Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 viewsHirschsprungs Disease Handout
Hirschsprungs Disease Handout
Uploaded by
rigasanaoray1) Hirschsprung's disease is a birth defect where part of the colon lacks nerve cells causing blockage. Symptoms appear between 6-12 months including poor weight gain and infrequent hard stools.
2) Diagnosis involves rectal biopsy and other tests. Treatment includes decompression with NG tubes or irrigation, surgery to remove the blocked part of colon, and management of nutrition and infections.
3) Surgical options depend on age, health, and extent of blockage. They include colostomy then pull-through or single stage pull-through. Post-op care focuses on colostomy care, feeding, and managing complications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Sce Geriatric Medicine Sample QsDocument67 pagesSce Geriatric Medicine Sample QsZoya Annam100% (7)
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome Case PresentationDocument26 pagesMeconium Aspiration Syndrome Case Presentationkis100% (2)
- Urine Test Strips and Microscopy: Compendium of UrinalysisDocument180 pagesUrine Test Strips and Microscopy: Compendium of UrinalysisLory LaneNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Gastroenterology Flashcards - MemorangDocument4 pagesPediatric Gastroenterology Flashcards - MemorangRa ViNo ratings yet
- Ferna-Case AnalysisDocument13 pagesFerna-Case Analysisbea pegadNo ratings yet
- (Aganglionic Megacolon) : Hirschsprung'S DiseaseDocument2 pages(Aganglionic Megacolon) : Hirschsprung'S DiseaseLalisaM ActivityNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument7 pagesPeritonitisrina yulianaNo ratings yet
- Askep HisprungDocument25 pagesAskep HisprungRika AmaliyaNo ratings yet
- Gastro Key NotesDocument11 pagesGastro Key NotesHannah aswini100% (1)
- Cystic FibrosisDocument3 pagesCystic FibrosisRieza NurdinsyahNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNDocument14 pagesCommon Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- Maternal Finals Key TermsDocument5 pagesMaternal Finals Key TermsRomer Basadre Jr.No ratings yet
- Intestinal Atresia: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesIntestinal Atresia: A Case ReportOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Hirsch SprungDocument16 pagesHirsch SprungjessyNo ratings yet
- Paeds Bilious VomitingDocument2 pagesPaeds Bilious Vomitingsinghurvashi365No ratings yet
- Hirschsprun G'S Disease: Dr. Manish Kumar Gupta Assistant Professor Department of Paediatric Surgery AIIMS, RishikeshDocument48 pagesHirschsprun G'S Disease: Dr. Manish Kumar Gupta Assistant Professor Department of Paediatric Surgery AIIMS, RishikeshArchana Mahata100% (1)
- Ob2 Sas 19Document9 pagesOb2 Sas 19Ralph Louie ManagoNo ratings yet
- BALON, JOHN LOWIE O - Hirschsprung's DiseaseDocument12 pagesBALON, JOHN LOWIE O - Hirschsprung's Diseaseiamjamesvaldez28No ratings yet
- The Management of ChronicDocument6 pagesThe Management of ChronicAndreea PopescuNo ratings yet
- Management of Jejunoileal Atresia: Our 5 Year ExperienceDocument4 pagesManagement of Jejunoileal Atresia: Our 5 Year ExperienceOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiDocument5 pagesChronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiAndreea PopescuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of ConstipationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of ConstipationAndrea GallegoNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung'S Disease (Megacolon) : Mrs. Smitha.M Associate Professor Vijaya College of Nursing KottarakkaraDocument6 pagesHirschsprung'S Disease (Megacolon) : Mrs. Smitha.M Associate Professor Vijaya College of Nursing KottarakkarakrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- The Gentle Touch' Technique in The Treatment of GastroschisisDocument3 pagesThe Gentle Touch' Technique in The Treatment of Gastroschisisansar ahmedNo ratings yet
- DD Billous VomittingDocument2 pagesDD Billous VomittingdewiswahyuNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument47 pagesPyloric StenosisgeethsreesatNo ratings yet
- Total Colonic Aganglionosis (Zuelzer Wilson Syndrome) An EnigmaDocument2 pagesTotal Colonic Aganglionosis (Zuelzer Wilson Syndrome) An EnigmarmysdsNo ratings yet
- Congenital Megacolon: (Hirschsprung'SDocument20 pagesCongenital Megacolon: (Hirschsprung'STni JolieNo ratings yet
