Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3-Phase Synchronous Motor
3-Phase Synchronous Motor
Uploaded by
abhioptimus00Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Diesel Engine Ajm Atj Avb Avf Awx Repair Manual EngDocument172 pagesDiesel Engine Ajm Atj Avb Avf Awx Repair Manual EngAndsanta 130% (1)
- Bell 407GX ChecklistDocument2 pagesBell 407GX ChecklistAmanullah RafiNo ratings yet
- Manual de Armado de Motor Caterpillar 3024cDocument59 pagesManual de Armado de Motor Caterpillar 3024cmarcos astete78% (9)
- Yamaha BWS Manual Con DiagramaDocument214 pagesYamaha BWS Manual Con DiagramaManuel CortezNo ratings yet
- Unit8-Induction MotorDocument40 pagesUnit8-Induction MotorsaravananNo ratings yet
- 432zx ErrorCodesDocument28 pages432zx ErrorCodesmushfiq66100% (4)
- Manual de Motores Vol 4Document75 pagesManual de Motores Vol 4Gabriel Piñon Conde100% (1)
- 1000-0004 enDocument20 pages1000-0004 enMuhammad Mujtaba Tariq100% (2)
- TPSMDocument26 pagesTPSMLaasya RevillaNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machines Synchronous Machines: OutlineDocument31 pagesSynchronous Machines Synchronous Machines: Outlinesameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- 3.basic Concept of Rotating Electrical Machine PDFDocument126 pages3.basic Concept of Rotating Electrical Machine PDFStadpyrkhat lyngkhoiNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument5 pagesBasic ConceptsRodrigo BobNo ratings yet
- LN08Document9 pagesLN08ruzgaryilmazz5No ratings yet
- EE - 3410 Electric Power: Introduction To Electric MachinesDocument30 pagesEE - 3410 Electric Power: Introduction To Electric MachinesDiyanel OriginalNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motor FundamentalsDocument24 pagesAC Induction Motor Fundamentalsrohtahir100% (3)
- Modeling and Simulation of A Stepping Motor, 1969.Document3 pagesModeling and Simulation of A Stepping Motor, 1969.Ali H. NumanNo ratings yet
- Rotating Magnetic Field: ©2010, The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, IncDocument20 pagesRotating Magnetic Field: ©2010, The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, IncEdison ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Induction Motor Drives - Part1Document45 pagesChapter 4 - Induction Motor Drives - Part1Zafirah HanafiNo ratings yet
- E M II: Synchronous MotorDocument14 pagesE M II: Synchronous MotorAkashman ShakyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Wind Turbine GeneratorsDocument14 pages4 Wind Turbine Generatorsabhishek dubeyNo ratings yet
- AC Motor ReportDocument8 pagesAC Motor ReportbafulcherNo ratings yet
- Module 6: A.C. Electrical Machines For Hybrid and Electric VehiclesDocument65 pagesModule 6: A.C. Electrical Machines For Hybrid and Electric VehiclesDeepak mishraNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document45 pagesModule 3prashanth9.n.sNo ratings yet
- 01-Synchronous Motor PDFDocument48 pages01-Synchronous Motor PDFGeneral ZodNo ratings yet
- STSPIN820: Microstepping Management: Application NoteDocument19 pagesSTSPIN820: Microstepping Management: Application NoteguptaamitalwNo ratings yet
- EM214Induction Motorchapter 3Document46 pagesEM214Induction Motorchapter 3mahrusNo ratings yet
- Information-No - 1 1 7-1Document12 pagesInformation-No - 1 1 7-1Black PearlNo ratings yet
- BLDCDocument6 pagesBLDCquocyenkcdNo ratings yet
- 21EE44-Module 5Document23 pages21EE44-Module 5AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Module 15: C28x Digital Motor ControlDocument41 pagesModule 15: C28x Digital Motor ControlRamana ManoharNo ratings yet
- 1 AlternatorDocument29 pages1 AlternatorMwasi KivingeNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motors: ChapterDocument16 pagesSynchronous Motors: ChapterAashrith GangamNo ratings yet
- Construction of AlternatorDocument4 pagesConstruction of AlternatorMeet SatheyNo ratings yet
- 244 - Synchronous MotorsDocument16 pages244 - Synchronous MotorssnghvishalNo ratings yet
