Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 viewsHri Cheat
Hri Cheat
Uploaded by
Animesh MaityThe document discusses several techniques used in management development programs:
1) Vestibule training simulates on-the-job training in a training center close to the workplace.
2) In-basket training involves simulating management problems for trainees to solve.
3) Sensitivity training makes participants aware of their own behavior and how others perceive them to improve group dynamics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Collins-Donnelly, Kate (2014) Starving The Anxiety Gremlin For Children Aged 5-9 A CBT Workbook On Anxiety ManagementDocument193 pagesCollins-Donnelly, Kate (2014) Starving The Anxiety Gremlin For Children Aged 5-9 A CBT Workbook On Anxiety ManagementG100% (1)
- Manpower Planning and Resourcing (MCQ)Document25 pagesManpower Planning and Resourcing (MCQ)bijay67% (3)
- Modern Methods of Vocational and Industrial TrainingFrom EverandModern Methods of Vocational and Industrial TrainingNo ratings yet
- Mumbai CxoDocument9 pagesMumbai CxopoonamNo ratings yet
- Tvet in BruneiDocument17 pagesTvet in Bruneiarchim_azymaNo ratings yet
- Assignment HRMDocument12 pagesAssignment HRMkulfamorNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ManagementDocument15 pagesManufacturing ManagementsscribNo ratings yet
- Basic HRMDocument38 pagesBasic HRMPrushni JoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document6 pagesUnit 5Abdullahi ahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 StaffingDocument19 pagesChapter 6 StaffingGetahun Mulat100% (1)
- Management Chapter FourDocument6 pagesManagement Chapter FourchuchuNo ratings yet
- CH-5,6&7 MGT IntDocument15 pagesCH-5,6&7 MGT IntwubeNo ratings yet
- Bu1104 SDLDocument40 pagesBu1104 SDLdashidalgoNo ratings yet
- Int. To MGT Chapter SixDocument27 pagesInt. To MGT Chapter SixmisganabbbbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Essentials of HRMDocument4 pagesEssentials of HRMVinitaNo ratings yet
- Staffing The Engineering OrganizationDocument32 pagesStaffing The Engineering OrganizationAbegail Ada Calayo MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 MGTDocument6 pagesCh-4 MGThai manNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument7 pagesHuman Resource PlanningMerinNo ratings yet
- Intr MGMT Chapter Five and SixDocument16 pagesIntr MGMT Chapter Five and SixAYNETU TEREFENo ratings yet
- HRM CapsuleDocument61 pagesHRM CapsuleNupur Agarwal Jain100% (2)
- 203 HRMDocument37 pages203 HRMshubhamatilkar04No ratings yet
- Part-A: o Give Details About Pay, Benefits, Holidays, Leave, Etc. Emphasize The Importance of Attendance or PunctualityDocument51 pagesPart-A: o Give Details About Pay, Benefits, Holidays, Leave, Etc. Emphasize The Importance of Attendance or PunctualityDeep NarayanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 StaffingDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 6 StaffingMercyNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document6 pagesCH 4Ebsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- Staffing Chester Dela CruzDocument32 pagesStaffing Chester Dela CruzangeloNo ratings yet
- Functions of Personnel Management Are Categorized UnderDocument8 pagesFunctions of Personnel Management Are Categorized UnderMangue AlaizaNo ratings yet
- 005 PPM 05 Sept 2022Document56 pages005 PPM 05 Sept 2022Nikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Internship Preparatory Note ISTDDocument8 pagesInternship Preparatory Note ISTDAnkur Sharma100% (3)
- III. Job Enrichment: - : 3. Problem With Union MembersDocument11 pagesIII. Job Enrichment: - : 3. Problem With Union MembersJitendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Career PLNG DevelopDocument8 pagesCareer PLNG DevelopTanu NarangNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument15 pagesHRMMittal SahabNo ratings yet
- 1ST UnitDocument11 pages1ST UnitAswin P SubhashNo ratings yet
- According To: Blum, "A Job Analysis Is An Accurate Study of The Various JobDocument4 pagesAccording To: Blum, "A Job Analysis Is An Accurate Study of The Various Jobpriyanshi rankaNo ratings yet
- BusinessDocument3 pagesBusinessjiyadkunnummalNo ratings yet
- 1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1Document35 pages1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1JNo ratings yet
- HR Audit Assignment Dt. 1.12.2018 by Prakash Chand Kandpal PDFDocument12 pagesHR Audit Assignment Dt. 1.12.2018 by Prakash Chand Kandpal PDFPrakashNo ratings yet
- Training Process: Training Process in HRM - Steps, Process and PhasesDocument14 pagesTraining Process: Training Process in HRM - Steps, Process and PhasesbojaNo ratings yet
- Staffing Function of ManagementDocument12 pagesStaffing Function of ManagementnduhiukariukiNo ratings yet
- 2Document7 pages2LAKSHAY SHARMANo ratings yet
- CH 5Document22 pagesCH 5King HeniNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument87 pagesHuman Resource PlanningParul JainNo ratings yet
- BTS 07Document21 pagesBTS 07Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- ObDocument46 pagesObJerry MataiNo ratings yet
- Staffing Notes Term 2, 2022Document8 pagesStaffing Notes Term 2, 2022Leela JainNo ratings yet
- HRM Final: I. Short AnswersDocument21 pagesHRM Final: I. Short AnswersBảo CườngNo ratings yet
