Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 viewsSci.9 Weeks 1-3
Sci.9 Weeks 1-3
Uploaded by
Jaime CrispinoThis document is a summative test for a 9th grade science class covering topics in projectile motion, momentum, and impulse over the first 3 weeks. It contains 30 multiple choice questions testing student understanding of concepts like trajectory, gravity, velocity, range, angle of release, momentum, impulse, and elastic collisions. The test also includes word problems requiring calculations and analysis of scenarios involving projectiles and moving objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Midterm Examination in General Physics 1Document10 pagesMidterm Examination in General Physics 1zamora pegafi100% (2)
- 4th Periodic Test Grade 9 ScienceDocument4 pages4th Periodic Test Grade 9 ScienceMark Ryan J Bacus80% (5)
- 1 3 3 A IntroductionThermodynamicsDocument34 pages1 3 3 A IntroductionThermodynamicsZoinkedNo ratings yet
- May 8 2023Document3 pagesMay 8 2023Krisha Kate DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- 4Q Sci 9 PTDocument4 pages4Q Sci 9 PTRogelio EscobarNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument5 pagesSummative TestYbette Anorico VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Assessment Wk1&2Document2 pagesSci9 Assessment Wk1&2Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- 4Q Sci 9 PTDocument3 pages4Q Sci 9 PTmay flor obonNo ratings yet
- Sci-Curr ExamDocument3 pagesSci-Curr ExamGelliane UbaganNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 TQDocument9 pagesScience Grade 9 TQLae GadgudeNo ratings yet
- Summative Test-Quarter 4: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument11 pagesSummative Test-Quarter 4: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationGlaiza CancioNo ratings yet
- Advanced PhysicsDocument5 pagesAdvanced PhysicsMichelle MalataNo ratings yet
- TQ Q4 Science-9Document5 pagesTQ Q4 Science-9Jovie Erma AtonNo ratings yet
- Science Revision G7Document17 pagesScience Revision G7Ahmed SalemNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion TestDocument8 pagesForces and Motion TestFahadImranXhiekhNo ratings yet
- TQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 9 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaDocument5 pagesTQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 9 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaKhim YabesNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ExaminationDocument5 pages3rd Quarter ExaminationClaire EstimadaNo ratings yet
- Q4SCIENCE9Document6 pagesQ4SCIENCE9SHIRLEY JEAN SuganoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 9-Q4Document6 pagesReviewer in Science 9-Q4katherine bacallaNo ratings yet
- Test-Questions-Physics IDocument7 pagesTest-Questions-Physics INheszie Cortez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Summative-1Document4 pagesQ4 Summative-1artNo ratings yet
- 4Q Science G9Document3 pages4Q Science G9Kimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Kawit 2017Document15 pagesMath 8 Kawit 2017HELMA B. JABELLONo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- Genphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingDocument5 pagesGenphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingRonilo Rivera CaringalNo ratings yet
- Part I: Modified True or FalseDocument2 pagesPart I: Modified True or FalseGelliane UbaganNo ratings yet
- Quarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9 Final Na NamanDocument4 pagesQuarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9 Final Na NamanVanessa Joy Saavedra100% (1)
- Quarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9Document4 pagesQuarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9Vanessa Joy SaavedraNo ratings yet
- PretestDocument6 pagesPretestEdna Mae CruzNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsDocument6 pagesQuiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsChristian Nathaniel Ramon Palma100% (1)
- SCIENCE 9 4th QuarterDocument8 pagesSCIENCE 9 4th QuarterJezha Mae NelmidaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Assessment Wk3&4Document2 pagesSci9 Assessment Wk3&4Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics Reviewerfroilance100% (1)
- S M K I A S M K J A B X ADocument22 pagesS M K I A S M K J A B X ADanielNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1.finalDocument12 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1.finalzamora pegafiNo ratings yet
