Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Lesson 13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Uploaded by
yamizenaku040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views31 pagesGlobal food security is defined by the UN as all people having physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food at all times. There are four pillars of food security - availability, access, utilization, and stability. Poverty decreases countries' abilities to develop agriculture and economies, reducing food security. Food access refers to affordability, allocation, and preferences in acquiring food. Factors like production, distribution, exchange can affect food availability.
Original Description:
Original Title
Lesson-13-SUSTAINABLE-WORLD-SUSTAINABLE-DEVELOPMENT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlobal food security is defined by the UN as all people having physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food at all times. There are four pillars of food security - availability, access, utilization, and stability. Poverty decreases countries' abilities to develop agriculture and economies, reducing food security. Food access refers to affordability, allocation, and preferences in acquiring food. Factors like production, distribution, exchange can affect food availability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views31 pagesLesson 13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Lesson 13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Uploaded by
yamizenaku04Global food security is defined by the UN as all people having physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food at all times. There are four pillars of food security - availability, access, utilization, and stability. Poverty decreases countries' abilities to develop agriculture and economies, reducing food security. Food access refers to affordability, allocation, and preferences in acquiring food. Factors like production, distribution, exchange can affect food availability.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 31
GEN005
LESSON:13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD:
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
What is meant by the global food security?
Food security as defined by the United Nations’ Committee on World
Food Security; means that all people,at all times ,have physical,social
and economic access to sufficient,safe,and nutritious food that meets
their food preferences and dietary needs for an active and healthy life.
Importance of Global Food Security
1. Food insecurity - often rooted in poverty.
2. Poverty decreases the ability of countries to develop their
agricultural markets and economies.
3. Access to quality ,nutritious food is fundamental to human existence
4. Increased global security and stability. Improved health and
healthcare.
Why is food security a global issue?
Need to have sufficient incomes and resources to obtain food .
but with proper nutrition,sanitation,and hygiene ,many
diseases-especially those caused by food and waterborne
contaminants-are less likely to occur. Food security is an issue
both globally and at home in the United States. The 1996
World Summit on Food Security declared that ‘’food should
not be used as an instrument for political and economic
pressure’’
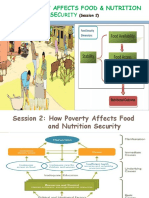
Pillars of Food Security
Growth of World Food Supply (caloric base) per
capital. The WHO states that three pillars determine
food security: food availability ,food access,and food
use and misuse. The FAO adds a fourth pillar;the
stability of the first three dimension of food security
over time. In 2009 the World Summit on Food
Security stated that the ‘’ four pillars of food security
are availability,access,utilization and stability.
1.Food Availability
Food Availability relates to the supply of food
through production ,distribution and exchange.
Enough nutritious food of sufficient quality needs
to be available to people for their consumption
Availability can be affected by.
Production ,distribution and exchange.
Production: how much and what types of food
are available through produced and storage
locally. Crop production is affected by rainfall,
land use ,management ,harvesting ,etc.Not all
countries can have food like Japan and
Singapore.
Goats are an essential part of global food
security because they are relatively low-
maintenance and easy to raise and farm.
Distribution : how is food made
available (physically mode),in what
form,when,and to whom. It also involves
storing ,processing, transport, packaging
and marketing foods.
Exchange: how much available food can
be obtained through exchange mechanisms
such as barter, trade,purchase,or loans. The
exchange of food requires efficient trading
systems and market institutions, which can
affect food security. Per capita world food
supplies are more than adequate to provide
food security to all , and thus food
accessibility is a greater barrier to achieving
food security.
2. Food Process
Food access refers to the affordability and
allocation of food and the preferences of
individuals and households.
Individuals and Households must acquire
sufficient food to eat a healthy, nutritious diet or
have access to adequate resources needed to
grow their food (e.g.,land). Food access can be
affected by:
Affordability is the ability of individuals,
households, or communities to afford the
price of food or land for producing food
relative to their incomes. Location can affect
access to food and which type of access a
family will rely on? A households assets,
including payment, land, products of labor,
inheritances and gifts can determine a
households access to food.
