Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Spot The Difference: Name - Class
Spot The Difference: Name - Class
Uploaded by
NonuCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 4 Reactivity of MetalsDocument21 pagesScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 4 Reactivity of MetalsYusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- CH U5 A1 Balancing WorksheetDocument3 pagesCH U5 A1 Balancing WorksheetLayna HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Peroxo Compounds, InorganicDocument32 pagesPeroxo Compounds, InorganicKilsys AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Progtest Paper 2-2014 PDFDocument16 pagesScience 8 Progtest Paper 2-2014 PDFsean gillmore100% (2)
- Preventing Scale Loss During Heat Treatment & Hot Forging - With ImagesDocument17 pagesPreventing Scale Loss During Heat Treatment & Hot Forging - With ImagesSrikar Shenoy100% (1)
- Chem Paper 1 Pracs QPDocument21 pagesChem Paper 1 Pracs QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Module Chapter 4Document21 pagesModule Chapter 4Hannan NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Test (Levels 5-7) : Name - ClassDocument6 pagesTest (Levels 5-7) : Name - ClassJayNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Document17 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Soraya DeenNo ratings yet
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 14.1 Metals and Alloys Metals 1.: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document10 pagesWorksheet 14.1 Metals and Alloys Metals 1.: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Apple kokNo ratings yet
- 7 Sci Elements and CompoundsDocument2 pages7 Sci Elements and CompoundsKanwal JamilNo ratings yet
- F3 SN CHP 4 2023Document38 pagesF3 SN CHP 4 2023NG YI ZHI MoeNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Mac F4 Chemistry SALT Workshop (Student Version) Original PDFDocument20 pages1.0 Mac F4 Chemistry SALT Workshop (Student Version) Original PDFNurul AlyaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Use of Amount of Substance on Volumes of Gases QP (separate only)Document17 pages3.5 Use of Amount of Substance on Volumes of Gases QP (separate only)Charu KochharNo ratings yet
- SC8c.2 - Bases and Salts - StrengthenDocument1 pageSC8c.2 - Bases and Salts - Strengthenarnavpatel138No ratings yet
- 3.5 Use of Amount of Substance On Volumes of Gases QPDocument17 pages3.5 Use of Amount of Substance On Volumes of Gases QPTang Hing Yiu, SamuelNo ratings yet
- Matter Homework MATTERDocument5 pagesMatter Homework MATTERJOHN REY FABILLONo ratings yet
- Sep 2013Document28 pagesSep 2013Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- Chemical Calculations Questions - Many and HardDocument26 pagesChemical Calculations Questions - Many and Hard19gururNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Document25 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Bineta NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SaltsDocument1 pageChapter 9 SaltsahsanNo ratings yet
- Excel ChemistryDocument14 pagesExcel ChemistrySumathi GanasenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Study GuideDocument3 pagesChemical Reactions Study Guidejaydon geyerNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Use of Amount of Substance On Pure Substances QP PDFDocument31 pages3.2 Use of Amount of Substance On Pure Substances QP PDFDanish FiverNo ratings yet
- Sc11.4w - Group 1 Homework1Document1 pageSc11.4w - Group 1 Homework10220141106No ratings yet
- BALANCING Worksheet 3Document1 pageBALANCING Worksheet 3Amanda Leigh ResuelloNo ratings yet
- 4thq 3rd Modular SummDocument1 page4thq 3rd Modular SummPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Bonding and Structure QPDocument42 pages2.2 Bonding and Structure QPabisolafaluyi5No ratings yet
- S9 Unit 5 WorksheetsDocument15 pagesS9 Unit 5 Worksheetsbuddyfigther8No ratings yet
- S9 - End-Of-Unit 5 TestDocument2 pagesS9 - End-Of-Unit 5 TestMoganoni MogaNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesandsaltsDocument26 pagesAcids Basesandsaltsremaselshazly76No ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysisTeena SheikhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test Review - Mar 2023Document4 pagesChemistry Test Review - Mar 2023rblxproNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument6 pagesIlovepdf Mergedasdasd1414196No ratings yet
- Notes and Questions: Aqa GcseDocument31 pagesNotes and Questions: Aqa Gcseapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Gases and Solutions QPDocument13 pagesGases and Solutions QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SC8 Full Topic WorksheetsDocument34 pagesChemistry SC8 Full Topic WorksheetscramdamdageNo ratings yet