- NCM 102: Gynecology Nursing ManagementDocument7 pagesNCM 102: Gynecology Nursing ManagementdubhieNo ratings yet
- Interesting Case FINALE 3Document33 pagesInteresting Case FINALE 3Jerwin GilberoNo ratings yet
- Hirschprung's DiseaseDocument26 pagesHirschprung's DiseaseAbdur RaqibNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationDocument3 pagesIntestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationSaurav SultaniaNo ratings yet
- Term Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportDocument3 pagesTerm Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportLeannarys Mendoza DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Document6 pagesHirschsprung Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Julliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- Sick Growing Child: Hirschsprung Disease Anorectal Malformation Maluenda CamilleDocument46 pagesSick Growing Child: Hirschsprung Disease Anorectal Malformation Maluenda CamilleCamille Maluenda - TanNo ratings yet
- Placino HIRSCHPRUNG DX PDFDocument15 pagesPlacino HIRSCHPRUNG DX PDFSiena PlacinoNo ratings yet
- Rectal Computer 2Document5 pagesRectal Computer 2Su-sake KonichiwaNo ratings yet
- Ijcp-4257 CDocument4 pagesIjcp-4257 CFatima Al ZahraNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument3 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- IntussusceptionDocument13 pagesIntussusceptionwydiake3No ratings yet
- Ms Prelim NotesDocument6 pagesMs Prelim NotesJane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataDocument9 pagesCase Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataImee JenNo ratings yet
- Indian AediatricDocument2 pagesIndian AediatricMuhamad RizauddinNo ratings yet
- 2 Common Congenital Anomalies of The GI TractDocument27 pages2 Common Congenital Anomalies of The GI TractZyke NovenoNo ratings yet
- HirschsprungDocument11 pagesHirschsprungKarl JoseNo ratings yet
- Intussusception TransDocument4 pagesIntussusception TransJames Maravillas100% (1)
- Acquired Colonic Atresia in A 4-Month Old Term Male Infant: A Rare Case ReportDocument3 pagesAcquired Colonic Atresia in A 4-Month Old Term Male Infant: A Rare Case ReportDenise CssNo ratings yet
- Topics Pediatric SurgeryDocument6 pagesTopics Pediatric SurgeryPatrycjaSkierkaNo ratings yet
- Ob Topic 1 - Pprom - NCPDocument2 pagesOb Topic 1 - Pprom - NCPThelly MargalloNo ratings yet
- Imperforate Anus: Preoperative CareDocument2 pagesImperforate Anus: Preoperative CareLalisaM ActivityNo ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation in Children: BMJ (Online) December 2006Document6 pagesChronic Constipation in Children: BMJ (Online) December 2006Residen KardiologiNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Mimicry of A Rare Case of Early Diagnosed DolichocolDocument1 pageAppendicitis Mimicry of A Rare Case of Early Diagnosed DolichocolSimina ZarmaNo ratings yet
- Early Feeding After Digestive Surgery Is 43f243f3Document4 pagesEarly Feeding After Digestive Surgery Is 43f243f3sarahsamaliaNo ratings yet
- Lima 2022Document9 pagesLima 2022segoc54661No ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation in Infants and Children: RticleDocument6 pagesChronic Constipation in Infants and Children: RticleCaio AmaralNo ratings yet
- Hirschprung DiseaseDocument61 pagesHirschprung DiseaseAdditi Satyal100% (1)
- Induction AND Augmentation OF LabourDocument42 pagesInduction AND Augmentation OF LabourDakshayini MbNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction in A Child: With Massive AscariasisDocument4 pagesIntestinal Obstruction in A Child: With Massive AscariasisAbigail AngelesNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: Read By: Krisna (KNA)Document26 pagesIntussusception: Read By: Krisna (KNA)krisnaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument12 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAiley DumpNo ratings yet
- Apple Peel Small Bowel, A Review of Four Cases: Surgical and Radiographic AspectsDocument8 pagesApple Peel Small Bowel, A Review of Four Cases: Surgical and Radiographic AspectsraecmyNo ratings yet
- Adhesive Intestinal Obstruction. What A Resident Should KnowDocument6 pagesAdhesive Intestinal Obstruction. What A Resident Should Knowrahul ranjanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Insights into Abdominal Adhesions: Understanding, Management, and Future FrontiersFrom EverandComprehensive Insights into Abdominal Adhesions: Understanding, Management, and Future FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- Chapter 23 HomeworkDocument10 pagesChapter 23 HomeworkKvn4N6No ratings yet