- IM Unit-2Document5 pagesIM Unit-2sabyasachibbaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Document16 pagesFunctions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Mittal SahabNo ratings yet
- Inc DoDocument7 pagesInc DoPreetiNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument11 pagesStaffingHimanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- MB0043 HRM Assignment Set 1Document8 pagesMB0043 HRM Assignment Set 1Bipin SinghNo ratings yet
- HRDPDocument8 pagesHRDPhetvi TankNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management (DME-S6)Document60 pagesIndustrial Management (DME-S6)Devraj RoyNo ratings yet
- HRM CH-3Document195 pagesHRM CH-3Sukanya KaduNo ratings yet
- MBA 106 - Human Resource ManagementDocument8 pagesMBA 106 - Human Resource ManagementRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Mayank 16521Document18 pagesMayank 16521naman kumarNo ratings yet
- BSBMGT517.doc Task 1Document4 pagesBSBMGT517.doc Task 1harman randhawaNo ratings yet
- Mpa 5Document16 pagesMpa 5subashrao5522No ratings yet
- C3 HMPDocument6 pagesC3 HMP37.Thảo VânNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document5 pagesLesson 5JOHN IRVIN TAERNo ratings yet
- Block - 1Document15 pagesBlock - 1madhaviNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Practice of Business AdministrationFrom EverandBasic Principles and Practice of Business AdministrationNo ratings yet
- Route KPL Train Feb Web2Document7 pagesRoute KPL Train Feb Web2Bernard MivilleNo ratings yet
- B Com English 2016Document12 pagesB Com English 2016PRIYANK PATEL67% (3)
- Federal Resume SampleDocument5 pagesFederal Resume Samplef5dq3ch5100% (2)
- M-Sand in Tamil NaduDocument9 pagesM-Sand in Tamil Nadurameshkanu1No ratings yet
- Collins Sentence MemoDocument17 pagesCollins Sentence MemoRoy S. JohnsonNo ratings yet
- SSB Tanitim CatalogDocument201 pagesSSB Tanitim CatalogAmir Cahyadi100% (1)
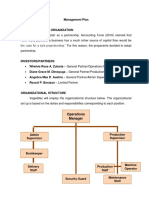
- Management Plan: Operations ManagerDocument14 pagesManagement Plan: Operations Manager弗朗兹No ratings yet
- New English File - Elementary File 10 - Test 10Document5 pagesNew English File - Elementary File 10 - Test 10Sanja IlovaNo ratings yet
- Vivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFDocument28 pagesVivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFNikhil VermaNo ratings yet
- Biology Ecology Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Ecology Revision NotesGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0160738323001846 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S0160738323001846 Mainussual humanNo ratings yet
- Prepositions After AdjectivesDocument2 pagesPrepositions After AdjectivesJosé María OrtigueiraNo ratings yet
- C5. Catholic Vicar Apostolic of The Mt. Province v. Court of Appeals, 165 SCRA 515Document5 pagesC5. Catholic Vicar Apostolic of The Mt. Province v. Court of Appeals, 165 SCRA 515dondzNo ratings yet
- L'Altra Montessori School Inc.,: High School Department First Periodical Exam Technology and Livelihood Education 9Document4 pagesL'Altra Montessori School Inc.,: High School Department First Periodical Exam Technology and Livelihood Education 9Kristine HensonNo ratings yet
- Emirates Airlines Company StudyDocument17 pagesEmirates Airlines Company StudyluciusNo ratings yet
- Repair Appx V3Document18 pagesRepair Appx V3soniaNo ratings yet
- 40K - Malcador Tank v1Document2 pages40K - Malcador Tank v1SKL2002No ratings yet
- Programmed Instruction and SimulationDocument86 pagesProgrammed Instruction and SimulationRemyaKiranNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare A Construction Traffic Management Plan (CTMP) ReportDocument1 pageHow To Prepare A Construction Traffic Management Plan (CTMP) Reportmyco samNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitDocument52 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- CHN Transes Week 1Document5 pagesCHN Transes Week 1cheskalyka.asiloNo ratings yet
- Aerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsDocument3 pagesAerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsАндрей МошкинNo ratings yet
- RHPA46 FreeDocument5 pagesRHPA46 Freeheyimdee5No ratings yet
- A7X ManualDocument32 pagesA7X ManualStephen LichotaNo ratings yet
- Automating Inequality - Virginia EubanksDocument223 pagesAutomating Inequality - Virginia EubanksTanmay100% (1)
- Managing Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesDocument59 pagesManaging Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesGLEN KGATLANo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Post-TestDocument4 pagesQuarter 2 Post-TestRoberto Del CarmenNo ratings yet
Hri Cheat
Hri Cheat
Uploaded by
Animesh Maity0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views13 pagesThe document discusses several techniques used in management development programs:
1) Vestibule training simulates on-the-job training in a training center close to the workplace.
2) In-basket training involves simulating management problems for trainees to solve.
3) Sensitivity training makes participants aware of their own behavior and how others perceive them to improve group dynamics.
Original Description:
Original Title
hri cheat
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several techniques used in management development programs:
1) Vestibule training simulates on-the-job training in a training center close to the workplace.
2) In-basket training involves simulating management problems for trainees to solve.
