Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsDefine The Following Terms
Define The Following Terms
Uploaded by
Kelly CardejonThe document defines key terms related to management science including management science, mathematical models, variables, parameters, algorithms, and quantitative analysis approaches. It then discusses the nature of management science, outlines the steps in a quantitative analysis approach, describes types of models, discusses limitations of management science, and lists quantitative techniques used in management science.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Deciphering Data Architectures: Choosing Between A Modern Data Warehouse, Data Fabric, Data Lakehouse, and Data Mesh 1st Edition James SerraDocument43 pagesDeciphering Data Architectures: Choosing Between A Modern Data Warehouse, Data Fabric, Data Lakehouse, and Data Mesh 1st Edition James Serratimothy.thompson101100% (15)
- MODULE FOR MGMT 31 Lesson 1 3Document30 pagesMODULE FOR MGMT 31 Lesson 1 3Rotsen SebiosNo ratings yet
- Group 1report Management ScienceDocument8 pagesGroup 1report Management Scienceka3rine2022No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction HandoutDocument6 pages1 Introduction HandoutveejaydetablanNo ratings yet
- Che514 V01 Notes 1Document9 pagesChe514 V01 Notes 1Ryle ArbonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantitative AnalysisDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Quantitative AnalysisDiti biswasNo ratings yet
- TYIT SEM VI BI Nov 2019 SolutionDocument20 pagesTYIT SEM VI BI Nov 2019 SolutionvivekNo ratings yet
- Management Science (Introduction)Document15 pagesManagement Science (Introduction)rhrrakibforayeziNo ratings yet
- MBA201 OptimizationModelsforBDDocument56 pagesMBA201 OptimizationModelsforBD9801ashuNo ratings yet
- De TABLAN, Dan Alfonso (Decision-Making)Document3 pagesDe TABLAN, Dan Alfonso (Decision-Making)Dan Alfonso de TablanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative TechniquesDocument2 pagesQuantitative TechniquesPrateek Dave100% (1)
- What Is Operations Research?: Optimization Tools 1.1Document6 pagesWhat Is Operations Research?: Optimization Tools 1.1mehmetozerNo ratings yet
- MBA Quantative AnaliysisDocument123 pagesMBA Quantative AnaliysisJirka LamiNo ratings yet
- Print APUNTES TEMA 1Document7 pagesPrint APUNTES TEMA 1Amaia MartinicorenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management ScienceDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Management ScienceCheska AgrabioNo ratings yet
- Assignment in MathDocument4 pagesAssignment in Mathjulie anne mae mendozaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics 5Document15 pagesBusiness Analytics 5yadnyesh1804No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Quantitative Mangement ApproachDocument19 pagesChapter 1 - Quantitative Mangement ApproachLetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Production and Operations ManagementDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Production and Operations Managementhello_khayNo ratings yet
- MGT Science Introduction Lecture1Document26 pagesMGT Science Introduction Lecture1Nusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Quantitative Analysis For ManagementDocument1 pageCH 1 Quantitative Analysis For ManagementYna MendezNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming, Designing Awork System and Decision AnalysisDocument9 pagesLinear Programming, Designing Awork System and Decision AnalysisUMAR FAROOQNo ratings yet
- 105 - Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsDocument21 pages105 - Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsMycareer RamNo ratings yet
- Production and Operation ManagementDocument11 pagesProduction and Operation ManagementNageshwar singhNo ratings yet
- Stages of Management Consulting - Part IIDocument5 pagesStages of Management Consulting - Part IIElizabeth Espinosa ManilagNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intro To Modeling 1 - wk1Document7 pagesModule 1 - Intro To Modeling 1 - wk1bh21500155No ratings yet
- Engineering Management: Chapter 2: Decision-MakingDocument5 pagesEngineering Management: Chapter 2: Decision-MakingVincent CorpuzNo ratings yet
- It 305 - QM Lesson 1Document3 pagesIt 305 - QM Lesson 1Pia Joy Dua ReyesNo ratings yet
- Decision Making. Singapore: Cengage Learning Asia Pte LTDDocument7 pagesDecision Making. Singapore: Cengage Learning Asia Pte LTDPATRICIA COLINANo ratings yet
- BACC6A Lecture1 Jan22,2024Document4 pagesBACC6A Lecture1 Jan22,2024brythmithNo ratings yet
- Optimization Methods TheoryDocument28 pagesOptimization Methods Theorykd vlogsNo ratings yet
- Development of Quantitative Techniques or Models: By: Ruby Ellica & Gretchen JazonDocument17 pagesDevelopment of Quantitative Techniques or Models: By: Ruby Ellica & Gretchen JazonQueen Ann NavalloNo ratings yet
- Management Science Ouput 4 PDFDocument4 pagesManagement Science Ouput 4 PDFMyles Ninon LazoNo ratings yet