- Evaluation of TILs Molecular Grade StageDocument9 pagesEvaluation of TILs Molecular Grade StageTam PhamNo ratings yet
- Class Presentation ON Acute Tubular NecrosisDocument39 pagesClass Presentation ON Acute Tubular NecrosisDeeksha RajputNo ratings yet
- Administration of Oxygen Retdem NotesDocument2 pagesAdministration of Oxygen Retdem NotesJhayneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentKawaljit KaurNo ratings yet
- Course PacketDocument176 pagesCourse Packethgfree41392No ratings yet
- Kaufman Cerina RDRDocument3 pagesKaufman Cerina RDRapi-730043203No ratings yet
- Josielene Lara Chan vs. Johnny T. Chan G.R. No. 179786 July 24, 2013Document2 pagesJosielene Lara Chan vs. Johnny T. Chan G.R. No. 179786 July 24, 2013Tootsie GuzmaNo ratings yet
- Ringer2013 2Document8 pagesRinger2013 2BenjamÍn Alejandro Ruiz ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Rs Case SheetDocument8 pagesRs Case SheetBhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Railway PharmasistDocument2 pagesRailway PharmasistprashantNo ratings yet
- Moh New Requirements For Foreign Workers ContractDocument3 pagesMoh New Requirements For Foreign Workers ContractaikalessNo ratings yet
- Outbreak of Hendra-Like Virus - Malaysia and Singapore, 1998-1999Document20 pagesOutbreak of Hendra-Like Virus - Malaysia and Singapore, 1998-1999Sarasvathi KumarNo ratings yet
- State Director Letter - Joint ACF CMS and SAMHSA On Psychotropic Drug Use in Foster CareDocument7 pagesState Director Letter - Joint ACF CMS and SAMHSA On Psychotropic Drug Use in Foster CareBeverly TranNo ratings yet
- Cardiology MCQDocument7 pagesCardiology MCQNesma Adel100% (1)
- Hubungan Pengetahuan Pasien Tentang Informasi Pre Operasi Dengan Kecemasan Pasien Pre OperasiDocument7 pagesHubungan Pengetahuan Pasien Tentang Informasi Pre Operasi Dengan Kecemasan Pasien Pre OperasiMuhammad ZulfhyNo ratings yet
- Snapshots (L 7 Birth)Document2 pagesSnapshots (L 7 Birth)Suryansh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Omr CaseDocument38 pagesOmr CaseAnuMPaulNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggrisenaf fantiahNo ratings yet
- Eunjoo Rombu: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesEunjoo Rombu: ObjectiveEunjoo RombuNo ratings yet
- History of Medicine PDFDocument12 pagesHistory of Medicine PDFaditya_2kNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument23 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingTakeru Ferry100% (2)
- FNCP 1 - DiabetesDocument3 pagesFNCP 1 - DiabetesBianca Joy GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Clabsi Qi Martinez GibbsDocument11 pagesClabsi Qi Martinez Gibbsapi-437349589100% (1)
- Directory of HSP Referral Facilities in Metro ManilaDocument2 pagesDirectory of HSP Referral Facilities in Metro ManilaWilhelmina EspejoNo ratings yet
- Lumber Puncture ProcedureDocument8 pagesLumber Puncture ProcedureDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
Hirschsprungs Disease Handout
Hirschsprungs Disease Handout
Uploaded by
rigasanaoray0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pages1) Hirschsprung's disease is a birth defect where part of the colon lacks nerve cells causing blockage. Symptoms appear between 6-12 months including poor weight gain and infrequent hard stools.
2) Diagnosis involves rectal biopsy and other tests. Treatment includes decompression with NG tubes or irrigation, surgery to remove the blocked part of colon, and management of nutrition and infections.
3) Surgical options depend on age, health, and extent of blockage. They include colostomy then pull-through or single stage pull-through. Post-op care focuses on colostomy care, feeding, and managing complications.
Original Description:
Original Title
Hirschsprungs-Disease-Handout
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) Hirschsprung's disease is a birth defect where part of the colon lacks nerve cells causing blockage. Symptoms appear between 6-12 months including poor weight gain and infrequent hard stools.
2) Diagnosis involves rectal biopsy and other tests. Treatment includes decompression with NG tubes or irrigation, surgery to remove the blocked part of colon, and management of nutrition and infections.