3) Sensitivity training makes participants aware of their own behavior and how others perceive them to improve group dynamics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views13 pagesHri Cheat
Hri Cheat
Uploaded by
Animesh MaityThe document discusses several techniques used in management development programs:
1) Vestibule training simulates on-the-job training in a training center close to the workplace.
2) In-basket training involves simulating management problems for trainees to solve.
3) Sensitivity training makes participants aware of their own behavior and how others perceive them to improve group dynamics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 13
Q)Techniques of management development program
→ 1)Vestibule training: Vestibule training takes place at a training centre. In the
early 1800s, vestibule training was introduced for factory workers to train them
in a training centre close to the actual work place.The vestibule training was
provided by a skilled trainer, and it simulates on-the-job training. It does not
affect the production speed or quality, as it is not done in a factory.
2)In-Basket Training :It is also called as in-tray training technique. It involves
simulation of a series of decisions, which a trainee may have to perform in real
life. The trainees are presented with a pack of papers and files in a tray
containing simulated management problems. Nowadays, due to the popularity
of computers, the simulated management problems are e-mailed to the
trainees. 3) Programmed Instructions: The subject matter to be learned is
condensed into logical units.The units are arranged from simple to complex
levels of instructions. The trainees go through these units and provide answers
to questions. The programme involves: *Presenting questions along with
facts or problems to the trainees. *The trainee has to provide answers, and
gets instant feedback from the expert trainers.4)Sensitivity Training: It is also
known as laboratory or T-group training. This technique is developed from the
group dynamics concept of Kurt Lewin. *Sensitivity training is an interaction
process in a small group,which requires participants to become sensitive to
feelings of others so as to develop effective teams. *The objectives of
sensitivity training are: (a) To make the participants aware of their own
behaviour and of how others perceive them. (b) To make the participants
sensitive to the behaviour of others.(c) To increase the understanding of
participants relating to group process or group dynamics. (d) To achieve greater
behavioural effectiveness in transactions with one's various environments.
5)Case Study Method: It is a technique of class room method of learning.
Managers can be trained with the help of a case study. Case studies are
analyses of persons, events, decisions, periods, projects, policies,institutions, or
other systems that are studied holistically by one or more method.
The main objectives of case study method are:
(a) To acquaint the learner of the principles and. practices of
management.
(b) To familiarize the learner with goals, problems, conflicts,
conditions, situations, etc., of organisations.
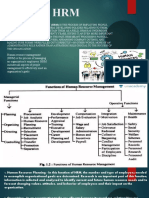
Q)Function of human resource management.
→1)Human Resource Planning: HRM facilitates human resource planning
(HRP). HRP is a process of identifying manpower requirements in terms of
quality and quantity, to undertake various activities of the organisation. In HRP,
the HR manager adopts the following steps: *Review of organisational goals.
*Forecast of human resource requirements.*Forecast of human resource
supply.*Comparison of HR requirements and supply.*Corrective action, if there
is shortage or surplus of manpower. 2)Acquisition Function/Selection: The
acquisition function begins with human resource planning.For acquiring the
right type of manpower, the HR manager should make necessary arrangements
for recruitment and selection of human resources. For instance, systematic
selection procedure needs to be followed to select the right person for the
right job. 3)Placement Function: The HR manager is also responsible for proper
placement of employees in the organisation. Placement refers to fitting the
right person at the right place of work. Proper placement brings job satisfaction
to the employees and results in higher efficiency to the organisation.
4)Performance Appraisal: The HR manager may be involved in designing and
implementing performance appraisal programmes.Performance appraisal is a
systematic description of employees job relevant strengths and weakness.
Systematic performance feedback to the employees helps to correct their
weaknesses through training and motivation Performance feedback also helps
to consolidate employee strengths. 5)Promotion: An important element of
HRM is promotion of employees. In professional organisations, HR managers
frame promotion policies: *Merit as the basis of promotion, especially at the
top level. *Seniority as the basis of promotion, especially at the lower level.
Promotion gives recognition to committed and dedicated employees, especially
those who excel in their work performance. 6)Training and Development: One
of the major activities of HRM is to provide training and development to the
employees of the organisation. Training and development programmes enable
the employees to: *Acquire additional knowledge *Develop attitudes
*Improve skills *Improve social behaviour.
Q)process of human resource planning.
→1)Review of Organisational Objectives: The first step in HRP is to review the
objectives of the organisation. Proper review of the objectives enables the
organisation to list various activities that are required to achieve the objectives.
2)HR Requirements Forecast: The HRD manager forecasts human resource
requirements to undertake the various activities. The human requirements
forecast must be both in terms of quantity (number of employees) and quality
(knowledge, attitude and skills). 3)HR Supply Forecast: The HRD manager
forecasts the availability of manpower. The required manpower may be
available within the company, or they may be required to be hired from the
labour market. 4)Comparison: The HRD manager makes a comparison between
HR requirement and HR supply, to find out whether the required personnel is
available or not. 5)No Differences: The comparison between HR requirements
and HR supply may indicate differences between HR requirements and HR
supply.If human resource requirements are equal to human resource supply,
then there are no differences. Therefore, there is no need to take any action.
6)Differences : The comparison may reveal differences between the human
resource requirements and human resource supply. There may be HR surplus,
or shortage. Action needs to be taken to deal with the problem of HR shortage
or surplus. 7)Motivating the Manpower: An important aspect of human
resource planning is to motivate the personnel by providing monetary and non-
monetary incentives.