- Making Salts WorksheetDocument2 pagesMaking Salts WorksheetSarah KKC0% (1)
- Screenshot 2024-01-21 at 15.55.50Document22 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-21 at 15.55.50b4jdv8bq4xNo ratings yet
- Chem 209A Pre-Test 2 Semester, AY 2021-2022Document3 pagesChem 209A Pre-Test 2 Semester, AY 2021-2022JEZELLE KAYE BOCONo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 CH6.3 PrintDocument3 pagesScience Form 1 CH6.3 PrintnisaNo ratings yet
- C Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesC Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes Revision Workbook 2Document12 pagesChemical Changes Revision Workbook 2haleeza648No ratings yet
- Ch2 -4 revision note (stu)Document6 pagesCh2 -4 revision note (stu)mtauNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsNameDocument2 pagesRedox ReactionsNamesondos tawfiqNo ratings yet
- Y9 Chem Eot 2Document3 pagesY9 Chem Eot 2Sandy BelleNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chem Equations SeDocument3 pagesBalancing Chem Equations SeNoah BloniarzNo ratings yet
- 7 Revision Sheet - IIDocument2 pages7 Revision Sheet - IIsakshampaharia1No ratings yet
- Physical/ Chemical Changes: CGA #2 ReviewDocument8 pagesPhysical/ Chemical Changes: CGA #2 Reviewengchemistry18No ratings yet
- WS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSDocument7 pagesWS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesTopic 3 Covalent BondingufukNo ratings yet
- A. Magnesium Chloride B. Sodium Nitride C. Potassium Bromide D. Lithium OxideDocument4 pagesA. Magnesium Chloride B. Sodium Nitride C. Potassium Bromide D. Lithium Oxidesawyeranthony2009No ratings yet
- 2017 Unit 2 Chemistry KTT 3 Stoichiometry - Question BookDocument11 pages2017 Unit 2 Chemistry KTT 3 Stoichiometry - Question BookYue WeiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction PracticeDocument3 pagesChemical Reaction PracticeYeseo ChoiNo ratings yet
- Chemcial Reactions Cloze PassageDocument5 pagesChemcial Reactions Cloze PassageNadia CzeredreckiNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions For Year 9 ChemistryDocument15 pagesRevision Questions For Year 9 ChemistryKostas TampakisNo ratings yet
- ShapesofcomplexionsDocument41 pagesShapesofcomplexions/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Test1 StoichiometryDocument2 pagesTest1 StoichiometryHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument11 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The P-BlockDocument10 pages2.1 The P-BlockNonuNo ratings yet
- October 2021 MS - Component 3 Eduqas Chemistry A-LevelDocument15 pagesOctober 2021 MS - Component 3 Eduqas Chemistry A-LevelNonuNo ratings yet
- June 2015 QP - Unit 5 WJEC Biology A-LevelDocument24 pagesJune 2015 QP - Unit 5 WJEC Biology A-LevelNonuNo ratings yet
- 2.4. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument10 pages2.4. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsNonuNo ratings yet
- 3.C. Neurobiology and Behaviour QPDocument35 pages3.C. Neurobiology and Behaviour QPNonuNo ratings yet
- 3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy MSDocument11 pages3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy MSNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: AUTUMN 2021Document15 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: AUTUMN 2021NonuNo ratings yet
- Eduqas Component 3 Nerve ImpulseDocument1 pageEduqas Component 3 Nerve ImpulseNonuNo ratings yet
- 3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy QPDocument40 pages3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy QPNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022Document18 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022NonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022Document21 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022NonuNo ratings yet
- Name - Class - : Exploring Science 9 Page 47 © Pearson Education Limited 2003Document8 pagesName - Class - : Exploring Science 9 Page 47 © Pearson Education Limited 2003NonuNo ratings yet
- Energy and Electricity SOWDocument53 pagesEnergy and Electricity SOWNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level: Thursday, 9 June 2022 - Afternoon Energy For LifeDocument32 pagesGce A Level: Thursday, 9 June 2022 - Afternoon Energy For LifeNonuNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources SOWDocument20 pagesEnergy Resources SOWNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022Document18 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022NonuNo ratings yet
- 2022 - 20 Reproduction IGCSE EdexcelDocument55 pages2022 - 20 Reproduction IGCSE EdexcelNonuNo ratings yet
- Eduqas PaperDocument36 pagesEduqas PaperNonuNo ratings yet
- Unit 9aDocument3 pagesUnit 9aNonuNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelNonuNo ratings yet
