Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1.tehran Yalta Potsdam Revsion Card.123423431
1.tehran Yalta Potsdam Revsion Card.123423431
Uploaded by
tsuyaa2506Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Igcse History Cold War Notes PDFDocument16 pagesIgcse History Cold War Notes PDFLily Potter100% (2)
- The Third Reich Beginners Strategy GuideDocument4 pagesThe Third Reich Beginners Strategy Guidenemesisuk100% (2)
- Chapter 1 and 2 Fact File: HistoryDocument12 pagesChapter 1 and 2 Fact File: HistoryJemima KaishaNo ratings yet
- 2 Post War Conferences S7his2Document15 pages2 Post War Conferences S7his2louNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FOUR Who Was To Blame For The Cold War PDFDocument80 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Who Was To Blame For The Cold War PDFMuhammadhNo ratings yet
- Treaty of VersaillesDocument21 pagesTreaty of Versaillesapi-334758672No ratings yet
- Essential Question: - What Were The Terms of The Treaty of Versailles That Ended World War I?Document21 pagesEssential Question: - What Were The Terms of The Treaty of Versailles That Ended World War I?Reshma Dhital Student - PantherCreekHSNo ratings yet
- Cold WarDocument28 pagesCold Warkismut.badeshaNo ratings yet
- History: Treaties Signed During 1900-1980Document2 pagesHistory: Treaties Signed During 1900-1980Jeremy Ang Wei YaoNo ratings yet
- Who Was To Blame For The Cold War NOTESDocument3 pagesWho Was To Blame For The Cold War NOTESM8 GETTHECAMERANo ratings yet
- Berlin BlocadeDocument2 pagesBerlin BlocadeRitik TyagiNo ratings yet
- Cold War Knowledge MapsDocument10 pagesCold War Knowledge MapsWolfwood ManilagNo ratings yet
- Causes of ww2Document3 pagesCauses of ww2rudramohit7No ratings yet
- IGCSE History SummaryDocument5 pagesIGCSE History SummaryMithunSheregar100% (1)
- 3.2 The Grand Alliance - PowerPoint PresentationDocument15 pages3.2 The Grand Alliance - PowerPoint Presentationwon0006.norwood.vic.eduNo ratings yet
- Treaty of VersaillesDocument36 pagesTreaty of VersaillesdickNo ratings yet
- The Inter-War Years Work Book Paris and Post War TreatiesDocument14 pagesThe Inter-War Years Work Book Paris and Post War TreatiesRhea AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 1 Cold War Reading Assignment 1Document7 pages1 Cold War Reading Assignment 1mcurdiaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Who Was To Blame For The Cold WarDocument18 pages4 - Who Was To Blame For The Cold Warlil NemoNo ratings yet
- Cold WarDocument9 pagesCold WarIna NordsethNo ratings yet
- A10: Superpower Relations 1945-1962: Key Events: Causes Key Features ConsequencesDocument15 pagesA10: Superpower Relations 1945-1962: Key Events: Causes Key Features ConsequencesMok 144No ratings yet
- Paper 1, Section B Conflict and Tension, 1918-1939 The Treaty of VersaillesDocument25 pagesPaper 1, Section B Conflict and Tension, 1918-1939 The Treaty of VersaillesKondwani LunguNo ratings yet
- Conflict and Tension Checkist and Revision BookDocument19 pagesConflict and Tension Checkist and Revision Book20sirohiuNo ratings yet
- Treaty of Versailles - History NotesDocument3 pagesTreaty of Versailles - History Noteswaveki6188No ratings yet
- Coursework Final Proposal Sofia MDocument7 pagesCoursework Final Proposal Sofia MHola con SofiNo ratings yet
- International Relations in The 20th Century Treaty of VersaillesDocument17 pagesInternational Relations in The 20th Century Treaty of VersaillesWatuzana Kasengele100% (1)
- IGCSE History - Lucas LehmannDocument135 pagesIGCSE History - Lucas LehmannLucas LehmannNo ratings yet
