Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COMMUNICATION
COMMUNICATION
Uploaded by
wannabeeurzCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Advanced Practice Test 3Document5 pagesAdvanced Practice Test 3Quyen DoanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer CommunicationJaimNo ratings yet
- Purcom MidtermDocument1 pagePurcom MidtermNene OcampoNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument5 pagesOral ComVenise RevillaNo ratings yet
- Sanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheDocument11 pagesSanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheLei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- 2ND Day ReviewerDocument4 pages2ND Day ReviewerJasmine de LeonNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm HandoutDocument25 pagesOral Comm HandoutRina Tubera100% (1)
- PURCPPTDocument24 pagesPURCPPTSamantha MendozaNo ratings yet
- PurposiveCommunication ModuleDocument5 pagesPurposiveCommunication Modulequeenie opelioNo ratings yet
- Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesCommunication ReviewerJESTON AMBUNANNo ratings yet
- Ge-Pc Midterm NotesDocument7 pagesGe-Pc Midterm NotesJamaica JaneNo ratings yet
- DIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleDocument18 pagesDIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleMikex Mike100% (2)
- Purp Com Reviewer 1Document5 pagesPurp Com Reviewer 1Janica Pauline DaydayNo ratings yet
- Purc111 Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesPurc111 Prelim ReviewerJamaica EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument15 pagesPurcom ReviewerJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDA SulitNo ratings yet
- Munication in The Digital AgeDocument37 pagesMunication in The Digital AgeRechiel A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerDaennise Louiseanna SebastianNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 - Oral CommunicationDocument5 pagesStem 11 - Oral CommunicationLance CastroNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed - Purposive CommunicationDocument21 pagesGen Ed - Purposive CommunicationWilson Del Rosario IINo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument5 pagesOral CommmackyjusainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4Document16 pagesChapter 1-4SJ SuingNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument14 pagesOral CommunicationBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument20 pagesPurposive Communicationmika miculobNo ratings yet
- PURCDocument7 pagesPURCFLEUR MARIE MICHELLE CAHAPAYNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication PrelimDocument2 pagesOral Communication PrelimAngelika ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Purcomm Notes Wk1 To Wk7Document16 pagesPurcomm Notes Wk1 To Wk7Jenny GarciaNo ratings yet
- J. Paul LeaganDocument15 pagesJ. Paul LeaganAries C. GavinoNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes Principles and EthicsDocument41 pagesCommunication Processes Principles and EthicsJohn Flores100% (1)
- COMMUNICATIONDocument2 pagesCOMMUNICATIONramoskynchNo ratings yet
- Purposive ComDocument7 pagesPurposive ComAlliah Mickah GallegaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Oral CommDocument20 pagesLesson 1 Oral CommRaymond CorreaNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument6 pagesPurposive CommunicationLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Purc Prelim ReviewerDocument2 pagesPurc Prelim ReviewerWansun MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer For Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesMidterm Reviewer For Purposive CommunicationAnne RiegoNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesPurposive CommunicationMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Small Group Communication - When: Jmba2019Document2 pagesSmall Group Communication - When: Jmba2019Maverick AlviarNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Complete Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesPurposive Communication Complete Lecture NotesShiela Mae CasNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PURC111Document10 pagesReviewer PURC111priya garciaNo ratings yet
- Purp CommDocument5 pagesPurp CommKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 OutlineDocument5 pagesLesson 1 OutlineXHYRICH ISLETANo ratings yet
- Bmancomskillpdfassign PDFDocument6 pagesBmancomskillpdfassign PDFRODWELL ZVENYIKANo ratings yet