- Wjec Paper 1Document19 pagesWjec Paper 1NonuNo ratings yet
- 9E SciDocument48 pages9E SciNonuNo ratings yet
- Eduqas Paper 2Document44 pagesEduqas Paper 2NonuNo ratings yet
- Wjec Paper 3Document32 pagesWjec Paper 3NonuNo ratings yet
- Sound 2Document12 pagesSound 2NonuNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials For Dental Implants: PART II Basic SciencesDocument29 pagesBiomaterials For Dental Implants: PART II Basic SciencesAna-Maria RoșuNo ratings yet
- R&S Oscar Cutting Oil MSDSDocument5 pagesR&S Oscar Cutting Oil MSDSZhi Hou NgNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module 2010 Answer SchemeDocument47 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Module 2010 Answer SchemedhuulhudaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Final Term PaperDocument8 pagesClass 7 Final Term PaperYakshitha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sample FileDocument8 pagesSample FileBrajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- CLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionDocument12 pagesCLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionHirakjyoti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy (Mega)Document20 pagesMetallurgy (Mega)Anant JainNo ratings yet
- Abdolmohsen Shabib-Asl, 2014 Referensi PPMDocument8 pagesAbdolmohsen Shabib-Asl, 2014 Referensi PPMAdzan Topaz AdityaNo ratings yet
- 08-Metals and Non-Metals Theory PDFDocument51 pages08-Metals and Non-Metals Theory PDFvikash singh rajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Msds-Of M 220-Eng - 43-29357Document13 pagesMsds-Of M 220-Eng - 43-29357Lennier SaezNo ratings yet
- Importance of TreesDocument3 pagesImportance of TreesNirmala SugurNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document3 pagesLab Report 3Nayli QistinaNo ratings yet
- Summary of As QuestionDocument4 pagesSummary of As QuestionYuan XintongNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Titanium Part 1 Aggressive EnvironmenDocument13 pagesCorrosion of Titanium Part 1 Aggressive EnvironmenHamza FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chm131 Chapter 1 Atoms Molecules Ions Chemical EqDocument106 pagesChm131 Chapter 1 Atoms Molecules Ions Chemical EqAdibah Qistina QistinaNo ratings yet
- Test MolesDocument5 pagesTest MolesadilNo ratings yet
- All NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.onlineDocument16 pagesAll NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.onlineKaushik RajNo ratings yet
- Gas Fittings and Adapters: Always There For LifeDocument53 pagesGas Fittings and Adapters: Always There For LifetaibkNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Environmental ManagementDocument6 pagesResearch Paper Environmental Managementgw219k4y100% (1)
- 10th Chemistry Revision Assignments - All Chapters CombinedDocument11 pages10th Chemistry Revision Assignments - All Chapters CombinedYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Climeworks - US20120076711Document26 pagesClimeworks - US20120076711Alberto Moreno GomezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1.exercise 1ADocument28 pagesChemistry Chapter 1.exercise 1AAsifNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument184 pagesUntitledKalin BhayiaNo ratings yet
- Msds EthanolDocument7 pagesMsds EthanolHeru HarnadiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions CHAPTER 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Chapter 1Document25 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions CHAPTER 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Chapter 1Govu GovardhanNo ratings yet
- Vidya Bal Bhawan SR - Sec School Half Yearly Examination (2020-21) Class X Subject-Science (086) Level-BDocument6 pagesVidya Bal Bhawan SR - Sec School Half Yearly Examination (2020-21) Class X Subject-Science (086) Level-BLakshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus CHEMISTRY Syllabus: Form 1Document8 pagesChemistry Syllabus CHEMISTRY Syllabus: Form 1victorNo ratings yet
Spot The Difference: Name - Class
Spot The Difference: Name - Class
Uploaded by
NonuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Spot The Difference: Name - Class
Spot The Difference: Name - Class
Uploaded by
NonuCopyright:
Available Formats
9Ea Spot the difference
Name ______________________________ Class __________
Tick the correct boxes. One has been done for you.
Metals Non-metals
1 These are usually solid at room
temperature. b
2 These do not conduct electricity well.
3 These are not magnetic.
4 These react with oxygen to form bases.
5 These are usually brittle, and break when
you try to bend them.
6 These can make a ringing sound.
7 Half of these are gases.
8 These can be hammered into shape.
9 These are good conductors of heat and
electricity.