- Module-Chapter I-Introduction To Management Science.Document6 pagesModule-Chapter I-Introduction To Management Science.Guenivere FajaritoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document4 pagesLecture 02deadlyoverclockNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques in BusinessDocument36 pagesQuantitative Techniques in Businesstalha mudassirNo ratings yet
- New Global Vision College: Quantitative Analysis For Business DecisionDocument31 pagesNew Global Vision College: Quantitative Analysis For Business DecisionAyalew LakeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 POMDocument12 pagesAssignment 2 POMUMAR FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Or IntroductionDocument35 pagesOr IntroductionsmsmbaNo ratings yet
- Management Science NotesDocument13 pagesManagement Science NotesAndi Te'a Mari O. SimbalaNo ratings yet
- BUAD 812 Summary NotebookDocument11 pagesBUAD 812 Summary NotebookUnachukwu Sopulu SopsyNo ratings yet
- MB0044 / Set-1Document22 pagesMB0044 / Set-1cpwdroseNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 1.1 Management Science and Quantitative AnalysisDocument32 pagesUNIT-1 1.1 Management Science and Quantitative Analysisart galleryNo ratings yet
- What Is Quantitative Techniques: Evaluate The Alternatives Choose An Alternatives Implement The Selected AlternativesDocument2 pagesWhat Is Quantitative Techniques: Evaluate The Alternatives Choose An Alternatives Implement The Selected AlternativesAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Environmental Forecasting: Methods and TechniquesDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Forecasting: Methods and TechniquesCANAN HART REGO SDM COLLEGE OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT POST GRADUATE CENTRENo ratings yet
- Bba 2Document6 pagesBba 2Prajitha VPNo ratings yet
- Management Science Is A Study of ProblemDocument2 pagesManagement Science Is A Study of ProblemPauline Mariz HornillaNo ratings yet
- Management Science Power PointDocument69 pagesManagement Science Power Pointmonsourjay.gregorioNo ratings yet
- Mgt. Lecture 1Document7 pagesMgt. Lecture 1monsourjay.gregorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Decision Making: The Decision-Making Process According To David H. HoltDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Decision Making: The Decision-Making Process According To David H. HoltRoth AceNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument26 pagesDecision MakingSherwin Hila GammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.1 Introduction To Opretional ResearchDocument76 pagesChapter No.1 Introduction To Opretional Researchsuraj mauryaNo ratings yet
- TQM Trivia-Xploring Quality: Quiz #10 - Answer KeysDocument4 pagesTQM Trivia-Xploring Quality: Quiz #10 - Answer KeysShubham SouravNo ratings yet
- Operation Research by ADDocument36 pagesOperation Research by ADDaniyal AwanNo ratings yet
- Operations 1Document12 pagesOperations 1INCOGNITONo ratings yet
- Pre Mid Exam NotesDocument10 pagesPre Mid Exam NotesAngielyn PamandananNo ratings yet
- Management ScienceDocument2 pagesManagement Sciencekennethespadero00No ratings yet
- OR NoteDocument21 pagesOR Notebeth elNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1Document32 pagesMaster of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1vbolly12No ratings yet
- TaxxDocument4 pagesTaxxKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Harmonization - E-Commerce Is Global byDocument14 pagesHarmonization - E-Commerce Is Global byKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- RFBTDocument6 pagesRFBTKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document5 pagesChapter 10Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- KishaDocument1 pageKishaKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Output in EconDocument12 pagesOutput in EconKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Get Ready To Breakdown The BarrierDocument1 pageGet Ready To Breakdown The BarrierKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- DateDocument1 pageDateKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev ScriptDocument5 pagesEcon Dev ScriptKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Specialized Industry ReviewerDocument5 pagesSpecialized Industry ReviewerKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chaptr 7-12 Gov AccDocument7 pagesChaptr 7-12 Gov AccKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in STSDocument3 pagesReviewer in STSKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems Are Communities of LiDocument1 pageEcosystems Are Communities of LiKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document30 pagesChapter 4Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- TRANSACTIONCYCLESDocument26 pagesTRANSACTIONCYCLESKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- RFBT QuestionDocument7 pagesRFBT QuestionKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Are Resources Controlled by An Entity As A Result of Past EventsDocument3 pagesAre Resources Controlled by An Entity As A Result of Past EventsKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Donation of CapitalDocument1 pageDonation of CapitalKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Refers To The Percentage Change in A NationDocument1 pageRefers To The Percentage Change in A NationKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Reflection in StsDocument2 pagesReflection in StsKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument9 pagesDefinition of TermsKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Share CapitalDocument3 pagesAccounting For Share CapitalKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Add On 3Document1 pageAdd On 3Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- EXER01Document1 pageEXER01Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Unity - Control - Board Manuse c2Document11 pagesUnity - Control - Board Manuse c2Beltazor HellboyNo ratings yet
- Remotesensing 13 01279Document28 pagesRemotesensing 13 01279Ejaz ul Haq kakarNo ratings yet
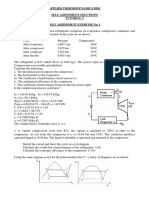
- Applied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Document4 pagesApplied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Private Vihicles POF Etag PDFDocument2 pagesPrivate Vihicles POF Etag PDFGM B&GNo ratings yet
- Basic Course in Biomedical Research Dr. Manickam Ponnaiah ICMR-National Institute of Epidemiology, Chennai Lecture - 17 Data ManagementDocument15 pagesBasic Course in Biomedical Research Dr. Manickam Ponnaiah ICMR-National Institute of Epidemiology, Chennai Lecture - 17 Data ManagementGksNo ratings yet
- LogDocument84 pagesLogputri sulungNo ratings yet
- Dynamic ProgrammingpdfDocument27 pagesDynamic ProgrammingpdfNiloy BarmonNo ratings yet
- Canon AF 514 XL-S Motor Not Working. It Used To But After Placing The Film and Left It There For A Few Days It Stopped - R - 8mmDocument6 pagesCanon AF 514 XL-S Motor Not Working. It Used To But After Placing The Film and Left It There For A Few Days It Stopped - R - 8mmsabo6181No ratings yet
- Reliability Standards - PRC-024-2Document12 pagesReliability Standards - PRC-024-2aji.isramboNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsDocument17 pagesA Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsRupert WalkerNo ratings yet
- Jessore Felicity BigData Data Center Solution - V1.0Document19 pagesJessore Felicity BigData Data Center Solution - V1.0Muhtadin IqbalNo ratings yet
- XI-921 Service ManualDocument31 pagesXI-921 Service ManualLuc YaoNo ratings yet
- CAT S61: The Advanced Tool To Help Get Any Job DoneDocument2 pagesCAT S61: The Advanced Tool To Help Get Any Job DoneDouglas Gaitan PotosmeNo ratings yet
- Bulk Flow - Micro/ultrafiltrationDocument5 pagesBulk Flow - Micro/ultrafiltrationjaNo ratings yet
- Software DevelopmentDocument272 pagesSoftware Developmentszpakos100% (1)
- PAPER ID: 1078: B. TechDocument7 pagesPAPER ID: 1078: B. TechLovish SheikhNo ratings yet
- Model Operator'S Manual: Non Contact TonometerDocument100 pagesModel Operator'S Manual: Non Contact TonometerRitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Https WWW - Kaad-Application - deDocument4 pagesHttps WWW - Kaad-Application - definrancotheranarciso NeuropathyNo ratings yet
- APBI Summary FY2017-2018Document35 pagesAPBI Summary FY2017-2018Osorio LuisNo ratings yet
- Certification Training Program Schedule 2023Document12 pagesCertification Training Program Schedule 2023Simon SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Awb200 Poh v.2.0.1Document180 pagesAwb200 Poh v.2.0.1Allanpilot100% (2)
- Ford FANUC R30iA R30iB NextGen E10Document19 pagesFord FANUC R30iA R30iB NextGen E10marialuisafloressanabriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quadratic FunctionDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Quadratic Functionmunxin02No ratings yet
- C1200 Manual VER1.02Document27 pagesC1200 Manual VER1.02ovidiug1982No ratings yet
- CEE 9531 Wind Energy Course Outline - January - April 2018Document4 pagesCEE 9531 Wind Energy Course Outline - January - April 2018Anonymous fYHyRa2XNo ratings yet
- DTV Group: Positions Job Description CertificationDocument6 pagesDTV Group: Positions Job Description CertificationhdnutzNo ratings yet
- Calculatecylinder HeadsDocument23 pagesCalculatecylinder HeadsAwingNo ratings yet
- KS0077 (78,79) Super Learning Kit For ArduinoDocument315 pagesKS0077 (78,79) Super Learning Kit For ArduinoАнтон ПыхаловNo ratings yet
- Agosto 2022.COMPUTERS FOR THE DISABLEDDocument2 pagesAgosto 2022.COMPUTERS FOR THE DISABLEDSoraSosaNo ratings yet
Define The Following Terms
Define The Following Terms
Uploaded by
Kelly Cardejon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesThe document defines key terms related to management science including management science, mathematical models, variables, parameters, algorithms, and quantitative analysis approaches. It then discusses the nature of management science, outlines the steps in a quantitative analysis approach, describes types of models, discusses limitations of management science, and lists quantitative techniques used in management science.