- LECTURE# 22 & 23 Induction Machines FinalDocument39 pagesLECTURE# 22 & 23 Induction Machines FinalAmmara RasheedNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator: Basic Principle Construction Speed and Frequency EMF Induced Principle of OperationDocument20 pagesSynchronous Generator: Basic Principle Construction Speed and Frequency EMF Induced Principle of OperationalolorNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument18 pagesElectromagnetism5814No ratings yet
- 7FB AC MotorDocument61 pages7FB AC Motoresteban muñozNo ratings yet
- DS2 - Unit 2-DC MachinesDocument57 pagesDS2 - Unit 2-DC MachinesTommba TommyNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Ac Machines TamilDocument25 pagesUnit IV Ac Machines TamilDeivathin adimaikalNo ratings yet
- 3 PhaseInductionMotors BookChapter 1Document19 pages3 PhaseInductionMotors BookChapter 1Rohan ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine Theory and ModelingDocument108 pagesSynchronous Machine Theory and Modelingnanavarasmdu100% (1)
- EPS Frequency Converters PrinciplesDocument43 pagesEPS Frequency Converters Principlesrichfron69No ratings yet
- EEE20005-week 4 5Document103 pagesEEE20005-week 4 5ShelbyNo ratings yet
- AGBellDocument3 pagesAGBellandy1144552No ratings yet
- Special Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorDocument51 pagesSpecial Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Synchronous. 5Document8 pagesSynchronous. 5K SDNo ratings yet
- Achine: Tructure Teady State Model and Basic Equations O Load Operation Ield Circuit Connections of A Machine EneratorDocument25 pagesAchine: Tructure Teady State Model and Basic Equations O Load Operation Ield Circuit Connections of A Machine EneratorAndrea VerdiNo ratings yet
- Lec 1-Chapter 1-Introduction - DraftDocument24 pagesLec 1-Chapter 1-Introduction - DraftMuhannad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Dual Rotor Generator Base PaperDocument4 pagesDual Rotor Generator Base Paperraja mNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 7 Induction Motor: Motor Construction: Stator: Rotor: RotorDocument19 pagesChapter # 7 Induction Motor: Motor Construction: Stator: Rotor: RotorSamiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Motors: Single-Phase Three-PhaseDocument56 pagesAlternating Current Motors: Single-Phase Three-Phaseeyd bartulabaNo ratings yet
- Complete Chapter1 and TutorialDocument19 pagesComplete Chapter1 and TutorialstevennguimsNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsDocument31 pagesUnit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsTuition MasterNo ratings yet
- 1 Electric Motor BasicsDocument13 pages1 Electric Motor BasicsPandaGendutNo ratings yet
- DC Machines: King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument10 pagesDC Machines: King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Electrical EngineeringMohmmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- M C Q ElectromagnetismDocument30 pagesM C Q ElectromagnetismShaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Document33 pagesInduction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Ramprakash89% (18)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsFrom EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsNo ratings yet
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- Conversations on Electric and Magnetic Fields in the CosmosFrom EverandConversations on Electric and Magnetic Fields in the CosmosNo ratings yet
- Dynamos and Electric Motors - How to Make and Run ThemFrom EverandDynamos and Electric Motors - How to Make and Run ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SPM Unit1 Part-2Document10 pagesSPM Unit1 Part-2abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit-4 Part-1Document54 pagesSPM Unit-4 Part-1abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit5 Part-1Document19 pagesSPM Unit5 Part-1abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit5 Part-2Document30 pagesSPM Unit5 Part-2abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit-4 Part-2Document12 pagesSPM Unit-4 Part-2abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's LawsDocument3 pagesKirchhoff's Lawsabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- Operating System NotesDocument86 pagesOperating System Notesabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- P.F. & P.F Improvement of Using CapacitorDocument3 pagesP.F. & P.F Improvement of Using Capacitorabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- 3-Phase Star ConnectionDocument6 pages3-Phase Star Connectionabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- 404A-22G1 ElectropaK PN2002 PDFDocument2 pages404A-22G1 ElectropaK PN2002 PDFMd ShNo ratings yet