Q)procedure of dematerialisation
→1)Opening a Demat Account: Investor must open a demat account with a
depository participant (DP). The DP is the link between the Depository and the
owner of security. In other words, DP is the agent of the depository. (Banks,
clearing houses of recognized stock exchanges, and non-banking financial
companies are eligible to become DP). 2)Submission of DRF and Share
Certificates: The demat account holder must submit the DRF properly filled in,
and also the physical share certificates. The share certificates must be rubber
stamped (available with the DP) with the words Surrendered for Demat'.
3)Forwarding of DRF and Share Certificates: The DP forwards the DRF and the
share certificates to the Transfer Agent (appointed by the company to look
after sharerelated matters) or the Company's Registrar. A second copy of DRF is
forwarded by DP to its depository - either NSDL or CDSL. 4)Confirmation from
Depository: The depository sends a confirmation letter to the company's
registrar or the share transfer agent regarding the receipt of Demat Request
Form. 5)Verification and Updating the Records: The transfer agent or the
company's registrar checks the shareholder' s records, and the signature. If the
signatures and other details are correct, then the physical share certificates are
cancelled and entries are made in the company's records regarding demat of
shares. 6)Recording by Depository: The depository records in its books, the
name of the shareholder as the beneficial owner. In other words, the
depository credits the account of the investor with the number of shares.
Q)process of capital budgeting
→1)Strategic Planning: A strategic plan is a grand plan of the firm.It states the
current position of the company and the company's future plans. Strategic
planning translates business goals and objectives into specific policies and
priorities. The vision and mission of the company is considered while
formulating strategic plans. Strategic plans provide the framework for resource
allocation and direct to search for profitable capital investments.
2)Identification of Investment Opportunities: Identification of investment
opportunities and generation of investment project proposals is an important
step in the capital budgeting process.Some investments are mandatory.
*Generally, an investment opportunity and proposal is suggested by:
*Consumers or advisors *Sales force or other employees
*Research and Development department, etc. 3)Screening of Projects:
Generally, there will be many potential investment proposals. A firm may have
to set up a committee to review and screen the proposals. The committee
should consider the attractiveness of the investment proposal in the long run.
The preliminary screening may involve some preliminary quantitative analysis
and judgements based on intuition and experience. 4)Financial Appraisal of
Projects: After passing through preliminary screening, the proposed investment
project is subject to financial appraisal so as to ascertain if it would add value
to the firm. In order to find out the profitability of the project, the firm may
undertake detailed: *Market analysis *Financial analysis *Technical analysis
5)Qualitative Factors in Project Evaluation: The proposed investment project
should be svaluated taking into consideration the qualitative factors.he
qualitative factors are those factors that have an impact on the project but
cannot be accurately evaluated in monetary terms)These factors are:
*The social impact of an increase or decrease in employee numbers.
*The environmental impact of the project. *The strategic consequences of
consumption of scarce raw materials, etc. 6)Accept or Reject Decision: Taking
into account the returns and risks of individual projects as well as the cost of
capital of the firm, the firm will choose the project that maximizes shareholders
wealth with its chosen criteria of selection. Projects not expected to meet this
criteria are rejected, while accepted projects are considered for
implementation. 7)Project Implementation: At this stage, the proposed
investment project is decided to be implemented by the management. The
project implementation stage involves
Q)importance of capital budgeting
→1)Large Investments for Long Time: Capital budgeting involves planning
capital expenditure. Capital expenditure includes sizable investments for a long
period of time. If large sums of money are allocated to one project, other
projects may be denied.The impact of investment decision is not limited to one
year.Its influence spreads over a series of years. Hence, it is necessary that
business firms take up sound decision on capital budgeting 2)Low Liquidity and
Irreversibility: Capital investment can be represented by purchase of fixed
assets. Fixed assets cannot generally be sold and encashed without spending
considerable time and effort. Also, some investment decisions are irreversible.
Once, these fixed assets are purchased, and if the decision made is faulty, it
often results in heavy losses.Therefore, careful capital budgeting is essential.
3)Modernization: The company may go for modernization of its plant and
machinery. Such modernization is necessary to increase efficiency and
productivity. To introduce modernization, the company has to introduce latest
technology and machinery, for which the company needs to take up capital
budgeting 4)Replacement of Old Assets: The company also needs to replace
obsolete assets such as worn out plant and machinery, furniture and fixtures
and so on. Such replacement is vital to increase efficiency and productivity of
the company. For the purpose of replacement, the company needs sufficient
funds for which capital budgeting is important. 5)Expansion and Diversification:
The company for go for expansion and diversification. To expand and diversify
the business, the firm needs substantial amount of capital investments, for
which capital budgeting is required. 6)Automation: Labour intensive industries
shifting to automation need large funds to purchase automatic machines and
other requirements, for which the company should have good capital
budgeting.
Q)Meaning and objectives of financial management
→Proper. Mobilisation of funds : Financial management is concerned with
proper mobilisation of funds. Funds can be mobilised from various sources.
