Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 1
Lecture 1
Uploaded by
Meriza CabacunganCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Physical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirDocument112 pagesPhysical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirKritika Singh100% (1)
- CHEM 1031 Final Exam Study GuideDocument43 pagesCHEM 1031 Final Exam Study GuidePranava MalluNo ratings yet
- AWWA C208 Elbow enDocument4 pagesAWWA C208 Elbow enjaimecneto1No ratings yet
- Physics Project On CyclotronDocument11 pagesPhysics Project On CyclotronasishNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRYSAN JOSE, KRIZZIA FAYE U.No ratings yet
- Kem حذف الصورDocument126 pagesKem حذف الصورturkiNo ratings yet
- CLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFDocument57 pagesCLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFSarah RashidNo ratings yet
- Std. 11 Sci EM Chemistry Chepterwise Chapter 01 ManishDocument49 pagesStd. 11 Sci EM Chemistry Chepterwise Chapter 01 Manishharshvora1000iqNo ratings yet
- سلايدات 101 كيم كاملةDocument276 pagesسلايدات 101 كيم كاملةNouf AlaskarNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Redox ReactionsDocument92 pagesStoichiometry and Redox ReactionsHjkkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)BaaM TVNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument19 pagesAtoms and MoleculesAbhishek VashistNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Matter and StoicheometryDocument14 pagesConservation of Matter and StoicheometryAltheaGuanzonNo ratings yet
- C3 Quantitative ChemistryDocument2 pagesC3 Quantitative ChemistrydeltaNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Chemistry MnemonicsDocument10 pagesJee Main Chemistry MnemonicsRishika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Concept Map 1Document1 pageConcept Map 1Divanshu KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Long Exam 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesChem 16 Long Exam 1 Reviewerdesperateboy100% (1)
- Edited Mole ConceptDocument22 pagesEdited Mole Conceptd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument22 pagesLecture 1. Basic Concepts of ChemistryВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- c4 Chemical CalculationsDocument4 pagesc4 Chemical CalculationsNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- BSC 1st Year Notes ChemistryDocument33 pagesBSC 1st Year Notes ChemistrySandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- K04 Chap 1b Processes and Process VariablesDocument42 pagesK04 Chap 1b Processes and Process VariablesSasmilah KandsamyNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - SampleDocument22 pagesCHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - Sampleviswajithv66No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document51 pagesChapter 3Toka TariqNo ratings yet
- FT - Matter & Its Properties - v2Document79 pagesFT - Matter & Its Properties - v2aliyasin200000No ratings yet
- Chemistry - June 2015Document1 pageChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- MATE 152-24 Lec 2Document25 pagesMATE 152-24 Lec 2andrew.dungoNo ratings yet
- Ib Nitrogenotes HL/SL Chemistry Summary: Some DisclaimersDocument6 pagesIb Nitrogenotes HL/SL Chemistry Summary: Some Disclaimers刘峻宏No ratings yet
- FundamentalsDocument15 pagesFundamentalsmhdaslam440No ratings yet
- CHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1Document74 pagesCHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1meamatafarms KennethNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument2 pagesIlovepdf Mergedjawhar impressionNo ratings yet
- Geometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDocument29 pagesGeometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDinkar YeoleNo ratings yet
- Chem 131 Final ReviewDocument13 pagesChem 131 Final ReviewShahd MuhamedNo ratings yet