- A320 Amm - Ata 74 (Pw11) - Ignition (P 78)Document78 pagesA320 Amm - Ata 74 (Pw11) - Ignition (P 78)gola.ashwaniNo ratings yet
- KYMCO Downtown 350i Service ManualDocument611 pagesKYMCO Downtown 350i Service ManualYahya USallamiNo ratings yet
- Spark-Glow-Plugs-Ignition-Catalogue 777Document1 pageSpark-Glow-Plugs-Ignition-Catalogue 777АлександрNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor - WikipediaDocument27 pagesUniversal Motor - WikipediaAlejandro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi 4M41Document6 pagesMitsubishi 4M41Sebastian Tabares RiosNo ratings yet
- RCGF21TWINDocument21 pagesRCGF21TWINejunsunNo ratings yet
- PVL Racing Ignition 1Document8 pagesPVL Racing Ignition 1GabrielCaravana100% (1)
- Engine Simulation in Power Programs (Chat GPT)Document2 pagesEngine Simulation in Power Programs (Chat GPT)konstadinos evangelouNo ratings yet
- RecommendationDocument3 pagesRecommendationKams KingNo ratings yet
- Demon CarburetorsDocument2 pagesDemon CarburetorsawalsumNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Motor Cat 1.1Document193 pagesManual de Partes Motor Cat 1.1Emanuel Nicolas Villarruel100% (1)
- Kubota Kx71 Parts Sec WatDocument20 pagesKubota Kx71 Parts Sec Watjoshua100% (56)
- Fadec: Navigation SearchDocument4 pagesFadec: Navigation SearchArjun AnduriNo ratings yet
- Every 1 500 Miles (2 400 KM) Lubricate Grease Points (Nipples) On Front-Axle (Document2 pagesEvery 1 500 Miles (2 400 KM) Lubricate Grease Points (Nipples) On Front-Axle (Maria ClaytonNo ratings yet
- Carbon X Combustion Chamber Cleaner K1+KDocument2 pagesCarbon X Combustion Chamber Cleaner K1+KDhany SSatNo ratings yet
- Camless Engines Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesCamless Engines Seminar ReportVineet Jason64% (11)
- Workshop Manual Lga 280 OhcDocument100 pagesWorkshop Manual Lga 280 Ohcptheo2088No ratings yet
- ENGINE Timing 4ZZ-FEDocument31 pagesENGINE Timing 4ZZ-FEAriel100% (1)
- Flash Powertrain Control Module (PCM) UpdatesDocument4 pagesFlash Powertrain Control Module (PCM) UpdatesPipis FakidomitisNo ratings yet
- SD313 26 Engine Control System (D4BH: 4D56 TCI 2.5L) (6) : (SD313 25) Cmdjc1 MC13 M01 ADocument1 pageSD313 26 Engine Control System (D4BH: 4D56 TCI 2.5L) (6) : (SD313 25) Cmdjc1 MC13 M01 AhaiderNo ratings yet
- EXPORT MM60 Material List - 22092022Document1,920 pagesEXPORT MM60 Material List - 22092022robbi wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Automotive FundamentalsDocument26 pagesUnit - 1: Automotive FundamentalsvedhhNo ratings yet
3-Phase Synchronous Motor
3-Phase Synchronous Motor
Uploaded by
abhioptimus00Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3-Phase Synchronous Motor
3-Phase Synchronous Motor
Uploaded by
abhioptimus00Copyright:
Available Formats
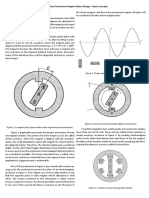
Stator
o3phaso
D.C -Supply
Stator winding
Field
winding Salient pole rotor
motor
Flg. 12.7.1 Schematic representatlon of three phaso synchronous
The synchronous motor construction is basically similar to rotating field type
alternator. It consists of two parts:
) Stator: Consisting of a three phase star or delta connected winding. This is excited
by a three phase a.c. supply.
i) Rotor: Rotor is a field winding, the construction of which can be salient (proj.cted
pole) or non salient (cylindrical) type. Practically most of the synchronous motors use
salient ie. projected pole type construction. The field winding is excited by a separate
d.c. supply through slip rings.