10 These often have low melting and boiling
points.
Exploring Science 9 page 64 ©Pearson Education Limited 2003
9Eb Metallic fizz
Name ______________________________ Class __________
1 Match up
Formula Name Elements in the
substance
Zn hydrochloric acid hydrogen, sulphur and
oxygen
H2SO4 zinc metal hydrogen and chlorine
HCl sulphuric acid zinc
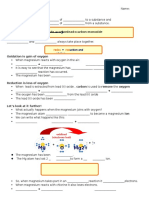
2 Fill in the gaps.
Word equation
hydrochloric __ __ __ __
+ __ __ __ __ + __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __
Symbol equation
2HCl _______ _______ + _______
+
General equation
__ __ __ __ + metal __ __ __ __ hydrogen
+
3 The test for hydrogen is
a) limewater turns cloudy
b) puts out a lighted splint
c) explodes with a squeaky pop when a lighted splint is brought near
Exploring Science 9 pages 66-67 ©Pearson Education Limited 2003
9Ec More bubbles 1
Name ___________________________________Class _______________
Fill in the gaps.
Word equation
sulphuric __ __ __ __ __ __
+
__ __ __ __ carbonate
copper __ __ __ __ __ __
+ + __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ dioxide
General word equation
__ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __ +
carbonate
__ __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __ + + __ __ __ __ __
dioxide
Exploring Science 9 pages 68-69 ©Pearson Education Limited 2003
9Ec More bubbles 2
Name ______________________________ Class ___________
1 Complete these sentences using the words below.
Rocks such as l __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __, chalk and m __ __ __ __ __ contain a metal
c __ __ __ __ __ __ __ called calcium carbonate.
All carbonates react with a __ __ __ __. The c __ __ __ __ __ __ carbonate in rocks
reacts with the acid in r __ __ __. New chemicals are made.
The piece of rock left behind is s __ __ __ __ __ __. It has been
w __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __.
There are signs that tell us when a chemical reaction takes place.
These may include
• a change in __ __ m __ __ __ __ __ u __ __
• production of a new m __ __ __ __ __ __ l, this may be a __ a __ .
rain material compound
limestone calcium
gas temperature marble
smaller weathered
acids
Exploring Science 9 pages 68-69 ©Pearson Education Limited 2003
9Ed Metal oxides and acids
Name ______________________________ Class _____________
1 a What ‘B’ is a compound that reacts with acids?
b What ‘MC’ is an example of a base?
c What ‘MO’ is an example of a base?
d What ‘N’ describes the reaction between sulphuric acid and copper oxide ?
e What ‘S’ is a compound produced when an acid and a base react?
f What ‘N’ describes a liquid with a pH of 7?
MC N N
B MO S
2 Fill in the gaps.
sulphuric __ __ __ __ __ __
+
__ __ __ __ oxide
copper
+ __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
__ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ + __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __
acid oxide
magnesium sulphate + water
Exploring Science 9 pages 70-71 ©Pearson Education Limited 2003
9Ed All about salts
Name _____________________________ Class __________
1 Match up
Acids can be neutralised using … alkalis
Bases that are soluble in water are called … sodium hydroxide
An example of a base is … bases
An example of an alkali is … chlorides
Salts made from hydrochloric acid are called … a metal oxide
To make nitrates you use … sulphates
Sulphuric acid makes salts called … nitric acid
2 Fill in the gaps.
acid + __ __ __ __ __ oxide __ __ __ __ + water
(or __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ )
Exploring Science 9 page 72 ©Pearson Education Limited 2003
9Ed Ready salted
Name _______________________________ Class ____________
Match up.