Original Description:
Original Title
Define the following terms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines key terms related to management science including management science, mathematical models, variables, parameters, algorithms, and quantitative analysis approaches. It then discusses the nature of management science, outlines the steps in a quantitative analysis approach, describes types of models, discusses limitations of management science, and lists quantitative techniques used in management science.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesDefine The Following Terms
Define The Following Terms
Uploaded by
Kelly CardejonThe document defines key terms related to management science including management science, mathematical models, variables, parameters, algorithms, and quantitative analysis approaches. It then discusses the nature of management science, outlines the steps in a quantitative analysis approach, describes types of models, discusses limitations of management science, and lists quantitative techniques used in management science.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
1.
Define the following terms:
a. Management Science is applying a scientific approach to solving management
problems to help managers make better decisions. It encompasses several
mathematically oriented techniques that have either been developed within the
field of management science or been adopted from other disciplines such as
natural sciences, mathematics, statistics and engineers. Management Science is
a recognized and established discipline in business. The application of
management science techniques is widespread and has been frequently credited
with increasing the efficiency and productivity of firms.
b. A mathematical model represents a mathematical relationship of variables and
their parameters. It is expressed in inequalities and equations. Mathematical
models are a critical part of any quantitative approach to decision-making. The
predictions then provide a road map for further experimentation.
c. Variables are unknown quantities whose values must be determined. Models
generally contain variables, either controllable or uncontrollable. Controllable
variables usually are the decision variables and are generally unknown. The
symbols x and Z are variables. The term variables is used because no set
numeric value has been specified for these items. The number of unjt sold, x,
and the profit, Z, can be any amount (within limits); they can vary.
d. Parameters are known quantities that are a part of the problem and whose
values are generally given. These are constant values that are generally
coefficients of the variables or symbols in an equation. Parameters usually
remain constant during the process of solving a specific problem.
e. Algorithm is a series of repeating steps to reach a solution. It is one of the
techniques to find the best solution to a problem. These are commonly found by
manipulating the model variables until a solution is found that is practical and can
be implemented.
f. A quantitative analysis approach is a scientific approach to managerial
decision-making whereby raw data are processed and manipulated, resulting in
meaningful information. It can be applied to a wide variety of problems.
Management science employs this approach in handling managerial issues.
Management science encompasses a logical, systematic approach to problem-
solving, which parallels the scientific method for attacking problems.
2. State the nature of management science.
The major characteristics of management science are as follows:
a) It is a primarily intended to solve management problems or dilemmas.
b) It uses quantitative tools or mathematical models in finding solutions to
management problems.
c) It observes the assumptions inherent In a particular quantitative information
and analysis
d) It does not violate the constrains or limitations of a particular quantitative
model.
e) It adopts a decision based entirely on quantitative information and analysis.
f) It employs the quantitative and analysis approach in finding the optimal
solutions.