Review Questio
******** ***************"****************************
***************************"*** ** ***
1. Explain the construction of three phase synchronous motor.
28 Working Principle of Synchronous Motor
APIAKTU2009. 10 2010-112014-15,2015.16
Rwwww AwWW w.RRARODA ww...ww.NoA
Synchronous motor works on the principle of the magnetic locking. When two unlike
poles are brought near each other, if the magnets are strong, there exists a tremendou
force of attraction between those two poles. In such condition the two magnets are sai
to be magnetically locked. Rotation
of magnet 1
If now one of the two magnets is
N
rotated, the other also rotates in the same Tremendous
direction, with the same speed due to the force of
attraction
force of attraction i.e. due to magnetic ZMaçnet 2
ais geic
locking condition. The principle is shown rotated
schematically in the Fig. 12.8.1.
Fig. 12.8.1 Principie of magnetic tocking
Consider a three phase synchronous
i o r , whose 'ato: s wound for 2 poles. The two magnetic fields are produced in th
synchronouS motor bby exciting both the windings, stator and rotor with three phase aa.c
d.c. supply respectively.
supplyand.
winding is excited by a three phase a.c. supply then the flhux
When thu
phase stator
is rotating magnetic field rotating in space ata
b y the three phase winding
Wre the
produced
The rotating magnetic field creates the effect similar to
produ SVnchronous speed.
called s y n c h r o n d
of magnet in space with a synchronous speed.
the
cal rotation
physical
N = rp.m. Speed of rotating magnetic field
of understanding let us assume that the stator poles are N and S
For
simplicity
The direction of rotation of rotating magnetic field
re rotating at a speed of Ng
which
is sayclockwise.
d.c. supply, it also produces two
on rotor is excited by a
when the field winding salient type. Let these poles be Na
construction to be two pole,
nies, assuming rotor
and S and S1 while at start rotor is
is rotating N having poles
at N^
Now one magnet poles N2 and S. If
somehow the
second magnet is stationary having
stationary ie. near each other, the magnetic locking
or S and N2 are brought
N;
poles and S2 due to
unlike
between stator and rotor
As statorpoles. poles are rotating,
mav get established that of stator poles i.e. in
rotor will also rotate
in the same direction as
magnetic locking, with the same speed i.e. N. Hence synchronous
the direction of rotating magnetic field,
one speed i.e. synchronous
speed.
motor rotates at one and only
This is shown in the Fig. 12.8.2.
Stator
R Rotor
N
B
B
(a) (b)
motor
Fig. 12.8.2 Working principle of synchronous
from their
Pr the rotor poles
possible for stator poles to pull
not because of rotor inertia.
Hence
ary position into magnetic locking condition
synchronous motors are not self
starting
12.8.1 Why Synchronous Motor is Not Self Starting ?
Consider the rotating magnetic field as equivalent to physical rotation of two statee
poles N and S. Consider an instant when two poles are at such a position where stato stator
magnetic axis is vertical, along A-B as shown in the Fig. 12.8.3 (a). stator
Stator pole Stator
N Direction of rotating
magnetic field
s
( Salient pole rotor
(arbitrary position
at start)
Rotor
N
B Axis of stator magnetic fieid B
(a) Action of synchronous motor (b) Action of synchronous motor
Fig. 12.8.3
At this instant, rotor poles
arbitrarily positioned as shown in the Fig. 128.3 (a).
are
At this instant, rotor is stationary and unlike poles will
try to attract each other. Due
to this rotor will be subjected to an instantaneous torque in anticlockwise direction
as
shown in the Fig. 12.8.3 (a).
