Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Abdul in The Garden Class 4 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 19 (PDF)
Abdul in The Garden Class 4 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 19 (PDF)
Uploaded by
Hardeep SidhuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Abdul in The Garden Class 4 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 19 (PDF)
Abdul in The Garden Class 4 Notes CBSE EVS Chapter 19 (PDF)
Uploaded by
Hardeep SidhuCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision Notes
Class – 4 Environmental Studies
Chapter 19 – Abdul in the Garden
Summary of Abdul in the Garden
This chapter will help us to understand the different types of plants and role
of roots in a plant.
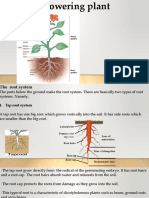
The part of a plant that connects it to the ground or to a support, usually
underground, and transports water and nutrients to the rest of the plant through
numerous branches and fibers is known as the roots of a plant.
Root has the following functions
The plant's connection to the soil
Water and nutrient absorption from the soil
Water and nutrients are absorbed and transported to the stem.
Vegetative reproduction and competition with other plants.
Food storage.
Image: Roots
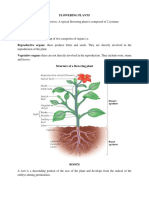
There are two main kinds of roots: taproots and fibrous roots.
Taproots
When one main root grows straight down deep into the soil, it is called a
taproot.
Class IV Environmental Studies www.vedantu.com 1
It has a very small number of lateral roots that develop and grow from the
main root.
The taproot is a secondary root that differs from the primary root.
During seed development, the primary root is formed from the seedling's
radicle.
Taproots are found in dicotyledons and gymnosperms.
Image: Taproot
Examples: Beetroot, Burdock, Carrot, Sugar bee, Dandelion, Parsley, Parsnip,
Poppy mallow.
Image: Examples of the taproot
Fibrous Roots
The opposite of a taproot system is a fibrous root system.
Class IV Environmental Studies www.vedantu.com 2
It is usually formed by the stem's thin, moderately branching roots.
Monocotyledonous plants and ferns all have a fibrous root system.
When the tree has reached full maturity, the fibrous root systems resemble a
root mat.
Image: Fibrous Root System
Examples: Rice, wheat, maize, marigold, and banana.
Image: Examples of fibrous root system
Vegetables that have roots
1. Beets.
2. Parsnips.
3. Turnips.
4. Rutabagas.
5. Carrots.
6. Jicama.
7. Maca.
Class IV Environmental Studies www.vedantu.com 3
Image: Vegetable that have roots
Unusual Roots
In a Banyan Tree, the tree's roots can be seen hanging from the branches.
These sprout from the branches and descend to the ground.
These roots act as pillars, providing the tree with strong support.
The banyan tree, like all other trees, has roots in the ground.
Image: Banyan tree
Practice Questions
Q 1. Fill in the blanks by selecting the correct word from those given in
brackets.
1. The ............... (potato/carrot) can also be eaten raw.
Ans: Carrot
2. A vegetable with ............... (rough/smooth) surface is a root.
Ans: Rough
Class IV Environmental Studies www.vedantu.com 4
3. The ............... (neem/banyan) tree has hanging roots.
Ans: Banyan
4. The ............... (cotton/desert oak) tree has very long roots.
Ans: Desert Oak
Q 2. How does a desert oak tree get water for its roots?
Ans: The long roots of desert oak trees provide water. Explanation: Oak trees, like
most desert trees, have adapted to the dry environment.
Class IV Environmental Studies www.vedantu.com 5
You might also like
- Plant List With Butterfly 2023Document3 pagesPlant List With Butterfly 2023api-523327389100% (2)
- End of Unit Test Higher (H) : Give Two ReasonsDocument5 pagesEnd of Unit Test Higher (H) : Give Two Reasonschan myae75% (4)
- Botany Handbook For Florida PDFDocument23 pagesBotany Handbook For Florida PDFBá Tùng Phan100% (2)
- Pre A1 Starters Bobbie WorksheetDocument3 pagesPre A1 Starters Bobbie WorksheetНаталья БойчукNo ratings yet
- Table of Electrohomeopathy Remedies and Plants Used in ThemDocument3 pagesTable of Electrohomeopathy Remedies and Plants Used in ThemDev Sarova100% (3)
- SCIENCEDocument10 pagesSCIENCESomen SahaNo ratings yet
- B5-Plant & Animal ClassificationDocument11 pagesB5-Plant & Animal ClassificationHarshaWakodkar100% (1)
- PRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4Document26 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 3 & 4CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Root SystemDocument12 pagesRoot SystemLawrence KasambaNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Plants: ClimbersDocument8 pagesGetting To Know Plants: ClimbersShivam Zakhmi100% (1)