3. Identify the steps in the quantitative analysis approach.
The quantitative analysis approach consists of the following steps:
a) Defining the management problem
-This step involves the process of clearly identifying the problem that besets
management. The process of identifying the real management problem is difficult
task to undertake. The main concern is to improve the profitability level and
reduce the costs of business organization.
b) Developing a Mathematical Model
-A model is a representation of an event, situation, relationship or reality. The
quantitative model can only handle one problem at a time. The different types of
models may include a physical model, scale model, schematic model, or
mathematical model.
c) Gathering Quantitative Model
-The two important factors that must be considered in collection of quantitative
data are the accuracy of the data and the reliability of the source. The result
become misleading and doubtful when there is a question on the correctness of
the data or reliability of the source.
d) Finding Optimal Solution
-This step involves the mathematical manipulation of a model to arrive at the
optimal solution.
e) Checking the Results
-This process involves reviewing the accuracy and completeness of the data
used in the model. The gathering of additional data may be undertaken to
collaborate or support the findings or results of previously collected data.
f) Analyzing and Evaluating the Findings
-Analysis involves the breaking of the entire quantitative approach into several
parts and evaluating the results refers to making judgements based on a
particular standard.
g) Implementing Findings
-This happens when management has understood the underlying concepts of the
approach conducted and is fully convinced of the likelihood that the quantitative
findings will provide financial benefits to the business organizations.
4. Describe the different types of models.
The different type of models include:
A. Physical Model- is a representation of a building, condominium, or hotel that
engineers may construct or develop.
B. Scale Model- is a representation of a car, airplane, heavy equipment, tools, or
machinery that manufacturers may produce.
C. Schematic Model- is a graphical diagram, picture, drawing, or image of device
or mechanical parts.
D. Mathematical Model- is a representation of mathematical relationships of
variables and their parameter. It is expressed in inequalities or equations.
5. Discuss the LimPitations of Management Science
a. The members of management may have contradicting perspectives
regarding a problem, which could lead to resistance. A solution to one
might have a contrasting outcome to other as it may provide a negative
outlook or additional effort and time that is not included on the initial plan.
Such as when the inventory of the marketing department does not reach
its average level, one way to solve this problem is to increase the
production. The Finance and Operation Department will resist s it would
greatly affect the cash flow problems, product quality, availability of raw
materials and cost efficiency problems.
b. A mathematical model cannot be fitted to all kinds of management
processes as the assumptions fall short of real-world situations.
Management problems that are more human that technical such as
staffing, leadership and organizing can hardly be solved using the
quantitative tools of Management Sciences.
c. The collected data by either accounting department or other functional
areas may be insufficient for quantitative analysis. It prescribes a limited
number of tools for solving specific problems, and the effective utilization
of these tools requires some level of expertise and technical skills.
d. The quantitative analysis approach employs only quantitative data and
provide solutions based on mathematical representation. The theory
ignores the importance of people, relationships and other non-quantifiable
factors. Some aspects of management activities cannot be easily
quantified because they involve some human elements which are
unpredictable.
6. State the different quantitative techniques used in management science.
Various quantitative techniques and those that are included in the new curriculum of
the business program are as follows:
a. Linear Programming- Linear Programming is a problem-solving approach
developed for situations involving maximizing or minimizing a linear function
subject to linear constraints that limit the degree to which the objective an be
pursued.
b. Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis- modeling technique to determine the number of
units to sell or produce that will result in zero profit. It evaluated the
relationship among revenue, cost, and expenses.
c. Economic order Quantity model- is a company's optimal order quantity for
minimizing its total costs related to ordering, receiving, and holding inventory.
d. Decision theory- it is a systematic approach to making a decision from
different alternatives under a particular decision-making environment.
e. Regression Analysis- it is a quantitative technique used in determining the
relationship between the dependent variable and independent variable in
terms of linearity and strength.
f. Queuing theory- it is a quantitative study that examines every component of a
queue or waiting line, including congestion and delays.
g. Program evaluation review technique/ Critical path method- it is a quantitative
technique used in scheduling, organizing, and coordinating different
interrelated activities of particular project.
h. Probability Concept- it is a quantitative technique designed to determine the
expected value of estimates in relation to the occurrence of an event.