Salt Used in
potassium nitrate soap
sodium stearate wood preservative
fertilisers and fireproof
calcium phosphate
materials
copper sulphate photographic film
sodium laureth sulphate shampoos and bath foams
magnesium sulphate animal bones and fertilisers
silver nitrate fireworks
Exploring Science 9 page 73 ©Pearson Education Limited 2003
You might also like
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Science Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 4 Reactivity of MetalsDocument21 pagesScience Form 3 2020 (Notes, PBD, Exercise) : Chapter: 4 Reactivity of MetalsYusfalina Mohd YusoffNo ratings yet
- CH U5 A1 Balancing WorksheetDocument3 pagesCH U5 A1 Balancing WorksheetLayna HarrisonNo ratings yet
- Peroxo Compounds, InorganicDocument32 pagesPeroxo Compounds, InorganicKilsys AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Progtest Paper 2-2014 PDFDocument16 pagesScience 8 Progtest Paper 2-2014 PDFsean gillmore100% (2)
- Preventing Scale Loss During Heat Treatment & Hot Forging - With ImagesDocument17 pagesPreventing Scale Loss During Heat Treatment & Hot Forging - With ImagesSrikar Shenoy100% (1)
- Chem Paper 1 Pracs QPDocument21 pagesChem Paper 1 Pracs QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Module Chapter 4Document21 pagesModule Chapter 4Hannan NashruddinNo ratings yet
- Test (Levels 5-7) : Name - ClassDocument6 pagesTest (Levels 5-7) : Name - ClassJayNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Document17 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Soraya DeenNo ratings yet
- Theory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument4 pagesTheory Worksheet: Acids, Bases and Saltsخانزاده بلال احمدخان لودہیNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 14.1 Metals and Alloys Metals 1.: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Document10 pagesWorksheet 14.1 Metals and Alloys Metals 1.: © 2013 Marshall Cavendish International (Singapore) Private Limited 1Apple kokNo ratings yet
- 7 Sci Elements and CompoundsDocument2 pages7 Sci Elements and CompoundsKanwal JamilNo ratings yet
- F3 SN CHP 4 2023Document38 pagesF3 SN CHP 4 2023NG YI ZHI MoeNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Mac F4 Chemistry SALT Workshop (Student Version) Original PDFDocument20 pages1.0 Mac F4 Chemistry SALT Workshop (Student Version) Original PDFNurul AlyaNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Use of Amount of Substance on Volumes of Gases QP (separate only)Document17 pages3.5 Use of Amount of Substance on Volumes of Gases QP (separate only)Charu KochharNo ratings yet
- SC8c.2 - Bases and Salts - StrengthenDocument1 pageSC8c.2 - Bases and Salts - Strengthenarnavpatel138No ratings yet
- 3.5 Use of Amount of Substance On Volumes of Gases QPDocument17 pages3.5 Use of Amount of Substance On Volumes of Gases QPTang Hing Yiu, SamuelNo ratings yet
- Matter Homework MATTERDocument5 pagesMatter Homework MATTERJOHN REY FABILLONo ratings yet
- Sep 2013Document28 pagesSep 2013Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- Chemical Calculations Questions - Many and HardDocument26 pagesChemical Calculations Questions - Many and Hard19gururNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Document25 pagesIGCSE Chemistry Section 3 and 4Bineta NdiayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 SaltsDocument1 pageChapter 9 SaltsahsanNo ratings yet
- Excel ChemistryDocument14 pagesExcel ChemistrySumathi GanasenNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions Study GuideDocument3 pagesChemical Reactions Study Guidejaydon geyerNo ratings yet
- 3.2 Use of Amount of Substance On Pure Substances QP PDFDocument31 pages3.2 Use of Amount of Substance On Pure Substances QP PDFDanish FiverNo ratings yet
- Sc11.4w - Group 1 Homework1Document1 pageSc11.4w - Group 1 Homework10220141106No ratings yet
- BALANCING Worksheet 3Document1 pageBALANCING Worksheet 3Amanda Leigh ResuelloNo ratings yet
- 4thq 3rd Modular SummDocument1 page4thq 3rd Modular SummPaulo M. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Bonding and Structure QPDocument42 pages2.2 Bonding and Structure QPabisolafaluyi5No ratings yet
- S9 Unit 5 WorksheetsDocument15 pagesS9 Unit 5 Worksheetsbuddyfigther8No ratings yet
- S9 - End-Of-Unit 5 TestDocument2 pagesS9 - End-Of-Unit 5 TestMoganoni MogaNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesandsaltsDocument26 pagesAcids Basesandsaltsremaselshazly76No ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysisTeena SheikhNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test Review - Mar 2023Document4 pagesChemistry Test Review - Mar 2023rblxproNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument6 pagesIlovepdf Mergedasdasd1414196No ratings yet