Now stator poles are rotating
very fast i.e. at a speed N, r.p.m. Due to inertia, betore
rotor hardly rotates in the direction of anticlockwise
torque, to which it is
stator poles change their positions. Consider an instant half a
subjected,the
period latter where stator
poles are exactly reversed but due to inertia rotor is unable to rotate from its mu
This is
position. shown in the Fig. 12.8.3 (b)
At this instant, due to the unlike poles trying to attract each other, the rotor w illlbe
subjected to a torque in clockwise direction. This will tend to rotate rotor in te
direction of rotating magnetic field.
e
But before this happens, stator poles again change their positions reversing
direction of the torque exerted on the rotor.
tne
As a result, the average torque exerted on the rotor is zero. And hence
motor is not self starting.
synchronous
vteweestions ns
operation of synchronous motor.
theprinciple of
L LExplain
APJAKTU 2009.10, 2010-11, 2014-15, Mark 5
W h ysymchron
ronous motor is not selfstarting? APJAKTU: 2015-16 Marke 5 **************** ****.**************
Starting Synchronous Motor
1 2 9Methods
Methods of
synchronous motor is not self starting. It is necessary to rotate the
earlier,
As
As
s e e n
very
ve near to synchronous speed. This is possible by various methods in
speed
at a methods to start the synehronous
meth
motor are,
various
r o t o r .
v a n o u s
The
P at
practice.
motors
2,Øsing damper winding
pony
1. Using 4. Using small d.c. machine coupled to it.
i n d u c t i o n motor
ring
3.Aga slip
Motors
Using Pony
291 to the synchronous speed with the help of
some
method, the rotor is brought
his
In t motor. Such an external device
is called Pony
like small induction
exterma
device
the dc. excitation to the rotor is
Motor
attains the syrnchronous speed,
the rotor The motor
established pony motor is decoupled.
Once
the synchronism is
on. Once
Switched motor.
continues to rotate as a synchronous
then
2.9.2 Using Damper Winding
synchronous motor, in Damper
In a
addidion to the normal field winding, winding
of
the additional winding consisting
in
copper bars is placed in the slots
the pole faces. The bars are short
O-
dircuited with the help of end rings.
Such an additional winding on the
QQ09
rotor is called damper winding. This
Winding as short circuited, acts as a
squirrel cage rotor winding of an
Normal
rotor winding
dog
induction motor. The schematic
as a squirrel cage l.M.
representation of such damper Fig. 12.9.1 Starting
winding is shown in the Fig. 12.9..
as
tator is excited by a supply, the motor starts
three phase
rotating an
dtoction iven to the field
is
motor at subsynchronous speed. Then d.c. supply and starts rotaing
winding.
at a
At
partid a
paricular instant motor gets pulled into synchronism
relative monon
at synchronous
speed, the
r o t o r rotor rotates
between damper winding and the rotating magnetic field is zero. Hence when mot
running as synchronous motor, there cannot be any induced e.m.f. in the dam
motor is
winding. So damper winding is active only at start, to run the motor as an indu. damper
tion
motor at start. Afterwards it is out of the circuit. As damper winding is short circ
ited
and motor gets started as induction motoc, it draws high current at start so inductio
tion
motor starters like star-delta, autotransformer etc. are used to start the synchrone
nous
motor as an induction motor.
12:9.3 As a Slip Ring Induction Motor
The above method of starting synchronous motor as a squirrel
cage induction motor
does not provide high starting torque. So to achieve this, instead of
shorting the damper
winding, it isdesigned to form a three phase star or delta connected winding. The three
ends of this winding are brought out through slip rings. An external rheostat then can
be introduced in series with the rotor circuit. So when stator is excited, the motor
starts
as a slip
ring induction motor and due to resistance added in the rotor, provides
high
starting torque. The resistance is then gradually cut off, as motor gathers
motor attains speed near
speed. When
synchronous, d.c. excitation is provided to the rotor, then
motor gets pulled into
synchronism and starts rotating at synchronous speed. The
damper winding is shorted by shorting
the slip rings. The initial resistance added in the
rotor not only provides high starting torque but also limits high inrush of
current. Hence it acts as a rotor resistance starter.
starting
The synchronous motor started this method is called
by a
slip ring induction motor
as shown in the Fig. 12.9.2.
Stator
Rotor
I2
3 phase
supply Slip rings
0000 1/2 Shaft
-Brush
Starting
resistance
D. C. w
supply ww
Rur Start
wi
TPDT switch
Fig. 12.9.2 Starting as a slip ring LM.
