Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aap 1
Aap 1
Uploaded by
eisaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aap 1
Aap 1
Uploaded by
eisaCopyright:
Available Formats
ELEMENTS OF ARTS
Art Appreciation
are made.
- Complementary - the opposite hues on the color wheel. In their
ELEMENTS OF ART
most basic form, they are one primary color and the secondary
- The elements of art and principles of design are the color that is created by mixing the other two primaries.
fundamental parts of an artwork. - Analogous - are colors that are next to each other on the color
- Building blocks of every artwork. wheel.
- Identifying these elements is one way to understand an artwork. - Warm - yellow, red, orange and different shades of these colors
- Mastery of these elements can make analysis more meaningful. are warm colors
- Elements of art includes: - Cool - green, blue, and purple, and variations of those three
1. Line colors
2. Shape - PROPERTIES OF COLOR:
3. Color 1. Hue - the name of the color.
4. Space 2. Value - a color’s lightness or darkness.
5. Texture 3. Intensity - refers to the brightness of a color, often
6. Form measured by boldness or dullness.
7. Value
SPACE
LINE
- How an artwork uses or depicts depth or distance.
- The path of a point moving through space. Note: Depth and distance can be perceived because of the size
- There are many types of line. We can look for the direction of the differences, the placement, and the value.
line, the feeling of the line, the quality of the line, and how the - Space can give the illusion of objects in an artwork being close
lines move our eye through artworks. or far away.
- TYPES OF LINE: - Positive Space is the areas of the artwork filled with the content.
1. active-passive - Negative Space is the space in between.
2. flowing-light - Sculptors and Architects work with all three dimensions of space
3. thick-thin – height, width, and depth.
4. broken-continuous - Artists who work on a flat surface can make a two-dimensional
5. implied-actual surface appear three-dimensional.
6. contour-outline
7. perpendicular-parallel
TEXTURE
8. bold-delicate
9. straight-curved - Tactile qualities of a surface – the way objects actually feel or
10. long-short the way they look like they would feel.
11. geometric-organic - A painting, drawing, print, or other two-dimensional work can be
12. precise-irregular made to look like a textured surface – implied texture.
13. vertical-horizontal - 2 TYPES OF TEXTURE:
14. zig-zag – direct 1. Implied Texture - created using other elements of art,
including form, line, shape and color.
2. Real Texture - things feel just as they appear.
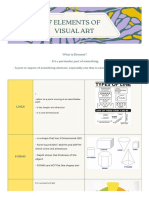
SHAPE
- An enclosed area of space created through lines and other
FORM
elements of the composition. Shapes can be geometric or
free-form. - Closely related to shape, but form is always three-dimensional.
- KINDS OF SHAPE: - Measurable by length, width, and height, and encloses volume.
1. Organic - free-form and curved, like people, animals, - Can be actual 3-D forms created with sculpture or architecture,
trees, and other natural elements. or they can be implied forms where the artist creates the illusion
2. Geometric - precise – like squares, triangles, rectangles, of the form onto a flat surface.
polygons, etc. - 2D & 3D
1. 2-Dimensional - can be seen only from one side
2. 3-Dimensional - can be viewed from any side.
COLOR
- Produced by the way an object reflects or emits light. By placing
VALUE
colors next to each other in different ways, artists can create a
variety of effects. - Refers to the lightness and darkness of colors.
- Primary Colors - Blue, Yellow, Red, from which all other colors - Often described in varying levels of contrast.
ELEMENTS OF ARTS
Art Appreciation
- Value Scale: shows the range of tones from white, which is the
CONTRAST
lightest, to black, which is the darkest.
- The closer together the values are on a scale, the less contrast - Refers to the arrangement of opposite elements and effects.
we see. - Can be used to create variety, visual interest, and drama in an
artwork.
PRINCIPLES OF ART AND DESIGN
MOVEMENT
- The elements of art and the principles of design are the
fundamental parts of an artwork. - Can be thought in two-ways.
- Identifying these elements is one way to understand an artwork. - 1st refers to how an artist depicts movement using the
This includes: elements and principles of art.