- Notes and Questions: Aqa GcseDocument31 pagesNotes and Questions: Aqa Gcseapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Gases and Solutions QPDocument13 pagesGases and Solutions QPGbenga AjibikeNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SC8 Full Topic WorksheetsDocument34 pagesChemistry SC8 Full Topic WorksheetscramdamdageNo ratings yet
- Making Salts WorksheetDocument2 pagesMaking Salts WorksheetSarah KKC0% (1)
- Screenshot 2024-01-21 at 15.55.50Document22 pagesScreenshot 2024-01-21 at 15.55.50b4jdv8bq4xNo ratings yet
- Chem 209A Pre-Test 2 Semester, AY 2021-2022Document3 pagesChem 209A Pre-Test 2 Semester, AY 2021-2022JEZELLE KAYE BOCONo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 CH6.3 PrintDocument3 pagesScience Form 1 CH6.3 PrintnisaNo ratings yet
- C Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023Document12 pagesC Yr09 MQF Lev1to3 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Changes Revision Workbook 2Document12 pagesChemical Changes Revision Workbook 2haleeza648No ratings yet
- Ch2 -4 revision note (stu)Document6 pagesCh2 -4 revision note (stu)mtauNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionsNameDocument2 pagesRedox ReactionsNamesondos tawfiqNo ratings yet
- Y9 Chem Eot 2Document3 pagesY9 Chem Eot 2Sandy BelleNo ratings yet
- Balancing Chem Equations SeDocument3 pagesBalancing Chem Equations SeNoah BloniarzNo ratings yet
- 7 Revision Sheet - IIDocument2 pages7 Revision Sheet - IIsakshampaharia1No ratings yet
- Physical/ Chemical Changes: CGA #2 ReviewDocument8 pagesPhysical/ Chemical Changes: CGA #2 Reviewengchemistry18No ratings yet
- WS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSDocument7 pagesWS 4 IG I Chemistry BEHAVIOUR OF METALSRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Covalent BondingDocument2 pagesTopic 3 Covalent BondingufukNo ratings yet
- A. Magnesium Chloride B. Sodium Nitride C. Potassium Bromide D. Lithium OxideDocument4 pagesA. Magnesium Chloride B. Sodium Nitride C. Potassium Bromide D. Lithium Oxidesawyeranthony2009No ratings yet
- 2017 Unit 2 Chemistry KTT 3 Stoichiometry - Question BookDocument11 pages2017 Unit 2 Chemistry KTT 3 Stoichiometry - Question BookYue WeiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction PracticeDocument3 pagesChemical Reaction PracticeYeseo ChoiNo ratings yet
- Chemcial Reactions Cloze PassageDocument5 pagesChemcial Reactions Cloze PassageNadia CzeredreckiNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions For Year 9 ChemistryDocument15 pagesRevision Questions For Year 9 ChemistryKostas TampakisNo ratings yet
- ShapesofcomplexionsDocument41 pagesShapesofcomplexions/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Test1 StoichiometryDocument2 pagesTest1 StoichiometryHakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument11 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- 2.1 The P-BlockDocument10 pages2.1 The P-BlockNonuNo ratings yet
- October 2021 MS - Component 3 Eduqas Chemistry A-LevelDocument15 pagesOctober 2021 MS - Component 3 Eduqas Chemistry A-LevelNonuNo ratings yet
- June 2015 QP - Unit 5 WJEC Biology A-LevelDocument24 pagesJune 2015 QP - Unit 5 WJEC Biology A-LevelNonuNo ratings yet
- 2.4. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument10 pages2.4. Sexual Reproduction in PlantsNonuNo ratings yet
- 3.C. Neurobiology and Behaviour QPDocument35 pages3.C. Neurobiology and Behaviour QPNonuNo ratings yet
- 3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy MSDocument11 pages3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy MSNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: AUTUMN 2021Document15 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: AUTUMN 2021NonuNo ratings yet
- Eduqas Component 3 Nerve ImpulseDocument1 pageEduqas Component 3 Nerve ImpulseNonuNo ratings yet
- 3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy QPDocument40 pages3.B. Human Musculoskeletal Anatomy QPNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022Document18 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022NonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022Document21 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022NonuNo ratings yet
- Name - Class - : Exploring Science 9 Page 47 © Pearson Education Limited 2003Document8 pagesName - Class - : Exploring Science 9 Page 47 © Pearson Education Limited 2003NonuNo ratings yet