There must be a balance between owned fund and borrowed funds. One
should not place too much emphasis on borrowed funds as it puts a burden on
repayment and debt servicing. Also, too much emphasis on shareholders funds
(owned funds) dilutes the equity. 2)Proper Utilisation of Funds: The main
important responsibility of finance managers is to ensure proper utilisation of
funds.The funds which have been mobilised through various sources must be
put to best use. There must be value addition. Value addition means the
utilisation of funds must generate more value. For instance, if funds are utilised
on raw materials, then the raw materials which are converted into finished
goods must generate higher value. 3).Profit Maximisation : It is one of the
primary objectives of the firm. If a firm is in a position to generate higher level
of value addition, then this will lead to higher profits. The finance managers
should ensure that the firm generates profits not only in the short term but
also in the long term. It is to be noted that one cannot guarantee profits in the
long term due to business uncertainties, but finance managers need to use
proper judgement and skills in financial decisions to ensure long term
profitability of the firm. 4)Maintenance of Liquid Assets: A firm should have
adequate liquid assets or cash to meet working capital requirements, such as
payment of raw materials, wages, and other overheads. For this purpose a firm
should ensure proper cash flow. 5)Ensure Fair Return to Shareholders: A firm
should ensure fair return to the shareholders. The finance activities should be
undertaken to generate shareholders wealth. A firm that ensures fair return to
the shareholders by way of regular dividend, and bonus issues, do enjoy a good
image in the financial circles. 6)Retained Earnings : One of the objectives of
financial management is to build up reserves. A good amount of reserves is
required for the purpose of growth and expansion. Reserves are also useful to
face contingencies in future.
Q)Meaning and objective of inventory managements
→1)To achieve economy in buying: Inventory management enables a firm to
achieve economy in purchasing. For instance, purchase of raw materials in bulk
enables a firm to get bulk discounts.Apart from bulk discounts, the firm can
negotiate for delivery of materials on easy terms. 2)To overcome seasonal
fluctuations in supply: Certain materials are subject to seasonal fluctuations in
supply. For instance,certain agriculture related materials are seasonal in nature,
and therefore, there is a need to keep them in adequate stock in order to
overcome seasonal fluctuations in supply. 3)To enable smooth flow of
production: Inventory management ensures smooth flow of production.
Adequate stock of inventories reduces the problem of shortages, and
therefore,production can take place uninterrupted. 4)To achieve operational
efficiency: Scientific inventory management is required so that neither excess
stock nor shortage affects the operational efficiency and production
costs.Excess stocks not only involve interest costs (cost of invested funds) but
also holding costs, i.e., expenses towards storage,maintenance, insurance, etc.
5)To enable prompt delivery of goods: Inventory management facilitates
prompt execution of orders. Due to inventory management, there can be
smooth flow of production. Also adequate amount of finished stocks would
enable a firm to supply the goods on time, which in turn can develop good
customer relationships. 6)To avoid emergency orders: Proper inventory
management facilitates the ordering of right amount of materials. Under
stocking of materials is avoided. Therefore, it does not lead to unwarranted
emergency orders, which are normally procured at higher costs. 7)To generate
quality output: Inventory management ensures the purchase of right quality of
inputs. The use of quality inputs results in quality of output.
Q)Benfits/Advantages of ISO 14000:
→1)Compliance with Regulatory Framework: ISO 14000 certified companies
comply with the internationally regulated framework with respect to
environmental management standards, environmental audit, environmental
accounting, etc. 2)Optimum Use of Resources : ISO 14000 facilitates the
company to reduce the consumption of materials and energy. It helps in
reduction of wastage of resources. Hence, the company utilizes its resources at
optimum level. 3)increase in Profits : The company that follows ISO 14000
experiences higher productivity and efficiency. Productivity is the ratio of
output to input. Efficiency is the ratio of returns to costs. Higher productivity
and efficiency generates higher profits to the firm. The increased profits can be
utilized for expansion and other productive activities of the firm. 4)Corporate
Image : A company which adopts ISO 14000 earns good name and goodwill in
the minds of the customers. This is because; customers get environmental-
friendly products which generates customer delight. 5)Competitive Advantage :
ISO 14000 enables a firm to gain competitive advantage. It ensures continuous
improvement in environmental performance of the firm. This involves
producing environmental-friendly products at reduced costs.Thus, the
customers can get quality products at lower price. 6)Better Relations : Due to-
adoption of ISO 14000, the organization can develop better relations with
various stakeholders, such as: *Government * Suppliers *Employees, etc.
7)Increase in Shareholders' Wealth : Since ISO 14000 helps in increase in
productivity and efficiency, the shareholders may earn high return on
investment. Thus, the firm may pay higher dividends and issue bonus shares to
the shareholders.