Allocation: the economic ,social and
political mechanisms are governing
when,where and how food can be
accessed by consumers and on what
terms. For examples , food may be
unequally allocated according to age
and gender within households.
Preference: social,religious and cultural norms and
values that influence the consumer demand for
certain types of food (e.g.,religious prohibitions or the
desire to follow a specific dietary pattern such us
vegetarianism,weight management sets aside a
specific group of foodstuffs)
The USDA adds that access to food must be available
in socially acceptable ways. Without,for
example,resorting to emergency food
supplies,scavenging,stealing or other coping strategies.
3. Food utilization:
Food utilization: people must have
access to a sufficient quantity and
diversity of foods to meet their
nutritional needs and must also eat and
properly metabolize such food.
Utilization can be affected by:
Nutritional value : the nutritional value
provided by the foods that are consumed, as
measured in calories, vitamins, protein and
various micronutrients ( e.g., iron, iodine,
vitamin A). Education about nutrition and
food preparation can affect food utilization
and improve this pillar of food security.
Health status: Access to healthcare is
another determinant of food utilization since
the health of individuals controls how the
food is metabolized. For example, intestinal
parasites can take nutrients from the body
and decrease food utilization. Sanitation can
also reduce the occurrence and spread of
diseases that can affect food utilization.
Food Safety: Food safety affects food
utilization and can be affected by the food
preparation,processing and cooking in the
community and household. Nutritional
values of the family determine food choice
and access to food free from food spoilage or
toxic contamination introduced during the
production,processing,packaging ,distributio
n or marketing of food ,and from the food-
borne disease such as salmonella.
Preparation and consumption:
sanitation and hygiene are essential in
food preparation. The resources (e.g.,
cooking tools and fuel). Knowledge and
ability to prepare and consume food in a
healthy and hygienic way.
Food stability
Food stability refers to the ability to
obtain adequate food over time. Food
may be available and accessible to all
people at all times ,access,availability
and utilization should be stable over
time.
The concept of stability can therefore
refer to both the availability and access
dimensions of food security. People
should not risk long access to food due to
sudden shocks ( e.g.,economic or climatic
crisis ) or cyclical events such as seasonal
food insecurity.
Buffer stock-A buffer stock is a system or scheme
which buys and stores stocks at times of good harvest
to prevent prices falling below a target range (or price
level) and releases stocks during bad harvests to avoid
prices rising above a target range (or price level). A
buffer stock scheme attempts to use commodity
storage to stabilize prices in an entire economy or an
individual market. Specifically, commodities are
bought when a surplus exists in the economy, stored,
and sold from these stores when economic shortages
occur.
Public distribution system- is a government-
sponsored chain of shops entrusted with distributing
basic food and non-food commodities to the needy
sections of the society at very low prices.
Advantages are:
(1) it has helped in stabilizing food prices and making
food available to consumers at affordable prices.
(2) it has helped in avoiding hunger and famine by
supplying food from surplus regions of the country to
deficient regions are the two important components of
food security system in a state.
How can food security be assessed?
The state of food security varies over a range of
scales, ranging from the individual to global.even
where food security is present at a particular
individual or household level, it may not be so
regional conversely, while a nation or region may
be generally considered food secure certain
(groups of) individuals may still suffer from food
insecurity.
Food Insecurity -food insecurity , on the
other hand , is defined by the United States
Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a
situation of limited or uncertain availability
of nutritionally adequate and safe foods or
limited or uncertain ability to acquire
acceptable foods in socially acceptable ways.
EFFECTS OF FOOD INSECURITY
1. Famine and hunger are both rooted in
food insecurity. Chronic food insecurity
translates into a high degree of vulnerability
to famine and hunger ensuring food security
presupposes elimination of vulnerability;
EFFECTS OF FOOD INSECURITY
2. Stunting and chronic nutritional deficiencies among
children with symptoms of low calorie and low protein
intake results to decreasing body size (stunted growth).
This process starts in utero if the mother is
malnourished and continues through approximately
the third year of life. It leads to higher infant and child
mortality, but at rates far lower than during famines.
