Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Media Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To Communication
Media Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To Communication
Uploaded by
Ma Chelyn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesThis document provides an overview of media information literacy. It discusses the evolution of media from the pre-industrial age to the current information age. It also defines key concepts related to media including different types of media, content delivery, media language, and the functions of communication through media. The document aims to introduce readers to understanding and evaluating various media forms and the role media plays in communication.
Original Description:
Original Title
Mil
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of media information literacy. It discusses the evolution of media from the pre-industrial age to the current information age. It also defines key concepts related to media including different types of media, content delivery, media language, and the functions of communication through media. The document aims to introduce readers to understanding and evaluating various media forms and the role media plays in communication.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views3 pagesMedia Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To Communication
Media Information Literacy Reviewer Introduction To M.I.L. The Influence of Media and Information To Communication
Uploaded by
Ma ChelynThis document provides an overview of media information literacy. It discusses the evolution of media from the pre-industrial age to the current information age. It also defines key concepts related to media including different types of media, content delivery, media language, and the functions of communication through media. The document aims to introduce readers to understanding and evaluating various media forms and the role media plays in communication.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
MEDIA INFORMATION LITERACY REVIEWER 4.
Visual Arts
5. Physical Medium
INTRODUCTION TO M.I.L. 6. Digital or Interactive
Media THE INFLUENCE OF MEDIA AND INFORMATION TO
- Encompasses various channels. COMMUNICATION
- Physical Objects that we are using to communicate.
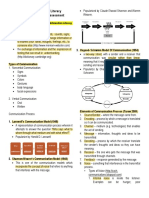
Information Communication
- Data that has been organized, processed, presented in - Act of transferring information from one place to another.
meaningful context. - Latin word “working as one”.
- Knowledge Communication Process
- Data 1. Sender - Source of message.
Literacy 2. Message - Meaning produce by the sender for the receiver.
- Ability to read, write, and understand written and printed 3. Receiver - The one who receives the message.
language.
- Evaluate SOURCE OF INFORMATION
Media Literacy
- Ability to evaluate media content in various form. Indigenous Media
- Understanding how media constructed. - Variety of media expression produced by indigenous people
Information Literacy with information appropriate with their culture.
- Ability to evaluate information effectively. Characteristics of Indigenous Media
Technology Literacy 1. Oral tradition of communication
- Ability to understand and use with various digital tools 2. Store Information in memories
effectively. 3. Information exchange in face to face
Media and Information Literacy 4. Information is contained within the borderline of the
- Ability to access, critically evaluate and effectively utilise community
media and information in various form. Forms of Indigenous Media
Communication Mediums 1. Folk or traditional media
1. Conversation 2. Gatherings and social organizations
2. Public Speaking 3. Direct Conversations
3. Documents, Letters, or Mails 4. Records 5. Oral Instructions
Libraries the manufacturing of various products (including books
- Is a place where artistics, literacy, musical, and reference through the printing press).
1. Printing Press
materials are kept for use and not for sale.
2. Telegraph
Types of libraries 3. Motion Picture
- Academic Library
- Public Library Electronic Age
- School Library - (1930s-1980s) - The invention of the transistor ushered in
the electronic age. People harnessed the power of
- Special Library transistors that led to the transistor radio, electronic circuits,
Internet and the early computers. In this age, long distance
- Global computer network providing a variety of information communication became more efficient.
and communication facilities. 1. Transistor Radio
Evaluation criteria that will help you to assess online 2. Large Electronic Computers
3. LCD projectors
resources : 4. Mainframe Computers
1. Currency
2. Relevance New Age or Information Age
3. Authority - (1900s-2000s) - The Internet paved the way for faster
communication and the creation of the social network.
4. Accuracy
People advanced the use of microelectronics with the
5. Purpose invention of personal computers, mobile devices, and
wearable technology. Moreover, voice, image, sound and
EVOLUTION OF MEDIA data are digitalized. We are now living in the information age
1. Laptop
2. Facebook
Pre-Industrial Age
3. Google Meet
- (Before 1700s) People discovered fire, developed paper Functions of Communication of Media
from plants, and forged weapons and tools with stone, 1. Monitoring Function - This is to inform the citizens on what
bronze, copper and iron. is happening around them.