You might also like
- Deciphering Data Architectures: Choosing Between A Modern Data Warehouse, Data Fabric, Data Lakehouse, and Data Mesh 1st Edition James SerraDocument43 pagesDeciphering Data Architectures: Choosing Between A Modern Data Warehouse, Data Fabric, Data Lakehouse, and Data Mesh 1st Edition James Serratimothy.thompson101100% (15)
- MODULE FOR MGMT 31 Lesson 1 3Document30 pagesMODULE FOR MGMT 31 Lesson 1 3Rotsen SebiosNo ratings yet
- Group 1report Management ScienceDocument8 pagesGroup 1report Management Scienceka3rine2022No ratings yet
- 1 Introduction HandoutDocument6 pages1 Introduction HandoutveejaydetablanNo ratings yet
- Che514 V01 Notes 1Document9 pagesChe514 V01 Notes 1Ryle ArbonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantitative AnalysisDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Quantitative AnalysisDiti biswasNo ratings yet
- TYIT SEM VI BI Nov 2019 SolutionDocument20 pagesTYIT SEM VI BI Nov 2019 SolutionvivekNo ratings yet
- Management Science (Introduction)Document15 pagesManagement Science (Introduction)rhrrakibforayeziNo ratings yet
- MBA201 OptimizationModelsforBDDocument56 pagesMBA201 OptimizationModelsforBD9801ashuNo ratings yet
- De TABLAN, Dan Alfonso (Decision-Making)Document3 pagesDe TABLAN, Dan Alfonso (Decision-Making)Dan Alfonso de TablanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative TechniquesDocument2 pagesQuantitative TechniquesPrateek Dave100% (1)
- What Is Operations Research?: Optimization Tools 1.1Document6 pagesWhat Is Operations Research?: Optimization Tools 1.1mehmetozerNo ratings yet
- MBA Quantative AnaliysisDocument123 pagesMBA Quantative AnaliysisJirka LamiNo ratings yet
- Print APUNTES TEMA 1Document7 pagesPrint APUNTES TEMA 1Amaia MartinicorenaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Management ScienceDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Management ScienceCheska AgrabioNo ratings yet
- Assignment in MathDocument4 pagesAssignment in Mathjulie anne mae mendozaNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics 5Document15 pagesBusiness Analytics 5yadnyesh1804No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Quantitative Mangement ApproachDocument19 pagesChapter 1 - Quantitative Mangement ApproachLetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Production and Operations ManagementDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Production and Operations Managementhello_khayNo ratings yet
- MGT Science Introduction Lecture1Document26 pagesMGT Science Introduction Lecture1Nusrat JahanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Quantitative Analysis For ManagementDocument1 pageCH 1 Quantitative Analysis For ManagementYna MendezNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming, Designing Awork System and Decision AnalysisDocument9 pagesLinear Programming, Designing Awork System and Decision AnalysisUMAR FAROOQNo ratings yet
- 105 - Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsDocument21 pages105 - Quantitative Analysis For Management DecisionsMycareer RamNo ratings yet
- Production and Operation ManagementDocument11 pagesProduction and Operation ManagementNageshwar singhNo ratings yet
- Stages of Management Consulting - Part IIDocument5 pagesStages of Management Consulting - Part IIElizabeth Espinosa ManilagNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intro To Modeling 1 - wk1Document7 pagesModule 1 - Intro To Modeling 1 - wk1bh21500155No ratings yet
- Engineering Management: Chapter 2: Decision-MakingDocument5 pagesEngineering Management: Chapter 2: Decision-MakingVincent CorpuzNo ratings yet
- It 305 - QM Lesson 1Document3 pagesIt 305 - QM Lesson 1Pia Joy Dua ReyesNo ratings yet
- Decision Making. Singapore: Cengage Learning Asia Pte LTDDocument7 pagesDecision Making. Singapore: Cengage Learning Asia Pte LTDPATRICIA COLINANo ratings yet
- BACC6A Lecture1 Jan22,2024Document4 pagesBACC6A Lecture1 Jan22,2024brythmithNo ratings yet
- Optimization Methods TheoryDocument28 pagesOptimization Methods Theorykd vlogsNo ratings yet
- Development of Quantitative Techniques or Models: By: Ruby Ellica & Gretchen JazonDocument17 pagesDevelopment of Quantitative Techniques or Models: By: Ruby Ellica & Gretchen JazonQueen Ann NavalloNo ratings yet
- Management Science Ouput 4 PDFDocument4 pagesManagement Science Ouput 4 PDFMyles Ninon LazoNo ratings yet
- Module-Chapter I-Introduction To Management Science.Document6 pagesModule-Chapter I-Introduction To Management Science.Guenivere FajaritoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document4 pagesLecture 02deadlyoverclockNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Techniques in BusinessDocument36 pagesQuantitative Techniques in Businesstalha mudassirNo ratings yet
