Professional Documents
Culture Documents
cONCEPT OF POLYGON
cONCEPT OF POLYGON
Uploaded by
Jezrael Nacion0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views17 pagesThe document discusses two theorems about polygon angles:
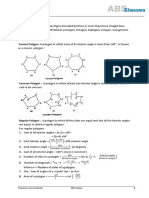
1) The interior angle sum theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of an n-sided polygon is (n-2)×180 degrees.
2) The exterior angle sum theorem states that the sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees. The theorem is proved and an example is given to demonstrate finding an unknown exterior angle.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses two theorems about polygon angles:
1) The interior angle sum theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of an n-sided polygon is (n-2)×180 degrees.
2) The exterior angle sum theorem states that the sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees. The theorem is proved and an example is given to demonstrate finding an unknown exterior angle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views17 pagescONCEPT OF POLYGON
cONCEPT OF POLYGON
Uploaded by
Jezrael NacionThe document discusses two theorems about polygon angles:
1) The interior angle sum theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of an n-sided polygon is (n-2)×180 degrees.
2) The exterior angle sum theorem states that the sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360 degrees. The theorem is proved and an example is given to demonstrate finding an unknown exterior angle.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 17
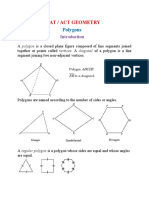
POLYGON
Polygon Interior Angles Sum Theorem
Polygon Interior Angles Sum Theorem
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a convex polygon
with n� sides is
(n−2)180°(�−2)180° .
Example :
Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of an octagon.
Solution:
An octagon has 8 sides. So, n=8�=8 .
Substitute 8 for n� in the formula.
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of an
octagon =(8−2)180°=6×180°=1080°
The sum of the measures of the interior angles of an octagon is 1080°
Polygon Exterior Angle Sum Theorem
If a polygon is a convex polygon, then the sum of its exterior angles (one at each vertex)
is equal to 360 degrees. Let us prove this theorem:
Proof: Consider a polygon with n number of sides or an n-gon. The sum of its exterior
angles is N.
For any closed structure, formed by sides and vertex, the sum of the exterior angles is
always equal to the sum of linear pairs and sum of interior angles. Therefore,
N = 180n – 180(n-2)
N = 180n – 180n + 360
N = 360
Hence, we got the sum of exterior angles of n vertex equal to 360 degrees.
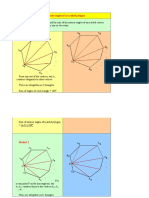
Example 1: In the given figure, find the value of x.
Exterior angle example
Solution: We know that the sum of exterior angles of a polygon is 360 degrees.
Thus, 70° + 60° + 65° + 40° + x = 360°
235° + x = 360°
X = 360° – 235° = 125°
You might also like
- JSS2 Maths 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFDocument60 pagesJSS2 Maths 3rd Term Lesson Note PDFmichael nwoye100% (1)
- Angles - Exam Revision and QuestionsDocument11 pagesAngles - Exam Revision and QuestionsShah Hasan FarazNo ratings yet
- ACT Geometry - PolygonsDocument8 pagesACT Geometry - PolygonsaftabNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Q3 Week 5Document4 pagesWorksheet Q3 Week 5Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Polygon and Angles: DefinitionDocument5 pagesPolygon and Angles: DefinitionWisal muhammedNo ratings yet
- Angles of PolygonsDocument3 pagesAngles of PolygonsLhoy Guisihan Asoy IdulsaNo ratings yet
- CBSE NCERT CLASS 8 MATH CH 3 WORKSHEETDocument4 pagesCBSE NCERT CLASS 8 MATH CH 3 WORKSHEETSwarupa KannaNo ratings yet
- COT1 Polygon CLAROSDocument42 pagesCOT1 Polygon CLAROSShengrace GavinoNo ratings yet
- Find The Sum of The Interior Angles of A HeptagonDocument1 pageFind The Sum of The Interior Angles of A HeptagonEver Sanchez Capuras CalipayNo ratings yet
- 8 Polygons Solved Questions PaperDocument2 pages8 Polygons Solved Questions PaperSandeep KamatNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument21 pagesPolygon2ways69No ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 Page 1Document3 pagesWorksheet 1 Page 1Nathaniel PascuaNo ratings yet
- Mathintiiu28polygons AreaDocument29 pagesMathintiiu28polygons AreaJohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Polygon PDFDocument32 pagesChapter2 Polygon PDFNurmala Bt JamaludinNo ratings yet
- Grade 7: Applications of PolygonDocument9 pagesGrade 7: Applications of PolygonMa Teneza BarberoNo ratings yet
- figtree_POLYGONS1Document16 pagesfigtree_POLYGONS1prince.usheNo ratings yet
- Relationship Exterior and Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonDocument10 pagesRelationship Exterior and Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonpamfilodavejohnNo ratings yet
