Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle Theory)
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle Theory)
Uploaded by
JiajunOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle Theory)
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle Theory)
Uploaded by
JiajunCopyright:
Available Formats
🥰
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle
theory) ✔️
Content
Definition
The Kinetic particle theory states that all matter is made up of tiny particles
and that these particles are in constant random motion
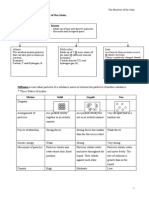
What are the three states of matter
Solid
Diagram
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle theory) ✔️ 1
Arrangement of particles
Closely packed in an orderly manner
movement of particles
Vibrate and rotate about their fixed position
Forces of attraction between particles
Very strong
kinetic energy of particles
Very slow
Liquids
Diagram
Arrangement of particles
Arranged in a disorderly manner; closely packed (less close than in
solid)
movement of particles
Slide over each other about their fixed position
Forces of attraction between particles
Strong but weaker than solid
kinetic energy of particles
More kinetic than in a solid
Gases
Diagram
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle theory) ✔️ 2
Arrangement of particles
Randomly spread very far apart from one another
movement of particles
Move about rapidly in any direction
Forces of attraction between particles
Very weak; weaker than in liquid
kinetic energy of particles
A lot of kinetic energy
Change of state
definition
Matter can change from one state to another. Changes in state is a physical
process and is reversible
What are the 6 physical changes in state of matter:
Energy taken in (4)
Melting
Boiling
Evaporation
Sublimation
Energy given out (2)
Condensation
Freezing
Heating and cooling curve
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle theory) ✔️ 3
Heating curve
ANS TEMPLATE
What happens when the substance starts to heat
the particles will gain kinetic energy and move faster
When will the temperature stop increasing
Temperature increases until it reaches melting/boiling point.
What do the energy used when it reaches melting/boiling point
They are used to overcome forces of attraction between the
particles. Therefore, kinetic energy remains constant. Therefore,
temperature remains constant
Cooling curve
Diagram
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle theory) ✔️ 4
question
What happened to the particles when it is cold
do the Temperature stop decreasing
Freezing and condensation
Whats the reason for the stop of the decrease of temperature
Thermal energy is given out to the surroundings and the
particles are are attracted to each other, kinetic energy of
particles remain constant
How is kinetic energy of particle related to temperature
Kinetic energy is proportional to temperature
During state change, KE remains Constant
Boiling VS evaporation
Temperature
Boiling
at boiling point
Evaporation
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle theory) ✔️ 5
at any temperature
where would it happen
Boiling
throughout the liquid
evaporation
only at the surface of the liquid
Speed
Boiling
fast
evaporation
slow
Bubble formation
Boiling
Yes, rise to the surface
evaporation
no
Diffusion
Definition
Is the net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to a
region of lower concentration
Factors affecting rate of diffusion
Relative molecular mass (mr)
trend
Lower the Mr, the faster the gas particles diffuse
Temperature
trend
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle theory) ✔️ 6
The higher the temperature, the higher rate of diffusion
Chapter 1 (Kinetic Particle theory) ✔️ 7
You might also like
- NZS 3101-2006 Example 001Document8 pagesNZS 3101-2006 Example 001RMM100% (1)
- Chapter 2: The Structure of The Atom.: Atoms Molecules IonsDocument9 pagesChapter 2: The Structure of The Atom.: Atoms Molecules Ionschiet pingNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument53 pagesKinetic Particle TheoryAaditya MKNo ratings yet
- Changes in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Document11 pagesChanges in The States of Matter: Chapter 4 Matter and Substance 4.1Jia JiaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Theory of ParticlesDocument14 pagesKinetic Theory of ParticlesMenaga A/P IlangkovanNo ratings yet
- C1 - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument8 pagesC1 - The Particulate Nature of MatterMariyam AfreenNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The AtomDocument57 pagesThe Structure of The AtomGranville RegalarioNo ratings yet
- Particulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Document15 pagesParticulate Nature of Matter, Unit1Keeertththana SaravananNo ratings yet
- Physics (DONE)Document17 pagesPhysics (DONE)austinchan0728No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of MatterDocument11 pagesChapter 2: Matter and The Atomic Structure: 2.1 Basic Concept of Matterforyourhonour wongNo ratings yet