- New Global Vision College: Quantitative Analysis For Business DecisionDocument31 pagesNew Global Vision College: Quantitative Analysis For Business DecisionAyalew LakeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 POMDocument12 pagesAssignment 2 POMUMAR FAROOQNo ratings yet
- Or IntroductionDocument35 pagesOr IntroductionsmsmbaNo ratings yet
- Management Science NotesDocument13 pagesManagement Science NotesAndi Te'a Mari O. SimbalaNo ratings yet
- BUAD 812 Summary NotebookDocument11 pagesBUAD 812 Summary NotebookUnachukwu Sopulu SopsyNo ratings yet
- MB0044 / Set-1Document22 pagesMB0044 / Set-1cpwdroseNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1 1.1 Management Science and Quantitative AnalysisDocument32 pagesUNIT-1 1.1 Management Science and Quantitative Analysisart galleryNo ratings yet
- What Is Quantitative Techniques: Evaluate The Alternatives Choose An Alternatives Implement The Selected AlternativesDocument2 pagesWhat Is Quantitative Techniques: Evaluate The Alternatives Choose An Alternatives Implement The Selected AlternativesAbrahamNo ratings yet
- Environmental Forecasting: Methods and TechniquesDocument5 pagesEnvironmental Forecasting: Methods and TechniquesCANAN HART REGO SDM COLLEGE OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT POST GRADUATE CENTRENo ratings yet
- Bba 2Document6 pagesBba 2Prajitha VPNo ratings yet
- Management Science Is A Study of ProblemDocument2 pagesManagement Science Is A Study of ProblemPauline Mariz HornillaNo ratings yet
- Management Science Power PointDocument69 pagesManagement Science Power Pointmonsourjay.gregorioNo ratings yet
- Mgt. Lecture 1Document7 pagesMgt. Lecture 1monsourjay.gregorioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Decision Making: The Decision-Making Process According To David H. HoltDocument2 pagesChapter 2: Decision Making: The Decision-Making Process According To David H. HoltRoth AceNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument26 pagesDecision MakingSherwin Hila GammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter No.1 Introduction To Opretional ResearchDocument76 pagesChapter No.1 Introduction To Opretional Researchsuraj mauryaNo ratings yet
- TQM Trivia-Xploring Quality: Quiz #10 - Answer KeysDocument4 pagesTQM Trivia-Xploring Quality: Quiz #10 - Answer KeysShubham SouravNo ratings yet
- Operation Research by ADDocument36 pagesOperation Research by ADDaniyal AwanNo ratings yet
- Operations 1Document12 pagesOperations 1INCOGNITONo ratings yet
- Pre Mid Exam NotesDocument10 pagesPre Mid Exam NotesAngielyn PamandananNo ratings yet
- Management ScienceDocument2 pagesManagement Sciencekennethespadero00No ratings yet
- OR NoteDocument21 pagesOR Notebeth elNo ratings yet
- Master of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1Document32 pagesMaster of Business Administration Semester 2 Project Management Assignment Set-1vbolly12No ratings yet
- TaxxDocument4 pagesTaxxKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Harmonization - E-Commerce Is Global byDocument14 pagesHarmonization - E-Commerce Is Global byKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- RFBTDocument6 pagesRFBTKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document5 pagesChapter 10Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- KishaDocument1 pageKishaKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Output in EconDocument12 pagesOutput in EconKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Get Ready To Breakdown The BarrierDocument1 pageGet Ready To Breakdown The BarrierKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- DateDocument1 pageDateKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Econ Dev ScriptDocument5 pagesEcon Dev ScriptKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Specialized Industry ReviewerDocument5 pagesSpecialized Industry ReviewerKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chaptr 7-12 Gov AccDocument7 pagesChaptr 7-12 Gov AccKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in STSDocument3 pagesReviewer in STSKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems Are Communities of LiDocument1 pageEcosystems Are Communities of LiKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document30 pagesChapter 4Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- TRANSACTIONCYCLESDocument26 pagesTRANSACTIONCYCLESKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- RFBT QuestionDocument7 pagesRFBT QuestionKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document20 pagesChapter 1Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Are