3) Surgical options depend on age, health, and extent of blockage. They include colostomy then pull-through or single stage pull-through. Post-op care focuses on colostomy care, feeding, and managing complications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesHirschsprungs Disease Handout
Hirschsprungs Disease Handout
Uploaded by
rigasanaoray1) Hirschsprung's disease is a birth defect where part of the colon lacks nerve cells causing blockage. Symptoms appear between 6-12 months including poor weight gain and infrequent hard stools.
2) Diagnosis involves rectal biopsy and other tests. Treatment includes decompression with NG tubes or irrigation, surgery to remove the blocked part of colon, and management of nutrition and infections.
3) Surgical options depend on age, health, and extent of blockage. They include colostomy then pull-through or single stage pull-through. Post-op care focuses on colostomy care, feeding, and managing complications.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
HIRSCHSPRUNG’S DISEASE of the internal sphincter by inserting
a balloon catheter into the rectum
HIRSCHSPRUNG’S DISEASE is also and measuring the pressure exerted
known as congenital aganglionic against it.
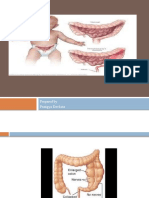
megacolon, so Hirschsprung’s is a disease NURSING DIAGNOSIS:
that is present since birth in which a Imbalanced nutrition, less than the
ganglion, or cluster of nerves is missing, body requirements, related to
which ultimately leads to a blocked colon, reduced bowel function
causing it to enlarge. Constipation related to reduced
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY bowel function
Risk for compromised family coping
Due to the absence of ganglionic cells related to chronic illness in child
Deficient knowledge of caregivers
There is lack of peristalsis in the affected portion
related to understanding of
Functional Obstruction
postoperative care of colostomy
Fear (in older children) related to
Accumulation of gas & feces proximal to the defect impending surgery
Acute pain related to the surgical
Enlargement of the colon occurs and called MEGACOLON
procedure
Risk for skin integrity related to
ASSESSMENT:
irritation from the colostomy
Symptoms of aganglionic megacolon Impaired oral and nasal mucous
do not become apparent until 6-12 months membranes related to NPO and
age. irritation from NG Tube
NURSING INTERVENTIONS:
Thin and undernourished
Preoperative Phase
Large distended abdomen
Informed Consent
Hx of not having a bowel movement
Preoperative Assessment:
more than once a weak
Physical Assessment
Ribbonlike or watery stools
Pre-surgical Screening Test
Vomiting
Health Factors
Diarrhea (enterocolitis)
Physiological Preparations:
Delayed passage of meconium
DIAGNOSTIC TOOLS: Managing nutrition and Fluids
Laboratory Studies Managing Infections – Colorectal
Rectal Biopsy Irrigation
Rectal Examination Psychosocial Preparation:
Plain Abdominal Radiography ‘ Explain the disease properly to the
Contrast Barium Enema parents
Anorectal Manometry – a technique
that tests the strength or innervation
Diet: 2. Decompression
Patient should have nothing by Nasogastric Tube
mouth before the operation Normal Saline Rectal Irrigations
Post-Operative Phase 3. Diet
Regular colostomy care to be done Breast milk
following aseptic guidelines SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
IV fluids are given to maintain Surgical options vary according to:
adequate hydration and electrolyte Patient’s age
balance Mental status
To prevent contamination of the Ability to perform activities of
wound with urine of baby, diaper daily living
must be pinned below the dressing Length of aganglionic segment
or urethral catheterization can be Degree of colonic dilation
done. Presence of enterocolitis
Explain to significant others about Leveling Colostomy
procedure of skin care, frequency of Leveling Colostomy, which is
care, signs of complication. colostomy at the level of normal bowel; a
Follow-Up: staged procedure with placement of a
Further Inpatient Care leveled colostomy followed by a pull through
If a diverting colostomy is created in procedure.
a newborn, he/she must remain in Single-Stage Pull-Through Procedure
the hospital until the colostomy is The single-stage pull-through
functioning and feeding goals are procedure may be performed with
obtained. Feeding are usually laparoscopic, open, or transnasal
initiated 24-48 hours after the techniques. This procedure can be
surgery. performed at the time of diagnosis or after
After definitive pull-through the newborn has had rectal irrigation at
procedure is performed, the patient home and has passed the physiologic nadir.
is hospitalized until full feeding are PHARMACOLOGIC THERAPY
possible and evidence of the return 1) Ampicillin
of bowel functions is obtained. 2) Gentamicin
Colorectal Irrigation may still be 3) Metronidazole
needed.