- Use The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Document4 pagesUse The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Melvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- PhEd. 2311 Mid ExamDocument4 pagesPhEd. 2311 Mid Examnegi diribaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 3RD QDocument7 pagesGrade 7 3RD QShielo Marie CabañeroNo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument12 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- Class Xi PhysicsDocument160 pagesClass Xi PhysicsAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesFourth Periodical ExaminationReymart VillapeñaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionAlbert Ascher100% (41)
- GRAND TEST 9 Chap 2Document2 pagesGRAND TEST 9 Chap 2HNTARIQNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Science 9Document3 pages4th Summative Test Science 9odette carzanoNo ratings yet
- First Written Test in Science 9 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022Document7 pagesFirst Written Test in Science 9 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022joan marie Pelias0% (1)
- General Physics 1-1Sst Quarter ExamDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 1-1Sst Quarter ExamJaver Degorio100% (1)
- SEMI FINAL Examination SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSEMI FINAL Examination SCIENCErhenz marie cadelinia germanNo ratings yet
- General Physics-1 CPT U2Document4 pagesGeneral Physics-1 CPT U2Tracy Nicole MaurilloNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test Science 8 SY 2019-2020Document6 pages1st Periodical Test Science 8 SY 2019-2020Dayen Bison100% (1)
- Grade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Document4 pagesGrade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Jerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- 3RD Grading Mastery Test Grade 7Document4 pages3RD Grading Mastery Test Grade 7Marjorie Baya BidlanNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseDocument11 pagesPhysics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseCarmen JuranovicNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Examination in Science 9: For Items 6-8, Refer To This SituationDocument5 pagesFourth Quarter Examination in Science 9: For Items 6-8, Refer To This SituationJ DNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter - Science 9Document7 pages4TH Quarter - Science 9MARIA THERESA TULALINo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Periodical ExamDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Periodical Exammarjoriebidlan445No ratings yet
- SCI9 TQ 4thquarterDocument4 pagesSCI9 TQ 4thquarterAilen Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- Q4 Long TestDocument9 pagesQ4 Long TestMelanie Ibarra CarlosNo ratings yet
- Reviwer in Gen. Physics 1Document4 pagesReviwer in Gen. Physics 1Romero, Ken Angelo B.No ratings yet
- Professional Golf Management (PGM) Practice Question Workbook: A Supplement to PGM Coursework for Levels 1, 2, and 3 (4th Edition)From EverandProfessional Golf Management (PGM) Practice Question Workbook: A Supplement to PGM Coursework for Levels 1, 2, and 3 (4th Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sci10 PT W1-3Document2 pagesSci10 PT W1-3Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 PT Weeks 1-3 - 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesSci.10 PT Weeks 1-3 - 2nd QuarterJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 PT Weeks 4-5 - 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesSci.10 PT Weeks 4-5 - 2nd QuarterJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 PT Weeks 6-8 - 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesSci.9 PT Weeks 6-8 - 2nd QuarterJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Performance Task-SCI.9 - Weeks 4-5 3rd QDocument2 pagesPerformance Task-SCI.9 - Weeks 4-5 3rd QJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 W1-3 TOSDocument2 pagesSci.9 W1-3 TOSJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-2Document3 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-2Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 Weeks 4-6Document3 pagesSci.9 Weeks 4-6Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-3Document4 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-3Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 8.2Document3 pagesSci.10 Weeks 8.2Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 Weeks 1-2Document4 pagesSci.9 Weeks 1-2Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 4-5Document2 pagesSci.10 Weeks 4-5Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-3Document3 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-3Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Climate Compilation VideoDocument2 pagesClimate Compilation VideoJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 W3-4 TOSDocument2 pagesSci.9 W3-4 TOSJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- PT - Q1-W1-2 LifestyleDocument3 pagesPT - Q1-W1-2 LifestyleJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PROPOSAL - Material Waste RecoveryDocument2 pagesPROJECT PROPOSAL - Material Waste RecoveryJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Notes Ch.3-Es205Document4 pagesNotes Ch.3-Es205indayieee.12No ratings yet