Q)Feature of TQM -
→1)Customer Focus: TQM places emphasis in meeting the requirements of
both the internal and the external customer. In order to meet the requirements
of the external customer, it is necessary to meet the needs of the internal
customer. If the internal customers'requirements are agreed and met, then it is
possible to meet the requirements of the external customers. 2)Continuous
Process:TQM is a continuous process. Continuous efforts are made to improve
the quality, and to reduce internal costs. Quality improvement helps the
organisation to face the challenges of the competitors and to meet the
requirements of the customers.Reduction in costs helps to generate higher
returns to the organisation. 3)Defect-free Approach: TQM place emphasis on
the defect-free work most of the time.The defect-free approach is phrased in
various ways as right first time, working smarter or zero defects. The idea is to
strive for perfection in the work, the way a footballer aims to shoot the penalty
kick or an archer aims for the bull's eye on a target. 4)Employees
Involvement:In TOM everyone is involved in the process from the managing
director to the junior clerk or worker in the organisation. It is not just
manufacturing people, but also the accounting, finance,marketing and even
the canteen people are involved in the TQM process. 5)Recognition and
Rewards: Recognition and rewards is an integral part of company's TQM
programme. Positive reinforcement through recognition and rewards is
essential to ensure continuous improvement in quality. 6)Synergy in Team
Work: The Japanese are great believers in synergy (to work
together).Engineers, technicians, and workers look upon themselves as equals
and communicate easily as they work side by side. They create what Professor
Okuda has called a 'synergetic partnership
Q)Feature of quality management (QM)
→1)Components of Quality Management: Quality management is focused not
only on product quality,but also the means to achieve it. Therefore, quality
management has four main components: *Quality planning *Quality control
*Quality assurance *Quality improvement. 2)Customer Oriented: Quality
management is a customer oriented approach Therefore, all the activities and
processes must be directed to generate customer satisfaction. Ultimately, the
customer is the final judge of quality. Therefore, the quality of the products
must conform to target customers requirements. 3)Continuous in Nature:
Quality management is a continuous process. Committed efforts on continuous
basis are required on the part of everyone in the organisation to improve the
quality at lower internal costs. The OM process goes on forever. At no point of
time quality can be 100% right. Therefore, there is always a possibility of new
and better way of doing things, i.e., improvement in quality. 4)Commitment
from Top Management: To make quality management more effective, there is
utmost need of commitment from the top management. The leadership of top
management must be quality focused. Without the commitment of top
management, quality cannot happen in any organisation. Therefore, the top
management must: *Be proactive and lead by example. *Establish a clear
vision of the organisation's future. *Establish shared values and ethical role
models at all levels of the organisation. *Provide people with the required
resources and freedom to act with responsibility and accountability. *Inspire,
encourage and recognise people's contributions, *Promote open and honest
communication. *Educate, train and coach people, and so on.
5)All Pervasive: Quality management has universal application. It is applicable
in any organisation. Large and smali firms, whether business or social need to
focus on quality performance For example, an educational institution like a
University must focus on quality syllabus, quality academics, and at the same
must focus on extra curricular activities in order to groom the overall
pérsonality of students. 6)Employees Involvement: People at all levels are the
essence of an organisation. Therefore,there is a need for their dedication to
undertake organisational activities, *To secure employees involvement, the
management must: *Frame and implement effective HR policies with reference
to selection, training, placement, promotion, performance appraisal, career
development, compensation, etc. *Effective communication at all levels in the
organisation. *Develop good superior-subordinate relationships. *Freely share
knowledge and experience to employees.
Q)steps in production planning and control
→1. Routing : Production planning and control starts with routing. Routing can
be defined as "the process of deciding the path of work and the sequence of
operations." Objective : The main objective of routing is to find out the
best and cheapest sequence of operation to be followed in the manufacturing
process.It ensures smooth flow of work. Procedure:
(a) Determining what to make and what to purchase. (b) Decision on quality
and quantity of materials required. (c) Determination of lot sizes. (d) Decision
on scrap factors (e) Preparation of route sheet, (f)Preparation of production
control forms. 2.Loading: Loading involves computation of total operation
time required for various processes. The total time required to perform the
operation is computed by multiplying the unit operation time (Stated on the
standard process sheet) by the number of units or parts to be processed. This
total time is then added to the work already planned for the workstation.
3. Scheduling : It specifies the starting and finishing time for each operation in
the manufacturing process. It involves preparation of time table for production
activities. Objective: The main objective of scheduling is to ensure the
completion of each operation or activity on time.
Procedure : (a) Listing out all production activities. (b) Deciding the start time
for every activity(c) Deciding the finish time for every activity.(d) Preparation of
time table. 4. Dispatching: It involves assigning of work and giving orders and
instructions to the machine operators and others involved in the
manufacturing process, so that the work is completed as per the schedule.
Objective: The purpose of dispatching orders and instructions is to ensure that
the machine operators understand what is expected of them and that they do
the right thing at the right time and complete the production on time.
Procedure: Dispatching involves the following procedure: (a) Arrangement of
machines and tools. (b) Procurement of raw materials as per the requirements.
(c) Assigning work to the machine operators and others. (d) Issuing orders and
instructions to the workers. (e) Issuing orders to the tools department to
supply tools and other requirements as and when required. (f)Maintaining a
proper record of the start time and finish time of each operation
5.)Follow-up : It refers to reporting and monitoring of actual performance. Il
necessary, corrective measures are taken to obtain the right quality and
quantity of production. Objective: The purpose of follow up is to monitor
the actual performance, an0 to expedite the production if required. A proper
follow-up ensure the right quality and quantity of production.
Procedure: The following are the steps involved in follow up:
(a) Measuring actual production.
(b) Comparing actual production with planned targets.
(c) Identifying causes of deviations, if any..
(d) Identifying corrective measures to correct deviations.
(e) Analyzing the corrective measures.
(f) Selecting the best corrective measure(s).(g) Implementation of corrective
measures.(h) Review of corrective measures.
6. Re-planning
In some instances re-planning is necessary to ensure the effective utilization of
the manufacturing facilities and personnel. Replanning revises routes, loads,
and schedules, and a new plan is developed.