- CT - Gaseous State - Module Gaseous State - 10112021 - 7. Xi - Gaseous State ModuleDocument80 pagesCT - Gaseous State - Module Gaseous State - 10112021 - 7. Xi - Gaseous State ModuleAnita Akhilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Brex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 6 SlidesDocument228 pagesBrex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 6 SlidesNEIL RYAN LAGARDENo ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula BookletDocument193 pagesChemistry Formula BookletGadde Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Brex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 9 SlidesDocument153 pagesBrex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 9 SlidesNEIL RYAN LAGARDENo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - 11th NCERTDocument25 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - 11th NCERTThe Boring CompanyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Chemistrylopa39018No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument11 pagesChemistryBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- 108 Chapter 3 StoichiometryDocument29 pages108 Chapter 3 Stoichiometryzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument6 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Handouts Introduction To Chemistry Theory 2016 eDocument4 pagesHandouts Introduction To Chemistry Theory 2016 eIshhdNo ratings yet
- 1st Law: Conservation of EnergyDocument85 pages1st Law: Conservation of EnergyAyu MilineaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 Part 2 DJJ20063 AKDocument27 pagesTOPIC 2 Part 2 DJJ20063 AKdhanheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Matter & Measurement: AP Chemistry Unit 1 Notes Chapters 1 - 3Document28 pagesChapter 1: Matter & Measurement: AP Chemistry Unit 1 Notes Chapters 1 - 3Fwaaz AlbarqiNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - Basic ConceptsDocument11 pagesLec1 - Basic ConceptsKaryl CoronelNo ratings yet
- Slot 1 - Chapter 2-5 (Edit)Document51 pagesSlot 1 - Chapter 2-5 (Edit)Rabbi 08No ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula SheetDocument314 pagesChemistry Formula SheetAd Adarsh Navneet SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesChem 111 Cheat Sheet: by ViaWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Basic of Thermodynamics)Document46 pagesChapter 2 (Basic of Thermodynamics)kitcha sonsaartNo ratings yet
- chm#03 - 1st Year-Ch (1,2,3) - OkDocument1 pagechm#03 - 1st Year-Ch (1,2,3) - OkAhmed MahmoodNo ratings yet
- A Two-Phase One-Dimensional Biomass Gasification Kinetics ModelDocument12 pagesA Two-Phase One-Dimensional Biomass Gasification Kinetics Modelapi-3799861No ratings yet
- Lecture4 AstrochemistryDocument34 pagesLecture4 AstrochemistryEfrain Andre ViraNo ratings yet
- Academy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument4 pagesAcademy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryYash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Ch2Document13 pagesFluid Mechanics Ch2AVCNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Phase BehaviorDocument2 pagesThermodynamics and Phase Behaviorsaurabh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Created by James Riddle With Guidance From Dr. Matthew T. BalhoffDocument2 pagesCreated by James Riddle With Guidance From Dr. Matthew T. BalhoffChrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - StoichiometryDocument42 pagesChapter 3 - StoichiometrymachungwachishimbaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Jurnal EugenolDocument9 pagesJurnal EugenolMillenia AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography Chap 1Document21 pagesQuantum Cryptography Chap 1Anees Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Technical Data and Curve Characteristics: Technical Guide P12X/En T04/B44 Micom P120/P121/P122/P123Document34 pagesTechnical Data and Curve Characteristics: Technical Guide P12X/En T04/B44 Micom P120/P121/P122/P123Leo TranNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electricity and MagnetismDocument81 pagesUnit 1 Electricity and Magnetismeric appiahNo ratings yet
- Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)Document1 pageInductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)AriantoNo ratings yet
- Tolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationDocument9 pagesTolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationCahyono IriawanNo ratings yet
- FluidDocument6 pagesFluidMoosa NaseerNo ratings yet
- RPT Add Math Form 5Document9 pagesRPT Add Math Form 5Suziana MohamadNo ratings yet
- 45 Days Checklist - JEE Main 2024 Jan AttemptDocument3 pages45 Days Checklist - JEE Main 2024 Jan AttemptdevanshbcollabNo ratings yet
- M 3Document5 pagesM 3Varunan VarunNo ratings yet
- Possion Equation SolutionDocument11 pagesPossion Equation SolutionChandan YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry JokesDocument5 pagesChemistry JokesDaisy LuNo ratings yet
- Answer Discussion Share: VectorDocument51 pagesAnswer Discussion Share: Vectorneela94No ratings yet
- DCVCDocument4 pagesDCVCRhosuna AinaNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Mind MapDocument16 pagesRadioactive Mind Mapwahidms840% (1)
- Quantum Theory: Von Neumann vs. DiracDocument20 pagesQuantum Theory: Von Neumann vs. DiracsonirocksNo ratings yet
- 2 3A Lecture FatigueDocument38 pages2 3A Lecture FatigueEhsanJzrNo ratings yet
- Physics 4AL - Complete Lab Report 3Document11 pagesPhysics 4AL - Complete Lab Report 3ViceregalNo ratings yet
- Day-1 Lecture 1 Welding TechnologyDocument142 pagesDay-1 Lecture 1 Welding TechnologySamNo ratings yet
- Rotation Representation (Mathematics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesRotation Representation (Mathematics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaYoonjin HwangNo ratings yet
- Jameco Manmual NTC P92Document1 pageJameco Manmual NTC P92pecarriNo ratings yet
- Experimental Aspects of The Gyroscope's MovementDocument7 pagesExperimental Aspects of The Gyroscope's MovementCassie MinorNo ratings yet
- Mixture Problems PDFDocument3 pagesMixture Problems PDFKnspeisNo ratings yet
- Notes 3rd QuarterDocument36 pagesNotes 3rd QuarterKent DanielNo ratings yet
- Geas Iecep PDFDocument26 pagesGeas Iecep PDFMichael Cabrera RabinoNo ratings yet
- More Is Different Author(s) : P. W. Anderson Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 177, No. 4047 (Aug. 4, 1972), Pp. 393-396 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/09/2014 20:50Document5 pagesMore Is Different Author(s) : P. W. Anderson Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 177, No. 4047 (Aug. 4, 1972), Pp. 393-396 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/09/2014 20:50thebestNo ratings yet
- Pahal ChemistryDocument98 pagesPahal ChemistryMahesh BabuNo ratings yet
Lecture 1
Lecture 1
Uploaded by
Meriza CabacunganOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 1
Lecture 1
Uploaded by
Meriza CabacunganCopyright:
Available Formats
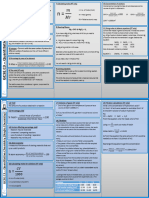
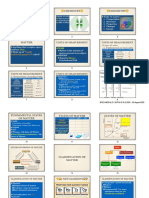
MATTER
CHEM 16
3) Time (s)
4) Temperature (K)
MATTER 5) Amount of substance (mol)
6) Luminosity (cd)
7) Electric current (amp)
INTRODUCTION TO MATTER SI Unit Prefixes
Prefix Abbreviation Factor
STATES OF MATTER Pico p 10-12
Bose-Einstein 🡪 Operate as a single entity Nano n 10-9
Condensate
(near absolute 0) Micro μ 10-6
Solid Milli m 10-3
Liquid Centi c 10-2
Gas Deci d 10-1
Plasma 🡪 Superheated gas (breaking Kilo k 103
all molecular bonds) Mega M 106
Giga G 109
MEASUREMENTS OF MATTER
CLASSIFICATIONS OF MATTER
Energy 🡪 Capacity to do work in Joules (J)
Mass 🡪 Qty of matter in an object (g)
Weight 🡪 W = mg (g=9.8 m/s2)
Density 🡪 p = mass/volume
Percent
Composition
🡪
PURE SUBSTANCE ℃ to K 🡪 K = ℃ +273.15
Fixed composition and distinct qualities (1 particle) ℃ to℉ 🡪 ℉ = (9/5)(℃) + 32
Element 🡪 Cannot be further broken
down ATOMIC THEORY OF MATTER
Compound 🡪 Atoms chemically united
MIXTURE DALTON’S ATOMIC THEORY
2 or more substances retain their distinct identities 1 Each element is composed of atoms.
Homogeneous 🡪 Uniform composition
Heterogeneous 🡪 Not uniform composition
2 All atoms of a given element are identical.
PROPERTIES OF MATTER
1 Physical Chemical
e.g. state, malleability e.g. flammability, corrosion
2 Quantitative Qualitative
e.g. solubility, mass e.g. odor, malleability 3 Atoms are neither created nor destroyed.
