Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FLOWERS
FLOWERS
Uploaded by
Ravindra Persaud 9A0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe document describes the main parts of a flower and their functions in reproduction. Sepals protect the developing flower, petals attract pollinators, stamens produce and disperse pollen containing male gametes, carpels receive pollen on their stigma and contain the ovary housing female gametes (ovules) that become seeds after fertilization, and nectaries attract pollinators with a sugar reward. Together, these floral parts enable the transfer of pollen for fertilization and the production of fruits and seeds.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the main parts of a flower and their functions in reproduction. Sepals protect the developing flower, petals attract pollinators, stamens produce and disperse pollen containing male gametes, carpels receive pollen on their stigma and contain the ovary housing female gametes (ovules) that become seeds after fertilization, and nectaries attract pollinators with a sugar reward. Together, these floral parts enable the transfer of pollen for fertilization and the production of fruits and seeds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesFLOWERS
FLOWERS
Uploaded by
Ravindra Persaud 9AThe document describes the main parts of a flower and their functions in reproduction. Sepals protect the developing flower, petals attract pollinators, stamens produce and disperse pollen containing male gametes, carpels receive pollen on their stigma and contain the ovary housing female gametes (ovules) that become seeds after fertilization, and nectaries attract pollinators with a sugar reward. Together, these floral parts enable the transfer of pollen for fertilization and the production of fruits and seeds.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
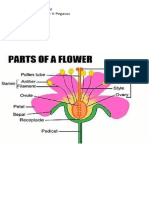
1. Sepals: Sepals are the outermost floral whorl.
They protect the developing flower bud and
provide support to the petals.
2. Petals: Petals are often brightly colored to attract pollinators. They play a crucial role in the
reproductive process by luring pollinators toward the reproductive organs.
3. Stamens:
Anther: The anther is where pollen grains are produced. Pollen contains male gametes
(sperm cells).
Filament: The filament supports the anther, positioning it for effective pollen dispersal.
4. Carpels (Pistil):
Stigma: The stigma is the receptive surface where pollen grains land during pollination.
Style: The style is a tube-like structure that connects the stigma to the ovary.
Ovary: The ovary contains ovules, which are the female gametes. After fertilization, the
ovary matures into a fruit, and the ovules develop into seeds.
5. Ovule: Ovules are the female reproductive cells housed within the ovary. After fertilization,
they develop into seeds.
6. Receptacle: The receptacle is the tip of the stem to which all floral parts are attached. It
supports the flower's structure.
7. Nectaries: Nectaries are specialized structures that produce nectar. Nectar attracts pollinators
and serves as a reward for their assistance in pollination.
You might also like
- PlantsDocument22 pagesPlantsPotato ManNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity For Flower DissectionDocument3 pagesLab Activity For Flower Dissectionlheninyamoo50% (2)
- Parts of The FlowersDocument2 pagesParts of The Flowersmaricel100% (1)
- Plant Parts - Flowers: PistilDocument8 pagesPlant Parts - Flowers: PistilDiana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument40 pagesLecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument2 pagesParts of A FlowerIrish cambriNo ratings yet
- 3RD Grading ScienceDocument16 pages3RD Grading ScienceJohannah Eleiya CalimagNo ratings yet
- Plants Reproduction and DevelopmentDocument6 pagesPlants Reproduction and DevelopmentAlwìn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Sania Khalil (Roll No.54) AssignmentDocument4 pagesSania Khalil (Roll No.54) Assignmentkhanmuhammadm463No ratings yet
- Cot 2 Reproductive Parts of FlowerDocument36 pagesCot 2 Reproductive Parts of FlowerArlyn MirandaNo ratings yet
- Reproductive StructuresDocument30 pagesReproductive StructuresDaniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- EaSc 001 - Learning Task 3.1 - ABMDocument2 pagesEaSc 001 - Learning Task 3.1 - ABMColein FranleighNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pages4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsYu HasNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 - Organismal Body of PlantsDocument5 pagesLesson1 - Organismal Body of PlantsJennylyn Como BarbechoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument1 pageParts of A FlowerArjie Hiludo LagahidNo ratings yet
- Pollination - NotesDocument2 pagesPollination - Notesnandana jammulaNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesFlower Structure and Functionwafwfw0% (1)
- Reproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingDocument34 pagesReproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- Second Term Science 5 Modules 5-8Document18 pagesSecond Term Science 5 Modules 5-8Kathleen FernandezNo ratings yet
- Meljim Parts of A FlowerDocument2 pagesMeljim Parts of A FlowerMeljim GabrielNo ratings yet
- Wa0005Document6 pagesWa0005sanglapghNo ratings yet
- SIM-Science-Week 4Document12 pagesSIM-Science-Week 4Rocheel P. JandusayNo ratings yet
- Notes - Flower StructureDocument2 pagesNotes - Flower Structureapi-238421605No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Sexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesLesson 6 - Sexual ReproductionAbegail HernandezNo ratings yet
- PLANTS REviewerDocument3 pagesPLANTS REviewerJunie YeeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document21 pagesPresentation 2Maro Ridhwan RidhiwaniNo ratings yet
- PRPM110 LEC Module 5Document25 pagesPRPM110 LEC Module 5CASSANDRA REIGN CONSTANTINONo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AngiospermsDocument19 pagesReproduction in Angiospermstapas kunduNo ratings yet
- Biology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)Document6 pagesBiology Project (Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants)47. Anas SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument13 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsshikaanara8686No ratings yet
- FUnctions Pt3Document1 pageFUnctions Pt3STEM STUDENTSNo ratings yet
- Tanmay Sir'S Biology Private Tuition: 4. The Flower Q. Name The FollowingDocument8 pagesTanmay Sir'S Biology Private Tuition: 4. The Flower Q. Name The FollowingDheer MehtaNo ratings yet
- AngiospermDocument14 pagesAngiospermJoy EscamillasNo ratings yet
- Classification of PlantsDocument2 pagesClassification of PlantsNhecel PascuaNo ratings yet
- Andromeda Botanic Gardens: Flower Structure and FunctionDocument2 pagesAndromeda Botanic Gardens: Flower Structure and FunctionEmmanuel GuitangnaNo ratings yet
- Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesFlowering PlantsIntan pratiwiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part 2Document6 pagesReproduction Part 2KELVIN CHIBINDANo ratings yet
- FlowerPollinationVocab PDFDocument1 pageFlowerPollinationVocab PDFShahed Bulbul PaponNo ratings yet
- FlowerPollinationVocab PDFDocument1 pageFlowerPollinationVocab PDFShahed Bulbul PaponNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantshithereNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document1 pageWeek 2api-329058241No ratings yet
- Q.11 (A) Name The Important Parts of A FlowerDocument6 pagesQ.11 (A) Name The Important Parts of A FlowerFari NaheedNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Document22 pagesReproduction in Flowering Plants 2020Kestina MillerNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument21 pagesSexual ReproductionLawrence AnDrew FrondaNo ratings yet
- 15 Parts of A FlowerDocument12 pages15 Parts of A FlowerGeorgina SunilNo ratings yet
- 01 Plant Reproductive SystemDocument13 pages01 Plant Reproductive SystemAlwaysSaugstNo ratings yet
- Botany (Flower)Document15 pagesBotany (Flower)Louis Fetilo FabunanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in planTSSDocument56 pagesReproduction in planTSSParis JarrettNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5Document75 pagesGrade 5 PPT Science Q2 W6 Day 1-5gerelyn matuteNo ratings yet
- Plant DevelopmentDocument18 pagesPlant Developmentjohn frebNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Part Two 2021Document6 pagesPlant Diversity Part Two 2021sulimansmart22No ratings yet
- MATERI ANATOMI BUNGA - Id.enDocument2 pagesMATERI ANATOMI BUNGA - Id.enJuwita PardedeNo ratings yet
- Alberto P. Navarette Jr. Earth and Life Gas 11 Boyle Mrs. CruzDocument4 pagesAlberto P. Navarette Jr. Earth and Life Gas 11 Boyle Mrs. CruzJobadzNo ratings yet
- Grade-7-Q2-Module-4-Sexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdDocument20 pagesGrade-7-Q2-Module-4-Sexual-Reproduction-2nd-EdroseNo ratings yet
- Science 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesScience 6 - Week 6 - 2nd QuarterHoneylet Alberto Castro ArilloNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Flower MorphologyDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Flower MorphologyNur SabrinaNo ratings yet
- Bunga-Anthers Dan OvaryDocument4 pagesBunga-Anthers Dan OvaryJuwita PardedeNo ratings yet
- The Flower and PollinationDocument4 pagesThe Flower and PollinationMichaelNo ratings yet
- All Questions On SpeciesDocument4 pagesAll Questions On SpeciesRavindra Persaud 9ANo ratings yet
- Elce QuestionDocument2 pagesElce QuestionRavindra Persaud 9ANo ratings yet
- Biology Content Easter Term 2024Document13 pagesBiology Content Easter Term 2024Ravindra Persaud 9ANo ratings yet
- Eelec SBA Options A Section 1Document11 pagesEelec SBA Options A Section 1Ravindra Persaud 9ANo ratings yet
- Math Assigment TransforamtionDocument8 pagesMath Assigment TransforamtionRavindra Persaud 9ANo ratings yet