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument8 pagesGetting To Know PlantsHappy HomeNo ratings yet
- Exp SC 3 - Chapter 02Document9 pagesExp SC 3 - Chapter 02megamind publicationNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument29 pagesGetting To Know Plantsashutoshbombatkar2No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 5 (PDF)Document29 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants Class 11 Notes CBSE Biology Chapter 5 (PDF)pranjalutherNo ratings yet
- 6 ThscicenceDocument4 pages6 Thscicencelearn4chatgptNo ratings yet
- Which Root System Is Best Adapted For Anchorage? Why Do You Say So? (N.D.) - Https://StudyDocument2 pagesWhich Root System Is Best Adapted For Anchorage? Why Do You Say So? (N.D.) - Https://StudyJhey SiNo ratings yet
- Ncert BookDocument20 pagesNcert BookAmu SontakkeNo ratings yet
- STD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesSTD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsSudip GhoshNo ratings yet
- CRS Laboratory Exercise No.2aDocument12 pagesCRS Laboratory Exercise No.2aBaisa A. UsmanNo ratings yet
- PLANTDocument23 pagesPLANTAngelito HalmainNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument29 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantssaleemNo ratings yet
- Types of Commercial Food Crops in The PhilippinesDocument34 pagesTypes of Commercial Food Crops in The Philippinesmarjorie gomezNo ratings yet
- Basic Botany 2Document92 pagesBasic Botany 2Michael OduorNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About The Part of A PlantDocument51 pagesThis Article Is About The Part of A PlantTess TubieronNo ratings yet
- Grade.4 ch.1, l.3Document26 pagesGrade.4 ch.1, l.3Hibara AliNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 5: Answers in Red ColorDocument9 pagesActivity No. 5: Answers in Red Colormasor100% (1)
- 11 Biology NcertSolutions ChapterDocument11 pages11 Biology NcertSolutions ChapterjyotibhalaNo ratings yet
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Document18 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 4shinu goyalNo ratings yet
- Project PlantsDocument21 pagesProject Plantsapi-239496035No ratings yet
- T HN Yi TF Ux WDKi Miaq SLVDocument29 pagesT HN Yi TF Ux WDKi Miaq SLVjennblair0830No ratings yet
- Class 6 Biology Getting To Know PlantsDocument14 pagesClass 6 Biology Getting To Know PlantsRishabh SahuNo ratings yet
- PLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesDocument78 pagesPLANT MORPHOLOGY NotesAsam100% (1)
- Parts of A Plant - Notes-1Document3 pagesParts of A Plant - Notes-1shilpkakkNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument8 pagesPlantsReanna Mae A. BaganiNo ratings yet
- ROOTS5Document20 pagesROOTS5mobilyacitakurNo ratings yet
- Biology M7 Plant Parts & FunctionsDocument22 pagesBiology M7 Plant Parts & FunctionsSheila Pardines100% (4)
- Activity Sheet 1 GenBio2Document4 pagesActivity Sheet 1 GenBio2Sean MatuguinasNo ratings yet
- Plants Around YouDocument6 pagesPlants Around YouJovilyn JardielNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument6 pagesGetting To Know Plantsgunishgoyal0510No ratings yet
- 03-Flowering PlantsDocument45 pages03-Flowering PlantsMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- UCXg D56 Iu 1 DJ P5 HKPL HJDocument11 pagesUCXg D56 Iu 1 DJ P5 HKPL HJdhairyasuthar2749No ratings yet
- Answers - Class 6Document6 pagesAnswers - Class 6Laiq Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument4 pagesGetting To Know PlantsSonam BaghaNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants: The RootDocument14 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants: The RootbOKALNo ratings yet
- Root Modifications Storage RootsDocument17 pagesRoot Modifications Storage Rootsmbg1110100% (1)
- CSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Document17 pagesCSO Olympiad Book For Class 4Aswani PokuriNo ratings yet
- B 4 Ev 6 y 22 WR Getting 20 To 20 Know 20 Plants 20 PPTDocument46 pagesB 4 Ev 6 y 22 WR Getting 20 To 20 Know 20 Plants 20 PPTatharNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W6 Science 5Document45 pagesQ2 - W6 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- BIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedDocument18 pagesBIOLO001plants Parts and Function EditedChristine angel mae BalsomoNo ratings yet
- Inter-material-Istyearem-botany-unit II Morphology of Flowering Plants 5Document18 pagesInter-material-Istyearem-botany-unit II Morphology of Flowering Plants 5shashinetharapolu2925No ratings yet
- SM3Document3 pagesSM3kishoreprithikaNo ratings yet
- Plant Organs RootsDocument38 pagesPlant Organs RootsMuammar KhadafiNo ratings yet
- Flowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Document4 pagesFlowers and Pine Trees Are Both Seed-Producing Plants.: How Does The Plant Reproduce and Make New Plants?Anchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Plants Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 7 - Learn CBSEDocument1 pageGetting To Know Plants Class 6 Notes Science Chapter 7 - Learn CBSEAaditi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Science CH 7Document3 pagesScience CH 7JAYASHREE VNo ratings yet
- SEM II UNIT II Root Morphology DR - Prashant ShahareDocument37 pagesSEM II UNIT II Root Morphology DR - Prashant Shaharesourov546vermaNo ratings yet
- Quisao Lab Act 4Document3 pagesQuisao Lab Act 4PaulNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Plant and Their Functions q2 w6Document51 pagesParts of A Plant and Their Functions q2 w6Nor-Jaina Musa Mina-Calulong100% (1)
- DATE: 14.8.20 L-12 Plants and Their Care: Very Short Answer QuestionsDocument2 pagesDATE: 14.8.20 L-12 Plants and Their Care: Very Short Answer QuestionsbarkhavijhNo ratings yet
- Ch-7 Getting To Know PlantsDocument4 pagesCh-7 Getting To Know PlantsAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- The Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Incredible World of Plants - Cool Facts You Need to Know - Nature for Kids | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Test - Food Groups - Vegetables and Legumes - QuizletDocument8 pagesTest - Food Groups - Vegetables and Legumes - QuizletGrover VillegasNo ratings yet
- Description: Syringa (Lilac) Is A Genus of 12 Currently RecognizedDocument8 pagesDescription: Syringa (Lilac) Is A Genus of 12 Currently RecognizedKiana DouglasNo ratings yet
- Rodale's 21st-Century Herbal - A Practical Guide For Healthy Living Using Nature's Most Powerful Plants (PDFDrive) (116-119)Document4 pagesRodale's 21st-Century Herbal - A Practical Guide For Healthy Living Using Nature's Most Powerful Plants (PDFDrive) (116-119)ANGELO NHARNo ratings yet
- Brinjal / Egg PlantDocument4 pagesBrinjal / Egg Plantdevanshkatiyar122No ratings yet
- Long Term Seed BucketDocument8 pagesLong Term Seed BucketseattlesevenNo ratings yet
- Roof Garden and Vertical Garden: Rahul Rapaka Id.b.design Sem 6, Slot 1Document12 pagesRoof Garden and Vertical Garden: Rahul Rapaka Id.b.design Sem 6, Slot 1Rahul RapakaNo ratings yet
- Special Horticultural Practices of Flower Crops: Swapnil RaghatateDocument5 pagesSpecial Horticultural Practices of Flower Crops: Swapnil RaghatateEbadur Rahman BarbhuiyaNo ratings yet
- SH Prambanan - Mariani Raisin Sdjul22Document6 pagesSH Prambanan - Mariani Raisin Sdjul22Phillia NambarisaNo ratings yet
- Cold Hardy Fruits and Nuts IntroductionDocument4 pagesCold Hardy Fruits and Nuts IntroductionChelsea Green PublishingNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction Plant Process Flow Diagram: Pre-CleaningDocument1 pageSolvent Extraction Plant Process Flow Diagram: Pre-Cleaningsan dip100% (1)
- TLE6 AGRI. 2nd Quarter TestDocument3 pagesTLE6 AGRI. 2nd Quarter TestElona Jane CapangpanganNo ratings yet
- Urban Medicinal Plants Production For The Prepping FilipinosDocument42 pagesUrban Medicinal Plants Production For The Prepping FilipinosBernard Dayot100% (1)
- Uits PDFDocument36 pagesUits PDFCrystal ParkerNo ratings yet
- Table 1 Storage Requirements of Vegetables, Fresh Fruits, and MelonsDocument8 pagesTable 1 Storage Requirements of Vegetables, Fresh Fruits, and Melonsaly_wael71No ratings yet
- TLE6 - Quarter1 - Mod7 - Develops Plan For Expansion of Planting Trees and Seedling Production - Version3Document40 pagesTLE6 - Quarter1 - Mod7 - Develops Plan For Expansion of Planting Trees and Seedling Production - Version3LYNN MADDAWATNo ratings yet
- Flower Seeds Biology and TechnologyDocument383 pagesFlower Seeds Biology and TechnologyCodrean VladNo ratings yet
- Roundup Powermax: Bag LabelDocument28 pagesRoundup Powermax: Bag LabelMinenhle ChristianNo ratings yet
- Ajwain and Honasparagus The Golden Combination For Weight LossDocument2 pagesAjwain and Honasparagus The Golden Combination For Weight LossJoseph JohnNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF A SEED - PartiDocument6 pagesPARTS OF A SEED - Partichristian capunongNo ratings yet
- Arces Grupo Dwarf - PDF Versión 1Document36 pagesArces Grupo Dwarf - PDF Versión 1JimyNo ratings yet
- 2019 Gulayan Sa Paaralan Program Monthly ReportDocument2 pages2019 Gulayan Sa Paaralan Program Monthly ReportRENATO VICMUDONo ratings yet
- SDSC Succession Planting WorksheetDocument1 pageSDSC Succession Planting WorksheetjhNo ratings yet
- AgohoDocument4 pagesAgohoBTS ARMY100% (1)
- List of Nurseries - 2020Document52 pagesList of Nurseries - 2020Sadanand KumarNo ratings yet
- Plant Propagation CuttingsDocument25 pagesPlant Propagation Cuttingsricabaloyo2002No ratings yet
- Buah Awetan BasahDocument2 pagesBuah Awetan BasahNelah Thea NelahNo ratings yet