- Forces P2Document76 pagesForces P2arjunboruto1234No ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument16 pagesSteam TablesVishal ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For High School - Types of ThermometerDocument8 pagesPhysics Notes For High School - Types of ThermometerZeroseveen Seveen100% (1)
- دوسية المهندس ابراهيم حسين النوافلة (Autosaved) - 230719 - 100837Document59 pagesدوسية المهندس ابراهيم حسين النوافلة (Autosaved) - 230719 - 100837Doha LababnehNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing Entrance Paper PatternDocument22 pagesBSC Nursing Entrance Paper Patternrk91553280No ratings yet
- Water Cooled Chiller Performance Qualification Report: Godrej OneDocument16 pagesWater Cooled Chiller Performance Qualification Report: Godrej OneAnurag KumbhareNo ratings yet
- AY2223 EoY V1 PHY60A AKDocument16 pagesAY2223 EoY V1 PHY60A AKabdlurhman.ali.alaliNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesPhysical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsJerome SadudaquilNo ratings yet
- Full Conceptual Physics 11Th Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual PDFDocument31 pagesFull Conceptual Physics 11Th Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual PDFblaine.nevill224100% (15)
- Cross-Section Properties: GeometryDocument2 pagesCross-Section Properties: GeometryDaniel MewsNo ratings yet
- General resistance in a two-phase fluid branch - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国Document3 pagesGeneral resistance in a two-phase fluid branch - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国944062528qqNo ratings yet
- Marine Hvac SystemDocument58 pagesMarine Hvac SystemSiti Aishah Hussien100% (3)
- AlıştırmaDocument3 pagesAlıştırmaJanet Baker100% (1)
- Grofcsik Andras-Physical Chemistry - 1Document195 pagesGrofcsik Andras-Physical Chemistry - 1György SzidóniaNo ratings yet
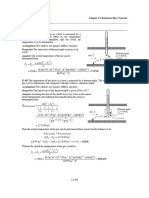
- Radiation Heat Transfer: H T T T TDocument18 pagesRadiation Heat Transfer: H T T T TiosuarizNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument86 pagesChemical Engineering ThermodynamicsSreedhar BabuNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Test RigDocument3 pagesVapor Compression Test RigTARUN DHUNNA0% (1)
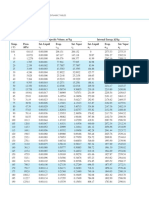
- ASME Steam Tables - Compact Edition-American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2006)Document32 pagesASME Steam Tables - Compact Edition-American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2006)Jesús CbNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1daejung1025No ratings yet
- Heat Recovery Calculation SheetDocument3 pagesHeat Recovery Calculation SheetAnand sNo ratings yet
- JJ207 Sesi Jun2013Document15 pagesJJ207 Sesi Jun2013afiqzeroNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Electrostatics (Exercise) (81-118) - OrganizedDocument10 pages1.2 Electrostatics (Exercise) (81-118) - OrganizedRohan GubbaNo ratings yet
- Slides For F2F Week 1 Part 2 of 2 Heat Conduction and UnitsDocument33 pagesSlides For F2F Week 1 Part 2 of 2 Heat Conduction and Unitsashwinraj562No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Chapter 05 Upthrust in Fluids Archimedes Principle and FloatationDocument21 pagesICSE Class 9 Physics Chapter 05 Upthrust in Fluids Archimedes Principle and FloatationgpfphysicsNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems, Physics 111 Common Exam 3, Spring 2024Document8 pagesPractice Problems, Physics 111 Common Exam 3, Spring 2024av742No ratings yet
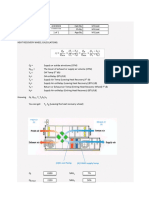
- Vam Machine Flow DiagramDocument2 pagesVam Machine Flow DiagramDevNo ratings yet
- Math 5 DLP 57 - Application of Measuring TemperatureDocument8 pagesMath 5 DLP 57 - Application of Measuring TemperatureGenalyn Tambiao AchanzarNo ratings yet
- HumidificationDocument5 pagesHumidificationAlbert Junior EvangelistaNo ratings yet
Sci.9 Weeks 1-3
Sci.9 Weeks 1-3
Uploaded by