3 Intensive Extensive
e.g. MP, BP, pressure e.g. volume, mass
CHANGES OF MATTER 4 Compounds are formed when more than 2
Physical 🡪 No change in chemical identity elements combine in a definite ratio.
Chemical 🡪 Change in chemical identity
INDICATORS
✔ Color change
✔ Effervescence
✔ Precipitate
✔ Temperature change ATOMIC THEORY OF MATTER
Law of 🡪 Matter is neither created nor
Conservation destroyed (Total reactant mass
MEASUREMENTS OF MATTER of Mass = Total product mass)
Law of 🡪 A given compound contains
SI Base Units Definite elements in a certain proportion
1) Mass (kg) Composition (Limiting + excess reactants)
2) Length (m)
MATTER
CHEM 16
Law of 🡪 A and B can combine in the
Multiple ratio of small whole numbers to
Proportions form more than one compound.
(NO and NO2)
THE ATOM
🡪 Mass number (A): #p + #n
🡪 Atomic number (Z): #p
🡪 Net charge: #p - #e
** Anion (-), Cation (+)
Isotope 🡪 Same element, different
neutron number (e.g. 235U and
238
U)
AVERAGE ATOMIC MASS
You might also like
- Physical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirDocument112 pagesPhysical Chemistry Mole Concept Sheet by AKK SirKritika Singh100% (1)
- CHEM 1031 Final Exam Study GuideDocument43 pagesCHEM 1031 Final Exam Study GuidePranava MalluNo ratings yet
- AWWA C208 Elbow enDocument4 pagesAWWA C208 Elbow enjaimecneto1No ratings yet
- Physics Project On CyclotronDocument11 pagesPhysics Project On CyclotronasishNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument3 pagesCHEMISTRYSAN JOSE, KRIZZIA FAYE U.No ratings yet
- Kem حذف الصورDocument126 pagesKem حذف الصورturkiNo ratings yet
- CLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFDocument57 pagesCLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFSarah RashidNo ratings yet
- Std. 11 Sci EM Chemistry Chepterwise Chapter 01 ManishDocument49 pagesStd. 11 Sci EM Chemistry Chepterwise Chapter 01 Manishharshvora1000iqNo ratings yet
- سلايدات 101 كيم كاملةDocument276 pagesسلايدات 101 كيم كاملةNouf AlaskarNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry and Redox ReactionsDocument92 pagesStoichiometry and Redox ReactionsHjkkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)Document5 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: Target: JEE (Main+Advanced)BaaM TVNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument19 pagesAtoms and MoleculesAbhishek VashistNo ratings yet
- Conservation of Matter and StoicheometryDocument14 pagesConservation of Matter and StoicheometryAltheaGuanzonNo ratings yet
- C3 Quantitative ChemistryDocument2 pagesC3 Quantitative ChemistrydeltaNo ratings yet
- Jee Main Chemistry MnemonicsDocument10 pagesJee Main Chemistry MnemonicsRishika ReddyNo ratings yet
- Concept Map 1Document1 pageConcept Map 1Divanshu KapoorNo ratings yet
- Chem 16 Long Exam 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesChem 16 Long Exam 1 Reviewerdesperateboy100% (1)
- Edited Mole ConceptDocument22 pagesEdited Mole Conceptd anjilappaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1. Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument22 pagesLecture 1. Basic Concepts of ChemistryВалентина ЮзьковаNo ratings yet
- c4 Chemical CalculationsDocument4 pagesc4 Chemical CalculationsNavdha SachdevaNo ratings yet
- BSC 1st Year Notes ChemistryDocument33 pagesBSC 1st Year Notes ChemistrySandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- K04 Chap 1b Processes and Process VariablesDocument42 pagesK04 Chap 1b Processes and Process VariablesSasmilah KandsamyNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - SampleDocument22 pagesCHEMISTRY - IIT - JEE - Sampleviswajithv66No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document51 pagesChapter 3Toka TariqNo ratings yet
- FT - Matter & Its Properties - v2Document79 pagesFT - Matter & Its Properties - v2aliyasin200000No ratings yet