- E-Book: HOW DID THE COLD WAR DEVELOP? 1943-56 (Origins) (Studyguide - PK) The Widening Gulf Between The AlliesDocument32 pagesE-Book: HOW DID THE COLD WAR DEVELOP? 1943-56 (Origins) (Studyguide - PK) The Widening Gulf Between The AlliesKabeloNo ratings yet
- The Second World WarDocument6 pagesThe Second World WarVINCENT MUHARINo ratings yet
- The Second World WarDocument6 pagesThe Second World WarVINCENT MUHARINo ratings yet
- Unit 6 World War Ii: Causes and Consequences: 6.0 ObjectivesDocument18 pagesUnit 6 World War Ii: Causes and Consequences: 6.0 ObjectivesPrateek BhagatNo ratings yet
- Causes of WWII 2021Document18 pagesCauses of WWII 2021Shajra AkramNo ratings yet
- Were The Peace Treaties of 1919-23 FairDocument13 pagesWere The Peace Treaties of 1919-23 Fairvishrutta5No ratings yet
- Causes of World War TwoDocument2 pagesCauses of World War TwoenyonamampNo ratings yet
- The Big Three During The War Links:: Yalta (Feb 1945)Document3 pagesThe Big Three During The War Links:: Yalta (Feb 1945)Zaina ImamNo ratings yet
- Script: Was Germany Who Chose To Start The War. Thus Why Germany Is Responsible For Causing WorldDocument3 pagesScript: Was Germany Who Chose To Start The War. Thus Why Germany Is Responsible For Causing World5ryng3No ratings yet
- Period 4 - Politics and Power IDocument18 pagesPeriod 4 - Politics and Power IFlounderNo ratings yet
- Causes of WW2Document15 pagesCauses of WW2spade.ace07No ratings yet
- This Is A Transcript of The Podcast From: Terms and Effects of The Treaty of VersaillesDocument4 pagesThis Is A Transcript of The Podcast From: Terms and Effects of The Treaty of VersaillesSoo Ke XinNo ratings yet
- The Treaty of Versaille 1Document4 pagesThe Treaty of Versaille 1api-263356428No ratings yet
- Yalta Conference: Done By: Kritika, Rupadri, Shneha, Shreyoshi, SwagataDocument7 pagesYalta Conference: Done By: Kritika, Rupadri, Shneha, Shreyoshi, SwagataSwagata Bhowmik RoyNo ratings yet
- Yalta vs. PotsdamDocument1 pageYalta vs. PotsdamChris Way50% (2)
- The 1930's Appeasement PolicyDocument3 pagesThe 1930's Appeasement PolicyAnnmar6No ratings yet
- Early Years BackgroundDocument5 pagesEarly Years BackgroundKrishrulesNo ratings yet
- History Notes Chapter 1Document9 pagesHistory Notes Chapter 1BeautifulNo ratings yet
- IGCSE HISTORY REVISION NOTES - Part 1 International Relations 1919 To 2000Document58 pagesIGCSE HISTORY REVISION NOTES - Part 1 International Relations 1919 To 2000Paul AniNo ratings yet
- 14 Outbreak of World War II and Its Impact in ColoniesDocument25 pages14 Outbreak of World War II and Its Impact in Coloniesnishaojha341No ratings yet
- KO4 (Origins of CW) Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesKO4 (Origins of CW) Knowledge OrganiserSamarjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Why Did LoN FailDocument3 pagesWhy Did LoN Failhello.hy123No ratings yet
- HISTORY Revision 2021 Semester 1Document17 pagesHISTORY Revision 2021 Semester 1aplloNo ratings yet
- The Yalta and Potsdam ConferencesDocument1 pageThe Yalta and Potsdam ConferencesOphélie Arnaud-MoineloNo ratings yet
- 9 2 Partition of AfricaDocument19 pages9 2 Partition of AfricaAngelo LagmayNo ratings yet
- Yalta Rough DraftDocument12 pagesYalta Rough Draftapi-314711687No ratings yet
- Friends and Family Quiz, Hitler's F PolicyDocument2 pagesFriends and Family Quiz, Hitler's F PolicykatelinzvitaNo ratings yet
- Super Power Relations - Diff StyleDocument11 pagesSuper Power Relations - Diff StylenftsaremyaddictionNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The Cold WarDocument2 pagesThe Origin of The Cold WarzeinabNo ratings yet
- 12Document17 pages12api-3723991No ratings yet
- History Essay - (Causes For WW2 Outbreak)Document3 pagesHistory Essay - (Causes For WW2 Outbreak)SarahNo ratings yet
- DeMarco Text PagesDocument36 pagesDeMarco Text Pagesr ylaplayeNo ratings yet