Jaime Crispino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesThis document is a summative test for a 9th grade science class covering topics in projectile motion, momentum, and impulse over the first 3 weeks. It contains 30 multiple choice questions testing student understanding of concepts like trajectory, gravity, velocity, range, angle of release, momentum, impulse, and elastic collisions. The test also includes word problems requiring calculations and analysis of scenarios involving projectiles and moving objects.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document is a summative test for a 9th grade science class covering topics in projectile motion, momentum, and impulse over the first 3 weeks. It contains 30 multiple choice questions testing student understanding of concepts like trajectory, gravity, velocity, range, angle of release, momentum, impulse, and elastic collisions. The test also includes word problems requiring calculations and analysis of scenarios involving projectiles and moving objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesSci.9 Weeks 1-3
Sci.9 Weeks 1-3
Uploaded by
Jaime CrispinoThis document is a summative test for a 9th grade science class covering topics in projectile motion, momentum, and impulse over the first 3 weeks. It contains 30 multiple choice questions testing student understanding of concepts like trajectory, gravity, velocity, range, angle of release, momentum, impulse, and elastic collisions. The test also includes word problems requiring calculations and analysis of scenarios involving projectiles and moving objects.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
DAWIS NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
SCIENCE 9- Weeks 1-3 Summative Test
Name: ______________________________________ Score:_____________________________
Grade & Section: ______________________________
I. Multiple Choice (1 point each item)
Choose the letter of your best answer and write on the space provided.
_______1. What do you call the path of the projectile?
A. Hyperbola B. parabola C. trajectory D. vertex
_______2. Projectile motion is a curved path we see in the mid-air where it moves in two dimensions,
horizontal and vertical components. What do you call that force which act on projectile motion accelerating
a downward force?
A. friction B. gravity C. height D. velocity
_______3. What is the value of acceleration due to gravity?
A. 9.8 m/s2 B. 9.8 m.s2 C. 9.8 m/s D. 9.8 m2/s
_______4. Which component of projectile motion is constant?
A. horizontal velocity B. vertical velocity C. both vertical and horizontal D. none
_______5. Which of the following shows an example of uniformly accelerated motion in vertical dimension?
B. Ball falling from 5th floor. C. Ball rolling down a slope.
C. Car accelerating from 10 m/s. D. Running boy in an inclined road.
_______6. Which of the following statements is NOT correct about projectile motion?
A. Horizontal velocity is always constant.
B. Gravity is one of the force acting on projectile motion.
C. Gravitational force is the acceleration of vertical dimension.
D. The highest point of the ball has zero velocity and acceleration.
_______7. A ball is thrown vertically upward. What is the instantaneous speed at its maximum height?
A. 0 m/s B. 5 m/s C. -9.8 m/s D. -9.8 m/s2
For items 8-10, read the given problem below. B C
A D
A 0.5 kg. ball was thrown at a horizontal velocity E
of 15 m/s.
Given: F
Mass = 0.5 kg.
Vx = 10 m/s
Vy = -9.8 m/s2
_______8. What is the horizontal velocity after
3 seconds?
A. -9.8 m/s2 B. 10 m/s C. 45 m/s D. -29.4 m/s2
_______9. At what point in the trajectory does the ball has the least velocity?
A. A B. C C. E D. F
_______10. What is the vertical distance of the ball at point F when it landed after 8 seconds?
A. 60 m B. 78.4 m C. 120 m D. 313.6 m
_______11. Based on the photo presented on the right side, which of the following
statements is NOT correct?
A. The highest point has a velocity of 0 m/s.
B. The acceleration at the highest point is -9.8 m/s 2.
C. The velocity is -10 m/s as it returned from the elevation. 10m/s
D. The velocity and acceleration of the ball at the highest point is zero.
_______12. What angle of elevation will travel the farthest distance?
A. 20o B. 30 o C. 45 o D. 60 o
_______13. What do you call the horizontal distance travelled by a projectile?
A. height B. slope C. range D. diameter
_______14 How does increasing the angle of release affect the height of a projectile?
A. The height increases C. The height decreases
B. The height remains constant D. The effect on the height cannot be determined
_______15. At what point in its path is the horizontal component of the velocity (𝑣!) of a projectile the
smallest?
