomes charges particle called ion
- Cation, positive charged
- Anion, negative charged
IONIC BOND FORMATION- The opposing charges of the ions creates an attractive force that binds the
atoms together, becomes ionic bond.
IONIC COMPOUNDS
- Substances results from ionic bonding are called ionic compound.
- Compounds that conduct electricity are called electrolytes.
- They have a high melting and boiling point
COVALENT BOND - A covalent bond is another type of chemical bond that exists between two nonmetal
atoms.
COVALENT BOND FORMATION
- Nonmetal atoms tend to gain electrons to achieve a noble gas configuration. Because of this,
the nonmetals do not give but instead they share.
- Covalent bond can exist between dissimilar or similar atoms.
- Diatomic bond (2 atom bonds)
TYPES OF COVALENT BOND
- Single covalent bonds- when A pair of electrons is shared.
- Double covalent bonds- when 2 pairs of electrons are shared.
- Triple covalent bonds- when 3 pairs of electrons are shared.
POLAR AND NONPOLAR COVALENT BOND- The higher the electronegativity value, the greater the
tendency of atom to attract shared electrons.
POLARITY OF MOLECULE
- Wala namang aaralin HASUDJASDHAKSHDKAJSH loveu guys
COVALENT COMPOUNDS
- Compounds that results in covalent bonding are covalent compound
- They are generally soft because the atoms are attracted by relatively weak covalent bonds.
- Compared to ionic compounds, they have lower boiling and melting point.
CHPATER 6
HYDROCARBON DERIVATIVES- hydrocarbons that contains atleast one hydrogen atom replaced by
another type of atom or groups of atom
FUNCTIONAL GROUP- the replacement atom or groups of atom
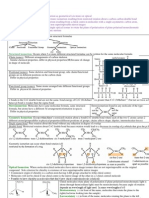
Compounds containing NITROGEN
- Alcohol- HYDROXYL- Methanol (simplest alcohol) Ethanol (primary alcohol, fuel additive,
industrial solvent)
- Ether- -O- GROUP- (used as solvents, incase of diethyl ether, anesthetic agents)
- Aldehyde- CARBONYL- (used as an insecticide, formaldehyde)
- Ketone- CARBONYL- (paints and lacquers, nail polish remover or acetone)
- Carboxylic Acid- CARBOXYL- (acetic acid or vinegar, methanoic acid, in ants)
- Ester- R-COO- (pleasant smell of fruits)
Hydrocarbons, only oxygen and carbon
Hydrocarbons- oxygen and carbon
Alkane-single bond- CNH2n=2-
Alkene- double bond- CnH2n-
Alkynes- triple bond-CnH2n-2-
Cycloalkanes- carbon atoms in a ring-cyclopropane, butane, pentane, hexane
Aromatic hydrocarbon- arenes- 6 membered carbon- smell of fuels
Compounds containing NITROGEN
Amines- production of dyes, PALATANDAAN TIE DYE
Amides- plastic, rubber industry, paper industry, sewage.
You might also like
- Chemistry Study Notes Grade 10Document10 pagesChemistry Study Notes Grade 10Jynxx1387% (15)
- O LVL Chem Definitions ListDocument6 pagesO LVL Chem Definitions Listacsbr4science170% (10)
- Cape Chemistry Unit 2 Crash CourseDocument75 pagesCape Chemistry Unit 2 Crash CourseKewi Love100% (3)
- BS 07273-1 2006 (En)Document18 pagesBS 07273-1 2006 (En)Emanuele MastrangeloNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper SPEDDocument5 pagesReflection Paper SPEDMariecris Barayuga Duldulao-AbelaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Organic ChemistryDocument5 pagesReviewer For Organic ChemistryJona MaeNo ratings yet
- 11-STEM Final Lesson (2nd Sem)Document9 pages11-STEM Final Lesson (2nd Sem)Lailah Rose AngkiNo ratings yet
- InamDocument4 pagesInamNicoleNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 ReviewerDocument3 pagesQuarter 2 Reviewervinz hanzel aguarillesNo ratings yet
- Module 8 Notes 61a82274d167fDocument39 pagesModule 8 Notes 61a82274d167fMahi ModiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes MYP4 5Document17 pagesChemistry Notes MYP4 5isharazil09No ratings yet
- Organic Reactions & Factors Affecting Boiling Points of Organic CompoundsDocument50 pagesOrganic Reactions & Factors Affecting Boiling Points of Organic CompoundsRegine BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience ReviewerLara RebaterNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Matter: in Water and Polar Solvents)Document3 pagesElectronic Structure of Matter: in Water and Polar Solvents)Chelsea DizonNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListDocument3 pagesChemistry Form 4 Definition ListAliif IsmailNo ratings yet
