Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cestodes PDF
Cestodes PDF
Uploaded by
bravojarleneOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cestodes PDF
Cestodes PDF
Uploaded by
bravojarleneCopyright:
Available Formats
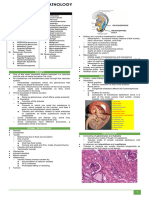
CESTODES ○
○
Immature:
Mature: completely functioning male and female
LIFE CYCLE
● Heteroxenous
reproductive organs ○ At least 1 IH
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS ○ Gravid: may uterus and eggs ○ Hymenolepis nana: one host
● Dorsoventrally: flattened
● Bilaterally symmetric
● Acoelomate & tripoblastic
● Tegument: syncitial membrane
● No circulatory organ
● Digestive tract
○ Absent (Cestodes)
○ Incomplete (Trematodes)
● Nervous system
○ Ladder type
○ Anterior: with paired ganglia
○ Posterior: nerve trunk
● Excretory: flame cell or protonephridium
STROBILA
○ With flagella extending into tubule
● Craspedote: proglottids overlap with one another
● Most are monoecious or hermaphroditic
● Acraspedote: no overlapping
○ Some dioecious: Schistosoma
● Apolytic: detached or rupture with mature eggs still
● Most are heteroxenous
inside
○ Few are monoxenous
● Anapolytic: detach after exhausting eggs
● Greek kestos: girdle or ribbon
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
● Exclusively parasitic
● Monoecious
● Segmented tape-like worms
● Generally one set
● Common names: reflect hosts or morphology
○ Two sets: Dipylidium caninum
● Self-fertilization and cross fertilization
● Human
● Female reproductive system
○ DH: intestinal infection
○ Uterus
○ IH: tissue infection
■ Lobulated: Hymenolepis
○ Exception:
■ Reticulate: Dipylidium
■ Hymenolepis nana: larva and adult
■ Branched: Taenia
develop in human intestine
■ Coiled: Diphyllobothrium
■ Taenia solium: ova develop into larvae
○ Pseudophyllidea
in tissues
■ Genital pores have common opening on
the ventral surface of the worm
○ Cyclophyllidea
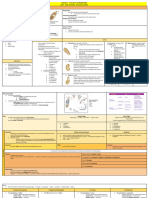
GROSS MORPHOLOGY ■ Genital opening on the lateral margin of
● Scolex: organ for attachment the proglottid
○ Rostellum/ Hooks ○ Genital pores
○ Sucker ■ Unilatera: Hymenolepis
● Neck: organ for growth ■ Irregulat: Taenia
● Strobila (chain): composed of proglottids ■ Bilateral: Dipylidium
● Proglottids
You might also like
- Bank Soal Literasi Bahasa InggrisDocument105 pagesBank Soal Literasi Bahasa Inggrissmkn1ksp bismen100% (2)
- IGCSE BIology Notes PDFDocument101 pagesIGCSE BIology Notes PDFTsz Ho Lam100% (2)
- CESTODESDocument7 pagesCESTODESKathleen Mae NatividadNo ratings yet
- Para Notes For Quiz 4Document36 pagesPara Notes For Quiz 4FebeirlenePonionesNo ratings yet
- Paralec M2Document7 pagesParalec M2VE NI CENo ratings yet
- 01 - Sexual Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pages01 - Sexual Anatomy and PhysiologyKyrriel CNo ratings yet
- Mycology VirologyDocument29 pagesMycology VirologyqlouisamarieNo ratings yet
- MycologyDocument9 pagesMycologyqlouisamarieNo ratings yet
- Paralec 3Document5 pagesParalec 3VE NI CENo ratings yet
- Module 9.4 + Microbio + Study GuideDocument33 pagesModule 9.4 + Microbio + Study GuideMikhail LamayoNo ratings yet
- PediatricDocument63 pagesPediatricReya Mae OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Biology Revision Part 1Document74 pagesIGCSE Biology Revision Part 1Will AndyNo ratings yet
- 02a GametogenesisDocument6 pages02a GametogenesiscarlgangcaNo ratings yet
- 03 - Human Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument5 pages03 - Human Conception and Fetal DevelopmentKyrriel CNo ratings yet
- Cytogen Notes 01Document6 pagesCytogen Notes 01Ushuaia Ira Marie L. GallaronNo ratings yet
- Blood FlagellatesDocument5 pagesBlood Flagellateschitocha8No ratings yet
- GYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsDocument3 pagesGYNECOLOGY Chief ComplaintsJennifer HerediaNo ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Part 3 - SPC MLS1 - Histo LecDocument11 pagesFemale Reproductive System Part 3 - SPC MLS1 - Histo LecCesmaine SanchezNo ratings yet
- Zoology Mammals (Rabbit)Document3 pagesZoology Mammals (Rabbit)PerrieNo ratings yet