C. As it nears the top C. Halfway to the top
D. At the top D. It is the same throughout the path
For items 16-18, read the situation below and answer the following questions.
Jessie, Migz, and Luke is playing a throwing ball game. The goal of the game is whoever will throw his ball
with the farthest distance will win the game. Jessie launched his ball at 20 0 while Migz uses 700 and Luke
throws it using 45o.
_______16. Who wins the game?
A. Jessie B. Luke C. Migz D. Cannot be determined
_______17. Which of the following statements below is TRUE based on the given situation?
A. Luke has the farthest and highest height of ball reached.
B. Jessie has the shortest range and height.
C. Jessie and Migz ball landed on the same range but different height of ball reached.
D. Migz and Luke has the same height of ball reached but Luke’s ball travel much farther.
_______18. Which of the following real-world examples requires an understanding of the relationship
between the angle of release and the height and range of a projectile?
A. Determining the speed of a moving car
B. Calculating the volume of a submerged object
C. Predicting the trajectory of a golf ball
D. Measuring the temperature of a liquid
_______19. Which of the following statements are true of the vertical motion of projectiles?
I. The vertical component of a projectile’s velocity is changing.
II. The vertical component of a projectile’s velocity is a constant value of 9.8 m/sec.
III. The vertical component of a projectile’s velocity is changing at a constant rate.
IV. The final vertical velocity of a projectile is always equal to the initial vertical velocity.
A. I, II and III B. II, III and IV C. I and III D. II and IV
_______20. Momentum is also called the mass in motion. Aside from mass, which is the other factor
affecting momentum?
A. acceleration B. height C. range D. velocity
_______21. What is the correct formula of impulse?
A. I= Ft B. I= mF C. I=F2/t D. I= ½ mFv
_______22. Bus, car, & motorcycle, which has the highest momentum?
A. Bus, because it has the biggest mass.
B. Car, because it can speed up the fastest.
C. Motorcycle, because it is the swiftest.
D. Cannot be determined.
_______23. What should car A must do to have a greater momentum than car B? Both car have the same
mass.
A. Car A must update its change oil.
B. Car A must travel faster than car B.
C. Car A must have more fuel than car B.
D. Car A must slower its velocity, gaining more weight.
_______24. Which of the following best defines impulse in the context of physics?
A. The change in velocity of an object C. The product of force and time
B. The product of mass and acceleration D. The resistance of an object to changes in motion
_______25. Which of the following statements is true about the law of conservation of momentum?
A. The total momentum of a system remains constant if no external forces act on it.
B. The momentum of an object is always conserved.
C. Momentum is only conserved in elastic collisions.
D. Momentum is inversely proportional to the velocity of an object.
_______26. A 23kg. girl runs in a velocity of 15 m/s achieving a distance of 45 m. What is the momentum
of the girl?
A. 250 kg-m/s B. 345 kg-m/s C. 675 kg-m/s D. 1035 kg-m/s
_______27. During collision, car A loses 50 units of momentum. What is the amount of momentum gained
by car B if momentum is conserved?
A. 0 B. still 50 units C. 25 units or half D. 100 units or double
For item 28-29:
Two 0.5 kg balls approach each other with the same speed of 1.0 m/s.
_______28. What is the total momentum of the system before collision?
A. 0 B.0.50 kgm/s C. 1.0 kgm/s D. -1.0 kgm/s
______29.) If there is no external force acting on the system, what is the total momentum of the system
after collision?
A. 0 B.0.50 kgm/s C. 1.0 kgm/s D.-1.0 kgm/s
_______30. Two billiard balls approach each other at equal speed. If they collide in a perfectly elastic
collision, what would be their velocities after collision?