- What Happened After World War II? History Book for Kids | Children's War & Military BooksFrom EverandWhat Happened After World War II? History Book for Kids | Children's War & Military BooksNo ratings yet
- Owen Connelly, Blundering To Glory (Wilmington: Scholarly Resources, 1987), 1. Ibid. Ibid., 2. Ibid., 80Document7 pagesOwen Connelly, Blundering To Glory (Wilmington: Scholarly Resources, 1987), 1. Ibid. Ibid., 2. Ibid., 80Andrew ZimmermanNo ratings yet
- Source Analysis Origins of NazismDocument2 pagesSource Analysis Origins of NazismEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Why Were Britain and France Willing To Go To War in 1939 and Not 1938Document7 pagesWhy Were Britain and France Willing To Go To War in 1939 and Not 1938Alexander LynskeyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Unit 4 StartcoldwarDocument2 pagesYear 10 Unit 4 Startcoldwarapi-237723807100% (1)
- Teks The Battle of SurabayaDocument1 pageTeks The Battle of SurabayaAdi PutraNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument1 pageBrochureRUDOLF ADRIASNo ratings yet
- D-Day 75th Anniversary: Daily News ArticleDocument9 pagesD-Day 75th Anniversary: Daily News ArticleMK PCNo ratings yet
- History Review - UNIT 6Document9 pagesHistory Review - UNIT 6E.DoolabhNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of Japanese Militarism TimelineDocument1 pageThe Rise and Fall of Japanese Militarism TimelineMikee D. ApaoNo ratings yet
- War and ConflictDocument4 pagesWar and ConflictReggie AguiarNo ratings yet
- Invasion of Poland, Fall 1939 - HolocaustDocument5 pagesInvasion of Poland, Fall 1939 - HolocaustKarolina PopławskaNo ratings yet
- World War IIDocument9 pagesWorld War IITinisha PurohitNo ratings yet
- World War II Timeline Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesWorld War II Timeline Worksheet PDFViviana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- How Had The USSR Gained Control Over Eastern EuropeDocument14 pagesHow Had The USSR Gained Control Over Eastern EuropeTom WatersNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 League of Nations Flash Card & Revision Grid.68037007Document4 pagesPaper 2 League of Nations Flash Card & Revision Grid.68037007Historia UNAB Viña del MarNo ratings yet
- VDC: The Weekly Statistical ReportDocument8 pagesVDC: The Weekly Statistical ReportimpunitywatchNo ratings yet
- WwiDocument3 pagesWwiapi-286829626No ratings yet
- Battle of The Somme RevisionDocument2 pagesBattle of The Somme RevisiontytrNo ratings yet
- Russia's War by Richard Overy - 9780140271690 - PenguinRandomHouse - Com - BooksDocument3 pagesRussia's War by Richard Overy - 9780140271690 - PenguinRandomHouse - Com - BooksMateus SoaresNo ratings yet
- Gold Coast in World War II - WikipediaDocument4 pagesGold Coast in World War II - WikipediaMichael NorteyNo ratings yet
- Post World War 1 and Aims of The Big 3Document19 pagesPost World War 1 and Aims of The Big 3ByeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 NotesDocument35 pagesChapter 16 NotesFawad Hayat MohmandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 World War I and Its AftermathDocument3 pagesChapter 16 World War I and Its Aftermathapi-264481761No ratings yet
- Apush Unit 7 DBQDocument5 pagesApush Unit 7 DBQfailures12No ratings yet
- Downfall of NapoleonDocument3 pagesDownfall of NapoleonValerie Angel MtemaNo ratings yet
- The Essential World History - All Chapter 25 QuestionsDocument4 pagesThe Essential World History - All Chapter 25 QuestionslegofriesNo ratings yet
- World War 1 - Lesson 2 NotesDocument3 pagesWorld War 1 - Lesson 2 Notesapi-644324581No ratings yet
- 1 SA Infantry Div WW2Document5 pages1 SA Infantry Div WW2pcojediNo ratings yet