- Definitions Module 4Document10 pagesDefinitions Module 4CHRONIKNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - BSN 1Document6 pagesChemistry - BSN 1Arianne Jen GenotivaNo ratings yet
- THE HYDROCARBONS (Alkanes, Alkenes)Document7 pagesTHE HYDROCARBONS (Alkanes, Alkenes)miriam harriottNo ratings yet
- Summary Materials and Molecules IvoDocument15 pagesSummary Materials and Molecules IvoSilvester Den BoerNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE REVIEWER EmeDocument6 pagesSCIENCE REVIEWER Emejessa suazoNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument10 pagesHydrocarbonsjoeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry NotesDocument21 pagesOrganic Chemistry NotesBobbyWhiteNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument16 pagesScienceIamBan “OficialBanzPlayz”No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Mass Spec IIDocument43 pagesChapter 10 Mass Spec IIAlex GanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument62 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryytutwNo ratings yet
- CH-4 Carbon and It, S CompoundsDocument19 pagesCH-4 Carbon and It, S CompoundsthemidnightismNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument2 pagesVolcanoJhaynnon AniezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2 Naming of CompoundsDocument28 pagesChemistry Unit 2 Naming of CompoundsAuvan HilarioNo ratings yet
- Chem Unit 1 RevisionDocument5 pagesChem Unit 1 RevisionAysu'z Quirky EsseNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds:: Download PDF HereDocument21 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds:: Download PDF HerePremela PremelaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer V2Document33 pagesScience Reviewer V2eliotrichard570No ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compound PDFDocument5 pagesCarbon and Its Compound PDFAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Unit 2 Revision.Document47 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Unit 2 Revision.NizŏǾŏ Wait For-it Ismail100% (2)
- Reviewer in ScienceDocument4 pagesReviewer in ScienceLeana Mae LaguneroNo ratings yet
- Science 9 2ndQ PointersDocument1 pageScience 9 2ndQ PointersDan Jenniel CedeñoNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument10 pagesScienceMazze Ashley SenaNo ratings yet
- 4.carbon and Its CompoundsDocument13 pages4.carbon and Its CompoundsayanNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundDocument14 pagesCarbon and Its Compoundapi-246793885No ratings yet
- Science Dictionary Grade 9Document4 pagesScience Dictionary Grade 9Kristel Kaye BasasNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Chapter - 4Document13 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds: Chapter - 4CT SectionNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Organic Chemistry II - AQA Chemistry A-LevelDocument11 pagesDefinitions - Organic Chemistry II - AQA Chemistry A-LevelJulien KhalilNo ratings yet
- Chem Reviewer (Lec & Lab)Document9 pagesChem Reviewer (Lec & Lab)adelaine perasNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem NotesDocument21 pagesOrganic Chem NotesVeer PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1-Chapter 3-Lecture NoteDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1-Chapter 3-Lecture Note남궁기택/학생/화학공학No ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument6 pagesDefinitionsali ahsan khanNo ratings yet
- ch02.ppt - Representative Carbon CompoundsDocument50 pagesch02.ppt - Representative Carbon CompoundscoltalbNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Revision NotesDocument63 pagesCBSE Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Revision NotesAjitesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CHEM7-Organic ChemistryDocument30 pagesCHEM7-Organic ChemistryEmily SalibNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding & Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons: Physical Science Week 4 HandoutsDocument2 pagesChemical Bonding & Nomenclature of Hydrocarbons: Physical Science Week 4 HandoutsBenj Jamieson DuagNo ratings yet
- L5-Q2-W5-Organic CompoundDocument46 pagesL5-Q2-W5-Organic CompoundColleen SerilNo ratings yet
- SCIENCEDocument10 pagesSCIENCEMazze Ashley SenaNo ratings yet