Resources Controlled by An Entity As A Result of Past EventsDocument3 pagesAre Resources Controlled by An Entity As A Result of Past EventsKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Donation of CapitalDocument1 pageDonation of CapitalKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Refers To The Percentage Change in A NationDocument1 pageRefers To The Percentage Change in A NationKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Reflection in StsDocument2 pagesReflection in StsKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument9 pagesDefinition of TermsKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Share CapitalDocument3 pagesAccounting For Share CapitalKelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Add On 3Document1 pageAdd On 3Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- EXER01Document1 pageEXER01Kelly CardejonNo ratings yet
- Unity - Control - Board Manuse c2Document11 pagesUnity - Control - Board Manuse c2Beltazor HellboyNo ratings yet
- Remotesensing 13 01279Document28 pagesRemotesensing 13 01279Ejaz ul Haq kakarNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Document4 pagesApplied Thermodynamics D201 Self Assessment Solutions Tutorial 5 Self Assessment Exercise No. 1Alexander MugabeNo ratings yet
- Private Vihicles POF Etag PDFDocument2 pagesPrivate Vihicles POF Etag PDFGM B&GNo ratings yet
- Basic Course in Biomedical Research Dr. Manickam Ponnaiah ICMR-National Institute of Epidemiology, Chennai Lecture - 17 Data ManagementDocument15 pagesBasic Course in Biomedical Research Dr. Manickam Ponnaiah ICMR-National Institute of Epidemiology, Chennai Lecture - 17 Data ManagementGksNo ratings yet
- LogDocument84 pagesLogputri sulungNo ratings yet
- Dynamic ProgrammingpdfDocument27 pagesDynamic ProgrammingpdfNiloy BarmonNo ratings yet
- Canon AF 514 XL-S Motor Not Working. It Used To But After Placing The Film and Left It There For A Few Days It Stopped - R - 8mmDocument6 pagesCanon AF 514 XL-S Motor Not Working. It Used To But After Placing The Film and Left It There For A Few Days It Stopped - R - 8mmsabo6181No ratings yet
- Reliability Standards - PRC-024-2Document12 pagesReliability Standards - PRC-024-2aji.isramboNo ratings yet
- A Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsDocument17 pagesA Quick Guide To Digital Video Resolution and Aspect Ratio ConversionsRupert WalkerNo ratings yet
- Jessore Felicity BigData Data Center Solution - V1.0Document19 pagesJessore Felicity BigData Data Center Solution - V1.0Muhtadin IqbalNo ratings yet
- XI-921 Service ManualDocument31 pagesXI-921 Service ManualLuc YaoNo ratings yet
- CAT S61: The Advanced Tool To Help Get Any Job DoneDocument2 pagesCAT S61: The Advanced Tool To Help Get Any Job DoneDouglas Gaitan PotosmeNo ratings yet
- Bulk Flow - Micro/ultrafiltrationDocument5 pagesBulk Flow - Micro/ultrafiltrationjaNo ratings yet
- Software DevelopmentDocument272 pagesSoftware Developmentszpakos100% (1)
- PAPER ID: 1078: B. TechDocument7 pagesPAPER ID: 1078: B. TechLovish SheikhNo ratings yet
- Model Operator'S Manual: Non Contact TonometerDocument100 pagesModel Operator'S Manual: Non Contact TonometerRitesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Https WWW - Kaad-Application - deDocument4 pagesHttps WWW - Kaad-Application - definrancotheranarciso NeuropathyNo ratings yet
- APBI Summary FY2017-2018Document35 pagesAPBI Summary FY2017-2018Osorio LuisNo ratings yet
- Certification Training Program Schedule 2023Document12 pagesCertification Training Program Schedule 2023Simon SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- Awb200 Poh v.2.0.1Document180 pagesAwb200 Poh v.2.0.1Allanpilot100% (2)
- Ford FANUC R30iA R30iB NextGen E10Document19 pagesFord FANUC R30iA R30iB NextGen E10marialuisafloressanabriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Quadratic FunctionDocument3 pagesChapter 2 Quadratic Functionmunxin02No ratings yet
- C1200 Manual VER1.02Document27 pagesC1200 Manual VER1.02ovidiug1982No ratings yet
- CEE 9531 Wind Energy Course Outline - January - April 2018Document4 pagesCEE 9531 Wind Energy Course Outline - January - April 2018Anonymous fYHyRa2XNo ratings yet
- DTV Group: Positions Job Description CertificationDocument6 pagesDTV Group: Positions Job Description CertificationhdnutzNo ratings yet
- Calculatecylinder HeadsDocument23 pagesCalculatecylinder HeadsAwingNo ratings yet
- KS0077 (78,79) Super Learning Kit For ArduinoDocument315 pagesKS0077 (78,79) Super Learning Kit For ArduinoАнтон ПыхаловNo ratings yet
- Agosto 2022.COMPUTERS FOR THE DISABLEDDocument2 pagesAgosto 2022.COMPUTERS FOR THE DISABLEDSoraSosaNo ratings yet