- Energy and Electricity SOWDocument53 pagesEnergy and Electricity SOWNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level: Thursday, 9 June 2022 - Afternoon Energy For LifeDocument32 pagesGce A Level: Thursday, 9 June 2022 - Afternoon Energy For LifeNonuNo ratings yet
- Energy Resources SOWDocument20 pagesEnergy Resources SOWNonuNo ratings yet
- Gce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022Document18 pagesGce A Level Marking Scheme: SUMMER 2022NonuNo ratings yet
- 2022 - 20 Reproduction IGCSE EdexcelDocument55 pages2022 - 20 Reproduction IGCSE EdexcelNonuNo ratings yet
- Eduqas PaperDocument36 pagesEduqas PaperNonuNo ratings yet
- Unit 9aDocument3 pagesUnit 9aNonuNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument24 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelNonuNo ratings yet
- Wjec Paper 1Document19 pagesWjec Paper 1NonuNo ratings yet
- 9E SciDocument48 pages9E SciNonuNo ratings yet
- Eduqas Paper 2Document44 pagesEduqas Paper 2NonuNo ratings yet
- Wjec Paper 3Document32 pagesWjec Paper 3NonuNo ratings yet
- Sound 2Document12 pagesSound 2NonuNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials For Dental Implants: PART II Basic SciencesDocument29 pagesBiomaterials For Dental Implants: PART II Basic SciencesAna-Maria RoșuNo ratings yet
- R&S Oscar Cutting Oil MSDSDocument5 pagesR&S Oscar Cutting Oil MSDSZhi Hou NgNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Perfect Score Module 2010 Answer SchemeDocument47 pagesChemistry Perfect Score Module 2010 Answer SchemedhuulhudaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Final Term PaperDocument8 pagesClass 7 Final Term PaperYakshitha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Sample FileDocument8 pagesSample FileBrajendra KumarNo ratings yet
- CLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionDocument12 pagesCLASS IX, Selina, Atmospheric PollutionHirakjyoti SarkarNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy (Mega)Document20 pagesMetallurgy (Mega)Anant JainNo ratings yet
- Abdolmohsen Shabib-Asl, 2014 Referensi PPMDocument8 pagesAbdolmohsen Shabib-Asl, 2014 Referensi PPMAdzan Topaz AdityaNo ratings yet
- 08-Metals and Non-Metals Theory PDFDocument51 pages08-Metals and Non-Metals Theory PDFvikash singh rajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Msds-Of M 220-Eng - 43-29357Document13 pagesMsds-Of M 220-Eng - 43-29357Lennier SaezNo ratings yet
- Importance of TreesDocument3 pagesImportance of TreesNirmala SugurNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3Document3 pagesLab Report 3Nayli QistinaNo ratings yet
- Summary of As QuestionDocument4 pagesSummary of As QuestionYuan XintongNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Titanium Part 1 Aggressive EnvironmenDocument13 pagesCorrosion of Titanium Part 1 Aggressive EnvironmenHamza FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chm131 Chapter 1 Atoms Molecules Ions Chemical EqDocument106 pagesChm131 Chapter 1 Atoms Molecules Ions Chemical EqAdibah Qistina QistinaNo ratings yet
- Test MolesDocument5 pagesTest MolesadilNo ratings yet
- All NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.onlineDocument16 pagesAll NCERT Books PDF From WWW - Ncert.onlineKaushik RajNo ratings yet
- Gas Fittings and Adapters: Always There For LifeDocument53 pagesGas Fittings and Adapters: Always There For LifetaibkNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Environmental ManagementDocument6 pagesResearch Paper Environmental Managementgw219k4y100% (1)
- 10th Chemistry Revision Assignments - All Chapters CombinedDocument11 pages10th Chemistry Revision Assignments - All Chapters CombinedYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Climeworks - US20120076711Document26 pagesClimeworks - US20120076711Alberto Moreno GomezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 1.exercise 1ADocument28 pagesChemistry Chapter 1.exercise 1AAsifNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument184 pagesUntitledKalin BhayiaNo ratings yet
- Msds EthanolDocument7 pagesMsds EthanolHeru HarnadiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions CHAPTER 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Chapter 1Document25 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions CHAPTER 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Chapter 1Govu GovardhanNo ratings yet
- Vidya Bal Bhawan SR - Sec School Half Yearly Examination (2020-21) Class X Subject-Science (086) Level-BDocument6 pagesVidya Bal Bhawan SR - Sec School Half Yearly Examination (2020-21) Class X Subject-Science (086) Level-BLakshNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Syllabus CHEMISTRY Syllabus: Form 1Document8 pagesChemistry Syllabus CHEMISTRY Syllabus: Form 1victorNo ratings yet