Further Outpatient:
Patients should be monitored for
normal bowel habits. Reporters:
MEDICAL MANAGEMENT SARIGALA, Putri Aisharoqayya B.
1. Initial Therapy SAUMAY, Norjannah
Intravenous Hydration SIGAYAN, Fais D.
Withholding of enteral intake
You might also like
- Sce Geriatric Medicine Sample QsDocument67 pagesSce Geriatric Medicine Sample QsZoya Annam100% (7)
- Meconium Aspiration Syndrome Case PresentationDocument26 pagesMeconium Aspiration Syndrome Case Presentationkis100% (2)
- Urine Test Strips and Microscopy: Compendium of UrinalysisDocument180 pagesUrine Test Strips and Microscopy: Compendium of UrinalysisLory LaneNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Gastroenterology Flashcards - MemorangDocument4 pagesPediatric Gastroenterology Flashcards - MemorangRa ViNo ratings yet
- Ferna-Case AnalysisDocument13 pagesFerna-Case Analysisbea pegadNo ratings yet
- (Aganglionic Megacolon) : Hirschsprung'S DiseaseDocument2 pages(Aganglionic Megacolon) : Hirschsprung'S DiseaseLalisaM ActivityNo ratings yet
- PeritonitisDocument7 pagesPeritonitisrina yulianaNo ratings yet
- Askep HisprungDocument25 pagesAskep HisprungRika AmaliyaNo ratings yet
- Gastro Key NotesDocument11 pagesGastro Key NotesHannah aswini100% (1)
- Cystic FibrosisDocument3 pagesCystic FibrosisRieza NurdinsyahNo ratings yet
- Common Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNDocument14 pagesCommon Health Problems That Develop During Infancy MPNShaii Whomewhat GuyguyonNo ratings yet
- Maternal Finals Key TermsDocument5 pagesMaternal Finals Key TermsRomer Basadre Jr.No ratings yet
- Intestinal Atresia: A Case ReportDocument3 pagesIntestinal Atresia: A Case ReportOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Hirsch SprungDocument16 pagesHirsch SprungjessyNo ratings yet
- Paeds Bilious VomitingDocument2 pagesPaeds Bilious Vomitingsinghurvashi365No ratings yet
- Hirschsprun G'S Disease: Dr. Manish Kumar Gupta Assistant Professor Department of Paediatric Surgery AIIMS, RishikeshDocument48 pagesHirschsprun G'S Disease: Dr. Manish Kumar Gupta Assistant Professor Department of Paediatric Surgery AIIMS, RishikeshArchana Mahata100% (1)
- Ob2 Sas 19Document9 pagesOb2 Sas 19Ralph Louie ManagoNo ratings yet
- BALON, JOHN LOWIE O - Hirschsprung's DiseaseDocument12 pagesBALON, JOHN LOWIE O - Hirschsprung's Diseaseiamjamesvaldez28No ratings yet
- The Management of ChronicDocument6 pagesThe Management of ChronicAndreea PopescuNo ratings yet
- Management of Jejunoileal Atresia: Our 5 Year ExperienceDocument4 pagesManagement of Jejunoileal Atresia: Our 5 Year ExperienceOvamelia JulioNo ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiDocument5 pagesChronic Constipation: Guest Editor: Bhim S. PandhiAndreea PopescuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of ConstipationDocument8 pagesEvaluation of ConstipationAndrea GallegoNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung'S Disease (Megacolon) : Mrs. Smitha.M Associate Professor Vijaya College of Nursing KottarakkaraDocument6 pagesHirschsprung'S Disease (Megacolon) : Mrs. Smitha.M Associate Professor Vijaya College of Nursing KottarakkarakrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- The Gentle Touch' Technique in The Treatment of GastroschisisDocument3 pagesThe Gentle Touch' Technique in The Treatment of Gastroschisisansar ahmedNo ratings yet
- DD Billous VomittingDocument2 pagesDD Billous VomittingdewiswahyuNo ratings yet
- Pyloric StenosisDocument47 pagesPyloric StenosisgeethsreesatNo ratings yet
- Total Colonic Aganglionosis (Zuelzer Wilson Syndrome) An EnigmaDocument2 pagesTotal Colonic Aganglionosis (Zuelzer Wilson Syndrome) An EnigmarmysdsNo ratings yet
- Congenital Megacolon: (Hirschsprung'SDocument20 pagesCongenital Megacolon: (Hirschsprung'STni JolieNo ratings yet