It can be observed from the i g 1292 that the same three phase rotor winding acs
as a normal rotor winding by shorting two of the phases. From the positive terminal
sitive terminal,
TM
You might also like
- Diesel Engine Ajm Atj Avb Avf Awx Repair Manual EngDocument172 pagesDiesel Engine Ajm Atj Avb Avf Awx Repair Manual EngAndsanta 130% (1)
- Bell 407GX ChecklistDocument2 pagesBell 407GX ChecklistAmanullah RafiNo ratings yet
- Manual de Armado de Motor Caterpillar 3024cDocument59 pagesManual de Armado de Motor Caterpillar 3024cmarcos astete78% (9)
- Yamaha BWS Manual Con DiagramaDocument214 pagesYamaha BWS Manual Con DiagramaManuel CortezNo ratings yet
- Unit8-Induction MotorDocument40 pagesUnit8-Induction MotorsaravananNo ratings yet
- 432zx ErrorCodesDocument28 pages432zx ErrorCodesmushfiq66100% (4)
- Manual de Motores Vol 4Document75 pagesManual de Motores Vol 4Gabriel Piñon Conde100% (1)
- 1000-0004 enDocument20 pages1000-0004 enMuhammad Mujtaba Tariq100% (2)
- TPSMDocument26 pagesTPSMLaasya RevillaNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machines Synchronous Machines: OutlineDocument31 pagesSynchronous Machines Synchronous Machines: Outlinesameerpatel15770No ratings yet
- 3.basic Concept of Rotating Electrical Machine PDFDocument126 pages3.basic Concept of Rotating Electrical Machine PDFStadpyrkhat lyngkhoiNo ratings yet
- Basic ConceptsDocument5 pagesBasic ConceptsRodrigo BobNo ratings yet
- LN08Document9 pagesLN08ruzgaryilmazz5No ratings yet
- EE - 3410 Electric Power: Introduction To Electric MachinesDocument30 pagesEE - 3410 Electric Power: Introduction To Electric MachinesDiyanel OriginalNo ratings yet
- AC Induction Motor FundamentalsDocument24 pagesAC Induction Motor Fundamentalsrohtahir100% (3)
- Modeling and Simulation of A Stepping Motor, 1969.Document3 pagesModeling and Simulation of A Stepping Motor, 1969.Ali H. NumanNo ratings yet
- Rotating Magnetic Field: ©2010, The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, IncDocument20 pagesRotating Magnetic Field: ©2010, The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, IncEdison ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Induction Motor Drives - Part1Document45 pagesChapter 4 - Induction Motor Drives - Part1Zafirah HanafiNo ratings yet
- E M II: Synchronous MotorDocument14 pagesE M II: Synchronous MotorAkashman ShakyaNo ratings yet
- 4 Wind Turbine GeneratorsDocument14 pages4 Wind Turbine Generatorsabhishek dubeyNo ratings yet
- AC Motor ReportDocument8 pagesAC Motor ReportbafulcherNo ratings yet
- Module 6: A.C. Electrical Machines For Hybrid and Electric VehiclesDocument65 pagesModule 6: A.C. Electrical Machines For Hybrid and Electric VehiclesDeepak mishraNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document45 pagesModule 3prashanth9.n.sNo ratings yet
- 01-Synchronous Motor PDFDocument48 pages01-Synchronous Motor PDFGeneral ZodNo ratings yet
- STSPIN820: Microstepping Management: Application NoteDocument19 pagesSTSPIN820: Microstepping Management: Application NoteguptaamitalwNo ratings yet
- EM214Induction Motorchapter 3Document46 pagesEM214Induction Motorchapter 3mahrusNo ratings yet
- Information-No - 1 1 7-1Document12 pagesInformation-No - 1 1 7-1Black PearlNo ratings yet
- BLDCDocument6 pagesBLDCquocyenkcdNo ratings yet
- 21EE44-Module 5Document23 pages21EE44-Module 5AshwiniNo ratings yet
- Module 15: C28x Digital Motor ControlDocument41 pagesModule 15: C28x Digital Motor ControlRamana ManoharNo ratings yet
- 1 AlternatorDocument29 pages1 AlternatorMwasi KivingeNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Motors: ChapterDocument16 pagesSynchronous Motors: ChapterAashrith GangamNo ratings yet
- Construction of AlternatorDocument4 pagesConstruction of AlternatorMeet SatheyNo ratings yet