Once stunting has occurred, improved nutritional
intake after about two years is unable to reverse the
damage;
EFFECTS OF FOOD INSECURITY
3. Premature failure of vital organs during
adulthood. For example, a 50-years-old
individual might die of heart failure because
his/her heart suffered structural defects during
early development; stunted individuals suffer a
higher rate of disease and illness than those who
have not undergone stunting;
EFFECTS OF FOOD INSECURITY
4. Severe malnutrition in early childhood
often leads to defects in cognitive
development . it,therefore, creates
disparity among children who did not
experience severe malnutrition and
those who share it;
EFFECTS OF FOOD INSECURITY
5. Depression ,anxiety and sleep disorders - a
recent comprehensive systematic review showed
that over 50 studies have shown that food
insecurity is strongly associated with a higher risk
of depression ,anxiety and sleep disorders. For
depression and anxiety, food insecure individuals
have almost a threefold risk increase compared
to food secure individuals.
QUESTIONS
1. What is the definition of global food
security?
2. What are the pillars of food security?
3. How does poverty affect food security?
4. How does food access relate to food
security?
5. What factors can affect food availability?
QUESTIONS
6. What is the role of food utilization in food security?
7. How does food stability contribute to food security?
8. What is a buffer stock scheme?
9. What is the role of the public distribution system in
food security?
10. How does food insecurity affect individuals and
communities?
GEN005
LESSON:13 SUSTAINABLE WORLD:
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT
Joanne Banog
Princess Prades
Nena Hermosa
You might also like
- Chicken Colour Genetics BasicsDocument16 pagesChicken Colour Genetics BasicsAnízio Luiz Freitas de Mesquita60% (5)
- Module 6 Food InsecurityDocument10 pagesModule 6 Food InsecurityNizea Camille Navarro JavierNo ratings yet
- Food InsecurityDocument7 pagesFood InsecurityJustine Ivan CapiralNo ratings yet
- Food Insecurity Duration: 6 HoursDocument13 pagesFood Insecurity Duration: 6 HoursLeila Mae L. InfanteNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument11 pagesGlobal Food SecurityMarjorie O. Malinao100% (1)
- PPH 324 Lecture 1Document5 pagesPPH 324 Lecture 1KendiNo ratings yet
- Contemp ExpalinDocument8 pagesContemp ExpalinEka MagsigayNo ratings yet
- FAO Introduction To FSDocument3 pagesFAO Introduction To FSBin LiuNo ratings yet
- 4 5861665975673294635Document17 pages4 5861665975673294635Asnake YohanisNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document20 pagesPresentation 2Khem AsucroNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Equity in Food SecurityDocument8 pagesThe Importance of Equity in Food SecurityScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Farm LawDocument14 pagesFarm LawDEEPALI KATIYARNo ratings yet
- Tuaia. Taranikai (S11235078)Document2 pagesTuaia. Taranikai (S11235078)ft8d7kfvyqNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument5 pagesFood SecurityNoor AfizahNo ratings yet
- Food Security: A PrimerDocument4 pagesFood Security: A PrimerjournalNo ratings yet
- Food Security: Hunger StarvationDocument15 pagesFood Security: Hunger StarvationhanumanthaiahgowdaNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument11 pagesFood SecurityJanedyl Mando Salvador100% (1)
- Global Food SecurityDocument20 pagesGlobal Food SecurityGenshin ImpactAccNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument6 pagesFood SecurityYukta PatilNo ratings yet
- MANDRILLA - BSCE 2D - Global-Food-SecurityDocument5 pagesMANDRILLA - BSCE 2D - Global-Food-SecurityJhomer MandrillaNo ratings yet
- Week 16 Global Food SecurityDocument5 pagesWeek 16 Global Food Securitydonnasison0929No ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument9 pagesFood SecurityMarc HeratoNo ratings yet
