Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
talhagg333 talhagg3330 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views20 pagesThis document provides an overview of programming fundamentals including problem solving techniques, algorithms, flowcharts, programming languages, and the program development process. It discusses how algorithms are used to solve problems through step-by-step procedures written in pseudocode. Flowcharts provide a graphical representation of algorithm logic and data flow. High-level programming languages make it easier for humans to write code that is then converted to machine-readable code through compilers, interpreters, or assemblers.
Original Description:
computer science
Original Title
Chapter 1 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides an overview of programming fundamentals including problem solving techniques, algorithms, flowcharts, programming languages, and the program development process. It discusses how algorithms are used to solve problems through step-by-step procedures written in pseudocode. Flowcharts provide a graphical representation of algorithm logic and data flow. High-level programming languages make it easier for humans to write code that is then converted to machine-readable code through compilers, interpreters, or assemblers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views20 pagesChapter 1
Chapter 1
Uploaded by
talhagg333 talhagg333This document provides an overview of programming fundamentals including problem solving techniques, algorithms, flowcharts, programming languages, and the program development process. It discusses how algorithms are used to solve problems through step-by-step procedures written in pseudocode. Flowcharts provide a graphical representation of algorithm logic and data flow. High-level programming languages make it easier for humans to write code that is then converted to machine-readable code through compilers, interpreters, or assemblers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 20
CS-308:Programming Fundamentals
Dr. Sumaira Nishat
Book
Problem Solving
• We face/solve different problems everyday.
• Problem Solving is a process of identifying a problem and finding the
best solution for it.
• Different strategies, techniques (Flowchart, Algorithm, Program) and
tools are used to solve a problem.
Algorithms
• Algorithm is step by step procedure to solve a problem.
• Better to wrote algorithm before writing the actual computer
program.
• Algorithms are written in simple English called pseudocode.
• It is independent of any programming language.
• The steps of algorithm/pseudocode should be written sequentially.
• Program development in two main steps:
• Logic Design – The logic of the program is designed.
• Coding – The algorithm is converted into a program.
Algorithms - Example
• Algorithm to calculate sum of two numbers given by user. Display the
result also.
1. Start
2. Input A
3. Input B
4. Total = A+B
5. Display Total
6. End
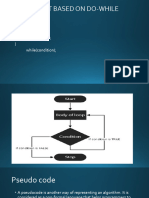
Flowchart
• It is a graphical
representation of an
algorithm.
• It is a visual
representation of flow
of data, operations
performed on data and
sequence of these
operations.
• Flowchart Symbols:
Flowchart - Example
Algorithm to calculate sum of two numbers given by user. Display the
result also.
Example
• Algorithm to calculate sum of two numbers given by user. Display the
result also.
1. Start
2. Input A
3. Input B
4. Total = A+B
5. Display Total
6. End
Program
• Computers are used as a tool to solve complex problems by
developing computer programs (Software).
• Program/software is a set of instruction given to computer to solve a
problem.
• Programmer writes these instructions and computer execute these
instructions to solve a problem.
• Computer programs are written in programming language.
• Programmers use programming language
Program Development Process
1. Defining and analyzing Problem
2. Designing the Algorithm
3. Coding or writing the program
4. Testing Program
5. Final Documentation
Programming Language
• A set of words, symbols and codes used to write programs is called
programming language.
• Different programming languages are available for writing different
types of programs.
• There are two types of computer programming languages:
• Low-level languages
• High-level Languages
Low-level languages
• These languages are near to computer hardware and far from human
languages.
• Computer can understand these languages easily.
• Writing a program in low-level languages requires a deep knowledge
of the internal structure of computer hardware.
• Two low-level programming languages are
• Machine language- instructions are written in binary.
• Assembly language – symbols are used to write instructions.
High-level languages
• A type of language that is close to human language.
• Easy to understand.
• Instructions are written in English-like words such as input and print
etc.
• Divided into following categories:
• Procedural Languages – FORTRAN, BASIC, COBOL, C
• Object-Oriented Languages – C++, Java
• Non-Procedural Languages – SQL, RPG.
Types of Codes
• Source Code
• Program written in high-level language is called source code.
• Object Code
• A program in machine language is called object code.