- 244 - Synchronous MotorsDocument16 pages244 - Synchronous MotorssnghvishalNo ratings yet
- LECTURE# 22 & 23 Induction Machines FinalDocument39 pagesLECTURE# 22 & 23 Induction Machines FinalAmmara RasheedNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Generator: Basic Principle Construction Speed and Frequency EMF Induced Principle of OperationDocument20 pagesSynchronous Generator: Basic Principle Construction Speed and Frequency EMF Induced Principle of OperationalolorNo ratings yet
- ElectromagnetismDocument18 pagesElectromagnetism5814No ratings yet
- 7FB AC MotorDocument61 pages7FB AC Motoresteban muñozNo ratings yet
- DS2 - Unit 2-DC MachinesDocument57 pagesDS2 - Unit 2-DC MachinesTommba TommyNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Ac Machines TamilDocument25 pagesUnit IV Ac Machines TamilDeivathin adimaikalNo ratings yet
- 3 PhaseInductionMotors BookChapter 1Document19 pages3 PhaseInductionMotors BookChapter 1Rohan ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Synchronous Machine Theory and ModelingDocument108 pagesSynchronous Machine Theory and Modelingnanavarasmdu100% (1)
- EPS Frequency Converters PrinciplesDocument43 pagesEPS Frequency Converters Principlesrichfron69No ratings yet
- EEE20005-week 4 5Document103 pagesEEE20005-week 4 5ShelbyNo ratings yet
- AGBellDocument3 pagesAGBellandy1144552No ratings yet
- Special Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorDocument51 pagesSpecial Electrical Machines: Unit-3: Stepper Motor & Switched Reluctance MotorVikash TiwariNo ratings yet
- Synchronous. 5Document8 pagesSynchronous. 5K SDNo ratings yet
- Achine: Tructure Teady State Model and Basic Equations O Load Operation Ield Circuit Connections of A Machine EneratorDocument25 pagesAchine: Tructure Teady State Model and Basic Equations O Load Operation Ield Circuit Connections of A Machine EneratorAndrea VerdiNo ratings yet
- Lec 1-Chapter 1-Introduction - DraftDocument24 pagesLec 1-Chapter 1-Introduction - DraftMuhannad MohammedNo ratings yet
- Dual Rotor Generator Base PaperDocument4 pagesDual Rotor Generator Base Paperraja mNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 7 Induction Motor: Motor Construction: Stator: Rotor: RotorDocument19 pagesChapter # 7 Induction Motor: Motor Construction: Stator: Rotor: RotorSamiNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current Motors: Single-Phase Three-PhaseDocument56 pagesAlternating Current Motors: Single-Phase Three-Phaseeyd bartulabaNo ratings yet
- Complete Chapter1 and TutorialDocument19 pagesComplete Chapter1 and TutorialstevennguimsNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsDocument31 pagesUnit 3 Magnetics Effect of CurrentsTuition MasterNo ratings yet
- 1 Electric Motor BasicsDocument13 pages1 Electric Motor BasicsPandaGendutNo ratings yet
- DC Machines: King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Electrical EngineeringDocument10 pagesDC Machines: King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Department of Electrical EngineeringMohmmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- M C Q ElectromagnetismDocument30 pagesM C Q ElectromagnetismShaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Document33 pagesInduction Motor (ALL TOPICS)Ramprakash89% (18)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersFrom EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsFrom EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsNo ratings yet
- Home-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsFrom EverandHome-made Toy Motors: A practical handbook giving detailed instructions for building simple but operative electric motorsNo ratings yet
- Conversations on Electric and Magnetic Fields in the CosmosFrom EverandConversations on Electric and Magnetic Fields in the CosmosNo ratings yet
