Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mid Term 2 2
Mid Term 2 2
Uploaded by
17athermon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageOriginal Title
mid term 2 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageMid Term 2 2
Mid Term 2 2
Uploaded by
17athermonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
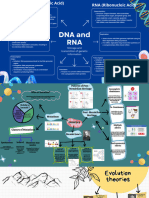
Proteins: Mitosis: DNA and RNA:
·Interphase = cell grows
DNA replicates
·Prophase = DNA supercoils
Chromosomes become visible
Nuclear membrane breaks down
R group Centrioles migrate to poles
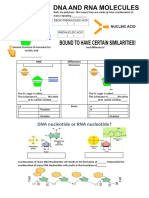
Spindle fibres develop ·DNA base = Adenine and Thymine
Guanine and Cytosine
·Metaphase = chromosomes line up on equator of ·RNA base = Uracil
·Peptide bond -> broken by hydrolysis cell
·Bond highlighted = phosphodiester
·Held together = H has positive charge
O has negative charge ·Anaphase = Spindles grip centromeres
Chromosomes migrate to poles ·RNA = single polypeptide chain
Opposites attract form weak H2 ·DNA = double polypeptide chain
bonds Sister chromatids pulled to opposite poles
·Polymerisation = amino acids joined forming ·RNA pentose sugar = ribose
polypeptides ·Telophase = Nuclear membrane reforms
Chromosomes disperse. ·DNA pentose sugar = deoxyribose
·Secondary = twists structure with charges shown Cytokinesis begins.
·mRNA = messenger -> protein synthesis
above forming alpha helix ·rRNA = ribosomal -> part of ribosomes
·Tertiary = one polypeptide chain ·Cytokinesis = cytoplasm divides
·tRNA = transfer -> make proteins at ribosomes
=alpha helices twisted
= contains -> disulphide bridges ·tRNA = clover leaf -> hydrogen bonds form to
-> Ionic bonds some sections of tRNA complementary to
-> Hydrogen bonds base pairing
·Quaternary = Many polypeptide chains
·DNA stable = backbone -> protects bases
= hydrogen bonds -> fprm bridges between
Test for proteins: 1) sample in test tube with equal phosphodiester uprights
volume sodium hydroxide
2) few drops dilute copper sulphate ·ADP to ATP is ATP catalyses reaction
and mix ·ATP to ADP is ATP hydrolase catalyses
3) Purple
You might also like
- CH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Document3 pagesCH 16 and 17 Worksheet-1Dani Jo OwensNo ratings yet
- CH 11.4 MeiosisDocument9 pagesCH 11.4 MeiosisKelsey Koehler0% (1)
- Memory: A Five-Day Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersDocument64 pagesMemory: A Five-Day Unit Lesson Plan For High School Psychology TeachersBeary7No ratings yet
- (1 - 2) - Leading Strand With Helicase - Lagging Strand Opposite HeliaseDocument7 pages(1 - 2) - Leading Strand With Helicase - Lagging Strand Opposite Heliasenevio.wirtgenNo ratings yet
- Dna Structure RenaturationDocument5 pagesDna Structure Renaturationcherushii shiNo ratings yet
- Case 1 SummeryDocument11 pagesCase 1 SummeryTtNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsbonoo.santuchoNo ratings yet
- DNA VS RNA - DNA REPLICATIONDocument2 pagesDNA VS RNA - DNA REPLICATIONJuan Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- VSU-2020-PPT Information Transfer Protein SynthesisDocument78 pagesVSU-2020-PPT Information Transfer Protein SynthesisAndreah BaylonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideDocument11 pagesChapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideabdulazizalobaidiNo ratings yet
- Mol. Basis Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesMol. Basis Cheat SheetShradha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Yarsiinez100% (1)
- Central Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiDocument27 pagesCentral Dogma: Etty Widayanti, Ssi. Mbiotech. Sub Bagian Biologi Bagian Anatomi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas YarsiPuja KhairunnisaNo ratings yet
- DNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytoDocument3 pagesDNA Kita Iiwan RNA CytozairahNo ratings yet
- Biology (2nd Semester) - Grade 12 ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiology (2nd Semester) - Grade 12 ReviewerPatricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Transcription & Translation Notes PDFDocument20 pagesTranscription & Translation Notes PDFManas RjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Prescott S 10 THDocument4 pagesChapter 13 Prescott S 10 THiamayesha725No ratings yet