- Communis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Document8 pagesCommunis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Angelica TañedoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Com PPT 2Document20 pagesPurposive Com PPT 2banderajakeson748No ratings yet
- PEOPLE." Keep As A Reminder.Document4 pagesPEOPLE." Keep As A Reminder.Angelica Ross de LunaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesOral CommunicationPaul RobertNo ratings yet
- P119 - Module 3Document4 pagesP119 - Module 3Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Gene Lourd HUFANCIA Module 1 Lesson 1 Communication Process - NEWDocument9 pagesGene Lourd HUFANCIA Module 1 Lesson 1 Communication Process - NEWGene Lourd Erlano HufanciaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument10 pagesOral Comm ReviewerLucille Marie SabioNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication (Reviewer)Document14 pagesOral Communication (Reviewer)Harchelo AndayaNo ratings yet
- Purc Transes PrelimDocument4 pagesPurc Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument4 pagesOral CommunicationKujira FloresNo ratings yet
- Kinesics Derived From The Greek Term "Kinesis"Document5 pagesKinesics Derived From The Greek Term "Kinesis"Mics RamosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Monthly Day 2 ReviewerDocument8 pages2nd Monthly Day 2 Reviewerbrandon radhNo ratings yet
- Oc ReviewerDocument3 pagesOc ReviewerRia RegaspiNo ratings yet
- PurComm (HW 1)Document2 pagesPurComm (HW 1)Charmaine Krystel RamosNo ratings yet
- Purposive ComDocument16 pagesPurposive ComGhleedel Mhae AquinoNo ratings yet
- ENG Short NotesDocument23 pagesENG Short Notesb423069No ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerElvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- THE SILENT CONVERSATION: Understanding the Power of Nonverbal Communication in Everyday Interactions (2024 Guide for Beginners)From EverandTHE SILENT CONVERSATION: Understanding the Power of Nonverbal Communication in Everyday Interactions (2024 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- Exercise On SummarizingDocument4 pagesExercise On Summarizingjaycee_evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Key Test 13Document4 pagesKey Test 1324. Võ Nguyễn Ngọc NhiNo ratings yet
- LynxDocument9 pagesLynxSunshine PowerNo ratings yet
- Interferensi Bahasa Ibu Terhadap Pemerolehan Bahasa KeduaDocument12 pagesInterferensi Bahasa Ibu Terhadap Pemerolehan Bahasa Keduagoblir gbNo ratings yet
- Ôn tập giữa học kì I - Unit 2 - Test 2Document4 pagesÔn tập giữa học kì I - Unit 2 - Test 2Vòng Bảo NgọcNo ratings yet
- Courtship BehaviourDocument36 pagesCourtship BehaviourMunzareen RiazNo ratings yet
- Purcom Chapter 1Document44 pagesPurcom Chapter 1bonbon.kentbriannNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 57 - Có Đáp ÁnDocument19 pagesĐỀ SỐ 57 - Có Đáp ÁnHao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Body Language & Grooming-1Document14 pagesBody Language & Grooming-1Ãjinkyaraje MáhagàòñkärNo ratings yet
- Afaan Karoorsuufi WaaltessuuDocument59 pagesAfaan Karoorsuufi WaaltessuuNaol Yordanos Gosa100% (1)
- Animal Communication - ParconDocument5 pagesAnimal Communication - ParconSaire Chrysbelle Parcon0% (1)
- Faragó Et Al. - 2010 - PLoS ONEDocument8 pagesFaragó Et Al. - 2010 - PLoS ONETamas FaragoNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Table (Data Underlying) :: Mysticeti (Baleen Whales)Document27 pagesSupplementary Table (Data Underlying) :: Mysticeti (Baleen Whales)rppawar_321203003No ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Human CommunicationDocument3 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Human Communicationhashamraza7469% (16)
- Egg Incubation Calendar For Budgies and CockatielsDocument2 pagesEgg Incubation Calendar For Budgies and Cockatielsrmcastro72No ratings yet
- Section B1 Topic Conversation Possible Questions AskedDocument7 pagesSection B1 Topic Conversation Possible Questions Askedkhamini dilly kannanNo ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Communication in Dogs-1-3Document3 pagesCommunication in Dogs-1-3harryNo ratings yet
- Westley and Maclean Model of CommunicationDocument4 pagesWestley and Maclean Model of Communicationjohnleegiba09No ratings yet
- A Word in The Hand: The Gestural Origins of Language: Michael C. CorballisDocument20 pagesA Word in The Hand: The Gestural Origins of Language: Michael C. CorballisEduardo Torres CastrejonNo ratings yet
