Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Uploaded by
Sam PitraudaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Receipt - Driver License Renewal and Address Change - Texas - GovDocument1 pageReceipt - Driver License Renewal and Address Change - Texas - GovAdalberto Lujan60% (10)
- PDF Politics in China An Introduction Joseph Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Politics in China An Introduction Joseph Ebook Full Chapterdeborah.holland887100% (1)
- GS Score - MAJOR - AMENDMENTS - TO - THE - CONSTITUTIONDocument20 pagesGS Score - MAJOR - AMENDMENTS - TO - THE - CONSTITUTIONnoorbashaumarNo ratings yet
- AmendmentsDocument4 pagesAmendmentsyashvermaNo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument6 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsAAYUSH SAXENANo ratings yet
- Recent Constitutional Amendments 1951 2019Document14 pagesRecent Constitutional Amendments 1951 2019chumki_DasNo ratings yet
- AMENDMENTDocument9 pagesAMENDMENTShreyaNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentsDocument1 pageImportant AmendmentsAmit 786No ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument53 pagesIndian PolityNagesh Reddy Katipelli100% (3)
- Important Constitutional AmendmantsDocument4 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmantsShiva Shankar PandianNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments To The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesImportant Amendments To The ConstitutionprinceNo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument11 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsselvaperumalvijayalNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments in Indian Constituion - ClatDocument10 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constituion - ClatSharvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Constitution AmendmentsDocument6 pagesConstitution Amendmentssahulala793No ratings yet
- List of Imp Ammendments in Indian ConstitutionDocument9 pagesList of Imp Ammendments in Indian ConstitutionParveen SainiNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentDocument7 pagesImportant AmendmentApoorva ChandraNo ratings yet
- Amendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951Document16 pagesAmendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951zahawaahmadNo ratings yet
- Major Constitutional Amendment Part 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMajor Constitutional Amendment Part 1 PDFSourabh PawarNo ratings yet
- Constitution AmendmentsDocument7 pagesConstitution Amendmentsmahafujalam22hNo ratings yet
- Polity-Important AmendmentsDocument4 pagesPolity-Important AmendmentsNithish KumarNo ratings yet
- List of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesList of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionpreetamdasNo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument3 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsNavya AroraNo ratings yet
- Polity by D.K. Chaudharysir: Constitutional AmendmentDocument30 pagesPolity by D.K. Chaudharysir: Constitutional AmendmentNitin Dangi100% (1)
- Constitutions Amendment - 7a1dc98c Ed4f 4f03 8a66 91c95f9c1944Document10 pagesConstitutions Amendment - 7a1dc98c Ed4f 4f03 8a66 91c95f9c1944Viru SehwagNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentDocument30 pagesImportant Amendmentomkumar7349No ratings yet
- Mportant Amendments in The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesMportant Amendments in The Indian ConstitutionNikunj VatsNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments in Indian Constitution: WWW - ByjusDocument7 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constitution: WWW - ByjuskumarprincelkhNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments of The Constitution: by Adv. Bhanu PratapDocument54 pagesImportant Amendments of The Constitution: by Adv. Bhanu PratapANUBHAV SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Constituion AmendmentsDocument4 pagesConstituion AmendmentsAdv Vaishali KamraNo ratings yet
- State Government: Tates and Nion ErritoriesDocument7 pagesState Government: Tates and Nion ErritoriespriyankaNo ratings yet
- 42,44 Amendment ActsDocument2 pages42,44 Amendment ActstarakNo ratings yet
- Amendments To The Indian ConstitutionDocument13 pagesAmendments To The Indian ConstitutionJaydeep SinghNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of India Amendment Procedure and Some Important Amendments (Part I)Document2 pagesThe Constitution of India Amendment Procedure and Some Important Amendments (Part I)ishk1989No ratings yet
- Constitution of India: Sample: Amendments To ConstitutionDocument16 pagesConstitution of India: Sample: Amendments To ConstitutionShweta GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document3 pagesChapter 9vivekhiremath58No ratings yet
- Important Amendments in Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constitutionkrishnasantana1988No ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights in The 1972 ConstitutionDocument35 pagesFundamental Rights in The 1972 ConstitutionUshanthy Sri GowthamanNo ratings yet
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)Document6 pagesINDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)workprofile440No ratings yet