- Matter and Atomic StructureDocument75 pagesMatter and Atomic StructureNurNo ratings yet
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocument6 pages2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerjohnyeapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Form 4 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 2 Form 4 PDFCikFasyareena MaoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Matters Chapter 1Document7 pagesChemistry Matters Chapter 1Ayan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Kinetic TheoryDocument6 pagesKinetic TheoryHAADiAH JAwwADNo ratings yet
- C1 Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular ForceDocument6 pagesC1 Lesson 1 Kinetic Molecular ForceAbiha Marquez KazmiNo ratings yet
- 04 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - The Particulate Nature of MatterDocument4 pages04 Copy of Compiled GenieDiary - The Particulate Nature of MatterEdric Teo Kai Feng (Msh)No ratings yet
- Definitions PhysicsDocument13 pagesDefinitions Physicslidiafnz12No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryKayla WNo ratings yet
- CHEM-Chapter 2 - State of MatterDocument13 pagesCHEM-Chapter 2 - State of Mattersecag45630No ratings yet
- 2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerDocument6 pages2A The Structure of The Atom-AnswerSiti Nursahidah0% (1)
- Igcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsDocument5 pagesIgcse Chemistry-Notes UNIT-1 The Nature of Matter: SolidsCHIO SHEUNG YONGNo ratings yet
- PHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFDocument28 pagesPHY111A 1.1.1 - Kinetic Particle Model PDFanton petrovNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v8Document24 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v8Rashi GhadiyaNo ratings yet
- 10-Kinetic Model of Matter-OrigDocument69 pages10-Kinetic Model of Matter-Origrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- 1 Kinetic Molecular ModelDocument95 pages1 Kinetic Molecular ModelMaria Khryzelle EspeñaNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Revision Notes On Thermal PhysicsDocument7 pagesIB Physics Revision Notes On Thermal PhysicsTheodore KimNo ratings yet
- Cell Practise: 1 Day 1 Main Points To Revise: Key Terms: Term DefinitionDocument3 pagesCell Practise: 1 Day 1 Main Points To Revise: Key Terms: Term DefinitionDony GregorNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v2Document24 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v2Family TimeNo ratings yet
- Mass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)Document2 pagesMass Space Atoms Molecules Electrons Three Solid Liquid Gas: (Subatomic Particles: Protons, Electrons and Neutrons)hajra chatthaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Atomic Structure 2020Document51 pagesMatter and Atomic Structure 2020caesar ljnkjtppNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v6Document22 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v6Muhammad TalalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Kinetic Particle TheorymartynchekycNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument38 pages1.1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryKéiNo ratings yet
- (CHEM CS) Chapter 2.1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryDocument11 pages(CHEM CS) Chapter 2.1 - Kinetic Particle TheoryhamzafayyazNo ratings yet
- Caie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v1Document24 pagesCaie Igcse Chemistry 0620 Theory v1mohammed darwazehNo ratings yet
- State of Matter-HighlightDocument21 pagesState of Matter-HighlightZhimingNo ratings yet
- 2021-22 - MODULE 7 - GASES - LIQUIDS - SOLIDSDocument80 pages2021-22 - MODULE 7 - GASES - LIQUIDS - SOLIDSFrancisDanielRoaNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 pagesStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinNo ratings yet
- T1 Particulate Nature of MatterDocument49 pagesT1 Particulate Nature of MatterHema LataNo ratings yet
- 2024 - Chapter 2 - KPTDocument11 pages2024 - Chapter 2 - KPTkaylamok3No ratings yet
- Liquids (Ira)Document18 pagesLiquids (Ira)Irena HaisleyNo ratings yet
- C07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)Document22 pagesC07 Kinetic Model of Matter (Teacher)a m i rNo ratings yet
- Gen - Chem - R1Document3 pagesGen - Chem - R1Kevin JamilNo ratings yet
- Bundled NotesDocument189 pagesBundled NotesAlliyah vidanesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Thermal Physics CIEDocument27 pagesUnit 2 Thermal Physics CIEShrirang ChandankhedeNo ratings yet
- SPM Chemistry 2017: AnswersDocument4 pagesSPM Chemistry 2017: AnswersLam Kah Lam KahNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Chemical KineticsDocument14 pages4.4 Chemical KineticsDamia AziziNo ratings yet
- 10-Kinetic Model of MatterDocument69 pages10-Kinetic Model of Matterrodel.verzosaNo ratings yet
- Revision Plan 2023-24 O Level ChemistryDocument14 pagesRevision Plan 2023-24 O Level ChemistryFarah LangrialNo ratings yet