- Kismet Is A Pioneering Sociable Robot Developed by DRDocument2 pagesKismet Is A Pioneering Sociable Robot Developed by DRfazfemtqeNo ratings yet
- Human Perception of Emotions From Canis Familiaris Barks: An Auditory-Perceptual StudyDocument5 pagesHuman Perception of Emotions From Canis Familiaris Barks: An Auditory-Perceptual StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Expression of Basic Emotions Across Different CulturesDocument17 pagesExpression of Basic Emotions Across Different CulturesAlex ResearchersNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Unit 1 NotesDocument88 pagesBusiness Communication Unit 1 Notessatyamss1233No ratings yet
- Mastering Arabic FluencyDocument3 pagesMastering Arabic FluencyHebamahmahmoud HeibaNo ratings yet
- Animal Communication!Document39 pagesAnimal Communication!νικος νικου100% (2)
- Questions About Language What Everyone Should Know About Language in The 21st Century (Laurie Bauer, Andreea S. Calude)Document199 pagesQuestions About Language What Everyone Should Know About Language in The 21st Century (Laurie Bauer, Andreea S. Calude)Duong Thi Tuyet B2112759No ratings yet
- Eduardo Coutinho, Klaus R. Scherer, and Nicola Dibben. Singing and Emotion.Document24 pagesEduardo Coutinho, Klaus R. Scherer, and Nicola Dibben. Singing and Emotion.Юрий СемёновNo ratings yet
- Proboscis Monkeys (Nasalis Larvatus (Wurmb, 1787) ) Have Unusually High-Pitched VocalizationsDocument5 pagesProboscis Monkeys (Nasalis Larvatus (Wurmb, 1787) ) Have Unusually High-Pitched VocalizationsMuhammad Fahreza Rizky WNo ratings yet
COMMUNICATION
COMMUNICATION
Uploaded by
wannabeeurzOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COMMUNICATION
COMMUNICATION
Uploaded by
wannabeeurzCopyright:
Available Formats
PURC
WEEK 1 / SEMESTER 1
COMMUNICATION PROCESS, PRINCIPLES, AND ETHICS
COMMUNICATION
Communis (Latin) means common or to
commune or to share something in common.
A process by which people send messages or
exchange thoughts, feelings, and ideas using
words, sounds, sign, or behaviors to someone
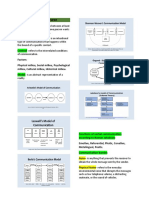
else. Berlo’s - one way. Sender and receiver should
It is reciprocal because we cannot separate have the same monologue
communicators into senders and receiver
It is a process because it keeps on evolving and
changing
Involves creating and sharing of meaning
NATURE OF COMMUNICATION -----------------
Related to human activity
Involves two or more parties
Could be a one – way or maybe a two – way
process
The success of communication depends on the
parties involved
ELEMENTS OF COMMUNICATION
Sender – the one responsible encoding,
transmitting, sending the message
Receiver – responsible decoding, understanding Helical model – represent as an individual
interpreting the message VERBAL AND NON – VERBAL COMMUNICATION
Message – considered the most vital, without it
there will be no communication VERBAL COMMUNICATION ---------------------
Channel – the route of the message
The form of communication in which a message
Noise – disturbing factor (negative)
is transmitted verbally; done by word of mouth
External: physical
and piece of writing
Internal: psychological; physiological
Divide into two: oral communication and written
Feedback – response given by the receiver to the
communication
sender
Involve the use of words
Setting – affects communication process
NON – VERBAL COMMUNICATION -------------
MODELS OF COMMUNICATION
A form of sharing insights and ideas, information,
experiences, etc. without the use of words
Most of the time verbal communication is
supported by non – verbal communication to
better portray the meanings a speaker would like
to share
VILLARAZA, YOJANN LOIS S. | BSN1 - 26
LESSON 1
Public distance – more than 12 feet; public
TYPES OF NON – VERBAL COMMUNICATION speaking
BODY MOVEMENTS – body kinetics TOUCH – haptic communication. Reflects the
Emblems – body movements that have a meaning of the relationship between sender and
direct translation into words receiver
Illustrators – used to accent, emphasize or Functional/Professional
reinforce words Social/Polite
Regulators -signs showing control of the back Friendship/Warmth
– and forth natures of speaking and listening Love/Intimacy
Display of feelings – a person’s face and body Sexual/Arousal
movements may convey how intense his TIME – chronemics, can also communicate
emotion is. message. Two kinds of people based on time;
Adaptors – non – verbal used in adopting the punctual and late.