- Chemistry - June 2015Document1 pageChemistry - June 2015Rahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- MATE 152-24 Lec 2Document25 pagesMATE 152-24 Lec 2andrew.dungoNo ratings yet
- Ib Nitrogenotes HL/SL Chemistry Summary: Some DisclaimersDocument6 pagesIb Nitrogenotes HL/SL Chemistry Summary: Some Disclaimers刘峻宏No ratings yet
- FundamentalsDocument15 pagesFundamentalsmhdaslam440No ratings yet
- CHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1Document74 pagesCHM 111-Introductory Physical Chemistry-1-1meamatafarms KennethNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument2 pagesIlovepdf Mergedjawhar impressionNo ratings yet
- Geometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDocument29 pagesGeometry Chapterwise PYQs-By-Galaxy-of-MathsDinkar YeoleNo ratings yet
- Chem 131 Final ReviewDocument13 pagesChem 131 Final ReviewShahd MuhamedNo ratings yet
- CT - Gaseous State - Module Gaseous State - 10112021 - 7. Xi - Gaseous State ModuleDocument80 pagesCT - Gaseous State - Module Gaseous State - 10112021 - 7. Xi - Gaseous State ModuleAnita Akhilesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Brex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 6 SlidesDocument228 pagesBrex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 6 SlidesNEIL RYAN LAGARDENo ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula BookletDocument193 pagesChemistry Formula BookletGadde Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Brex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 9 SlidesDocument153 pagesBrex Module 1 Batch 5 Ple 2020 - 9 SlidesNEIL RYAN LAGARDENo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry - 11th NCERTDocument25 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry - 11th NCERTThe Boring CompanyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ChemistryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Chemistrylopa39018No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument11 pagesChemistryBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- 108 Chapter 3 StoichiometryDocument29 pages108 Chapter 3 Stoichiometryzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument6 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryPoorni RenuNo ratings yet
- Handouts Introduction To Chemistry Theory 2016 eDocument4 pagesHandouts Introduction To Chemistry Theory 2016 eIshhdNo ratings yet
- 1st Law: Conservation of EnergyDocument85 pages1st Law: Conservation of EnergyAyu MilineaNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 Part 2 DJJ20063 AKDocument27 pagesTOPIC 2 Part 2 DJJ20063 AKdhanheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Matter & Measurement: AP Chemistry Unit 1 Notes Chapters 1 - 3Document28 pagesChapter 1: Matter & Measurement: AP Chemistry Unit 1 Notes Chapters 1 - 3Fwaaz AlbarqiNo ratings yet
- Lec1 - Basic ConceptsDocument11 pagesLec1 - Basic ConceptsKaryl CoronelNo ratings yet
- Slot 1 - Chapter 2-5 (Edit)Document51 pagesSlot 1 - Chapter 2-5 (Edit)Rabbi 08No ratings yet
- Chemistry Formula SheetDocument314 pagesChemistry Formula SheetAd Adarsh Navneet SinhaNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument3 pagesChem 111 Cheat Sheet: by ViaWalid EbaiedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 (Basic of Thermodynamics)Document46 pagesChapter 2 (Basic of Thermodynamics)kitcha sonsaartNo ratings yet
- chm#03 - 1st Year-Ch (1,2,3) - OkDocument1 pagechm#03 - 1st Year-Ch (1,2,3) - OkAhmed MahmoodNo ratings yet
- A Two-Phase One-Dimensional Biomass Gasification Kinetics ModelDocument12 pagesA Two-Phase One-Dimensional Biomass Gasification Kinetics Modelapi-3799861No ratings yet
- Lecture4 AstrochemistryDocument34 pagesLecture4 AstrochemistryEfrain Andre ViraNo ratings yet