In manufacturing units, re-planning is often required. Changes in market
conditions, manufacturing methods, or many other factors affecting the plant
often indicate that a new manufacturing plan is needed.
Note: Students may explain only the major 4 functions - routing scheduling,
dispatching and follow-up. Consult your Professor for the saie.
You might also like
- Collins-Donnelly, Kate (2014) Starving The Anxiety Gremlin For Children Aged 5-9 A CBT Workbook On Anxiety ManagementDocument193 pagesCollins-Donnelly, Kate (2014) Starving The Anxiety Gremlin For Children Aged 5-9 A CBT Workbook On Anxiety ManagementG100% (1)
- Manpower Planning and Resourcing (MCQ)Document25 pagesManpower Planning and Resourcing (MCQ)bijay67% (3)
- Modern Methods of Vocational and Industrial TrainingFrom EverandModern Methods of Vocational and Industrial TrainingNo ratings yet
- Mumbai CxoDocument9 pagesMumbai CxopoonamNo ratings yet
- Tvet in BruneiDocument17 pagesTvet in Bruneiarchim_azymaNo ratings yet
- Assignment HRMDocument12 pagesAssignment HRMkulfamorNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing ManagementDocument15 pagesManufacturing ManagementsscribNo ratings yet
- Basic HRMDocument38 pagesBasic HRMPrushni JoshiNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document6 pagesUnit 5Abdullahi ahmed mohamedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 StaffingDocument19 pagesChapter 6 StaffingGetahun Mulat100% (1)
- Management Chapter FourDocument6 pagesManagement Chapter FourchuchuNo ratings yet
- CH-5,6&7 MGT IntDocument15 pagesCH-5,6&7 MGT IntwubeNo ratings yet
- Bu1104 SDLDocument40 pagesBu1104 SDLdashidalgoNo ratings yet
- Int. To MGT Chapter SixDocument27 pagesInt. To MGT Chapter SixmisganabbbbbbbbbbNo ratings yet
- Essentials of HRMDocument4 pagesEssentials of HRMVinitaNo ratings yet
- Staffing The Engineering OrganizationDocument32 pagesStaffing The Engineering OrganizationAbegail Ada Calayo MontemayorNo ratings yet
- Ch-4 MGTDocument6 pagesCh-4 MGThai manNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument7 pagesHuman Resource PlanningMerinNo ratings yet
- Intr MGMT Chapter Five and SixDocument16 pagesIntr MGMT Chapter Five and SixAYNETU TEREFENo ratings yet
- HRM CapsuleDocument61 pagesHRM CapsuleNupur Agarwal Jain100% (2)
- 203 HRMDocument37 pages203 HRMshubhamatilkar04No ratings yet
- Part-A: o Give Details About Pay, Benefits, Holidays, Leave, Etc. Emphasize The Importance of Attendance or PunctualityDocument51 pagesPart-A: o Give Details About Pay, Benefits, Holidays, Leave, Etc. Emphasize The Importance of Attendance or PunctualityDeep NarayanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 StaffingDocument14 pagesCHAPTER 6 StaffingMercyNo ratings yet
- CH 4Document6 pagesCH 4Ebsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- Staffing Chester Dela CruzDocument32 pagesStaffing Chester Dela CruzangeloNo ratings yet
- Functions of Personnel Management Are Categorized UnderDocument8 pagesFunctions of Personnel Management Are Categorized UnderMangue AlaizaNo ratings yet
- 005 PPM 05 Sept 2022Document56 pages005 PPM 05 Sept 2022Nikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Internship Preparatory Note ISTDDocument8 pagesInternship Preparatory Note ISTDAnkur Sharma100% (3)
- III. Job Enrichment: - : 3. Problem With Union MembersDocument11 pagesIII. Job Enrichment: - : 3. Problem With Union MembersJitendra YadavNo ratings yet
- Career PLNG DevelopDocument8 pagesCareer PLNG DevelopTanu NarangNo ratings yet
- HRMDocument15 pagesHRMMittal SahabNo ratings yet
- 1ST UnitDocument11 pages1ST UnitAswin P SubhashNo ratings yet
- According To: Blum, "A Job Analysis Is An Accurate Study of The Various JobDocument4 pagesAccording To: Blum, "A Job Analysis Is An Accurate Study of The Various Jobpriyanshi rankaNo ratings yet
- BusinessDocument3 pagesBusinessjiyadkunnummalNo ratings yet
- 1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1Document35 pages1 Staffing The Engineering Organization 1JNo ratings yet
- HR Audit Assignment Dt. 1.12.2018 by Prakash Chand Kandpal PDFDocument12 pagesHR Audit Assignment Dt. 1.12.2018 by Prakash Chand Kandpal PDFPrakashNo ratings yet
- Training Process: Training Process in HRM - Steps, Process and PhasesDocument14 pagesTraining Process: Training Process in HRM - Steps, Process and PhasesbojaNo ratings yet
- Staffing Function of ManagementDocument12 pagesStaffing Function of ManagementnduhiukariukiNo ratings yet
- 2Document7 pages2LAKSHAY SHARMANo ratings yet
- CH 5Document22 pagesCH 5King HeniNo ratings yet
- Human Resource PlanningDocument87 pagesHuman Resource PlanningParul JainNo ratings yet
- BTS 07Document21 pagesBTS 07Rajni KumariNo ratings yet
- ObDocument46 pagesObJerry MataiNo ratings yet