- food security final research paper 1 1Document7 pagesfood security final research paper 1 1varad syedNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument5 pagesGlobal Food SecurityArianne Marie Omo100% (1)
- The Different Food SystemsDocument3 pagesThe Different Food SystemsAnie Faye AribuaboNo ratings yet
- Gender, Food Security and MigrationDocument33 pagesGender, Food Security and MigrationPrabina JoshiNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة الثانيةDocument24 pagesالمحاضرة الثانيةaya30.4.2018mohamedNo ratings yet
- Hunger Malnutrition and PovertyyyDocument22 pagesHunger Malnutrition and PovertyyyEnzoNo ratings yet
- Brian Kyle C. Unciano Bsce1CDocument3 pagesBrian Kyle C. Unciano Bsce1CBrian UncianoNo ratings yet
- Hunger and Food InsecurityDocument7 pagesHunger and Food InsecurityritipkNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument25 pagesGlobal Food SecurityMelanie JulianesNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument6 pagesFood SecurityRiya PandeyNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument21 pagesGlobal Food SecurityFelipe RamonNo ratings yet
- Food Security Final ReportDocument28 pagesFood Security Final ReportAqsa SarfarazNo ratings yet
- Lecture II Food and Nutrition SecurityDocument24 pagesLecture II Food and Nutrition SecurityJorge Mario Al IINo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument2 pagesFood SecurityZahid GujjarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food SafetyDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Food SafetyENJOY YOUR MUSICNo ratings yet
- Environmental Studies.: End Hunger and Achieve Food SecurityDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Studies.: End Hunger and Achieve Food SecurityRishita JalanNo ratings yet
- An Assignmennt On Food SecurityDocument16 pagesAn Assignmennt On Food SecuritySamira RahmanNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument26 pagesFood SecurityAqsa SarfarazNo ratings yet
- Food SectDocument8 pagesFood SectKhalil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Population and Poverty Analysis - Lecture Notes 19-04-2024 (Autosaved)Document73 pagesPopulation and Poverty Analysis - Lecture Notes 19-04-2024 (Autosaved)pallangyo185No ratings yet
- FNS eDocument71 pagesFNS eRaaz The ghostNo ratings yet
- Group 9 (Global Food Security Paper)Document7 pagesGroup 9 (Global Food Security Paper)Catherine Nicole IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument2 pagesFood SecurityJaymar ConsultaNo ratings yet
- Food Security: Meaning and ImportanceDocument4 pagesFood Security: Meaning and ImportanceNitish Thakur100% (1)
- Food SecurityDocument10 pagesFood SecurityKids Learning R.BNo ratings yet
- Food SecurityDocument20 pagesFood SecurityAqsa Sarfaraz67% (3)
- Global Food SecurityDocument7 pagesGlobal Food SecurityMizraim EmuslanNo ratings yet
- Ghattas Food Security and Nutrition PDFDocument18 pagesGhattas Food Security and Nutrition PDFRohmatul Bariroh Al FaiqohNo ratings yet
- Learner Notes 0411Document14 pagesLearner Notes 0411Mohamed AbdiNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument6 pagesGlobal Food SecurityKassandra Bravo SagunNo ratings yet
- Global Food SecurityDocument34 pagesGlobal Food SecurityAnnie Rose Argañoza OpongNo ratings yet
- Bobo Si KingDocument8 pagesBobo Si KingbookselfgamingNo ratings yet
- Nutritionpromotion 200327102308Document22 pagesNutritionpromotion 200327102308Giorgi TamazashviliNo ratings yet
- GLOBAL FOOD SECURITY By. Oñate, Richard Q.Document4 pagesGLOBAL FOOD SECURITY By. Oñate, Richard Q.Richard Queman Oñate100% (1)
- Report Global Food SecurityDocument3 pagesReport Global Food SecurityK8Y KattNo ratings yet
- Frankenberger 1998 HLS Sustainable Food Nutritional SecurityDocument6 pagesFrankenberger 1998 HLS Sustainable Food Nutritional SecurityAleneNo ratings yet