- NCM 102: Gynecology Nursing ManagementDocument7 pagesNCM 102: Gynecology Nursing ManagementdubhieNo ratings yet
- Interesting Case FINALE 3Document33 pagesInteresting Case FINALE 3Jerwin GilberoNo ratings yet
- Hirschprung's DiseaseDocument26 pagesHirschprung's DiseaseAbdur RaqibNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationDocument3 pagesIntestinal Malrotation in Neonates With Nonbilious Emesis: Perinatal/Neonatal Case PresentationSaurav SultaniaNo ratings yet
- Term Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportDocument3 pagesTerm Alive Intra Abdominal Ectopic Pregnancy: Case ReportLeannarys Mendoza DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Document6 pagesHirschsprung Disease (Aganglionic Megacolon)Julliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- Sick Growing Child: Hirschsprung Disease Anorectal Malformation Maluenda CamilleDocument46 pagesSick Growing Child: Hirschsprung Disease Anorectal Malformation Maluenda CamilleCamille Maluenda - TanNo ratings yet
- Placino HIRSCHPRUNG DX PDFDocument15 pagesPlacino HIRSCHPRUNG DX PDFSiena PlacinoNo ratings yet
- Rectal Computer 2Document5 pagesRectal Computer 2Su-sake KonichiwaNo ratings yet
- Ijcp-4257 CDocument4 pagesIjcp-4257 CFatima Al ZahraNo ratings yet
- Cues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermDocument3 pagesCues/Needs Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goals and Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Short Term Independent Short TermLatrell GelacioNo ratings yet
- IntussusceptionDocument13 pagesIntussusceptionwydiake3No ratings yet
- Ms Prelim NotesDocument6 pagesMs Prelim NotesJane LaquihonNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataDocument9 pagesCase Study of Placenta Previa: Patient's Demographic DataImee JenNo ratings yet
- Indian AediatricDocument2 pagesIndian AediatricMuhamad RizauddinNo ratings yet
- 2 Common Congenital Anomalies of The GI TractDocument27 pages2 Common Congenital Anomalies of The GI TractZyke NovenoNo ratings yet
- HirschsprungDocument11 pagesHirschsprungKarl JoseNo ratings yet
- Intussusception TransDocument4 pagesIntussusception TransJames Maravillas100% (1)
- Acquired Colonic Atresia in A 4-Month Old Term Male Infant: A Rare Case ReportDocument3 pagesAcquired Colonic Atresia in A 4-Month Old Term Male Infant: A Rare Case ReportDenise CssNo ratings yet
- Topics Pediatric SurgeryDocument6 pagesTopics Pediatric SurgeryPatrycjaSkierkaNo ratings yet
- Ob Topic 1 - Pprom - NCPDocument2 pagesOb Topic 1 - Pprom - NCPThelly MargalloNo ratings yet
- Imperforate Anus: Preoperative CareDocument2 pagesImperforate Anus: Preoperative CareLalisaM ActivityNo ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation in Children: BMJ (Online) December 2006Document6 pagesChronic Constipation in Children: BMJ (Online) December 2006Residen KardiologiNo ratings yet
- Appendicitis Mimicry of A Rare Case of Early Diagnosed DolichocolDocument1 pageAppendicitis Mimicry of A Rare Case of Early Diagnosed DolichocolSimina ZarmaNo ratings yet
- Early Feeding After Digestive Surgery Is 43f243f3Document4 pagesEarly Feeding After Digestive Surgery Is 43f243f3sarahsamaliaNo ratings yet
- Lima 2022Document9 pagesLima 2022segoc54661No ratings yet
- Chronic Constipation in Infants and Children: RticleDocument6 pagesChronic Constipation in Infants and Children: RticleCaio AmaralNo ratings yet
- Hirschprung DiseaseDocument61 pagesHirschprung DiseaseAdditi Satyal100% (1)
- Induction AND Augmentation OF LabourDocument42 pagesInduction AND Augmentation OF LabourDakshayini MbNo ratings yet
- Intestinal Obstruction in A Child: With Massive AscariasisDocument4 pagesIntestinal Obstruction in A Child: With Massive AscariasisAbigail AngelesNo ratings yet