Language Processor
• Computer understands only machine language.
• Program written in high-level or assembly language can not be run on
computer directly.
• It must be converted into machine language before execution.
• A language processor, or translator, is a computer program that
translates source code from one programming language (High-level
or assembly) to another (Machine language).
• Every computer Language has its own translator.
Language Processor
Compiler
• Converts instruction of high level language into machine language as
a whole.
• Compiler converts source code into object code.
Compiler
• Converts instruction of high level language into machine language as
a whole.
• Compiler converts source code into object code.
• Also checks syntax errors in the source code.
• A compiler can translate the programs of only that language for which
it is written. E.g. C Compiler can translate only those programs that
are written in C Language.
Interpreter
• Program that converts one statement of a program at one time.
• It does not produce an object program.
Assembler
• Program that translates the instruction of a assembly language into
machine language.
You might also like
- 2007 Engine IntroductionDocument16 pages2007 Engine IntroductionbernackiNo ratings yet
- Solution Four Stroke EngineDocument5 pagesSolution Four Stroke EngineJeisson Mendoza100% (1)
- EAGLE LSAR Product GuideDocument26 pagesEAGLE LSAR Product Guidejaved iqbal0% (1)
- Unit 1Document219 pagesUnit 1RaskshannaNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming (M1-Main) PDFDocument34 pagesComputer Programming (M1-Main) PDFMohamad LajaratoNo ratings yet
- C++ Chapter 2Document59 pagesC++ Chapter 2Gediyon MesfinNo ratings yet
- Principles of ProgrammingDocument15 pagesPrinciples of ProgrammingKay TeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Problem Solving Using ComputersDocument37 pagesChapter One: Problem Solving Using ComputerslalisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 291269165740Document36 pagesChapter 2 - 291269165740Täð Œvê MîðNo ratings yet
- ProgrammingDocument48 pagesProgrammingkfmimaanNo ratings yet
- Unit One: Introduction To ProgrammingDocument43 pagesUnit One: Introduction To ProgrammingabdiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Algorithm and Programming DevelopmentDocument23 pagesUnit 1: Algorithm and Programming DevelopmentPreeti ToppoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Ten: Introduction To ProgrammingDocument75 pagesLesson Ten: Introduction To ProgrammingEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Programming Fundamentals 01Document19 pagesProgramming Fundamentals 01Asmara MinhasNo ratings yet
- Input DevicesDocument11 pagesInput DevicesSomendra TomarNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1665049566062 6983724055135104435Document259 pagesOrca Share Media1665049566062 6983724055135104435Vanessa BuensalidaNo ratings yet
- (M2-MAIN) Introduction To Computer and Programming ConceptsDocument50 pages(M2-MAIN) Introduction To Computer and Programming Conceptsonly sizzlerNo ratings yet
- Ch-09 (Comp) - Programming LanguagesDocument27 pagesCh-09 (Comp) - Programming LanguagesMian AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document40 pagesUnit 1Jyotir BhattNo ratings yet
- Compiler Construction Week 1Document34 pagesCompiler Construction Week 1Zulfiqar AliNo ratings yet
- CP-Chapter 1Document44 pagesCP-Chapter 1Abel MulatuNo ratings yet
- IPT Lesson 2Document28 pagesIPT Lesson 2Franz Lawrenz De TorresNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document49 pagesUnit 1SamarNo ratings yet
- DIT 0202 - Week Four LecturesDocument16 pagesDIT 0202 - Week Four LecturesAli DoyoNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument26 pagesIntroductionKen MutaiNo ratings yet
- CMP 131 Introduction To Computer Programming: Violetta Cavalli-Sforza Week 1, LabDocument26 pagesCMP 131 Introduction To Computer Programming: Violetta Cavalli-Sforza Week 1, Labfriend4spicyNo ratings yet