- Important Amendments of Indian ConstitutionDocument24 pagesImportant Amendments of Indian Constitutionabhiswami000000No ratings yet
- Polity 4Document10 pagesPolity 4vishalbharati10230No ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument9 pagesArticlespankajpankaj18112002No ratings yet
- Vishnu SharmaDocument15 pagesVishnu SharmaSauravMishraNo ratings yet
- Major Constitutional Amendments in The History of Independent India and Is Useful For The Polity in Civil Services. Here Is The Detailed Explanation of Amendments To The Constitution of India.Document9 pagesMajor Constitutional Amendments in The History of Independent India and Is Useful For The Polity in Civil Services. Here Is The Detailed Explanation of Amendments To The Constitution of India.pradeepsambangiNo ratings yet
- 18th AmendmentDocument3 pages18th Amendmentshameeraqsa2No ratings yet
- Reorganization of States DivijaDocument24 pagesReorganization of States DivijaDivija PiduguNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments.....Document5 pagesImportant Amendments.....Pradnya KalambeNo ratings yet
- Major Constitutional Amendments: Part-2Document4 pagesMajor Constitutional Amendments: Part-2RAVI PRATAPNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Basic StructureDocument25 pagesDoctrine of Basic StructureHimanshu RajaNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesSalient Features of The ConstitutionIngith PrasanthNo ratings yet
- भारतीय संविधान के संशोधनों की सूची PDFDocument17 pagesभारतीय संविधान के संशोधनों की सूची PDFNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- Polity Revision Series Part 2 UpdatedDocument45 pagesPolity Revision Series Part 2 Updated2sushilkumar1234No ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument46 pagesIndian PolityAryan Raj100% (3)
- 1973 Constitution: Adnan BukhariDocument12 pages1973 Constitution: Adnan BukharisabirfurqanNo ratings yet
- Amendments To The Indian Constitution - UPSC Guide PDFDocument6 pagesAmendments To The Indian Constitution - UPSC Guide PDFKenneth DawsonNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments To Indian ConstitutionDocument3 pagesImportant Amendments To Indian Constitutionsurajjaan55No ratings yet
- 026dc3b6cb0b6-Recent Costitutional Amendments and LegislationsDocument31 pages026dc3b6cb0b6-Recent Costitutional Amendments and Legislationsshivam.adv.09No ratings yet
- Assesment Test - Hc16001Document6 pagesAssesment Test - Hc16001Abilash ShankarNo ratings yet
- Constitution of PakistanDocument12 pagesConstitution of PakistankingNo ratings yet
- 9 A Vision IAS Prelims 2020 TestDocument43 pages9 A Vision IAS Prelims 2020 TestGaurav MeenaNo ratings yet
- 24th AmendmentDocument27 pages24th Amendmentaman dwivediNo ratings yet
- 42 N 44 Constitutional AmendmentsDocument7 pages42 N 44 Constitutional AmendmentsShashwat SinghNo ratings yet
- History PYQ PrelimsDocument45 pagesHistory PYQ PrelimsSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Species in News Whole 2023Document29 pagesSpecies in News Whole 2023Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Art and Culture - 3000+ MCQsDocument17 pagesArt and Culture - 3000+ MCQsSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- CSAT 2023 - Plan of ActionDocument5 pagesCSAT 2023 - Plan of ActionSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Schemes & PolicsDocument110 pagesSchemes & PolicsSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Security Yearly 2023 VisionDocument81 pagesSecurity Yearly 2023 VisionSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy Comprehensive Notes Sankalp UPSCDocument515 pagesIndian Economy Comprehensive Notes Sankalp UPSCSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Footing ScheduleDocument1 pageFooting ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Security Workbook-2Document40 pagesSecurity Workbook-2Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology in Development StudiesDocument349 pagesResearch Methodology in Development StudiesSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Govt. Accounting Rules 1990Document80 pagesGovt. Accounting Rules 1990Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- The Hindu Newspaper April 2023 Synopsis For UPSC Prelims 2024Document6 pagesThe Hindu Newspaper April 2023 Synopsis For UPSC Prelims 2024Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Floor Slab ScheduleDocument1 pageFloor Slab ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- SDEEDocument115 pagesSDEESam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Methodsofconcreting 180304183706Document30 pagesMethodsofconcreting 180304183706Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Tunneling in Soft Ground and Hard RockDocument49 pagesTunneling in Soft Ground and Hard RockSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Nupur Mec 2nd Imp.Document7 pagesNupur Mec 2nd Imp.Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Second FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Second FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Ground FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Ground FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Micro Content Improvement Basic To AdvancedDocument4 pagesMicro Content Improvement Basic To AdvancedSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Third FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Third FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Plinth Beams ScheduleDocument1 pagePlinth Beams ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule First FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule First FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- 75 Hard Mains Micro Improvement Skills Schedule-2024Document22 pages75 Hard Mains Micro Improvement Skills Schedule-2024Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Below GroundDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Below GroundSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Floor Beams ScheduleDocument1 pageFloor Beams ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Decoding The PassageDocument1 pageDecoding The PassageSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- VT ON 1ST WK - 10.07.23 (Revised)Document1 pageVT ON 1ST WK - 10.07.23 (Revised)Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Switching and Signalling OVTDocument65 pagesSwitching and Signalling OVTSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- POLICE Under Brits FinalDocument4 pagesPOLICE Under Brits FinalSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Iecex Operational DocumentDocument27 pagesIecex Operational Documentcacalot93No ratings yet
- Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board Yatra Parchi ServicesDocument1 pageShri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board Yatra Parchi ServicesYogesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Gulbarga University CollegesDocument27 pagesGulbarga University CollegesprasadkulkarnigitNo ratings yet
- Notice: Air Pollution Control: State Operating Permits Programs— AlabamaDocument1 pageNotice: Air Pollution Control: State Operating Permits Programs— AlabamaJustia.comNo ratings yet
- (ADMIN) (Vinta Maritime v. NLRC)Document2 pages(ADMIN) (Vinta Maritime v. NLRC)Alyanna ApacibleNo ratings yet
- Lighthouse 112912Document32 pagesLighthouse 112912VCStarNo ratings yet
- Jetty-Ras-Kazone Design and Build - Prequalification Documents For Works 20.04.2023Document67 pagesJetty-Ras-Kazone Design and Build - Prequalification Documents For Works 20.04.2023Nyasimi GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Decision For EjectmentDocument7 pagesDecision For Ejectmentatty.estebanNo ratings yet
- Name of CaseDocument2 pagesName of CaseJoseff Anthony FernandezNo ratings yet
- Roads To Leningrad: Play BookletDocument24 pagesRoads To Leningrad: Play BookletNuno OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Injunction Under Specific Relief Act 1963Document9 pagesInjunction Under Specific Relief Act 1963Crash Car IndiaNo ratings yet
- Pil An Over ViewDocument21 pagesPil An Over Viewsailegummegister_768No ratings yet
- Major International AirportsDocument13 pagesMajor International AirportsEduardo Abad Jr100% (1)
- Gross Negligence in Haryana Khadi & Village Industries Board - Naresh KadyanDocument72 pagesGross Negligence in Haryana Khadi & Village Industries Board - Naresh KadyanNaresh KadyanNo ratings yet
- Taap Corporate MembersDocument2 pagesTaap Corporate MembersMuhammad ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Mootcourt Memorial PetitionerDocument15 pagesMootcourt Memorial PetitionerDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- PMBJP Application Form - 24032021Document9 pagesPMBJP Application Form - 24032021shashank parmar100% (1)
- PROrailDocument2 pagesPROrailDiana BarchukNo ratings yet
- Cano-Favela v. United States of America - Document No. 2Document11 pagesCano-Favela v. United States of America - Document No. 2Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Feminism Analysis On Maggie OsbroneDocument2 pagesFeminism Analysis On Maggie OsbroneFranciska WibowoNo ratings yet
- The Pang of Misfortune - Declamation PieceDocument2 pagesThe Pang of Misfortune - Declamation Piecemiathemermaid100% (1)
- Lesson 4 SalvationDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Salvationkemelo12No ratings yet
- The End of ..The MillDocument3 pagesThe End of ..The Millajay devganNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning Iii GroupDocument12 pagesUrban Planning Iii GroupNILU MAXINo ratings yet
- Tiet 4. SubjunctiveDocument4 pagesTiet 4. SubjunctiveNguyễn Gia TuệNo ratings yet
- NullDocument8 pagesNullUNHCR_ThailandNo ratings yet
- Doaldd 2023Document12 pagesDoaldd 2023dangtaimai6789No ratings yet
- Christmas and The New Year in BritainDocument2 pagesChristmas and The New Year in BritainToma Elena AlinaNo ratings yet
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Uploaded by
Sam PitraudaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Uploaded by
Sam PitraudaCopyright:
Available Formats
Constitutional Amendments
for
Civil Service Exam
by
ZERO NOTES
About Zero Notes
Zero Notes believes in providing authentic and relevant notes for Civil Service Examination in
a comprehensive, yet concise way. The notes are logically arranged, visually depicted and
optimised in a manner to make it interesting to read & understand and easy to memorise. At
Zero Notes, we believe in taking genuine feedback and course correction to provide the best
quality notes to help the genuine aspirants.