1. Composition - 2nd refers to the visual flow of an artwork, indicated by the path
2. Emphasis a viewer’s eye takes as the look at the artwork.
3. Rhythm - Lines, edges, shapes, and colors can be utilized by the artist to
4. Balance point the way through an artwork as a map for our eyes to
5. Contrast follow.
6. Movement
7. Proportion
PROPORTION
8. Unity
9. Variety - The size relationship between the various parts of an artwork.
- Artists can use scale and proportion to create sensations such
as depth, realism, disorientation, and drama.
COMPOSITION
- Refers to the placement or arrangement of the elements of art
UNITY
in a work of art.
- A formal analysis of work of art involves looking at the artists’ use - Also known as harmony
of the elements and principles of art and how they work together - Refers to the cohesiveness of an artwork, how whole, consistent,
to create meaning. and complete it appears.
- The pleasing combination of elements to create harmonious
composition.
EMPHASIS
- Achieved through
- Refers to the area of an artwork that dominates attention or 1. Repetition
draws interest. 2. Simplicity
- Often the place a viewer looks first. 3. Harmony
- Artist can create emphasis by contrasting the following 4. Contrast
elements of art: 5. Theme and Variation
1. Color 6. Proximity
2. Shape 7. Continuity
3. Size and Dominance
4. Detail
VARIETY
5. Contrast
6. Isolation - Refers to the elements of a composition that differ from one
another.
- Creates visual interest and energy
RHYTHM
- Achieved through:
- Refers to the movement or action of a composition, usually 1. Variety Color
achieved through repetition of lines, shapes, colors, and more. 2. Variety Shapes
- Creates visual tempo in artworks and provides a path for the 3. Variety Lines
viewer’s eye to follow. 4. Variety Size
5. Variety Perspective
6. Variety Texture
BALANCE
- Refers to the distribution of visual weight in a composition.
- Each part of the composition works with other parts of the
composition to appear equal and harmonious in balance.
You might also like
- Paul Overy-De StijlDocument172 pagesPaul Overy-De StijlŽeljka100% (1)
- Composition: The Anatomy of Picture MakingFrom EverandComposition: The Anatomy of Picture MakingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Elements and Principles of ArtDocument4 pagesElements and Principles of ArtKaryl AarientosNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art: Arta Midterms ReviewerDocument5 pagesElements of Art: Arta Midterms ReviewerJendeuk KimNo ratings yet
- PAINTINGDocument4 pagesPAINTINGAngela BarcebalNo ratings yet
- Elements of Visual Arts ReviewerDocument5 pagesElements of Visual Arts ReviewerElaine DondoyanoNo ratings yet
- Notes in Art (Lines and Colors)Document6 pagesNotes in Art (Lines and Colors)Trashy kawaNo ratings yet
- ArtsDocument3 pagesArtslheagomezsisonNo ratings yet
- ARTA111: (Diniscuss Ni Sir Nun Prelim)Document14 pagesARTA111: (Diniscuss Ni Sir Nun Prelim)Marian TorresNo ratings yet
- Arts ReviewerDocument3 pagesArts ReviewerJerome MagdaongNo ratings yet
- Notes For Artapp QuizDocument5 pagesNotes For Artapp QuizAubrey SanchezNo ratings yet
- CPARDocument6 pagesCPARJacqueline DonatoNo ratings yet
- CPAR ReviewerDocument10 pagesCPAR ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Elements of Visual ArtDocument24 pagesElements of Visual ArtAnghelica EuniceNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Visual ArtsDocument4 pagesThe Elements of Visual ArtsJessa CancinoNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions Hs Phil Art 001 - 12stemb10Document12 pagesContemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions Hs Phil Art 001 - 12stemb10Gabby OrtegaNo ratings yet
- CPAR NotesDocument4 pagesCPAR NotesJahzara Daveigh BolivarNo ratings yet