- Metallic Crystals: Molecular OrderDocument3 pagesMetallic Crystals: Molecular OrderBrylle Jack PerezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SummaryDocument4 pagesChapter 1 SummarykmbgtssnbmNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Particle Theory PDFDocument38 pagesKinetic Particle Theory PDFMuhammad Darrel Keefa100% (1)
- Chemistry Form4 Chapter2 SPMDocument10 pagesChemistry Form4 Chapter2 SPMkaiqianNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Physics and Chemistry Notes: Temperature & HeatDocument1 pageClass 7 Physics and Chemistry Notes: Temperature & Heatishwari vermaNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Model NotesDocument4 pagesKinetic Model NotesAbdul rafay ImranNo ratings yet
- M1-5A - Kinetic Theory-StatesDocument11 pagesM1-5A - Kinetic Theory-StatesestherNo ratings yet
- Year7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle8Document10 pagesYear7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle8wg2xq8kddhNo ratings yet
- 2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My ExamsDocument1 page2.1.1 States of Matter CIE IGCSE Physics Revision Notes 2023 Save My Examsyichenlin111No ratings yet
- C1 Chapter 1Document1 pageC1 Chapter 1Rehan ShahNo ratings yet
- CorrosionboxDocument4 pagesCorrosionboxmankari.kamal.18022963No ratings yet
- Ventilation Air For Indoor Pools: Technical Bulletin 5Document4 pagesVentilation Air For Indoor Pools: Technical Bulletin 5samirNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard: Specification For Bitumen Emulsion For Roads (Anionic Type) (HutbDocument22 pagesIndian Standard: Specification For Bitumen Emulsion For Roads (Anionic Type) (Hutbvara prasadNo ratings yet
- Chemours Refrigerant Expert Tool User GuidelinesDocument4 pagesChemours Refrigerant Expert Tool User GuidelinesEmilio VerónNo ratings yet
- WBPSC Assistant Engineer 2019 Civil EnglishDocument15 pagesWBPSC Assistant Engineer 2019 Civil EnglishBiki Rawdy DasNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics ReviewDocument25 pagesSoil Mechanics ReviewMARK KIPKORIR MARITIMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document18 pagesChapter 7René A. BarreraNo ratings yet
- اسعار قطع غيار هافال اتش 9 بعد التحديثDocument20 pagesاسعار قطع غيار هافال اتش 9 بعد التحديثWolfox 68No ratings yet
- List of All Physics Formulas of Inter 1st YearDocument6 pagesList of All Physics Formulas of Inter 1st YearnischayboyaNo ratings yet
- Graphene From Fundamental-From Fundamental To Future ApplicationsDocument40 pagesGraphene From Fundamental-From Fundamental To Future ApplicationsMustaque Ali100% (2)
- CH-#3 Fracture Mechanics PEFMDocument35 pagesCH-#3 Fracture Mechanics PEFMhaftamuNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration and Air ConditioningDocument6 pagesRefrigeration and Air ConditioningIbrahim HossainNo ratings yet
- (L3) Ray Optics - Refraction 14th Sept PDFDocument38 pages(L3) Ray Optics - Refraction 14th Sept PDFBhaswar DuttaNo ratings yet
- PC 2009 Powder Coating GlossaryDocument2 pagesPC 2009 Powder Coating GlossaryTamoor TariqNo ratings yet
- Fermi ProblemsDocument3 pagesFermi Problemsrc735iNo ratings yet
- Sieve Shaker: Instruction ManualDocument4 pagesSieve Shaker: Instruction ManualinstrutechNo ratings yet
- Stress Classification in Pressure Vessels and Piping As Per ASME B31 and BPVC CodesDocument16 pagesStress Classification in Pressure Vessels and Piping As Per ASME B31 and BPVC CodeslorenzoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Sections Subjected To Combined Shear and Torsion-A Theoretical ModelDocument13 pagesAnalysis of Sections Subjected To Combined Shear and Torsion-A Theoretical ModelMishraq ul quraishNo ratings yet
- Irst 19 2012Document65 pagesIrst 19 2012krischaever100% (1)
- States of Matter - Solutions and MixturesDocument25 pagesStates of Matter - Solutions and MixturesYasinth ThivagarNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer ProcessDocument17 pagesEnergy Transfer Processlolomo engineerNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 2000Document26 pagesStainless Steel 2000Purushothama Nanje GowdaNo ratings yet
- Master Chemical Engineering ProgramDocument7 pagesMaster Chemical Engineering ProgramrancakNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Lithium Ion BatteryDocument9 pagesResearch Paper On Lithium Ion Batterymajvbwund100% (1)
- Fiberstrong Product InformationDocument80 pagesFiberstrong Product InformationpradeepNo ratings yet
- Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement (R Pavement (Rrap) Rap)Document28 pagesReclaimed Asphalt Pavement (R Pavement (Rrap) Rap)Biprajit SahaNo ratings yet
- Lab Assignment 2Document7 pagesLab Assignment 2lasse.stiefelNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Wembley Stadium: DR Andrew Bond, Geocentrix LTD DR Francesco Basile, Geomarc LTDDocument11 pagesCase Study - Wembley Stadium: DR Andrew Bond, Geocentrix LTD DR Francesco Basile, Geomarc LTDTamaNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers - Ultrasonic Instrument Characterizations Level 2Document6 pagesQuestions & Answers - Ultrasonic Instrument Characterizations Level 2Sathishkumar Srinivasan100% (2)