- Bacterial Transcription 2Document120 pagesBacterial Transcription 2Theeta TanarugsNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBsaeed.khedrizaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0-1Document10 pagesLesson 0-1Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument9 pagesNucleic Acidgelary sousaNo ratings yet
- DNA Translation and Transcription PDFDocument2 pagesDNA Translation and Transcription PDFSim QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- DNA Overview Central DogmaDocument56 pagesDNA Overview Central DogmaBukhari DiangkaNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression - Protein SynthesisDocument39 pagesGene Expression - Protein SynthesisTawonga ManjiniNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- BacterialDocument2 pagesBacterialjulietaira quibilanNo ratings yet
- Cytogenetics ReviewerDocument46 pagesCytogenetics ReviewerSarah EugenioNo ratings yet
- Lesson 0Document6 pagesLesson 0Francesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes Lesson 4Document4 pagesGuided Notes Lesson 4Raine RagadioNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Lecture 4-5-CanvasDocument76 pages2018 - Lecture 4-5-CanvasAdam Bryant PoonawalaNo ratings yet
- Gene To Protein FlashcardsDocument2 pagesGene To Protein FlashcardsTim DAVISNo ratings yet
- MOLECULAR GENETICS AND EVOLUTION-activityDocument2 pagesMOLECULAR GENETICS AND EVOLUTION-activityIvy ManagNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Biochem For NucleotidesDocument3 pagesReviewer Biochem For NucleotidesNino D. AtilanoNo ratings yet
- FHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionDocument58 pagesFHCG 4 - Nucleic Acids Gene ExpressionLeena AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Key Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaDocument2 pagesKey Notes Genetic Material and Central DogmaSeiza WinchesterNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InherentDocument16 pagesMolecular Basis of Inherentvanshikachaudhary112007No ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesNucleic AcidsJovan SernaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry SemiDocument5 pagesBiochemistry SemiTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- Transes Biochem ProteinsynthesisDocument6 pagesTranses Biochem ProteinsynthesisPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- DNA (Scie)Document3 pagesDNA (Scie)Michaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- Biology Nucleic A-Level OCR NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Nucleic A-Level OCR Notestbrook2017No ratings yet
- XII CH 6 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCEDocument9 pagesXII CH 6 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCEAMAL 255No ratings yet
- XII CH 6 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE Rifa Hsslive PDFDocument9 pagesXII CH 6 MOLECULAR BASIS OF INHERITANCE Rifa Hsslive PDFAdithyavarsha A SNo ratings yet
- 6 Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pages6 Nucleic AcidsTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument17 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidJennifer YuNo ratings yet
- Lesson: SynthesisDocument3 pagesLesson: Synthesisisaspiegel2018No ratings yet
- Unit 6Document4 pagesUnit 6Leen Al-FouzanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LDocument7 pagesStudy Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LPepitinNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerFrancesca YanzonNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Document2 pagesNucleic Acids: DNA Nucleotide or RNA Nucleotide?Rachell RequellNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2025Document3 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notes - Lakshya NEET 2025anantpounikar02No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Short NotesDocument3 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance - Short Notesp11925885No ratings yet