- ArtsmoduleDocument8 pagesArtsmoduleapi-457177416No ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of ArtDocument5 pagesElements and Principles of ArtJade MonteverosNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Visual ArtsDocument4 pagesThe Elements of Visual ArtsCassey Ann PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8Document4 pagesLesson 8Aliyah PlaceNo ratings yet
- Visual Elements of ArtsDocument5 pagesVisual Elements of ArtsJan Mae EstaresNo ratings yet
- Cpar ReviewerDocument5 pagesCpar ReviewerADEM MARIONE C. INOVEJASNo ratings yet
- CPAR Modules 4 5 ONA GAMABADocument9 pagesCPAR Modules 4 5 ONA GAMABAYanlah LopezNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument2 pagesElements of ArtShekinah Mae SantosNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation LET ReviwerDocument6 pagesArt Appreciation LET ReviwerDanielle Angela TaccadNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - Elements and Principles of ArtDocument8 pagesMODULE 3 - Elements and Principles of ArtJan Patrick CastilloNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtDocument30 pagesElements of ArtKathleen MangualNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument10 pagesArt Appreciationyeri kimNo ratings yet
- Hums001 Chapter 4Document6 pagesHums001 Chapter 4Majalita DucayNo ratings yet
- Hums001 Chapter 4Document6 pagesHums001 Chapter 4Mitchelle Labitag RiveraNo ratings yet
- MAPEHDocument5 pagesMAPEHALLISONNo ratings yet
- LAHATDocument5 pagesLAHATMichiiee BatallaNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of Art (Notes)Document1 pageElements and Principles of Art (Notes)Karen CaelNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtsDocument2 pagesElements of ArtsJan SebyerNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of ArtDocument4 pagesElements and Principles of ArtjunquelalaNo ratings yet
- Art G1Tri1Document2 pagesArt G1Tri1lorenzomoloNo ratings yet
- LAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W2 ArtsDocument8 pagesLAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W2 ArtsJemalyn Hibaya LasacaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1: Principles of Design: A. Unity and VarietyDocument10 pagesLESSON 1: Principles of Design: A. Unity and VarietyJustine Dave rubaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 3:: Arts and Crafts of Luzon Elements of Beauty and UniquenessDocument18 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 3:: Arts and Crafts of Luzon Elements of Beauty and UniquenessDeo GaveriaNo ratings yet
- Cpar 12 NotesDocument5 pagesCpar 12 NotesAliNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJastin AmonNo ratings yet
- Cpfar Reviewer ST1Document2 pagesCpfar Reviewer ST1Shane NicoleNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Art: 3. FormDocument4 pagesThe Elements of Art: 3. FormJusteen BalcortaNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation - Prelim ReviewerDocument9 pagesArt Appreciation - Prelim ReviewerSab Sadorra100% (1)
- Lesson 6 Elements and Principles of Art HandoutDocument9 pagesLesson 6 Elements and Principles of Art HandoutVanissa MontillaNo ratings yet
- Elements of Beauty and UniquenessDocument18 pagesElements of Beauty and Uniquenessmaria kyla andradeNo ratings yet
- Week 5 REVIEWER Elements and Principles of ArtDocument6 pagesWeek 5 REVIEWER Elements and Principles of ArtJamilla Rose AndalNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Notes 230925 224412Document12 pagesContemporary Notes 230925 224412Ellah Iracielli TevesNo ratings yet
- Preparation IN ARTSDocument4 pagesPreparation IN ARTSTricia MorgaNo ratings yet
- Visual ArtsDocument8 pagesVisual ArtsLovely SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Daily Planner Doc in Pastel Purple Pastel Yellow Teal Fun Patterns Illustrations StyleDocument3 pagesDaily Planner Doc in Pastel Purple Pastel Yellow Teal Fun Patterns Illustrations StyleMax GrantozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Elements and Principles of TheDocument40 pagesUnit 4 Elements and Principles of TheJHEA BELLE GONZALESNo ratings yet