communication situation
PARALANGUAGE – the way of saying ▪ Communication is Schema – driven
something ▪ Communication is an interpretative act
Rate – speed of speaking ▪ Communication does not guarantee a direct or
Pitch – highness or lowness of tone automatic link between two minds
Volume – loudness ▪ Communication is active, powerful, or forceful
Quality – pleasing or unpleasing sound ▪ Communication is symbolic
BODY TYPES – can also communicate message ▪ Communication always results something
Ectomorphs (thin) – ambitious, younger, ▪ Communication is irreversible
more suspicious of others, more tense, etc. ▪ Communication is contextual
Endomorphs (fat) – more fashionable, lazier, ▪ Communication is development or progressive
weaker, more talkative, older, etc. ▪ Communication is a process
Mesomorphs (athletic) – stronger, more ▪ Communication is ethical
adventurous, more matured, younger, etc. ▪ Communication is influenced by media and
ATTRACTIVENESS – physical attributes of a technology
person may mean something to the people
around her.
BODY ADORNMENT – it involves jewelry,
clothing, make – up and hairstyle.
SPACE AND DISTANCE – proxemics. A person
way using the space around him as well as the
distance from where he stands
Intimate distance – direct contact with each
other or are no more than 18 inches apart
Personal distance – people may stay away
from 18 inches to 4 feet from each other as
casual and personal conversation
Social distance – when talking to unknown
person; keep distance of 4 feet to 12 feet
VILLARAZA, YOJANNA LOIS S. | BSN1 – 26
You might also like
- Advanced Practice Test 3Document5 pagesAdvanced Practice Test 3Quyen DoanNo ratings yet
- Reviewer CommunicationDocument2 pagesReviewer CommunicationJaimNo ratings yet
- Purcom MidtermDocument1 pagePurcom MidtermNene OcampoNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument5 pagesOral ComVenise RevillaNo ratings yet
- Sanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheDocument11 pagesSanchez (2017) : Non-Verbal Cues - Make TheLei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- 2ND Day ReviewerDocument4 pages2ND Day ReviewerJasmine de LeonNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm HandoutDocument25 pagesOral Comm HandoutRina Tubera100% (1)
- PURCPPTDocument24 pagesPURCPPTSamantha MendozaNo ratings yet
- PurposiveCommunication ModuleDocument5 pagesPurposiveCommunication Modulequeenie opelioNo ratings yet
- Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesCommunication ReviewerJESTON AMBUNANNo ratings yet
- Ge-Pc Midterm NotesDocument7 pagesGe-Pc Midterm NotesJamaica JaneNo ratings yet
- DIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleDocument18 pagesDIASS Fourth Quarter ModuleMikex Mike100% (2)
- Purp Com Reviewer 1Document5 pagesPurp Com Reviewer 1Janica Pauline DaydayNo ratings yet
- Purc111 Prelim ReviewerDocument8 pagesPurc111 Prelim ReviewerJamaica EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Purcom ReviewerDocument15 pagesPurcom ReviewerJhae Zharie Delasan PanosoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication - Second Sem - Midterms: Community. They Share Same Set of Rules in TheDA SulitNo ratings yet
- Munication in The Digital AgeDocument37 pagesMunication in The Digital AgeRechiel A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument3 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerDaennise Louiseanna SebastianNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 - Oral CommunicationDocument5 pagesStem 11 - Oral CommunicationLance CastroNo ratings yet
- Gen Ed - Purposive CommunicationDocument21 pagesGen Ed - Purposive CommunicationWilson Del Rosario IINo ratings yet
- Oral CommDocument5 pagesOral CommmackyjusainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-4Document16 pagesChapter 1-4SJ SuingNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument14 pagesOral CommunicationBlaire ReyesNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument20 pagesPurposive Communicationmika miculobNo ratings yet
