Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Meiosis
Meiosis
Uploaded by
EMMA SLAY0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageMeiosis is the process by which gametes are produced in the testes and ovaries. During meiosis, a diploid cell undergoes two divisions to form four haploid cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes. When a male and female gamete fuse during fertilization, the full chromosome number is restored, resulting in unique offspring that vary from the parents and each other. This genetic variation can provide advantages if the environment changes and lead to evolution over time.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentMeiosis is the process by which gametes are produced in the testes and ovaries. During meiosis, a diploid cell undergoes two divisions to form four haploid cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes. When a male and female gamete fuse during fertilization, the full chromosome number is restored, resulting in unique offspring that vary from the parents and each other. This genetic variation can provide advantages if the environment changes and lead to evolution over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageMeiosis
Meiosis
Uploaded by
EMMA SLAYMeiosis is the process by which gametes are produced in the testes and ovaries. During meiosis, a diploid cell undergoes two divisions to form four haploid cells, each containing half the number of chromosomes. When a male and female gamete fuse during fertilization, the full chromosome number is restored, resulting in unique offspring that vary from the parents and each other. This genetic variation can provide advantages if the environment changes and lead to evolution over time.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
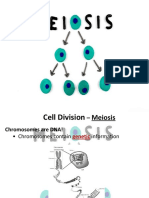
Meiosis:
• Each human cell contains 46 chromosomes. When two gametes fuse the resulting
zygote must contain 46 chromosomes.
• When a human cell divides by meiosis, four cells, each containing 23
chromosomes, are formed.
• Meiosis occurs in the reproductive organs, the testes and ovaries, where gametes
are produced.
• On fusion of the two haploid gametes, the diploid or original number of
chromosomes is restored.
• A cell with the full species chromosome number is called a diploid cell.
• A haploid cell has half the species chromosome number.
• Gametes, male and female, are formed when cells in the reproductive organs
divide by meiosis. They are haploid cells.
• Gametes are all different from each other and the parent cells.
• During meiosis, homologous chromosomes come together and crossing over
occurs, whereby genetic information is exchanged.
• Each gamete of the millions produced is unique and so each organism produced
by their fusion is unique.
• Inheritable genetic characteristics are transmitted from the parents to the
offspring by the gametes.
• The resulting offspring are all different to or vary from each other and to their
parents.
• This variation can be important if the environment changes, as those organism
better adapted will survive.
• This variation can lead to evolution.
You might also like
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument18 pagesMeiosis Powerpointdoubleyouem2003No ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument19 pagesMeiosis PowerpointAdeliesha CadleNo ratings yet
- Sexual Vs Asexual ReproductionDocument27 pagesSexual Vs Asexual ReproductionSadman Ishraq Sayef100% (1)
- 5 - MeiosisDocument52 pages5 - MeiosissalmaNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument20 pagesMitosisPari ValechaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument47 pagesMeiosis PowerpointMishaal IrfanNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Genetic VariationDocument30 pagesMeiosis and Genetic VariationAnne DawsonNo ratings yet
- Human Embryology: Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Medicine Hamadan University of Medical SciencesDocument51 pagesHuman Embryology: Professor of Anatomy and Embryology Faculty of Medicine Hamadan University of Medical SciencesGaziza MaaroofNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction MeiosisDocument56 pagesSexual Reproduction MeiosisAngelyn MironesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual LifecycleDocument44 pagesChapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual LifecycleRickyRefandiNo ratings yet
- 11 - Meiosis & Sexual ReproductionDocument23 pages11 - Meiosis & Sexual Reproductionwhether913No ratings yet
- AS Biology Unit 2 Revision CardsDocument16 pagesAS Biology Unit 2 Revision CardsGeorge NoorlandNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document12 pagesLecture 4rahaf.khalid226No ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument54 pagesGeneticsBrian James BurtonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document10 pagesChapter 10alaskamofoNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Chromosomes MeiosisDocument7 pages6.1 Chromosomes MeiosisOmar HishamNo ratings yet
- 6.3 MeiosisDocument38 pages6.3 Meiosiswickedbiology101No ratings yet
- Class Notes PersonalDocument2 pagesClass Notes PersonalLau FernandezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 OutlineDocument9 pagesChapter 13 OutlineJosephinemwNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 (Sexual Reproduction and Genetics)Document53 pagesChapter 19 (Sexual Reproduction and Genetics)Nellen BastismoNo ratings yet
- Compare Asexual Reproduction With Sexual Reproduction in Terms of Transmission of Traits Room One Generation To The NextDocument2 pagesCompare Asexual Reproduction With Sexual Reproduction in Terms of Transmission of Traits Room One Generation To The NextMckenzie DunfordNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Lecture OutlineDocument8 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Life Cycles: Lecture Outlinehaha_le12No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction and GeneticsDocument53 pagesSexual Reproduction and GeneticsNellen BastismoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 GametogenesisDocument37 pagesChapter 2 GametogenesisAdan ImanNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument16 pagesCell DivisionMonika DalalNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument12 pagesMeiosisapi-233981625No ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument20 pagesMeiosis PowerpointRia PerezNo ratings yet
- Meiosis PowerpointDocument20 pagesMeiosis PowerpointJared CoyagboNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument25 pagesSexual Reproductioncxmic19No ratings yet