- Sum of Interior Angles of An NDocument13 pagesSum of Interior Angles of An Nமாதவன் மகேஸ்வரிNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Angles of Polygons Powerpoint-2Document13 pages8.1 Angles of Polygons Powerpoint-2Ghia RelucioNo ratings yet
- Polygons: Plane and Solid GeometryDocument37 pagesPolygons: Plane and Solid GeometryMarjorie MalvedaNo ratings yet
- 2 CH 6-1 Sum of Interior and Exterior Angles in PolygonsDocument31 pages2 CH 6-1 Sum of Interior and Exterior Angles in PolygonshinitahNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals: AB, BC, CD, and DA Are Sides andDocument5 pagesQuadrilaterals: AB, BC, CD, and DA Are Sides andAlliah Mae CastilNo ratings yet
- Angles of A PolygonDocument3 pagesAngles of A PolygondeeniboyxaNo ratings yet
- Captura de Pantalla 2022-09-25 A La(s) 11.10.37 P.M.Document1 pageCaptura de Pantalla 2022-09-25 A La(s) 11.10.37 P.M.perlaaNo ratings yet
- Different Word Problem Involving PolygonsDocument11 pagesDifferent Word Problem Involving PolygonsAlice PaduaNo ratings yet
- LAS Week 9 - MELC 42Document4 pagesLAS Week 9 - MELC 42Angelo Rey NavaNo ratings yet
- Digital Text BookDocument12 pagesDigital Text BookBindu Vinu100% (1)
- Polygons: Submitted By, Reshma S Ravi Mathematics OptionDocument15 pagesPolygons: Submitted By, Reshma S Ravi Mathematics OptionPrasant NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Pre Calculus ReviewerDocument21 pagesPre Calculus ReviewerAndrei SamaritaNo ratings yet
- 6 - PolygonDocument11 pages6 - PolygonKevin Heather TVNo ratings yet
- Interior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsDocument16 pagesInterior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsKENO MARTIN ADVIENTONo ratings yet
- Interior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsDocument16 pagesInterior and Exterior Angles of Polygonsshivek2011guptaNo ratings yet
- Interior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsDocument16 pagesInterior and Exterior Angles of Polygonsshivek2011guptaNo ratings yet
- Write Up of All Angle RulesDocument6 pagesWrite Up of All Angle Rulesapi-233663523100% (1)
- 13.1 Interior Angles of Polygons PDFDocument6 pages13.1 Interior Angles of Polygons PDFMohamed ElsaadawiNo ratings yet
- Review in Plane TrigonometryDocument51 pagesReview in Plane TrigonometryDoone Heart Santander CabuguasNo ratings yet
- Angles in A Polygon... 1Document10 pagesAngles in A Polygon... 1aymanahmedbuhariNo ratings yet
- 1ro Sec PPT PoligonosDocument18 pages1ro Sec PPT PoligonosEnrique Espino MaravíNo ratings yet
- 227340285 Angles Exam Revision and QuestionsDocument10 pages227340285 Angles Exam Revision and QuestionsadryemmyokikiolajerryNo ratings yet
- SI Geometry Honors Edition chp6Document54 pagesSI Geometry Honors Edition chp6Renier Palma CruzNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions Dec2020 For Class 8 Maths Chapter 3Document17 pagesNcert Solutions Dec2020 For Class 8 Maths Chapter 3ArchanaNo ratings yet
- 2-Math 7-Q3-Week 6-Relationships of Exterior and Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonDocument45 pages2-Math 7-Q3-Week 6-Relationships of Exterior and Interior Angles of A Convex PolygonAngela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- g7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesDocument40 pagesg7 Polygons Interior and Exterior AnglesTenten Peter100% (1)
- Angles - Exam Revision and QuestionsDocument10 pagesAngles - Exam Revision and Questionsben chordNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument11 pagesPolygonMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Geom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketDocument22 pagesGeom CH 08 Polygon Angle Sum PacketAnela100% (1)
- Exact Trigonometric Constants 2Document16 pagesExact Trigonometric Constants 2Sahil JindalNo ratings yet
- Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding QuadrilateralsWai MarNo ratings yet
- QA - PolygonsDocument3 pagesQA - PolygonschaostheoristNo ratings yet
- Angles in Polygons (Print)Document6 pagesAngles in Polygons (Print)Suchaya AngsakulNo ratings yet
- 6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum TheoremsDocument18 pages6-1 The Polygon Angle-Sum TheoremsMary Ann Nazar100% (1)
- Polygons InvestigationDocument3 pagesPolygons InvestigationTomáš KňazeNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsDocument23 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 Maths May22 Chapter 3 Understanding QuadrilateralsmohnishsainiNo ratings yet
- Geometry: Simple Closed Union of Three or More Line Segments No Two Successive Line Segments Are CollinearDocument15 pagesGeometry: Simple Closed Union of Three or More Line Segments No Two Successive Line Segments Are Collinearzinawbizu filipos100% (1)
- Angles: Interior AngleDocument1 pageAngles: Interior AngleAliahMharuPabloNo ratings yet
- Properties of Regular PentagonsDocument3 pagesProperties of Regular PentagonshimanshujainnNo ratings yet
- PRECAL Final Module 1 4Document41 pagesPRECAL Final Module 1 4Glen MillarNo ratings yet