- PURCDocument7 pagesPURCFLEUR MARIE MICHELLE CAHAPAYNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication PrelimDocument2 pagesOral Communication PrelimAngelika ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Purcomm Notes Wk1 To Wk7Document16 pagesPurcomm Notes Wk1 To Wk7Jenny GarciaNo ratings yet
- J. Paul LeaganDocument15 pagesJ. Paul LeaganAries C. GavinoNo ratings yet
- Communication Processes Principles and EthicsDocument41 pagesCommunication Processes Principles and EthicsJohn Flores100% (1)
- COMMUNICATIONDocument2 pagesCOMMUNICATIONramoskynchNo ratings yet
- Purposive ComDocument7 pagesPurposive ComAlliah Mickah GallegaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Oral CommDocument20 pagesLesson 1 Oral CommRaymond CorreaNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument6 pagesPurposive CommunicationLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Purc Prelim ReviewerDocument2 pagesPurc Prelim ReviewerWansun MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer For Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesMidterm Reviewer For Purposive CommunicationAnne RiegoNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument4 pagesPurposive CommunicationMarinel VergaraNo ratings yet
- Small Group Communication - When: Jmba2019Document2 pagesSmall Group Communication - When: Jmba2019Maverick AlviarNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication Complete Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesPurposive Communication Complete Lecture NotesShiela Mae CasNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PURC111Document10 pagesReviewer PURC111priya garciaNo ratings yet
- Purp CommDocument5 pagesPurp CommKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 OutlineDocument5 pagesLesson 1 OutlineXHYRICH ISLETANo ratings yet
- Bmancomskillpdfassign PDFDocument6 pagesBmancomskillpdfassign PDFRODWELL ZVENYIKANo ratings yet
- Communis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Document8 pagesCommunis Which Means "Common" and Communico Which Means "To Confer"Angelica TañedoNo ratings yet
- Purposive Com PPT 2Document20 pagesPurposive Com PPT 2banderajakeson748No ratings yet
- PEOPLE." Keep As A Reminder.Document4 pagesPEOPLE." Keep As A Reminder.Angelica Ross de LunaNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesOral CommunicationPaul RobertNo ratings yet
- P119 - Module 3Document4 pagesP119 - Module 3Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Gene Lourd HUFANCIA Module 1 Lesson 1 Communication Process - NEWDocument9 pagesGene Lourd HUFANCIA Module 1 Lesson 1 Communication Process - NEWGene Lourd Erlano HufanciaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm ReviewerDocument10 pagesOral Comm ReviewerLucille Marie SabioNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication (Reviewer)Document14 pagesOral Communication (Reviewer)Harchelo AndayaNo ratings yet
- Purc Transes PrelimDocument4 pagesPurc Transes PrelimGelo AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument4 pagesOral CommunicationKujira FloresNo ratings yet
- Kinesics Derived From The Greek Term "Kinesis"Document5 pagesKinesics Derived From The Greek Term "Kinesis"Mics RamosNo ratings yet
- 2nd Monthly Day 2 ReviewerDocument8 pages2nd Monthly Day 2 Reviewerbrandon radhNo ratings yet
- Oc ReviewerDocument3 pagesOc ReviewerRia RegaspiNo ratings yet
- PurComm (HW 1)Document2 pagesPurComm (HW 1)Charmaine Krystel RamosNo ratings yet
- Purposive ComDocument16 pagesPurposive ComGhleedel Mhae AquinoNo ratings yet
- ENG Short NotesDocument23 pagesENG Short Notesb423069No ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ReviewerDocument7 pagesPurposive Communication ReviewerElvira MirajulNo ratings yet
- THE SILENT CONVERSATION: Understanding the Power of Nonverbal Communication in Everyday Interactions (2024 Guide for Beginners)From EverandTHE SILENT CONVERSATION: Understanding the Power of Nonverbal Communication in Everyday Interactions (2024 Guide for Beginners)No ratings yet