- CA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionDocument43 pagesCA Lesson 2 Meiosis+and+Sexual+ReproductionQbasantNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 3 Form 4Document16 pagesScience Chapter 3 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin100% (1)
- Cell Division - MeiosisDocument6 pagesCell Division - MeiosisSonia OmapersaudNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument20 pagesMeiosis975mgqypt7No ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Inheritance Igcse 0610 2023 NotesDocument24 pagesChapter 17 Inheritance Igcse 0610 2023 NotesAminah ShahzadNo ratings yet
- BA 09 - Cell Cycle (CNT.)Document9 pagesBA 09 - Cell Cycle (CNT.)minhanh051203No ratings yet
- GeneticDocument34 pagesGeneticDark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Revision of Mid TermDocument6 pagesRevision of Mid Term؟؟No ratings yet
- Cell Cycle HBRDocument42 pagesCell Cycle HBRMaliha TasnimNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Online Study GuideDocument6 pagesCH 13 Online Study Guideюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- 3rd Meiosis Cytology Lecture September 192020 2Document50 pages3rd Meiosis Cytology Lecture September 192020 2terryortiz825No ratings yet
- Group 1Document31 pagesGroup 1John DanaoNo ratings yet
- 03.chromosomes and MeiosisDocument4 pages03.chromosomes and Meiosisgabrielsalazar.tvNo ratings yet
- InheritanceDocument27 pagesInheritanceAhmad RamiNo ratings yet
- Unit 06 - Cell Reproduction: Mitosis and Meiosis: Text Chapter 08Document27 pagesUnit 06 - Cell Reproduction: Mitosis and Meiosis: Text Chapter 08AndoingNo ratings yet
- 10 - Meiosis NotesDocument7 pages10 - Meiosis NotesNichole DalrympleNo ratings yet
- L3 Meiosis LessonDocument16 pagesL3 Meiosis LessonJoan Ng'ongoloNo ratings yet
- 11 Cell Division Meiosis PowerpointDocument25 pages11 Cell Division Meiosis Powerpointmanoj9114No ratings yet
- Cell Devision (Mitosis and Meiosis)Document31 pagesCell Devision (Mitosis and Meiosis)Kent LacificarNo ratings yet
- Meiosis 2Document49 pagesMeiosis 2Rosalyn LucbanNo ratings yet
- 5 Pembelahan SelDocument46 pages5 Pembelahan SelArensi BeloNo ratings yet
- H) MITOSIS & MEIOSISDocument2 pagesH) MITOSIS & MEIOSISamarashah182No ratings yet
- Topic 15 - Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument32 pagesTopic 15 - Cell Cycle and MitosistnotchwNo ratings yet
- Hereditary Notes:: Types of ChromosomesDocument9 pagesHereditary Notes:: Types of ChromosomesClaudine Cabanero CaballeroNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument19 pagesMeiosisMimie Roslee100% (1)
- Human Inheritance and Modern Genetics 2Document55 pagesHuman Inheritance and Modern Genetics 2Tilak PatelNo ratings yet
- MosaicismDocument25 pagesMosaicismBabak NamiNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument17 pagesMeiosisEron SwandraNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian Inheritance: Genetics Analysis: An Integrated ApproachDocument46 pagesNon-Mendelian Inheritance: Genetics Analysis: An Integrated ApproachRafia ShahNo ratings yet
- BIO 1102. Basic Gen. Var. Evo. Lecture2,3,4,5NotesDocument43 pagesBIO 1102. Basic Gen. Var. Evo. Lecture2,3,4,5Notesnasonfreeman63No ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument1 pageElectrolysisEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument1 pageMitosisEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Physics Formulae F2Document4 pagesPhysics Formulae F2EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Gender Inequality - Violence Against WomenDocument2 pagesGender Inequality - Violence Against WomenEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- A Story On Life GHDocument2 pagesA Story On Life GHEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Pob NotesDocument1 pagePob NotesEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Notes - Digestive SystemDocument2 pagesNotes - Digestive SystemEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Vedanta ReviewDocument8 pagesVedanta ReviewEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- IsotopesDocument4 pagesIsotopesEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- The World Wide Web (WWW)Document4 pagesThe World Wide Web (WWW)EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Physics Term 1 EOTDocument7 pagesPhysics Term 1 EOTEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 For ChemDocument2 pagesLab 1 For ChemEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Worksheet#09Document1 pageWorksheet#09EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Grade 803K-WS#15Document2 pagesGrade 803K-WS#15EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Geography 703KDocument2 pagesGeography 703KEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Review For English B #01Document4 pagesReview For English B #01EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- UntiledDocument1 pageUntiledEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Data Verification-Grade 801KDocument2 pagesData Verification-Grade 801KEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Physics 703k SSN # 41Document4 pagesPhysics 703k SSN # 41EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Term 1 WK 5Document18 pagesTerm 1 WK 5EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Section 1 - Number Theory NotesDocument5 pagesSection 1 - Number Theory NotesEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Vedanta 802K P2Document3 pagesVedanta 802K P2EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Physics Review #01Document5 pagesPhysics Review #01EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Grade 803K-WS#18Document2 pagesGrade 803K-WS#18EMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- A Production and ProductivityDocument2 pagesA Production and ProductivityEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- 5 Organizational StructureDocument3 pages5 Organizational StructureEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- 8 FAMILY TYPES IN THE CARIBBEANDocument3 pages8 FAMILY TYPES IN THE CARIBBEANEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Wearing A Uniform Limits Self-ExpressionDocument3 pagesWearing A Uniform Limits Self-ExpressionEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Cell Phones Should Be Allowed in Secondary SchoolsDocument11 pagesCell Phones Should Be Allowed in Secondary SchoolsEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet
- Section 1 - Number Theory and Computation NotesDocument18 pagesSection 1 - Number Theory and Computation NotesEMMA SLAYNo ratings yet