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Join Telegram for updates: https://t.me/zeronotes | Send feedback: xeronotes@gmail.com (1)
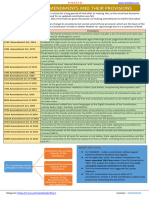
Constitutional Amendments
No Year Objectives
1 1951 Added special provision for the advancement of any socially and educationally backward classes
or for SCs and STs
To fully secure the constitutional validity of zamindari abolition laws and to place reasonable
restrictions on freedom of speech. A new constitutional device, called Schedule 9 introduced to
protect against laws that are contrary to the Constitutionally guaranteed fundamental rights.
7 1956 Reorganization of states on linguistic lines, abolition of Class A, B, C, D states and
introduction of UTs
33
+ 350A states that every State to provide facilities for instruction in mother Tongue at the
Primary stage to children belonging to linguistic minority groups and empowers the P to
issue directions to any State for securing such facilities
+ 350B inserted provides for appointment for the P to appoint Special Officers whose duty
shall to investigate all matters relating to safeguards provided for linguistic minorities under
the Constitution and to report to the President upon those matters. These reports shall be
laid before each house of Parliament and sent to the Governments of the States concerned
10 1961 Incorporation of Dadra, Nagar and Haveli as a UT, consequent to acquisition from Portugal.
11 1961 Election of Vice President by an Electoral College consisting of members of both Houses of
Parliament, instead of election by a Joint Sitting of Parliament.
12 1961 Incorporation of Goa, Daman and Diu as a UT, consequent to acquisition from Portugal.
13 1963 Formation of State of Nagaland, with special protection under Article 371A
14 1962 Incorporation of Pondicherry into the Union of India and creation of Legislative Assemblies for HP,
Tripura, Manipur and Goa
15 1963 Raise retirement age of High Court judges from 60 to 62
16 1963 Make it obligatory for seekers of public office to swear their allegiance to the Indian Republic
and prescribe the various obligatory templates
19 1966 Abolish Election Tribunals and enable trial of election petitions by regular High Courts
24 1971 Enable parliament to dilute fundamental rights through amendments to the constitution.
25 1972 Restrict property rights and compensation in case the state takes over private property
However, SC quashed a part of Article 31C, to the extent it took away the power of judicial review.
This was done in the landmark case of Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala (1973) which for the
first time enunciated the Basic structure doctrine.
26 1971 Abolition of privy purse paid to former rulers of princely states which were incorporated into the
Indian Republic
27 1972 Reorganization of Mizoram into a UT with a legislature and council of ministers
31 1973 Increase size of Parliament from 525 to 545 seats
33 1974 Prescribes procedure for resignation by members of parliament and state legislatures and the
procedure for verification and acceptance of resignation by house speaker
34 1974 Place land reform acts and amendments to these act under Schedule 9 of the constitution
36 1975 Formation of Sikkim as a State within the Indian Union
37 1975 Formation of Arunachal Pradesh legislative assembly
39 1975 Amendment designed to negate the judgement of Allahabad High Court invalidating Prime Minister
Indira Gandhi's election to parliament
Struck down by SC in case of Indira Nehru Gandhi vs Shri Raj Narain 1976, for being in violation of
basic structure
40 1976 Enable Parliament to make laws with respect to Exclusive Economic Zone and vest the mineral
wealth with Union of India
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Join Telegram for updates: https://t.me/zeronotes | Send feedback: xeronotes@gmail.com (2)
41 1976 Raise Retirement Age Limit of Chairmen and Members of JPSC and SPSC from 60→62
42 1976 "Mini-Constitution"
- Fundamental Duties
- Socialist Secular Integrity : Preamble
- It attempted to reduce the power of SC and HCs
Minerva Mills Case, SC declared unconstitutional two provisions of 42nd CAA
44 1976 The 44th CAA 1978 reversed the provision made by the 42nd CAA that allowed the government to
amend the constitution on its wish by Article 368. 44th Amendment Act nullified this unjustified
power to the government
Right to Property was removed from the list of FRs (Art 31) and was made a legal right under Art
300A
Proclamation of Emergency can be issued only when the security of India or any part of its territory
is threatened by war or external aggression or by armed rebellion. Internal disturbance not
amounting to armed rebellion would not be a ground for the issue of a Proclamation
It replaced the word “internal disturbance” with “armed rebellion”. It made P declare a NE only on
the written recommendation of the cabinet. Duration of NE should not be extended more than 6
months at a time
Empowered President to send back advice of CoM for reconsideration
FRs guaranteed by Articles 20 and 21 cannot be suspended during a NE
The right to liberty is further strengthened by the provision that law for preventive detention cannot
authorise, in any case, detention for a longer period than 2 months, unless an Advisory Board has
reported that there is sufficient cause for such detention.