A. Zero
B. Same in magnitude and direction
C. Same in magnitude but opposite in direction
D. Different in magnitude and opposite in direction
Prepared by:
JAIME S. CRISPINO
Science 9 Teacher
You might also like
- Midterm Examination in General Physics 1Document10 pagesMidterm Examination in General Physics 1zamora pegafi100% (2)
- 4th Periodic Test Grade 9 ScienceDocument4 pages4th Periodic Test Grade 9 ScienceMark Ryan J Bacus80% (5)
- 1 3 3 A IntroductionThermodynamicsDocument34 pages1 3 3 A IntroductionThermodynamicsZoinkedNo ratings yet
- May 8 2023Document3 pagesMay 8 2023Krisha Kate DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- 4Q Sci 9 PTDocument4 pages4Q Sci 9 PTRogelio EscobarNo ratings yet
- Summative TestDocument5 pagesSummative TestYbette Anorico VillamarinNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Assessment Wk1&2Document2 pagesSci9 Assessment Wk1&2Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- 4Q Sci 9 PTDocument3 pages4Q Sci 9 PTmay flor obonNo ratings yet
- Sci-Curr ExamDocument3 pagesSci-Curr ExamGelliane UbaganNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 TQDocument9 pagesScience Grade 9 TQLae GadgudeNo ratings yet
- Summative Test-Quarter 4: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationDocument11 pagesSummative Test-Quarter 4: Republic of The Philippines Department of EducationGlaiza CancioNo ratings yet
- Advanced PhysicsDocument5 pagesAdvanced PhysicsMichelle MalataNo ratings yet
- TQ Q4 Science-9Document5 pagesTQ Q4 Science-9Jovie Erma AtonNo ratings yet
- Science Revision G7Document17 pagesScience Revision G7Ahmed SalemNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion TestDocument8 pagesForces and Motion TestFahadImranXhiekhNo ratings yet
- TQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 9 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaDocument5 pagesTQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 9 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaKhim YabesNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter ExaminationDocument5 pages3rd Quarter ExaminationClaire EstimadaNo ratings yet
- Q4SCIENCE9Document6 pagesQ4SCIENCE9SHIRLEY JEAN SuganoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 9-Q4Document6 pagesReviewer in Science 9-Q4katherine bacallaNo ratings yet
- Test-Questions-Physics IDocument7 pagesTest-Questions-Physics INheszie Cortez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Q4 Summative-1Document4 pagesQ4 Summative-1artNo ratings yet
- 4Q Science G9Document3 pages4Q Science G9Kimmy Grace TañoNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Kawit 2017Document15 pagesMath 8 Kawit 2017HELMA B. JABELLONo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument10 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- Genphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingDocument5 pagesGenphysics 1ST Periodical Test For PrintingRonilo Rivera CaringalNo ratings yet
- Part I: Modified True or FalseDocument2 pagesPart I: Modified True or FalseGelliane UbaganNo ratings yet
- Quarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9 Final Na NamanDocument4 pagesQuarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9 Final Na NamanVanessa Joy Saavedra100% (1)
- Quarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9Document4 pagesQuarter-4-Exam SCIENCE9Vanessa Joy SaavedraNo ratings yet
- PretestDocument6 pagesPretestEdna Mae CruzNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsDocument6 pagesQuiz No. 1-Unit 1, 2, 3 - KINEMATICS, STATICS, DYNAMICS & ENERGY (SET A) - For StudentsChristian Nathaniel Ramon Palma100% (1)
- SCIENCE 9 4th QuarterDocument8 pagesSCIENCE 9 4th QuarterJezha Mae NelmidaNo ratings yet
- Sci9 Assessment Wk3&4Document2 pagesSci9 Assessment Wk3&4Jaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument6 pagesPhysics Reviewerfroilance100% (1)
- S M K I A S M K J A B X ADocument22 pagesS M K I A S M K J A B X ADanielNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1.finalDocument12 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1.finalzamora pegafiNo ratings yet
- Use The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Document4 pagesUse The Passage To Answer Questions 4 - 5Melvin CabonegroNo ratings yet