- Full Name: Doan Yen Ngoc Student Code: TA46C-078-1923 Class: Speaking English For Specific Purpose Topic: Food Security Position PaperDocument6 pagesFull Name: Doan Yen Ngoc Student Code: TA46C-078-1923 Class: Speaking English For Specific Purpose Topic: Food Security Position PaperDoan Yen-NgocNo ratings yet
- Gastronomic Guardians : Safeguarding Food Safety at Home and BeyondFrom EverandGastronomic Guardians : Safeguarding Food Safety at Home and BeyondNo ratings yet
- BÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ 10 - REVIEW 1-3Document3 pagesBÀI TẬP BỔ TRỢ 10 - REVIEW 1-3Phuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Anonymous Survival Guide For Citizens in A RevolutionDocument15 pagesAnonymous Survival Guide For Citizens in A RevolutionLala Paroubek100% (4)
- Bale Pro Highline Product Catalogue 2022 WebDocument27 pagesBale Pro Highline Product Catalogue 2022 Webayya samyNo ratings yet
- Jamaica: "Out of Many, One People"Document25 pagesJamaica: "Out of Many, One People"uranusangusNo ratings yet
- SMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun 2019 Bahasa Inggeris (Kertas 1) Tingkatan 1Document12 pagesSMJK Chung Ling Pulau Pinang Peperiksaan Akhir Tahun 2019 Bahasa Inggeris (Kertas 1) Tingkatan 1Chong Beng LimNo ratings yet
- MelakuDocument187 pagesMelakutyby77No ratings yet
- Culture Food Around The WorldDocument3 pagesCulture Food Around The WorldAlejandra OsorioNo ratings yet
- COOKERY G9 QUARTER 4 WEEK1 - Learning Tasks 1-3Document5 pagesCOOKERY G9 QUARTER 4 WEEK1 - Learning Tasks 1-3Marisol PonceNo ratings yet
- Salmon: Atlantic Salmon, Salmo SalarDocument14 pagesSalmon: Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salarenzo abrahamNo ratings yet
- MAPEH (P.E.) : Quarter 1 - Module 1: Active Recreation (Lifestyle)Document10 pagesMAPEH (P.E.) : Quarter 1 - Module 1: Active Recreation (Lifestyle)Albert Ian CasugaNo ratings yet
- Task 4 Preliminary Pages of CBLM - CARAQUEL, DIANNEDocument12 pagesTask 4 Preliminary Pages of CBLM - CARAQUEL, DIANNECharleneNo ratings yet
- Anushka GNM YmtDocument3 pagesAnushka GNM YmtPreetam ParabNo ratings yet
- 2019年12月雅思考试回忆机经Document53 pages2019年12月雅思考试回忆机经Ni PeterNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ SỐ 11 HSG ANH 9Document15 pagesĐỀ SỐ 11 HSG ANH 9Trần NhànNo ratings yet
- Family Case StudyDocument14 pagesFamily Case StudyArk Raphael N. LEONORNo ratings yet
- ENT300Document14 pagesENT300Muhammad Hamizan HakiemiNo ratings yet
- THC 2 FINAL Na GidDocument78 pagesTHC 2 FINAL Na GidMichael P. CelisNo ratings yet
- Fildayat Tholip: The Excellence HR. Recruitment ManagerDocument4 pagesFildayat Tholip: The Excellence HR. Recruitment ManagerFildayat TholipNo ratings yet
- Traduisez en Francais + Les TempsDocument3 pagesTraduisez en Francais + Les TempsNatasha DalalNo ratings yet
- REYES, SHARON - Plating and Food PresentationDocument41 pagesREYES, SHARON - Plating and Food PresentationSharon ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lemon Bars RecipeDocument1 pageLemon Bars RecipeEllie PommeNo ratings yet
- Recipe BookDocument50 pagesRecipe BookkikirikiNo ratings yet
- Pork4 PDFDocument24 pagesPork4 PDFSean AabergNo ratings yet
- Olde Hansa MenuDocument13 pagesOlde Hansa MenuЕвген АнтихайпNo ratings yet
- Perception of The Student of Pampanga Institute About School CanteenDocument4 pagesPerception of The Student of Pampanga Institute About School CanteenJocelyn ManuyagNo ratings yet
- LAS - Main-Idea - QuizDocument3 pagesLAS - Main-Idea - QuizMa. Luiggie Teresita PerezNo ratings yet
- WEEK6 DLL TLEDocument9 pagesWEEK6 DLL TLECharmine Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Marketing 13th Edition Kerin Solutions ManualDocument53 pagesMarketing 13th Edition Kerin Solutions Manualcalliopehilary05r9c100% (35)
- Taste Com Au Cookbooks Easy BakingDocument100 pagesTaste Com Au Cookbooks Easy BakingChaitra ReddyNo ratings yet