- Dynamos and Electric Motors - How to Make and Run ThemFrom EverandDynamos and Electric Motors - How to Make and Run ThemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SPM Unit1 Part-2Document10 pagesSPM Unit1 Part-2abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit-4 Part-1Document54 pagesSPM Unit-4 Part-1abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit5 Part-1Document19 pagesSPM Unit5 Part-1abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit5 Part-2Document30 pagesSPM Unit5 Part-2abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- SPM Unit-4 Part-2Document12 pagesSPM Unit-4 Part-2abhioptimus00No ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's LawsDocument3 pagesKirchhoff's Lawsabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- Operating System NotesDocument86 pagesOperating System Notesabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- P.F. & P.F Improvement of Using CapacitorDocument3 pagesP.F. & P.F Improvement of Using Capacitorabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- 3-Phase Star ConnectionDocument6 pages3-Phase Star Connectionabhioptimus00No ratings yet
- 404A-22G1 ElectropaK PN2002 PDFDocument2 pages404A-22G1 ElectropaK PN2002 PDFMd ShNo ratings yet
- A320 Amm - Ata 74 (Pw11) - Ignition (P 78)Document78 pagesA320 Amm - Ata 74 (Pw11) - Ignition (P 78)gola.ashwaniNo ratings yet
- KYMCO Downtown 350i Service ManualDocument611 pagesKYMCO Downtown 350i Service ManualYahya USallamiNo ratings yet
- Spark-Glow-Plugs-Ignition-Catalogue 777Document1 pageSpark-Glow-Plugs-Ignition-Catalogue 777АлександрNo ratings yet
- Universal Motor - WikipediaDocument27 pagesUniversal Motor - WikipediaAlejandro ReyesNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi 4M41Document6 pagesMitsubishi 4M41Sebastian Tabares RiosNo ratings yet
- RCGF21TWINDocument21 pagesRCGF21TWINejunsunNo ratings yet
- PVL Racing Ignition 1Document8 pagesPVL Racing Ignition 1GabrielCaravana100% (1)
- Engine Simulation in Power Programs (Chat GPT)Document2 pagesEngine Simulation in Power Programs (Chat GPT)konstadinos evangelouNo ratings yet
- RecommendationDocument3 pagesRecommendationKams KingNo ratings yet
- Demon CarburetorsDocument2 pagesDemon CarburetorsawalsumNo ratings yet
- Manual de Partes Motor Cat 1.1Document193 pagesManual de Partes Motor Cat 1.1Emanuel Nicolas Villarruel100% (1)
- Kubota Kx71 Parts Sec WatDocument20 pagesKubota Kx71 Parts Sec Watjoshua100% (56)
- Fadec: Navigation SearchDocument4 pagesFadec: Navigation SearchArjun AnduriNo ratings yet
- Every 1 500 Miles (2 400 KM) Lubricate Grease Points (Nipples) On Front-Axle (Document2 pagesEvery 1 500 Miles (2 400 KM) Lubricate Grease Points (Nipples) On Front-Axle (Maria ClaytonNo ratings yet
- Carbon X Combustion Chamber Cleaner K1+KDocument2 pagesCarbon X Combustion Chamber Cleaner K1+KDhany SSatNo ratings yet
- Camless Engines Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesCamless Engines Seminar ReportVineet Jason64% (11)
- Workshop Manual Lga 280 OhcDocument100 pagesWorkshop Manual Lga 280 Ohcptheo2088No ratings yet
- ENGINE Timing 4ZZ-FEDocument31 pagesENGINE Timing 4ZZ-FEAriel100% (1)
- Flash Powertrain Control Module (PCM) UpdatesDocument4 pagesFlash Powertrain Control Module (PCM) UpdatesPipis FakidomitisNo ratings yet
- SD313 26 Engine Control System (D4BH: 4D56 TCI 2.5L) (6) : (SD313 25) Cmdjc1 MC13 M01 ADocument1 pageSD313 26 Engine Control System (D4BH: 4D56 TCI 2.5L) (6) : (SD313 25) Cmdjc1 MC13 M01 AhaiderNo ratings yet
- EXPORT MM60 Material List - 22092022Document1,920 pagesEXPORT MM60 Material List - 22092022robbi wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Automotive FundamentalsDocument26 pagesUnit - 1: Automotive FundamentalsvedhhNo ratings yet