- Academy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument4 pagesAcademy: Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryYash ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Ch2Document13 pagesFluid Mechanics Ch2AVCNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics and Phase BehaviorDocument2 pagesThermodynamics and Phase Behaviorsaurabh pandeyNo ratings yet
- Created by James Riddle With Guidance From Dr. Matthew T. BalhoffDocument2 pagesCreated by James Riddle With Guidance From Dr. Matthew T. BalhoffChrisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - StoichiometryDocument42 pagesChapter 3 - StoichiometrymachungwachishimbaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Jurnal EugenolDocument9 pagesJurnal EugenolMillenia AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Cryptography Chap 1Document21 pagesQuantum Cryptography Chap 1Anees Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Technical Data and Curve Characteristics: Technical Guide P12X/En T04/B44 Micom P120/P121/P122/P123Document34 pagesTechnical Data and Curve Characteristics: Technical Guide P12X/En T04/B44 Micom P120/P121/P122/P123Leo TranNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electricity and MagnetismDocument81 pagesUnit 1 Electricity and Magnetismeric appiahNo ratings yet
- Inductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)Document1 pageInductively Coupled Plasma-Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)AriantoNo ratings yet
- Tolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationDocument9 pagesTolerance Map Models For Design and Manufacturing: MotivationCahyono IriawanNo ratings yet
- FluidDocument6 pagesFluidMoosa NaseerNo ratings yet
- RPT Add Math Form 5Document9 pagesRPT Add Math Form 5Suziana MohamadNo ratings yet
- 45 Days Checklist - JEE Main 2024 Jan AttemptDocument3 pages45 Days Checklist - JEE Main 2024 Jan AttemptdevanshbcollabNo ratings yet
- M 3Document5 pagesM 3Varunan VarunNo ratings yet
- Possion Equation SolutionDocument11 pagesPossion Equation SolutionChandan YadavNo ratings yet
- Chemistry JokesDocument5 pagesChemistry JokesDaisy LuNo ratings yet
- Answer Discussion Share: VectorDocument51 pagesAnswer Discussion Share: Vectorneela94No ratings yet
- DCVCDocument4 pagesDCVCRhosuna AinaNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Mind MapDocument16 pagesRadioactive Mind Mapwahidms840% (1)
- Quantum Theory: Von Neumann vs. DiracDocument20 pagesQuantum Theory: Von Neumann vs. DiracsonirocksNo ratings yet
- 2 3A Lecture FatigueDocument38 pages2 3A Lecture FatigueEhsanJzrNo ratings yet
- Physics 4AL - Complete Lab Report 3Document11 pagesPhysics 4AL - Complete Lab Report 3ViceregalNo ratings yet
- Day-1 Lecture 1 Welding TechnologyDocument142 pagesDay-1 Lecture 1 Welding TechnologySamNo ratings yet
- Rotation Representation (Mathematics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesRotation Representation (Mathematics) - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaYoonjin HwangNo ratings yet
- Jameco Manmual NTC P92Document1 pageJameco Manmual NTC P92pecarriNo ratings yet
- Experimental Aspects of The Gyroscope's MovementDocument7 pagesExperimental Aspects of The Gyroscope's MovementCassie MinorNo ratings yet
- Mixture Problems PDFDocument3 pagesMixture Problems PDFKnspeisNo ratings yet
- Notes 3rd QuarterDocument36 pagesNotes 3rd QuarterKent DanielNo ratings yet
- Geas Iecep PDFDocument26 pagesGeas Iecep PDFMichael Cabrera RabinoNo ratings yet
- More Is Different Author(s) : P. W. Anderson Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 177, No. 4047 (Aug. 4, 1972), Pp. 393-396 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/09/2014 20:50Document5 pagesMore Is Different Author(s) : P. W. Anderson Source: Science, New Series, Vol. 177, No. 4047 (Aug. 4, 1972), Pp. 393-396 Published By: Stable URL: Accessed: 02/09/2014 20:50thebestNo ratings yet
- Pahal ChemistryDocument98 pagesPahal ChemistryMahesh BabuNo ratings yet