1. Cave Paintings 2. Information Function - This is to educate the audience on
2. Clay Tablets the meaning and significance of the facts.
3. Papyrus 3. Opinion Function - This is to provide a platform for public
Industrial Age political discourse. It is to facilitate public opinion and
expression of dissent.
- (1700s-1930s) - People used the power of steam, 4. Watchdog Role of Journalism - It denounces the
developed machine tools, established iron production, and wrongdoing of the government and the private which leads
to increasing of accountability and spearheading positive Media Language
changes. - Are the codes, conventions, formats, symbols and
5. Channel for Advocacy of Political viewpoints narrative structure that indicate the meaning of media
messages to an audience.
TYPES OF MEDIA Messages
- Are the information sent from the source to receiver.
Print Media
- Paper publication 3 Types of Media Codes :
Broadcast Media
- Traditional forms of media that include radio and television 1. Symbolic Codes
Online Media - Are social in nature. Such codes exist beyond
- Is a medium which use internet to send information the media product themselves but can be
interpreted in similar ways in the everyday life of
Content the viewer
- Is the idea that is delivered to the audiences, in a form of - Setting
images still and moving, audio, documents and files. - Mise En Scene
- Acting
- Color
Delivery mode of content in different types of media
2. Technical Codes
- Are all the ways in which equipment is used to tell a
1. Live streaming allows a creator to share creation and idea
story in a media text like camera techniques,
in real time.
framing, lighting, etc.
2. Webinars create a room for seminars, trainings, lectures,
- Camerawork
and discussion using online media.
- Lighting
3. Podcast is known as “new radio” merged from the word
- Audio
iPod and broadcast.
3. Written Codes
4. Infographics is a visual presentation of information and
- are the formal written language used in a media
data.
product. These include language style and textual
5. E-books are electronic version of printed books.
layout like headlines, captions, speech bubbles, etc.
CODES, CONVENTION, AND LANGUAGE
Language
- pertains to the technical and symbolic ingredients or codes
and conventions that media and information professionals
may select and use in an effort to communicate ideas,
information and knowledge
You might also like
- Forte 2010Document106 pagesForte 2010Javikoo Javier Chicaiza Meza100% (2)
- Media and Information Literacy ReviewerDocument3 pagesMedia and Information Literacy ReviewerJeffsiccion100% (4)
- Oracle X86 Server Installation Specialist Online Assessment 2020Document21 pagesOracle X86 Server Installation Specialist Online Assessment 2020Josip BelinaNo ratings yet
- I U01 Introduction Standards Reading en V 2019 HL7Document43 pagesI U01 Introduction Standards Reading en V 2019 HL7Zubeen ShahNo ratings yet
- 9001 124 PDFDocument524 pages9001 124 PDFAlex ParaschivuNo ratings yet
- Aras Simulation Management 12.0R1 - User GuideDocument19 pagesAras Simulation Management 12.0R1 - User GuideHernan GiagnorioNo ratings yet
- 12 - Mil PointersDocument5 pages12 - Mil PointersMs Marylou CaballeroNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument7 pagesMIL ReviewerKrisha Mabel TabijeNo ratings yet
- MIL 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerDocument5 pagesMIL 3rd-Periodical-Exam ReviewerCourtney BaguinatNo ratings yet
- Media Information Literacy Reviewer 1st MidDocument4 pagesMedia Information Literacy Reviewer 1st MidKaiNo ratings yet
- Mil St1 Reviewer Ni ChesDocument3 pagesMil St1 Reviewer Ni ChesCzenia BarroNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewrDocument4 pagesMil Reviewr23-02707No ratings yet
- MEIL 121 ContinuationDocument6 pagesMEIL 121 ContinuationshahiraNo ratings yet
- MIL - 1st MQADocument4 pagesMIL - 1st MQALance LirioNo ratings yet