- Co2 - Chemical BondingDocument49 pagesCo2 - Chemical BondingKel SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Definitions - Organic Chemistry I - AQA Chemistry A-LevelDocument8 pagesDefinitions - Organic Chemistry I - AQA Chemistry A-LevelSaad AatirNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Hybridisation of OrbitalsDocument11 pagesAlkanes: Hybridisation of OrbitalsIsaa gabNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document16 pagesCH 4charanNo ratings yet
- REVIEWERDocument3 pagesREVIEWEREmelly PadillaNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer by Aneezah PascualDocument5 pagesScience Reviewer by Aneezah Pascualdalialia136iNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Form 4 Definition ListDocument3 pagesChemistry Form 4 Definition ListSyazana Mohd RosliNo ratings yet
- Cleansing Action of SoapDocument19 pagesCleansing Action of SoaptanyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4.5Document12 pagesUnit 4.5Tilak K CNo ratings yet
- GCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- DR Profile All Department Part 2Document50 pagesDR Profile All Department Part 2joynal abedeenNo ratings yet
- Food ChemistryDocument4 pagesFood ChemistryAkil LadzinrankNo ratings yet
- Affective AssessmentDocument34 pagesAffective AssessmentEdgar Miralles Inales ManriquezNo ratings yet
- Mabalacat National Senior High School Address: San Isidro, Dau, Mabalacat City, PampangaDocument5 pagesMabalacat National Senior High School Address: San Isidro, Dau, Mabalacat City, PampangaJel Louis LopezNo ratings yet
- M-MTRAC 1 ManualDocument19 pagesM-MTRAC 1 ManualCvijic DejanNo ratings yet
- Ethics ChecklistDocument3 pagesEthics ChecklistRaj Karthik RajasekaranNo ratings yet
- Assignment Ahamadul Islam Ananna ID: 19304077 Section: 3 Course: ANT101 Fall 2020Document3 pagesAssignment Ahamadul Islam Ananna ID: 19304077 Section: 3 Course: ANT101 Fall 2020Ahamadul Islam OnonnoNo ratings yet
- Ob13 Tif07Document20 pagesOb13 Tif07Lamis Alahmadi100% (1)
- Modulation WorksheetDocument13 pagesModulation WorksheetabellorodelcuteNo ratings yet
- Field Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFDocument132 pagesField Guide Alien Species in European Forests PDFIonut MarianNo ratings yet
- Notice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: InterCaribbean Cargo, Inc., Et Al.Document2 pagesNotice: Ocean Transportation Intermediary Licenses: InterCaribbean Cargo, Inc., Et Al.Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Journal: Lyceum Northwestern UniversityDocument4 pagesJournal: Lyceum Northwestern UniversityBrian Montales BaggayanNo ratings yet
- English Hand BookDocument55 pagesEnglish Hand BookVeena Jayaram Rao RajgopalNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument13 pagesPharmacologypratik chabhadiyaNo ratings yet
- Psychology Paper 3 Mark SchemeDocument20 pagesPsychology Paper 3 Mark SchemeAnaNo ratings yet
- Waterpoxy 751 July 2014 R2 ICDocument6 pagesWaterpoxy 751 July 2014 R2 IC陈辉No ratings yet
- Un Cisic E-Bulliten 5Document3 pagesUn Cisic E-Bulliten 5taha_basit2441No ratings yet
- UNIT-I CorrDocument42 pagesUNIT-I CorrArthi SelvaNo ratings yet
- Parle AgroDocument3 pagesParle AgroKumar GautamNo ratings yet
- G Ed Suc: Uide To The I OllegesDocument56 pagesG Ed Suc: Uide To The I OllegesZacNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Clinical Focus High Yield Gi and HepatologyDocument426 pagesGastroenterology Clinical Focus High Yield Gi and HepatologyAhana MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Evidencia Científica Sobre La FlexibilidadDocument28 pagesEvidencia Científica Sobre La Flexibilidadsulei222No ratings yet
- YCMOU-6th Semester Question Papers-7Document5 pagesYCMOU-6th Semester Question Papers-7phase_shekhar21No ratings yet
- Soal Uts Kelas 9 MtsDocument5 pagesSoal Uts Kelas 9 Mtsindah sNo ratings yet
- 1.2 - CEC342 - Post-Silicon Production Flow - Test and Packing - Characterization Versus Production TestingDocument3 pages1.2 - CEC342 - Post-Silicon Production Flow - Test and Packing - Characterization Versus Production TestingSriram Sundar SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Bank Management: Dr. Rania Salem Department of FinanceDocument22 pagesBank Management: Dr. Rania Salem Department of FinanceDoha KashNo ratings yet
- Corrguard Si PDFDocument18 pagesCorrguard Si PDFyolia16100% (1)
- Warum Blastx BenutzenDocument5 pagesWarum Blastx BenutzenLenzenMeiserNo ratings yet