- PhEd. 2311 Mid ExamDocument4 pagesPhEd. 2311 Mid Examnegi diribaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 3RD QDocument7 pagesGrade 7 3RD QShielo Marie CabañeroNo ratings yet
- Learning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterDocument12 pagesLearning Task in Science9 - 4th QuarterQin XianNo ratings yet
- Class Xi PhysicsDocument160 pagesClass Xi PhysicsAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- Fourth Periodical ExaminationDocument4 pagesFourth Periodical ExaminationReymart VillapeñaNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For College Physics 8th EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For College Physics 8th EditionAlbert Ascher100% (41)
- GRAND TEST 9 Chap 2Document2 pagesGRAND TEST 9 Chap 2HNTARIQNo ratings yet
- 4th Summative Test Science 9Document3 pages4th Summative Test Science 9odette carzanoNo ratings yet
- First Written Test in Science 9 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022Document7 pagesFirst Written Test in Science 9 QUARTER 4, SY 2021-2022joan marie Pelias0% (1)
- General Physics 1-1Sst Quarter ExamDocument11 pagesGeneral Physics 1-1Sst Quarter ExamJaver Degorio100% (1)
- SEMI FINAL Examination SCIENCEDocument3 pagesSEMI FINAL Examination SCIENCErhenz marie cadelinia germanNo ratings yet
- General Physics-1 CPT U2Document4 pagesGeneral Physics-1 CPT U2Tracy Nicole MaurilloNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test Science 8 SY 2019-2020Document6 pages1st Periodical Test Science 8 SY 2019-2020Dayen Bison100% (1)
- Grade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Document4 pagesGrade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013Jerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- 3RD Grading Mastery Test Grade 7Document4 pages3RD Grading Mastery Test Grade 7Marjorie Baya BidlanNo ratings yet
- Physics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseDocument11 pagesPhysics 11 Year End Review Package - New Curriculum - UseCarmen JuranovicNo ratings yet
- Fourth Quarter Examination in Science 9: For Items 6-8, Refer To This SituationDocument5 pagesFourth Quarter Examination in Science 9: For Items 6-8, Refer To This SituationJ DNo ratings yet
- 4TH Quarter - Science 9Document7 pages4TH Quarter - Science 9MARIA THERESA TULALINo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Periodical ExamDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Periodical Exammarjoriebidlan445No ratings yet
- SCI9 TQ 4thquarterDocument4 pagesSCI9 TQ 4thquarterAilen Rose SantosNo ratings yet
- Q4 Long TestDocument9 pagesQ4 Long TestMelanie Ibarra CarlosNo ratings yet
- Reviwer in Gen. Physics 1Document4 pagesReviwer in Gen. Physics 1Romero, Ken Angelo B.No ratings yet
- Professional Golf Management (PGM) Practice Question Workbook: A Supplement to PGM Coursework for Levels 1, 2, and 3 (4th Edition)From EverandProfessional Golf Management (PGM) Practice Question Workbook: A Supplement to PGM Coursework for Levels 1, 2, and 3 (4th Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sci10 PT W1-3Document2 pagesSci10 PT W1-3Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 PT Weeks 1-3 - 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesSci.10 PT Weeks 1-3 - 2nd QuarterJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 PT Weeks 4-5 - 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesSci.10 PT Weeks 4-5 - 2nd QuarterJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 PT Weeks 6-8 - 2nd QuarterDocument2 pagesSci.9 PT Weeks 6-8 - 2nd QuarterJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Performance Task-SCI.9 - Weeks 4-5 3rd QDocument2 pagesPerformance Task-SCI.9 - Weeks 4-5 3rd QJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 W1-3 TOSDocument2 pagesSci.9 W1-3 TOSJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-2Document3 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-2Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 Weeks 4-6Document3 pagesSci.9 Weeks 4-6Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-3Document4 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-3Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 8.2Document3 pagesSci.10 Weeks 8.2Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 Weeks 1-2Document4 pagesSci.9 Weeks 1-2Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 4-5Document2 pagesSci.10 Weeks 4-5Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.10 Weeks 1-3Document3 pagesSci.10 Weeks 1-3Jaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Climate Compilation VideoDocument2 pagesClimate Compilation VideoJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Sci.9 W3-4 TOSDocument2 pagesSci.9 W3-4 TOSJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- PT - Q1-W1-2 LifestyleDocument3 pagesPT - Q1-W1-2 LifestyleJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- PROJECT PROPOSAL - Material Waste RecoveryDocument2 pagesPROJECT PROPOSAL - Material Waste RecoveryJaime CrispinoNo ratings yet