- Staffing Notes Term 2, 2022Document8 pagesStaffing Notes Term 2, 2022Leela JainNo ratings yet
- HRM Final: I. Short AnswersDocument21 pagesHRM Final: I. Short AnswersBảo CườngNo ratings yet
- IM Unit-2Document5 pagesIM Unit-2sabyasachibbaNo ratings yet
- Functions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Document16 pagesFunctions and Role of Human Resource Manager: Submitted To: Mrs Jasleen Sehgal Submitted By: Shilpa Rani GMT 3Mittal SahabNo ratings yet
- Inc DoDocument7 pagesInc DoPreetiNo ratings yet
- StaffingDocument11 pagesStaffingHimanshu PatelNo ratings yet
- MB0043 HRM Assignment Set 1Document8 pagesMB0043 HRM Assignment Set 1Bipin SinghNo ratings yet
- HRDPDocument8 pagesHRDPhetvi TankNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management (DME-S6)Document60 pagesIndustrial Management (DME-S6)Devraj RoyNo ratings yet
- HRM CH-3Document195 pagesHRM CH-3Sukanya KaduNo ratings yet
- MBA 106 - Human Resource ManagementDocument8 pagesMBA 106 - Human Resource ManagementRahul YadavNo ratings yet
- Mayank 16521Document18 pagesMayank 16521naman kumarNo ratings yet
- BSBMGT517.doc Task 1Document4 pagesBSBMGT517.doc Task 1harman randhawaNo ratings yet
- Mpa 5Document16 pagesMpa 5subashrao5522No ratings yet
- C3 HMPDocument6 pagesC3 HMP37.Thảo VânNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5Document5 pagesLesson 5JOHN IRVIN TAERNo ratings yet
- Block - 1Document15 pagesBlock - 1madhaviNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Practice of Business AdministrationFrom EverandBasic Principles and Practice of Business AdministrationNo ratings yet
- Route KPL Train Feb Web2Document7 pagesRoute KPL Train Feb Web2Bernard MivilleNo ratings yet
- B Com English 2016Document12 pagesB Com English 2016PRIYANK PATEL67% (3)
- Federal Resume SampleDocument5 pagesFederal Resume Samplef5dq3ch5100% (2)
- M-Sand in Tamil NaduDocument9 pagesM-Sand in Tamil Nadurameshkanu1No ratings yet
- Collins Sentence MemoDocument17 pagesCollins Sentence MemoRoy S. JohnsonNo ratings yet
- SSB Tanitim CatalogDocument201 pagesSSB Tanitim CatalogAmir Cahyadi100% (1)
- Management Plan: Operations ManagerDocument14 pagesManagement Plan: Operations Manager弗朗兹No ratings yet
- New English File - Elementary File 10 - Test 10Document5 pagesNew English File - Elementary File 10 - Test 10Sanja IlovaNo ratings yet
- Vivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFDocument28 pagesVivo Placement Papers PDF Download PDFNikhil VermaNo ratings yet
- Biology Ecology Revision NotesDocument7 pagesBiology Ecology Revision NotesGeorge ArgyrouNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0160738323001846 MainDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S0160738323001846 Mainussual humanNo ratings yet
- Prepositions After AdjectivesDocument2 pagesPrepositions After AdjectivesJosé María OrtigueiraNo ratings yet
- C5. Catholic Vicar Apostolic of The Mt. Province v. Court of Appeals, 165 SCRA 515Document5 pagesC5. Catholic Vicar Apostolic of The Mt. Province v. Court of Appeals, 165 SCRA 515dondzNo ratings yet
- L'Altra Montessori School Inc.,: High School Department First Periodical Exam Technology and Livelihood Education 9Document4 pagesL'Altra Montessori School Inc.,: High School Department First Periodical Exam Technology and Livelihood Education 9Kristine HensonNo ratings yet
- Emirates Airlines Company StudyDocument17 pagesEmirates Airlines Company StudyluciusNo ratings yet
- Repair Appx V3Document18 pagesRepair Appx V3soniaNo ratings yet
- 40K - Malcador Tank v1Document2 pages40K - Malcador Tank v1SKL2002No ratings yet
- Programmed Instruction and SimulationDocument86 pagesProgrammed Instruction and SimulationRemyaKiranNo ratings yet
- How To Prepare A Construction Traffic Management Plan (CTMP) ReportDocument1 pageHow To Prepare A Construction Traffic Management Plan (CTMP) Reportmyco samNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitDocument52 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- CHN Transes Week 1Document5 pagesCHN Transes Week 1cheskalyka.asiloNo ratings yet
- Aerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsDocument3 pagesAerodur Finish HF A 130: ® Akzonobel Aerospace CoatingsАндрей МошкинNo ratings yet
- RHPA46 FreeDocument5 pagesRHPA46 Freeheyimdee5No ratings yet
- A7X ManualDocument32 pagesA7X ManualStephen LichotaNo ratings yet
- Automating Inequality - Virginia EubanksDocument223 pagesAutomating Inequality - Virginia EubanksTanmay100% (1)
- Managing Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesDocument59 pagesManaging Clean Core For SAP S4HANA Cloud NotesGLEN KGATLANo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Post-TestDocument4 pagesQuarter 2 Post-TestRoberto Del CarmenNo ratings yet