- MidtermhandoutsDocument6 pagesMidtermhandoutsCarlo MontejoNo ratings yet
- COT1 LP Q1Document5 pagesCOT1 LP Q1Ian Ray DughoNo ratings yet
- Mil Handout 1Document10 pagesMil Handout 1cklc5650No ratings yet
- MIL Reviewer Lesson 1: Lesson 2Document4 pagesMIL Reviewer Lesson 1: Lesson 2jhna mggyNo ratings yet
- MIl ReviewerDocument4 pagesMIl Reviewerallen alabaNo ratings yet
- Mil - Reviewer - Week 1 8 1Document8 pagesMil - Reviewer - Week 1 8 1ZannieNo ratings yet
- Mil NotesDocument4 pagesMil NotesDeltaNo ratings yet
- MINLIT1 Prelims 2nd SemesterDocument2 pagesMINLIT1 Prelims 2nd SemesterantekeithNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument7 pagesMIL ReviewerJuliana Shane OrapNo ratings yet
- MEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY ReviewerDocument4 pagesMEDIA AND INFORMATION LITERACY ReviewerConie Teña Macaraig AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument4 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyPrince CatubigNo ratings yet
- Cor 016Document7 pagesCor 016Rhea Ann Ramirez VenturaNo ratings yet
- Mil Reviewer Lessons 1-3Document2 pagesMil Reviewer Lessons 1-3Joana Paola GoneNo ratings yet
- 2019 2020.qa Lecture Reviewer - Media and Information LiteracyDocument8 pages2019 2020.qa Lecture Reviewer - Media and Information LiteracyJesusaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in MilDocument4 pagesReviewer in MilMariel OliverosNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy ReviewerDocument5 pagesMedia and Information Literacy ReviewerramNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument4 pagesMil ReviewerKylen FajardoNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument3 pagesMil Reviewertocoj18582No ratings yet
- Mid MilDocument4 pagesMid Mil12 EPHRAIM PRINCESS FAITH E. FRONTADANo ratings yet
- MINLIT1 Prelims 2nd SemesterDocument2 pagesMINLIT1 Prelims 2nd Semestermarcuspanopio91787No ratings yet
- Study Guide in MilDocument3 pagesStudy Guide in MilCj RomoNo ratings yet
- Mil!!!!Document8 pagesMil!!!!Bea Loreen CordovaNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument5 pagesMIL ReviewerDenise M JacoboNo ratings yet
- Media NotesDocument10 pagesMedia NotesSTEM-12 Mawac, James Clyde M.No ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyDocument6 pagesLesson 1: Introduction To Media and Information LiteracyBianze Norei Ibañez SerranoNo ratings yet
- Mil Reviewer2 For Grade 12Document8 pagesMil Reviewer2 For Grade 12pau mejaresNo ratings yet
- Media Information LiteracyDocument10 pagesMedia Information LiteracyThea Marie AganNo ratings yet
- Media Lit For Print FinalDocument5 pagesMedia Lit For Print FinalJinalyn B. AlvizoNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy ReviewerDocument3 pagesMedia and Information Literacy ReviewerJanelle NopuetoNo ratings yet
- Communicare CommunicareDocument3 pagesCommunicare CommunicareKathleen BatallerNo ratings yet
- "The Builder of Future Leaders" Senior High School Department Enerio Street, Balangasan District, Pagadian City Teaching GuideDocument5 pages"The Builder of Future Leaders" Senior High School Department Enerio Street, Balangasan District, Pagadian City Teaching GuideJoel Cabusao LacayNo ratings yet
- MIL Reviewer 3Document13 pagesMIL Reviewer 3Jewel Anne A. DimaguilaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy NotesDocument26 pagesMedia and Information Literacy NotesKesha Adelyn Gawidan100% (1)
- Mil Reviewer 1Document5 pagesMil Reviewer 1Ali HarrietaNo ratings yet
- CCOMDocument10 pagesCCOMchris santianaNo ratings yet
- Media and Information LiteracyDocument2 pagesMedia and Information LiteracyGerome Causapin100% (1)
- Mil Reviewer Lesson 1 and 3Document5 pagesMil Reviewer Lesson 1 and 3Anonymous K7EI41qjH50% (2)
- HandoutDocument2 pagesHandoutHange SanNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument4 pagesMil ReviewerJulianeNo ratings yet