- Notes Ch.3-Es205Document4 pagesNotes Ch.3-Es205indayieee.12No ratings yet
- Forces P2Document76 pagesForces P2arjunboruto1234No ratings yet
- Steam TablesDocument16 pagesSteam TablesVishal ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes For High School - Types of ThermometerDocument8 pagesPhysics Notes For High School - Types of ThermometerZeroseveen Seveen100% (1)
- دوسية المهندس ابراهيم حسين النوافلة (Autosaved) - 230719 - 100837Document59 pagesدوسية المهندس ابراهيم حسين النوافلة (Autosaved) - 230719 - 100837Doha LababnehNo ratings yet
- BSC Nursing Entrance Paper PatternDocument22 pagesBSC Nursing Entrance Paper Patternrk91553280No ratings yet
- Water Cooled Chiller Performance Qualification Report: Godrej OneDocument16 pagesWater Cooled Chiller Performance Qualification Report: Godrej OneAnurag KumbhareNo ratings yet
- AY2223 EoY V1 PHY60A AKDocument16 pagesAY2223 EoY V1 PHY60A AKabdlurhman.ali.alaliNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesPhysical Chemistry Reviewer - Laws of ThermodynamicsJerome SadudaquilNo ratings yet
- Full Conceptual Physics 11Th Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual PDFDocument31 pagesFull Conceptual Physics 11Th Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual PDFblaine.nevill224100% (15)
- Cross-Section Properties: GeometryDocument2 pagesCross-Section Properties: GeometryDaniel MewsNo ratings yet
- General resistance in a two-phase fluid branch - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国Document3 pagesGeneral resistance in a two-phase fluid branch - MATLAB - MathWorks 中国944062528qqNo ratings yet
- Marine Hvac SystemDocument58 pagesMarine Hvac SystemSiti Aishah Hussien100% (3)
- AlıştırmaDocument3 pagesAlıştırmaJanet Baker100% (1)
- Grofcsik Andras-Physical Chemistry - 1Document195 pagesGrofcsik Andras-Physical Chemistry - 1György SzidóniaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Heat Transfer: H T T T TDocument18 pagesRadiation Heat Transfer: H T T T TiosuarizNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument86 pagesChemical Engineering ThermodynamicsSreedhar BabuNo ratings yet
- Vapor Compression Test RigDocument3 pagesVapor Compression Test RigTARUN DHUNNA0% (1)
- ASME Steam Tables - Compact Edition-American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2006)Document32 pagesASME Steam Tables - Compact Edition-American Society of Mechanical Engineers (2006)Jesús CbNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1Document4 pagesProblem Set 1daejung1025No ratings yet
- Heat Recovery Calculation SheetDocument3 pagesHeat Recovery Calculation SheetAnand sNo ratings yet
- JJ207 Sesi Jun2013Document15 pagesJJ207 Sesi Jun2013afiqzeroNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Electrostatics (Exercise) (81-118) - OrganizedDocument10 pages1.2 Electrostatics (Exercise) (81-118) - OrganizedRohan GubbaNo ratings yet
- Slides For F2F Week 1 Part 2 of 2 Heat Conduction and UnitsDocument33 pagesSlides For F2F Week 1 Part 2 of 2 Heat Conduction and Unitsashwinraj562No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Physics Chapter 05 Upthrust in Fluids Archimedes Principle and FloatationDocument21 pagesICSE Class 9 Physics Chapter 05 Upthrust in Fluids Archimedes Principle and FloatationgpfphysicsNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems, Physics 111 Common Exam 3, Spring 2024Document8 pagesPractice Problems, Physics 111 Common Exam 3, Spring 2024av742No ratings yet
- Vam Machine Flow DiagramDocument2 pagesVam Machine Flow DiagramDevNo ratings yet
- Math 5 DLP 57 - Application of Measuring TemperatureDocument8 pagesMath 5 DLP 57 - Application of Measuring TemperatureGenalyn Tambiao AchanzarNo ratings yet
- HumidificationDocument5 pagesHumidificationAlbert Junior EvangelistaNo ratings yet