Right of the media to report freely and without censorship the proceedings in Parliament and the
State Legislatures
49 1984 Recognize Tripura as a Tribal State and enable the creation of a Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous
District Council.
52 1985 Anti Defection Law - Provide disqualification of members from parliament and assembly in case of
defection from one party to another.
However, parts of the 10th Schedule to the Constitution of India was struck down by the SC in the
case of Kihoto Hollohan v. Zachillhu for being in contravention with Article 368 of the Constitution
53 1986 Special provision with respect to the State of Mizoram
54 1986 Increase the salary of CJI & other Judges and to provide for determining future increases
without the need for constitutional amendment
55 1987 Special powers to Governor consequent to formation of state of Arunachal Pradesh
56 1987 Transition provision to enable formation of state of Goa
61 1989 Reduce age for voting rights from 21 to 18
69 1992 To provide for a legislative assembly and council of ministers for the Federal National Capital of
Delhi. Delhi continues to be a UT
70 1991 Include Delhi and Pondicherry in electoral college for P Election
73 1992 Statutory provisions for Panchayat Raj as third level of administration in villages
74 1992 Statutory provisions for Local Administrative bodies as third level of administration in urban areas
such as towns and cities.
75 1994 Provisions for setting up Rent Control Tribunals
76 1994 Enable continuance of 69% reservation in Tamil Nadu by including the relevant Tamil Nadu Act
under 9th Schedule of the constitution.
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Join Telegram for updates: https://t.me/zeronotes | Send feedback: xeronotes@gmail.com (3)
77 1995 A technical amendment to protect reservation to SC/ST Employees in promotions
81 2000 Protect SC / ST reservation in filling backlog of vacancies
83 2000 Exempt Arunachal Pradesh from reservation for SCs in PRIs
85 2002 A technical amendment to protect Consequential seniority in case of promotions of SC/ST
Employees
86 2002 Provides Right to Education until the age of 14 and Early childhood care until the age of 6
87 2003 Extend the usage of 2001 national census population figures for state wise distribution of
parliamentary seats
89 2003 National Commission for SCs and STs was bifurcated
91 2004 Restrict the size of council of ministers to 15% of legislative members & to strengthen Anti Defection
laws.
93 2006 To enable provision of reservation (27%) for OBC in government as well as private educational
institutions
94 2006 To provide for a Minister of Tribal Welfare in newly created Jharkhand and Chhattisgarh States
including MP, Orissa
95 2010 To extend the reservation of seats for SCs and STs in the Lok Sabha and state assemblies
from Sixty years to Seventy years
96 2011 Substituted "Odia" for "Oriya"
97 2012 Added the words "or co-operative societies" after the word "or unions" in Article 19(l)(c)
Insertion of article 43B → Promotion of Co-operative Societies
Added Part-IXB → The Co-operative Societies.