- Compre MolbioDocument93 pagesCompre MolbioDeniebev'z OrillosNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 6 GuideDocument7 pagesAP Biology Unit 6 Guidelolo2212008No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic DNA ReplicationDocument31 pagesProkaryotic DNA ReplicationAnonymous Ef3jslp8No ratings yet
- DNA Structure DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesDNA Structure DNA ReplicationBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument41 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biologyanmbeltran31No ratings yet
- Materi Kuliah Asam Nukleat - Ibu Dosen Wita BIOUMDocument38 pagesMateri Kuliah Asam Nukleat - Ibu Dosen Wita BIOUMitsnarachmawati18No ratings yet
- General Biology - DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - DNA ReplicationChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Regulation of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Mass DevelopmentDocument14 pagesMolecular Regulation of Pancreatic Beta-Cell Mass DevelopmentAndrei MitescuNo ratings yet
- BioEssays - 2002 - Tyson - The Dynamics of Cell Cycle RegulationDocument15 pagesBioEssays - 2002 - Tyson - The Dynamics of Cell Cycle RegulationNindya AgustiaNo ratings yet
- Test 2 Winter 2020 AnswersDocument10 pagesTest 2 Winter 2020 Answersproplayer910No ratings yet
- NOTES - 10.4 Cell DifferentiationDocument15 pagesNOTES - 10.4 Cell DifferentiationMUHAMMAD SHAYANNo ratings yet
- Matdid 207367Document40 pagesMatdid 207367Deblina JanaNo ratings yet
- Human Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Test BankDocument21 pagesHuman Genetics Concepts and Applications 11th Edition Ricki Lewis Test BankAdekunle Ologun100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Bilogy Holiday HomeworkDocument8 pagesChapter 2 Bilogy Holiday HomeworkAayush RastogiNo ratings yet
- Assignment Objective - Instructions SB015 SDS 21 - 22Document3 pagesAssignment Objective - Instructions SB015 SDS 21 - 22Adam AdemNo ratings yet
- Life Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Document21 pagesLife Processes in Living Organisms Part - 2 - 1Shyamal AryalNo ratings yet
- Somatic Embryogenesis PDFDocument6 pagesSomatic Embryogenesis PDFeduardo9119No ratings yet
- Science 2ND Grading Human Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesScience 2ND Grading Human Reproductive SystemYouls TorNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination in PlantsDocument16 pagesSex Determination in PlantsPRATAP100% (5)
- Cell Structure, Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesCell Structure, Reproduction and DevelopmentPinu CattoNo ratings yet
- AP FRQsDocument10 pagesAP FRQsanson3225877976No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants ScienceDocument3 pagesReproduction in Plants SciencegajulavarshithaaravNo ratings yet
- Repressible Operon System (Fig. 6.35)Document2 pagesRepressible Operon System (Fig. 6.35)Valar Mathei PadmanadhanNo ratings yet
- 7.013 Exam 2 PDFDocument6 pages7.013 Exam 2 PDF15klaNo ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesSexual and Asexual Reproductionapi-262424911No ratings yet
- Abeloff Clinical Oncology 2020 (Part 4)Document23 pagesAbeloff Clinical Oncology 2020 (Part 4)Emiliana LarionesiNo ratings yet
- Part I A. Basic Experiment in Embryology & SCB LabDocument75 pagesPart I A. Basic Experiment in Embryology & SCB LabNhư Quỳnh Vương ThịNo ratings yet
- DLL Template Asexual and Sexual g4Document8 pagesDLL Template Asexual and Sexual g4Jeffrey Selpo BondadNo ratings yet
- Embryo Sac TypeDocument5 pagesEmbryo Sac Typeakshita kumariNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1-3Document9 pagesExercise 1-3Patricia MedinaNo ratings yet
- List of g10 Graceful Completers.Document2 pagesList of g10 Graceful Completers.loretaNo ratings yet
- Cells AssignmentDocument18 pagesCells AssignmentMuqadasNo ratings yet
- Forgetting: Trace Decay Theory of ForgettingDocument12 pagesForgetting: Trace Decay Theory of ForgettingAddisu TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Obg Prenatal Period Golden Points: Nursing CrashDocument9 pagesObg Prenatal Period Golden Points: Nursing CrashOmprakash SainiNo ratings yet
- Chromosome MappingDocument9 pagesChromosome MappingPuddyNo ratings yet