- What Is A Computer?: SoftwareDocument24 pagesWhat Is A Computer?: SoftwareAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- CP Chapter 1Document52 pagesCP Chapter 1abelcreed1994No ratings yet
- Computer ProgrammingDocument16 pagesComputer ProgrammingNawszNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document17 pagesLecture 4clashofrawatNo ratings yet
- Unit1 2Document24 pagesUnit1 2meclinejoseflNo ratings yet
- SPM 2102 Programming Language 1Document9 pagesSPM 2102 Programming Language 1Asy LimNo ratings yet
- CS Micro 1 UnitDocument7 pagesCS Micro 1 UnitAtharv MandawkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Programming: Violetta Cavalli-SforzaDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Computer Programming: Violetta Cavalli-SforzaVladimir Pascua CanaoNo ratings yet
- InformaticsDocument127 pagesInformaticsharidhruvanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ComputerDocument19 pagesIntroduction To ComputerJoey L. ArguezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document50 pagesChapter 1saloniNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Intro To ProgrammingDocument33 pagesModule 1 - Intro To ProgrammingCARLA JOY TRINIDADNo ratings yet
- Sjcbi-2nd Module-App-Development-FinalDocument5 pagesSjcbi-2nd Module-App-Development-FinalJohn Kenneth CabreraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer ProgrammingDocument31 pagesIntroduction To Computer ProgrammingDinesh LasanthaNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming: SECT-M1082Document22 pagesComputer Programming: SECT-M1082ibrahim mohammedNo ratings yet
- Scientific Programming Language: Miss Faryal Batool BS Mathematics 3 SemesterDocument17 pagesScientific Programming Language: Miss Faryal Batool BS Mathematics 3 SemesterrimshaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computers and JavaDocument64 pagesIntroduction To Computers and JavaAmeer QuinnNo ratings yet
- Compiler ConstructionDocument29 pagesCompiler ConstructionMosam ShambharkarNo ratings yet
- Cape Notes Unit1 Module 3 Content 12Document33 pagesCape Notes Unit1 Module 3 Content 12Rayando Rajae WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Compiler Construction: By: Engr. Muhammad Adnan Malik Class of BS-CS, NCBA&E, MULTANDocument64 pagesCompiler Construction: By: Engr. Muhammad Adnan Malik Class of BS-CS, NCBA&E, MULTANNaziaNo ratings yet
- What Is Computer Program?Document60 pagesWhat Is Computer Program?Zed DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- CS101 Lecture 02 - Introduction To Computers & Programming Part 2Document52 pagesCS101 Lecture 02 - Introduction To Computers & Programming Part 2JohnNo ratings yet
- Form FourDocument22 pagesForm Fourcazmi AndirahmanNo ratings yet
- Software, and Language ProcessorsDocument16 pagesSoftware, and Language ProcessorsSandeep SahaNo ratings yet
- Pograming LanguageDocument25 pagesPograming LanguageSumaira GulzarNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 1Document28 pagesChapter2 1Yosef KirosNo ratings yet
- Software Categories: - System SW - Application SWDocument23 pagesSoftware Categories: - System SW - Application SWSimbarashe MataireNo ratings yet
- IT102-LecturePresentation 3Document59 pagesIT102-LecturePresentation 3deniel dacilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Software Concepts: IntroductionDocument12 pagesChapter-4 Software Concepts: IntroductionAskok RajNo ratings yet
- 12A-Creating Computer ProgramsDocument52 pages12A-Creating Computer ProgramsCristiano RonaldoNo ratings yet
- Computer NoteDocument40 pagesComputer Noteapi-3832224No ratings yet
- Structured ProgrammingDocument17 pagesStructured ProgrammingujjwolNo ratings yet
- Programming: (Autonomous) Shamshabad - 501 218, HyderabadDocument172 pagesProgramming: (Autonomous) Shamshabad - 501 218, Hyderabadkanishka RahejaNo ratings yet
- Programming and Logic Slide 1Document39 pagesProgramming and Logic Slide 1Kaaĩ Waweru NgothoNo ratings yet
- Module 13 Overview of Computer ProgrammingDocument32 pagesModule 13 Overview of Computer ProgrammingMadaraNo ratings yet