98 2013 To empower Governor of Karnataka to take steps to develop Hyderabad-Karnataka Region
99 2015 Formation of a NJAC (later struck down by SC)
100 2015 Exchange of certain enclave territories with Bangladesh and conferment of citizenship rights to
residents of enclaves consequent to signing of Land Boundary Agreement (LBA) Treaty
between India and Bangladesh
101 2017 Introduced GST
102 2018 Constitutional status to National Commission for Backward Classes
103 2019 A maximum of 10% Reservation for EWSs of citizens of classes other than the classes mentioned
in clauses (4) and (5) of Article 15, i.e. Classes other than socially and educationally backward
classes of citizens or SCs and STs
Amendment to Article 15, added Clause [6]
Amendment to Article 16, added Clause [6]
104 2020 To extend the reservation of seats for SCs and STs in the Lok Sabha and states assemblies from 70
years to 80 years
Removed the reserved seats for the Anglo-Indian community in the LS and state assemblies
Constitutional Amendments by ZERO NOTES
Join Telegram for updates: https://t.me/zeronotes | Send feedback: xeronotes@gmail.com (4)
You might also like
- Receipt - Driver License Renewal and Address Change - Texas - GovDocument1 pageReceipt - Driver License Renewal and Address Change - Texas - GovAdalberto Lujan60% (10)
- PDF Politics in China An Introduction Joseph Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Politics in China An Introduction Joseph Ebook Full Chapterdeborah.holland887100% (1)
- GS Score - MAJOR - AMENDMENTS - TO - THE - CONSTITUTIONDocument20 pagesGS Score - MAJOR - AMENDMENTS - TO - THE - CONSTITUTIONnoorbashaumarNo ratings yet
- AmendmentsDocument4 pagesAmendmentsyashvermaNo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument6 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsAAYUSH SAXENANo ratings yet
- Recent Constitutional Amendments 1951 2019Document14 pagesRecent Constitutional Amendments 1951 2019chumki_DasNo ratings yet
- AMENDMENTDocument9 pagesAMENDMENTShreyaNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentsDocument1 pageImportant AmendmentsAmit 786No ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument53 pagesIndian PolityNagesh Reddy Katipelli100% (3)
- Important Constitutional AmendmantsDocument4 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmantsShiva Shankar PandianNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments To The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesImportant Amendments To The ConstitutionprinceNo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument11 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsselvaperumalvijayalNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments in Indian Constituion - ClatDocument10 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constituion - ClatSharvi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Constitution AmendmentsDocument6 pagesConstitution Amendmentssahulala793No ratings yet
- List of Imp Ammendments in Indian ConstitutionDocument9 pagesList of Imp Ammendments in Indian ConstitutionParveen SainiNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentDocument7 pagesImportant AmendmentApoorva ChandraNo ratings yet
- Amendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951Document16 pagesAmendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951zahawaahmadNo ratings yet
- Major Constitutional Amendment Part 1 PDFDocument5 pagesMajor Constitutional Amendment Part 1 PDFSourabh PawarNo ratings yet
- Constitution AmendmentsDocument7 pagesConstitution Amendmentsmahafujalam22hNo ratings yet
- Polity-Important AmendmentsDocument4 pagesPolity-Important AmendmentsNithish KumarNo ratings yet
- List of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesList of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionpreetamdasNo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument3 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsNavya AroraNo ratings yet
- Polity by D.K. Chaudharysir: Constitutional AmendmentDocument30 pagesPolity by D.K. Chaudharysir: Constitutional AmendmentNitin Dangi100% (1)
- Constitutions Amendment - 7a1dc98c Ed4f 4f03 8a66 91c95f9c1944Document10 pagesConstitutions Amendment - 7a1dc98c Ed4f 4f03 8a66 91c95f9c1944Viru SehwagNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentDocument30 pagesImportant Amendmentomkumar7349No ratings yet
- Mportant Amendments in The Indian ConstitutionDocument10 pagesMportant Amendments in The Indian ConstitutionNikunj VatsNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments in Indian Constitution: WWW - ByjusDocument7 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constitution: WWW - ByjuskumarprincelkhNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments of The Constitution: by Adv. Bhanu PratapDocument54 pagesImportant Amendments of The Constitution: by Adv. Bhanu PratapANUBHAV SHUKLANo ratings yet
- Constituion AmendmentsDocument4 pagesConstituion AmendmentsAdv Vaishali KamraNo ratings yet
- State Government: Tates and Nion ErritoriesDocument7 pagesState Government: Tates and Nion ErritoriespriyankaNo ratings yet
- 42,44 Amendment ActsDocument2 pages42,44 Amendment ActstarakNo ratings yet
- Amendments To The Indian ConstitutionDocument13 pagesAmendments To The Indian ConstitutionJaydeep SinghNo ratings yet