- Intussusception: Read By: Krisna (KNA)Document26 pagesIntussusception: Read By: Krisna (KNA)krisnaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument12 pagesAbruptio PlacentaAiley DumpNo ratings yet
- Apple Peel Small Bowel, A Review of Four Cases: Surgical and Radiographic AspectsDocument8 pagesApple Peel Small Bowel, A Review of Four Cases: Surgical and Radiographic AspectsraecmyNo ratings yet
- Adhesive Intestinal Obstruction. What A Resident Should KnowDocument6 pagesAdhesive Intestinal Obstruction. What A Resident Should Knowrahul ranjanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Insights into Abdominal Adhesions: Understanding, Management, and Future FrontiersFrom EverandComprehensive Insights into Abdominal Adhesions: Understanding, Management, and Future FrontiersNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study - Acetaminophen, ParacetamolmikErlh100% (2)
- Chapter 23 HomeworkDocument10 pagesChapter 23 HomeworkKvn4N6No ratings yet
- Evaluation of TILs Molecular Grade StageDocument9 pagesEvaluation of TILs Molecular Grade StageTam PhamNo ratings yet
- Class Presentation ON Acute Tubular NecrosisDocument39 pagesClass Presentation ON Acute Tubular NecrosisDeeksha RajputNo ratings yet
- Administration of Oxygen Retdem NotesDocument2 pagesAdministration of Oxygen Retdem NotesJhayneNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentKawaljit KaurNo ratings yet
- Course PacketDocument176 pagesCourse Packethgfree41392No ratings yet
- Kaufman Cerina RDRDocument3 pagesKaufman Cerina RDRapi-730043203No ratings yet
- Josielene Lara Chan vs. Johnny T. Chan G.R. No. 179786 July 24, 2013Document2 pagesJosielene Lara Chan vs. Johnny T. Chan G.R. No. 179786 July 24, 2013Tootsie GuzmaNo ratings yet
- Ringer2013 2Document8 pagesRinger2013 2BenjamÍn Alejandro Ruiz ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Rs Case SheetDocument8 pagesRs Case SheetBhanu PrakashNo ratings yet
- Railway PharmasistDocument2 pagesRailway PharmasistprashantNo ratings yet
- Moh New Requirements For Foreign Workers ContractDocument3 pagesMoh New Requirements For Foreign Workers ContractaikalessNo ratings yet
- Outbreak of Hendra-Like Virus - Malaysia and Singapore, 1998-1999Document20 pagesOutbreak of Hendra-Like Virus - Malaysia and Singapore, 1998-1999Sarasvathi KumarNo ratings yet
- State Director Letter - Joint ACF CMS and SAMHSA On Psychotropic Drug Use in Foster CareDocument7 pagesState Director Letter - Joint ACF CMS and SAMHSA On Psychotropic Drug Use in Foster CareBeverly TranNo ratings yet
- Cardiology MCQDocument7 pagesCardiology MCQNesma Adel100% (1)
- Hubungan Pengetahuan Pasien Tentang Informasi Pre Operasi Dengan Kecemasan Pasien Pre OperasiDocument7 pagesHubungan Pengetahuan Pasien Tentang Informasi Pre Operasi Dengan Kecemasan Pasien Pre OperasiMuhammad ZulfhyNo ratings yet
- Snapshots (L 7 Birth)Document2 pagesSnapshots (L 7 Birth)Suryansh KapoorNo ratings yet
- Omr CaseDocument38 pagesOmr CaseAnuMPaulNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggrisenaf fantiahNo ratings yet
- Eunjoo Rombu: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesEunjoo Rombu: ObjectiveEunjoo RombuNo ratings yet
- History of Medicine PDFDocument12 pagesHistory of Medicine PDFaditya_2kNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Uterine BleedingDocument23 pagesAbnormal Uterine BleedingTakeru Ferry100% (2)
- FNCP 1 - DiabetesDocument3 pagesFNCP 1 - DiabetesBianca Joy GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Clabsi Qi Martinez GibbsDocument11 pagesClabsi Qi Martinez Gibbsapi-437349589100% (1)
- Directory of HSP Referral Facilities in Metro ManilaDocument2 pagesDirectory of HSP Referral Facilities in Metro ManilaWilhelmina EspejoNo ratings yet
- Lumber Puncture ProcedureDocument8 pagesLumber Puncture ProcedureDimpal ChoudharyNo ratings yet