- 2IE-B - Group 2Document13 pages2IE-B - Group 2Rexsielyn BarquerosNo ratings yet
- Art AppDocument5 pagesArt AppJanela Chloe Arizala BayNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Elements and Principles of The ArtsDocument40 pagesUnit 4 - Elements and Principles of The ArtsEj BeatoNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation ReviewerDocument10 pagesArt Appreciation ReviewerMystic LevisteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Art RevierDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Art RevierSherren Marie Nala100% (1)
- Elements of Visual Arts: Chapter 3 Art App ReviewerDocument18 pagesElements of Visual Arts: Chapter 3 Art App ReviewerYAGI, Miyuki F.No ratings yet
- ARTS 10 ElementsDocument22 pagesARTS 10 ElementsJoseph QuizanaNo ratings yet
- Grisebach Van Gogh 240 6Document6 pagesGrisebach Van Gogh 240 6Katharina Sumantri100% (1)
- Mapeh 9Document12 pagesMapeh 9Analiza QuimpanNo ratings yet
- LE01 - Introduction To Graphic Design 2021SPDocument16 pagesLE01 - Introduction To Graphic Design 2021SPHoang Ngan TRUONGNo ratings yet
- Branches of HumanitiesDocument4 pagesBranches of HumanitiesLede Ann Calipus YapNo ratings yet
- Recognizing The GAMABA and The National ArtistsDocument19 pagesRecognizing The GAMABA and The National Artistshentaiwtkouhai177013No ratings yet
- Week 11 - ARTA Online LectureDocument67 pagesWeek 11 - ARTA Online LectureAna Marie EboraNo ratings yet
- Ashapuri TempleDocument13 pagesAshapuri TempleGyandeep JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Ukiyo-e, or ukiyo-ye (浮世絵,: (u.ki.jo.e) woodblock prints Edo period kabuki sumoDocument2 pagesUkiyo-e, or ukiyo-ye (浮世絵,: (u.ki.jo.e) woodblock prints Edo period kabuki sumoZainab CheemaNo ratings yet
- Paper Assigment-Madonna and ChildDocument5 pagesPaper Assigment-Madonna and ChildMatthieu Jean-BaptisteNo ratings yet
- 10 Artworks by Michelangelo You Should Know.: ItalianDocument11 pages10 Artworks by Michelangelo You Should Know.: ItalianJennifer ScottNo ratings yet
- Van Gogh Wheatfield Plus PDFDocument2 pagesVan Gogh Wheatfield Plus PDFjasna69No ratings yet
- The Birth of Venus Exhibition CatalogDocument20 pagesThe Birth of Venus Exhibition CatalogMica CabildoNo ratings yet
- The Timeless Allure of "The Palay Maiden"Document2 pagesThe Timeless Allure of "The Palay Maiden"ST2MB 12No ratings yet
- CPAR JFECHALIN LAS QUARTER 4 WEEK1 PortfolioDocument3 pagesCPAR JFECHALIN LAS QUARTER 4 WEEK1 PortfolioJunell Santos FechalinNo ratings yet
- Initiative 1 WB Unit7Document8 pagesInitiative 1 WB Unit7Naty FleitesNo ratings yet
- Budget of Works in Grade 7 ArtsDocument2 pagesBudget of Works in Grade 7 ArtsRichard Marquez100% (1)
- Paintings of Juan LunaDocument39 pagesPaintings of Juan LunaMiss MellowNo ratings yet
- Tabel Profil BajaDocument29 pagesTabel Profil BajaAndre FredoNo ratings yet
- Filippo BrunelleschiDocument4 pagesFilippo BrunelleschiGayathri K GNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Chicana Art and ArtistsDocument5 pagesSyllabus Chicana Art and ArtistsUCLA_SPARCNo ratings yet
- A Kinsha 2013Document698 pagesA Kinsha 2013alexander2beshkovNo ratings yet
- Art AppreciationDocument26 pagesArt AppreciationNicolaNo ratings yet
- BTS2010 ProofDocument59 pagesBTS2010 ProoftaliekNo ratings yet
- Iwan Wijono BiographieDocument2 pagesIwan Wijono BiographieImas CahayaniNo ratings yet
- Buatan Malaysia - Mix Supplier Buy Malaysia PromoDocument1 pageBuatan Malaysia - Mix Supplier Buy Malaysia PromoHairul Izwan HashimNo ratings yet
- 21st Century Architecture Handout PDFDocument2 pages21st Century Architecture Handout PDFTon GomezNo ratings yet
- Egon SchieleDocument146 pagesEgon SchieleMicaela Costilla100% (7)
- Printmaking 6th and 7th GradeDocument160 pagesPrintmaking 6th and 7th Gradeapi-711870471No ratings yet
- Cross Borough ProgrammeDocument3 pagesCross Borough ProgrammeAlessandra SciarraNo ratings yet