- Exercise On SummarizingDocument4 pagesExercise On Summarizingjaycee_evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Key Test 13Document4 pagesKey Test 1324. Võ Nguyễn Ngọc NhiNo ratings yet
- LynxDocument9 pagesLynxSunshine PowerNo ratings yet
- Interferensi Bahasa Ibu Terhadap Pemerolehan Bahasa KeduaDocument12 pagesInterferensi Bahasa Ibu Terhadap Pemerolehan Bahasa Keduagoblir gbNo ratings yet
- Ôn tập giữa học kì I - Unit 2 - Test 2Document4 pagesÔn tập giữa học kì I - Unit 2 - Test 2Vòng Bảo NgọcNo ratings yet
- Courtship BehaviourDocument36 pagesCourtship BehaviourMunzareen RiazNo ratings yet
- Purcom Chapter 1Document44 pagesPurcom Chapter 1bonbon.kentbriannNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 57 - Có Đáp ÁnDocument19 pagesĐỀ SỐ 57 - Có Đáp ÁnHao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Body Language & Grooming-1Document14 pagesBody Language & Grooming-1Ãjinkyaraje MáhagàòñkärNo ratings yet
- Afaan Karoorsuufi WaaltessuuDocument59 pagesAfaan Karoorsuufi WaaltessuuNaol Yordanos Gosa100% (1)
- Animal Communication - ParconDocument5 pagesAnimal Communication - ParconSaire Chrysbelle Parcon0% (1)
- Faragó Et Al. - 2010 - PLoS ONEDocument8 pagesFaragó Et Al. - 2010 - PLoS ONETamas FaragoNo ratings yet
- Supplementary Table (Data Underlying) :: Mysticeti (Baleen Whales)Document27 pagesSupplementary Table (Data Underlying) :: Mysticeti (Baleen Whales)rppawar_321203003No ratings yet
- The Difference Between Animal and Human CommunicationDocument3 pagesThe Difference Between Animal and Human Communicationhashamraza7469% (16)
- Egg Incubation Calendar For Budgies and CockatielsDocument2 pagesEgg Incubation Calendar For Budgies and Cockatielsrmcastro72No ratings yet
- Section B1 Topic Conversation Possible Questions AskedDocument7 pagesSection B1 Topic Conversation Possible Questions Askedkhamini dilly kannanNo ratings yet
- Purcom Midterm Exam NotesDocument18 pagesPurcom Midterm Exam NotesShaina TelenNo ratings yet
- Communication in Dogs-1-3Document3 pagesCommunication in Dogs-1-3harryNo ratings yet
- Westley and Maclean Model of CommunicationDocument4 pagesWestley and Maclean Model of Communicationjohnleegiba09No ratings yet
- A Word in The Hand: The Gestural Origins of Language: Michael C. CorballisDocument20 pagesA Word in The Hand: The Gestural Origins of Language: Michael C. CorballisEduardo Torres CastrejonNo ratings yet
- Kismet Is A Pioneering Sociable Robot Developed by DRDocument2 pagesKismet Is A Pioneering Sociable Robot Developed by DRfazfemtqeNo ratings yet
- Human Perception of Emotions From Canis Familiaris Barks: An Auditory-Perceptual StudyDocument5 pagesHuman Perception of Emotions From Canis Familiaris Barks: An Auditory-Perceptual StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Expression of Basic Emotions Across Different CulturesDocument17 pagesExpression of Basic Emotions Across Different CulturesAlex ResearchersNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Unit 1 NotesDocument88 pagesBusiness Communication Unit 1 Notessatyamss1233No ratings yet
- Mastering Arabic FluencyDocument3 pagesMastering Arabic FluencyHebamahmahmoud HeibaNo ratings yet
- Animal Communication!Document39 pagesAnimal Communication!νικος νικου100% (2)
- Questions About Language What Everyone Should Know About Language in The 21st Century (Laurie Bauer, Andreea S. Calude)Document199 pagesQuestions About Language What Everyone Should Know About Language in The 21st Century (Laurie Bauer, Andreea S. Calude)Duong Thi Tuyet B2112759No ratings yet
- Eduardo Coutinho, Klaus R. Scherer, and Nicola Dibben. Singing and Emotion.Document24 pagesEduardo Coutinho, Klaus R. Scherer, and Nicola Dibben. Singing and Emotion.Юрий СемёновNo ratings yet
- Proboscis Monkeys (Nasalis Larvatus (Wurmb, 1787) ) Have Unusually High-Pitched VocalizationsDocument5 pagesProboscis Monkeys (Nasalis Larvatus (Wurmb, 1787) ) Have Unusually High-Pitched VocalizationsMuhammad Fahreza Rizky WNo ratings yet