- #1 &2 Myco & Viro + Definition of TermsDocument5 pages#1 &2 Myco & Viro + Definition of TermsJared SicorNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument7 pagesReproduction in OrganismsGauri JoshiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument7 pagesReproduction in OrganismsArchit GargNo ratings yet
- Bbeology PDFDocument7 pagesBbeology PDFSumit PatelNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument7 pagesReproduction in OrganismsAbhi AbhiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument7 pagesReproduction in OrganismsAbhi AbhiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument7 pagesReproduction in OrganismsJimineNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument7 pagesReproduction in Organisms.No ratings yet
- Reproduction in OrganismsDocument7 pagesReproduction in OrganismsJimineNo ratings yet
- 2DMT MT639 LEC - Third ShiftingDocument68 pages2DMT MT639 LEC - Third ShiftingKAREN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Histology Lecture FinalsDocument31 pagesHistology Lecture Finalsaly.urmz5No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 BiologyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 BiologyParshvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms PDFDocument7 pagesChapter 1 Reproduction in Organisms PDFAnurag KumarNo ratings yet
- Growing FetusDocument23 pagesGrowing FetusCARL JOHN MANALONo ratings yet
- II PUC Biology Notes. CH - 1 To 16Document164 pagesII PUC Biology Notes. CH - 1 To 16Vinay SawakarNo ratings yet
- Week9 Phylum NemathelminthesDocument26 pagesWeek9 Phylum NemathelminthesCzerinne Angela Justinne AlarillaNo ratings yet
- Phylum Platyhelminthes: Granulosus (Adult Lives inDocument12 pagesPhylum Platyhelminthes: Granulosus (Adult Lives inPatricia Mae SantosNo ratings yet
- Revised Pat 1 Slide-Review PDFDocument215 pagesRevised Pat 1 Slide-Review PDFChristine Mae DelimaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10. The Smaller Lophotrochozoan PhylaDocument2 pagesLesson 10. The Smaller Lophotrochozoan PhylaPaul DalomiasNo ratings yet
- Para 311 Lec Week 3Document81 pagesPara 311 Lec Week 3jeijai0827No ratings yet
- (Pathology) BreastDocument12 pages(Pathology) BreastKim DeeNo ratings yet
- Paralec M3Document4 pagesParalec M3VE NI CENo ratings yet
- Pedia NotesDocument14 pagesPedia NotesDen TupasNo ratings yet
- Physiological Psychology - FinalsDocument40 pagesPhysiological Psychology - Finalsmx2r6pv778No ratings yet
- 05 Fetal Development 1Document4 pages05 Fetal Development 1Gwen CastroNo ratings yet
- Is Lab P4 - Serologic Tests For SyphilisDocument4 pagesIs Lab P4 - Serologic Tests For SyphilisDanielle Anne LambanNo ratings yet
- 01A - Introduction To Basic Concepts, Key Questions, and Essential Principles of DevBiolDocument5 pages01A - Introduction To Basic Concepts, Key Questions, and Essential Principles of DevBiolcarlgangcaNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Ncma217 (2b) Lec Reproductive and Sexual HealthDocument10 pagesWeek 2 Ncma217 (2b) Lec Reproductive and Sexual HealthABEGAIL BALLORANNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System: PeristalsisDocument6 pagesReproductive System: PeristalsisJacquiline Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 PrepDocument14 pagesQuiz 1 PrepgdapbbbsybsuusrgnwNo ratings yet
- 6 - 16 NotesDocument7 pages6 - 16 NotesFefe JejeNo ratings yet
- 03 Second Trimester ConditionsDocument7 pages03 Second Trimester ConditionsJAN CAMILLE LENONNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument22 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingNur SanaaniNo ratings yet
- 12 KidneyDocument9 pages12 KidneycarlgangcaNo ratings yet
- THE ANGIOAPERMS (Part 1)Document5 pagesTHE ANGIOAPERMS (Part 1)PerrieNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Animal Morph and AnatomyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Animal Morph and AnatomyReanna NoelNo ratings yet
- SLH TopicsDocument10 pagesSLH TopicskulangkatunNo ratings yet