- Principles of Programming: DR Rajesh Panda, SR - Technical Officer - Cad/Cam, CipetDocument26 pagesPrinciples of Programming: DR Rajesh Panda, SR - Technical Officer - Cad/Cam, CipetRajesh PandaNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR KIDS: An Easy Step-by-Step Guide For Young Programmers To Learn Coding Skills (2022 Crash Course for Newbies)From EverandCOMPUTER PROGRAMMING FOR KIDS: An Easy Step-by-Step Guide For Young Programmers To Learn Coding Skills (2022 Crash Course for Newbies)No ratings yet
- Presentation Group #8Document29 pagesPresentation Group #8talhagg333 talhagg333No ratings yet
- Women Empowerment For BIDocument25 pagesWomen Empowerment For BItalhagg333 talhagg333No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document26 pagesChapter 3talhagg333 talhagg333No ratings yet
- Buffers 512.-1Document22 pagesBuffers 512.-1talhagg333 talhagg333No ratings yet
- Cybersecurity in Operational Technology: Special ReportDocument15 pagesCybersecurity in Operational Technology: Special ReportAdrian ReyesNo ratings yet
- Ecss M ST 40c Rev.1 (6march2009)Document103 pagesEcss M ST 40c Rev.1 (6march2009)jsadachiNo ratings yet
- Indonesian AP Agility v2.0Document9 pagesIndonesian AP Agility v2.0KOFAX TANKNo ratings yet
- 1 Introductionssqw: Java Programming ProblemDocument11 pages1 Introductionssqw: Java Programming ProblemrevanthNo ratings yet
- About SAP BTPDocument2 pagesAbout SAP BTPsouvik_c82No ratings yet
- 16 CVSSDocument23 pages16 CVSSIma Fathia WorkspaceNo ratings yet
- Egmclipz PDF 1686685663Document23 pagesEgmclipz PDF 1686685663Vrishabh SehgalNo ratings yet
- Uvic Engr120 Robot CodeDocument4 pagesUvic Engr120 Robot CodeDannyDucHuynhNo ratings yet
- 010RCM IntroDocument39 pages010RCM Introkhalid ahmedNo ratings yet
- Common RailDocument3 pagesCommon RailKariem R Noweer100% (1)
- Reference Data Types in JavaDocument3 pagesReference Data Types in Javaeyn batallaNo ratings yet
- IPM Product Testing With Selenium Learning Path123Document40 pagesIPM Product Testing With Selenium Learning Path123new bie testerNo ratings yet
- NASA - STD - 8719.13C Sftware Safety StandardsDocument60 pagesNASA - STD - 8719.13C Sftware Safety StandardsGoutam BiswasNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet: On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) For Vehicles - September 2014Document2 pagesFact Sheet: On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) For Vehicles - September 2014muslimNo ratings yet
- Unit 7: Parameters, Return, and LibrariesDocument146 pagesUnit 7: Parameters, Return, and Librariesfrancis zhengNo ratings yet
- Task - E Engine Mechanical, LKS-2019 WILKER 2 JATIM AutomobileDocument3 pagesTask - E Engine Mechanical, LKS-2019 WILKER 2 JATIM AutomobileIQ Twenty-SixNo ratings yet
- EX4 ConstraintDocument3 pagesEX4 ConstraintAbhinaya S AP CSENo ratings yet
- Design ControlDocument3 pagesDesign ControlMyra AwanNo ratings yet
- Textbook System Engineering Practices 1St Edition Ian Faulconbridge Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook System Engineering Practices 1St Edition Ian Faulconbridge Ebook All Chapter PDFgina.bigley995100% (2)
- Pu066 P-Drive: Mechanical System Fuel SystemDocument2 pagesPu066 P-Drive: Mechanical System Fuel SystemhNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Billing SystemDocument15 pagesPharmacy Billing SystemTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- BH0 013Document57 pagesBH0 013justinbowkerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-Project Planning and Control1Document78 pagesLecture 5-Project Planning and Control1FarEast RamdzanNo ratings yet
- Major Project Report Format For Final Year StudentsDocument3 pagesMajor Project Report Format For Final Year StudentsDeepak Kumar Rajak0% (1)
- Introduction To Software EngineeringDocument142 pagesIntroduction To Software EngineeringJaro Alexander AguilarNo ratings yet
- Angular Project StructureDocument7 pagesAngular Project StructureJyothi AmpallyNo ratings yet
- Selenium With Java Course ContentDocument26 pagesSelenium With Java Course Contentpraveen murugesanNo ratings yet