- The Constitution of India Amendment Procedure and Some Important Amendments (Part I)Document2 pagesThe Constitution of India Amendment Procedure and Some Important Amendments (Part I)ishk1989No ratings yet
- Constitution of India: Sample: Amendments To ConstitutionDocument16 pagesConstitution of India: Sample: Amendments To ConstitutionShweta GajbhiyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document3 pagesChapter 9vivekhiremath58No ratings yet
- Important Amendments in Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constitutionkrishnasantana1988No ratings yet
- Fundamental Rights in The 1972 ConstitutionDocument35 pagesFundamental Rights in The 1972 ConstitutionUshanthy Sri GowthamanNo ratings yet
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)Document6 pagesINDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)workprofile440No ratings yet
- Important Amendments of Indian ConstitutionDocument24 pagesImportant Amendments of Indian Constitutionabhiswami000000No ratings yet
- Polity 4Document10 pagesPolity 4vishalbharati10230No ratings yet
- ArticlesDocument9 pagesArticlespankajpankaj18112002No ratings yet
- Vishnu SharmaDocument15 pagesVishnu SharmaSauravMishraNo ratings yet
- Major Constitutional Amendments in The History of Independent India and Is Useful For The Polity in Civil Services. Here Is The Detailed Explanation of Amendments To The Constitution of India.Document9 pagesMajor Constitutional Amendments in The History of Independent India and Is Useful For The Polity in Civil Services. Here Is The Detailed Explanation of Amendments To The Constitution of India.pradeepsambangiNo ratings yet
- 18th AmendmentDocument3 pages18th Amendmentshameeraqsa2No ratings yet
- Reorganization of States DivijaDocument24 pagesReorganization of States DivijaDivija PiduguNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments.....Document5 pagesImportant Amendments.....Pradnya KalambeNo ratings yet
- Major Constitutional Amendments: Part-2Document4 pagesMajor Constitutional Amendments: Part-2RAVI PRATAPNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Basic StructureDocument25 pagesDoctrine of Basic StructureHimanshu RajaNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesSalient Features of The ConstitutionIngith PrasanthNo ratings yet
- भारतीय संविधान के संशोधनों की सूची PDFDocument17 pagesभारतीय संविधान के संशोधनों की सूची PDFNitin KumarNo ratings yet
- Polity Revision Series Part 2 UpdatedDocument45 pagesPolity Revision Series Part 2 Updated2sushilkumar1234No ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument46 pagesIndian PolityAryan Raj100% (3)
- 1973 Constitution: Adnan BukhariDocument12 pages1973 Constitution: Adnan BukharisabirfurqanNo ratings yet
- Amendments To The Indian Constitution - UPSC Guide PDFDocument6 pagesAmendments To The Indian Constitution - UPSC Guide PDFKenneth DawsonNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments To Indian ConstitutionDocument3 pagesImportant Amendments To Indian Constitutionsurajjaan55No ratings yet
- 026dc3b6cb0b6-Recent Costitutional Amendments and LegislationsDocument31 pages026dc3b6cb0b6-Recent Costitutional Amendments and Legislationsshivam.adv.09No ratings yet
- Assesment Test - Hc16001Document6 pagesAssesment Test - Hc16001Abilash ShankarNo ratings yet
- Constitution of PakistanDocument12 pagesConstitution of PakistankingNo ratings yet
- 9 A Vision IAS Prelims 2020 TestDocument43 pages9 A Vision IAS Prelims 2020 TestGaurav MeenaNo ratings yet
- 24th AmendmentDocument27 pages24th Amendmentaman dwivediNo ratings yet
- 42 N 44 Constitutional AmendmentsDocument7 pages42 N 44 Constitutional AmendmentsShashwat SinghNo ratings yet
- History PYQ PrelimsDocument45 pagesHistory PYQ PrelimsSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Species in News Whole 2023Document29 pagesSpecies in News Whole 2023Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Art and Culture - 3000+ MCQsDocument17 pagesArt and Culture - 3000+ MCQsSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- CSAT 2023 - Plan of ActionDocument5 pagesCSAT 2023 - Plan of ActionSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Schemes & PolicsDocument110 pagesSchemes & PolicsSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Security Yearly 2023 VisionDocument81 pagesSecurity Yearly 2023 VisionSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Indian Economy Comprehensive Notes Sankalp UPSCDocument515 pagesIndian Economy Comprehensive Notes Sankalp UPSCSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Footing ScheduleDocument1 pageFooting ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Security Workbook-2Document40 pagesSecurity Workbook-2Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology in Development StudiesDocument349 pagesResearch Methodology in Development StudiesSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Govt. Accounting Rules 1990Document80 pagesGovt. Accounting Rules 1990Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- The Hindu Newspaper April 2023 Synopsis For UPSC Prelims 2024Document6 pagesThe Hindu Newspaper April 2023 Synopsis For UPSC Prelims 2024Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Floor Slab ScheduleDocument1 pageFloor Slab ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- SDEEDocument115 pagesSDEESam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Methodsofconcreting 180304183706Document30 pagesMethodsofconcreting 180304183706Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Tunneling in Soft Ground and Hard RockDocument49 pagesTunneling in Soft Ground and Hard RockSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Nupur Mec 2nd Imp.Document7 pagesNupur Mec 2nd Imp.Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Second FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Second FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Ground FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Ground FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Micro Content Improvement Basic To AdvancedDocument4 pagesMicro Content Improvement Basic To AdvancedSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Third FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Third FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Plinth Beams ScheduleDocument1 pagePlinth Beams ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule First FloorDocument1 pageColumn Schedule First FloorSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- 75 Hard Mains Micro Improvement Skills Schedule-2024Document22 pages75 Hard Mains Micro Improvement Skills Schedule-2024Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Column Schedule Below GroundDocument1 pageColumn Schedule Below GroundSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Floor Beams ScheduleDocument1 pageFloor Beams ScheduleSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Decoding The PassageDocument1 pageDecoding The PassageSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- VT ON 1ST WK - 10.07.23 (Revised)Document1 pageVT ON 1ST WK - 10.07.23 (Revised)Sam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Switching and Signalling OVTDocument65 pagesSwitching and Signalling OVTSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- POLICE Under Brits FinalDocument4 pagesPOLICE Under Brits FinalSam PitraudaNo ratings yet
- Iecex Operational DocumentDocument27 pagesIecex Operational Documentcacalot93No ratings yet
- Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board Yatra Parchi ServicesDocument1 pageShri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board Yatra Parchi ServicesYogesh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Gulbarga University CollegesDocument27 pagesGulbarga University CollegesprasadkulkarnigitNo ratings yet
- Notice: Air Pollution Control: State Operating Permits Programs— AlabamaDocument1 pageNotice: Air Pollution Control: State Operating Permits Programs— AlabamaJustia.comNo ratings yet
- (ADMIN) (Vinta Maritime v. NLRC)Document2 pages(ADMIN) (Vinta Maritime v. NLRC)Alyanna ApacibleNo ratings yet
- Lighthouse 112912Document32 pagesLighthouse 112912VCStarNo ratings yet
- Jetty-Ras-Kazone Design and Build - Prequalification Documents For Works 20.04.2023Document67 pagesJetty-Ras-Kazone Design and Build - Prequalification Documents For Works 20.04.2023Nyasimi GeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Decision For EjectmentDocument7 pagesDecision For Ejectmentatty.estebanNo ratings yet
- Name of CaseDocument2 pagesName of CaseJoseff Anthony FernandezNo ratings yet
- Roads To Leningrad: Play BookletDocument24 pagesRoads To Leningrad: Play BookletNuno OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Injunction Under Specific Relief Act 1963Document9 pagesInjunction Under Specific Relief Act 1963Crash Car IndiaNo ratings yet
- Pil An Over ViewDocument21 pagesPil An Over Viewsailegummegister_768No ratings yet
- Major International AirportsDocument13 pagesMajor International AirportsEduardo Abad Jr100% (1)
- Gross Negligence in Haryana Khadi & Village Industries Board - Naresh KadyanDocument72 pagesGross Negligence in Haryana Khadi & Village Industries Board - Naresh KadyanNaresh KadyanNo ratings yet
- Taap Corporate MembersDocument2 pagesTaap Corporate MembersMuhammad ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Mootcourt Memorial PetitionerDocument15 pagesMootcourt Memorial PetitionerDilip KumarNo ratings yet
- PMBJP Application Form - 24032021Document9 pagesPMBJP Application Form - 24032021shashank parmar100% (1)
- PROrailDocument2 pagesPROrailDiana BarchukNo ratings yet
- Cano-Favela v. United States of America - Document No. 2Document11 pagesCano-Favela v. United States of America - Document No. 2Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Feminism Analysis On Maggie OsbroneDocument2 pagesFeminism Analysis On Maggie OsbroneFranciska WibowoNo ratings yet
- The Pang of Misfortune - Declamation PieceDocument2 pagesThe Pang of Misfortune - Declamation Piecemiathemermaid100% (1)
- Lesson 4 SalvationDocument2 pagesLesson 4 Salvationkemelo12No ratings yet
- The End of ..The MillDocument3 pagesThe End of ..The Millajay devganNo ratings yet
- Urban Planning Iii GroupDocument12 pagesUrban Planning Iii GroupNILU MAXINo ratings yet
- Tiet 4. SubjunctiveDocument4 pagesTiet 4. SubjunctiveNguyễn Gia TuệNo ratings yet
- NullDocument8 pagesNullUNHCR_ThailandNo ratings yet
- Doaldd 2023Document12 pagesDoaldd 2023dangtaimai6789No ratings yet
- Christmas and The New Year in BritainDocument2 pagesChristmas and The New Year in BritainToma Elena AlinaNo ratings yet