- NR 602 Week 8 Final Exam Completed Study GuideDocument20 pagesNR 602 Week 8 Final Exam Completed Study GuideTyler HemsworthNo ratings yet
- 4 - CestodesDocument12 pages4 - CestodesEsther Victoria TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Human ReproductionDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Human Reproductionsara DaphneNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Nucleic Acids and ProteinsDocument14 pagesCharacterization of Nucleic Acids and ProteinsBianca CarillaNo ratings yet
- Aubflab M3u2Document12 pagesAubflab M3u2bravojarleneNo ratings yet
- CestDocument7 pagesCestbravojarleneNo ratings yet
- AUBFLab Midterms PDFDocument8 pagesAUBFLab Midterms PDFbravojarleneNo ratings yet
- AUBF Lecture PDFDocument5 pagesAUBF Lecture PDFbravojarleneNo ratings yet
- A Bibliography and An Index List On Parasites and Parasitic Diseases of Fish in Northern EuropeDocument155 pagesA Bibliography and An Index List On Parasites and Parasitic Diseases of Fish in Northern EuropeBalog EndreNo ratings yet
- T. SaginataDocument11 pagesT. SaginataDorothyNo ratings yet
- The Full Moon Parasite Cleanse ProtocolDocument49 pagesThe Full Moon Parasite Cleanse Protocolparthvarandani100% (1)
- Times: 35 Minutes 30 Questions Question 1 Through 30 Are Based On The Following Passage Passage 1Document7 pagesTimes: 35 Minutes 30 Questions Question 1 Through 30 Are Based On The Following Passage Passage 1husnul khotimahNo ratings yet
- m1 - Helminthic InfectionDocument9 pagesm1 - Helminthic Infectionthe greatNo ratings yet
- ParasitologyDocument27 pagesParasitologyDreyden HaloNo ratings yet
- Biology M17 Animals Without BackbonesDocument40 pagesBiology M17 Animals Without BackboneschobynetNo ratings yet
- Marine InvertebratesDocument82 pagesMarine InvertebratesJohn Karuwal100% (1)
- Assignment in CestodesDocument2 pagesAssignment in CestodesDanzel MalicNo ratings yet
- ZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionDocument32 pagesZOO211 MATERIALS With IntroductionAdwale oluwatobi festusNo ratings yet
- HelmenthsDocument38 pagesHelmenthsKarwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8: The Triploblastic, Acoelomate Body PlanDocument5 pagesChapter 8: The Triploblastic, Acoelomate Body PlanJiboy MixNo ratings yet
- Anthelmintic Drugs - EDocument24 pagesAnthelmintic Drugs - EYeshaa MiraniNo ratings yet
- UC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Internal Parasite Control Guidelines - 2014-10-29Document8 pagesUC Davis Koret Shelter Medicine Program - Internal Parasite Control Guidelines - 2014-10-29Kitt KaosNo ratings yet
- Diplydium CaninumDocument12 pagesDiplydium CaninumIslaam SabriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 HomeworkDocument10 pagesChapter 23 HomeworkKvn4N6No ratings yet
- Para Midterm ExamDocument10 pagesPara Midterm ExamKlenn Orteza100% (2)
- Lecture6 Intro, Classification of ParasitesDocument38 pagesLecture6 Intro, Classification of ParasitesJumar Villegas100% (1)
- Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ SystemsDocument29 pagesOrgan Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ Systems Organ SystemsMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint TaeniasisDocument23 pagesPowerpoint TaeniasisAyshaShariff0% (1)
- Cestodes Flash CardsDocument5 pagesCestodes Flash CardsCvcp GamerNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 Helminth - EditedDocument58 pagesBab 6 Helminth - EditedChrisfenna MadihvolNo ratings yet
- Cestodes-Flatworms Trematodes-: Intestinal Flukes Liver Flukes Lung Flukes Blood FlukesDocument39 pagesCestodes-Flatworms Trematodes-: Intestinal Flukes Liver Flukes Lung Flukes Blood FlukesMicah MatibagNo ratings yet
- Parasitology Part 2Document124 pagesParasitology Part 2Mark Angelo JaurigueNo ratings yet
- RingwormsDocument5 pagesRingwormsCitrusNo ratings yet
- Taenias IsDocument56 pagesTaenias Iseliwaja100% (1)
- CestodesDocument39 pagesCestodesNachiket Vijay PotdarNo ratings yet
- Cestode SDocument79 pagesCestode SVincent Manganaan67% (3)
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument5 pagesPhylum Platyhelmintheskaran kundiNo ratings yet