- Mil NotesDocument30 pagesMil NotesninjarkNo ratings yet
- Media Information LiteracyDocument37 pagesMedia Information LiteracyIanVisteNo ratings yet
- D. Application What Is Your Essential Learning Today? What Is Your Essential Learning Today? What Is Your Essential Learning Today?Document2 pagesD. Application What Is Your Essential Learning Today? What Is Your Essential Learning Today? What Is Your Essential Learning Today?Daphney BalayoNo ratings yet
- Mil ReviewerDocument4 pagesMil ReviewerMa. Mae ManzoNo ratings yet
- MIL ReviewerDocument3 pagesMIL ReviewerChirsten ArabejoNo ratings yet
- New Political Media Fake NewsDocument7 pagesNew Political Media Fake NewsLyn BeautyNo ratings yet
- Cor 016 Media and Information LiteracyDocument9 pagesCor 016 Media and Information LiteracySuper HeroNo ratings yet
- Reviewer MilDocument16 pagesReviewer MilHera TendidoNo ratings yet
- Mil Reviewer 1ST Q ExaminationDocument12 pagesMil Reviewer 1ST Q ExaminationChristine JacobNo ratings yet
- Mil Notes in Quarter 1Document6 pagesMil Notes in Quarter 1InfiniteNo ratings yet
- Media LiteracyDocument3 pagesMedia LiteracyJulio FernandezNo ratings yet
- Iei Pe MC PDFDocument3 pagesIei Pe MC PDFSANKAR SIVANNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar Air Filter Pehp9013-03Document2 pagesCaterpillar Air Filter Pehp9013-03Parinpa Ketar100% (1)
- Precise Astrometry For SST and NEODocument15 pagesPrecise Astrometry For SST and NEOastroagaNo ratings yet
- Jasper Upgrade PDFDocument194 pagesJasper Upgrade PDFDhakshin87No ratings yet
- Ubuntu Install GuideDocument17 pagesUbuntu Install GuidesmdeepajpNo ratings yet
- QuickGuide 13650030 HG2300-Ver C WEBDocument27 pagesQuickGuide 13650030 HG2300-Ver C WEBBelahcen AmineNo ratings yet
- Champion CSA Brochure 2Document4 pagesChampion CSA Brochure 2fachjrianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document24 pagesChapter 1Anonymous tytJlPojNo ratings yet
- Assignment 05Document6 pagesAssignment 05Dil NawazNo ratings yet
- Hig - Ie SW Al10m 8TX 2GC - V1.1 - 2020 12 29Document2 pagesHig - Ie SW Al10m 8TX 2GC - V1.1 - 2020 12 29isaacsavioNo ratings yet
- A Zettelkasten PrimerDocument14 pagesA Zettelkasten PrimerZaglobaNo ratings yet
- Developing Analytical Equations For Determining Power MOSFET Switching TransientsDocument10 pagesDeveloping Analytical Equations For Determining Power MOSFET Switching TransientsTim PriceNo ratings yet
- Case Study Why Nokia FailedDocument3 pagesCase Study Why Nokia FailedMD. ISRAFIL PALASH67% (3)
- Cas 3a - Voved Vo WADDocument25 pagesCas 3a - Voved Vo WADAnaNo ratings yet
- Id SDK LogsDocument26 pagesId SDK LogseradcalakuNo ratings yet
- Santosh Kumar Mahatha: Career ObjectiveDocument1 pageSantosh Kumar Mahatha: Career ObjectiveSantosh MahathaNo ratings yet
- STP 7-11B1-SM-TG Infantry Common Task Level IDocument402 pagesSTP 7-11B1-SM-TG Infantry Common Task Level IJared A. Lang100% (3)
- Mil ReviewerDocument5 pagesMil Revieweranon_893182295No ratings yet
- Electronic Components, Packaging and Production: Leif Halbo and Per Ohlckers University of OsloDocument12 pagesElectronic Components, Packaging and Production: Leif Halbo and Per Ohlckers University of OsloengshimaaNo ratings yet
- CSEC Information Technology June 2009 P01Document10 pagesCSEC Information Technology June 2009 P01AshleyNo ratings yet
- PH Scalance W 700 76Document296 pagesPH Scalance W 700 76Ensis CaliburnusNo ratings yet
- Oracle Developers GuideDocument18 pagesOracle Developers GuideIonel GherasimNo ratings yet
- C2/C2C User Manual: © 2001-2013 Anviz Global IncDocument92 pagesC2/C2C User Manual: © 2001-2013 Anviz Global IncMarcelo CampaneroNo ratings yet
- 10 Advantages and 5 Disadvantages of Information Technology (IT ERA)Document3 pages10 Advantages and 5 Disadvantages of Information Technology (IT ERA)Erwin Joshua HonradaNo ratings yet
- MERN Stack CourseDocument5 pagesMERN Stack Courseneeteshyadav1552003No ratings yet