- NapoleanDocument28 pagesNapoleanFarhan AhmadNo ratings yet
1.tehran Yalta Potsdam Revsion Card.123423431
1.tehran Yalta Potsdam Revsion Card.123423431
Uploaded by
tsuyaa2506Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.tehran Yalta Potsdam Revsion Card.123423431
1.tehran Yalta Potsdam Revsion Card.123423431
Uploaded by
tsuyaa2506Copyright:
Available Formats
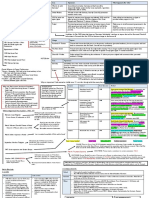
Superpower Relations and the Cold War
FLASHPOINT REVISION
Event: Tehran, Yalta Potsdam Date: Nov 1943, Feb 1943, July/August 1943
People: Stalin, Roosevelt, Churchill, Attlee, Truman
Exemplar answer: 8 marks
Cause:
Write a narrative account of the Tehran, Yalta and Potsdam conferences
1941- Grand Alliance formed between USA and USSR and GB to defeat Germany. USA and GB suspicious of
The first key event between 1943-45 was the Tehran meeting. This was a meeting between Roosevelt, Stalin
Stalin
and Churchill at Tehran in Iran in November 1943. Roosevelt tended to side with Stalin rather than Churchill
Leaderswas
and the meeting of Grand
seenAlliance met three
as a success times aThe
for Stalin. yearmain
during war
agreements were that: Britain and the USA agreed
to open a second front by invading France; the USSR agreed to wage war against Japan once Germany was
defeated; a United Nations was to be set up and eastern Poland would become part of the USSR.
Narrative:
The second
The Grand key event
Alliance was
first metatinYalta.
TehranThis wasathe
to plan last meeting
winning between
strategy to end thethe
war.big
Thethree. Churchill
following apparently
agreements were felt
alienated
made by how well Roosevelt and Stalin got on. Stalin wanted Germany to pay huge reparations but
Roosevelt and Churchill disagreed and did not want Germany punished too harshly. At Yalta it was agreed: that
he USSR would
The main agreements
enter were that:
the war against Britain
Japan andand
thisthe USA
was agreed
similar totowhat
openwas
a second
agreedfront by invading
at Tehran. France;
What was the
different to Tehran was that it was decided that Germany (and Berlin) would be divided into four zonesup
USSR agreed to wage war against Japan once Germany was defeated; a United Nations was to be set (US,
and
British, French andPoland
eastern Soviet) andbecome
would that there
partwould
of the be free elections for countries liberated from Germany and the
USSR.
right to join the United Nations and that Eastern Europe would be a Soviet ‘sphere of influence’.
Two years later the big three held a second meeting to discuss winning the war and the government of post war
The last key
Europe. event
Stalin wasof the peacetoconferences
determined was athePotsdam.
keep the territory had won. Between Yaltaagreements
The following and Potsdam wereamade:
lot had changed.
For example, Soviet troops had liberated Eastern Europe but had not removed their presence; a communist
At Yalta
government it wasset
had been agreed:
up inthe USSRby
Poland would enter
Stalin; thethe
Redwar against
Army wasJapan; Germany
the biggest in(and Berlin) and
the world would
thebeUSA
divided
had
into four zones (US, British, French and Soviet); free elections for countries liberated
secretly tested a nuclear bomb in the USA. When Truman told Stalin about this he was furious. The meeting from Germany; the
was between rightAttlee,
to join Truman
the United
andNations
Stalin.and that Eastern
At Potsdam Europe
it was wouldGermany
agreed: be a Soviet ‘sphere
would beofdivided
influence’.
into four zones
as previously agreed; Germany would be demilitarised; democracy was to be re-established in Germany;
Betweenhad
Germany Yalta
toand
payPotsdam a lot had
reparations andchanged.
the USSRFor example,
would Sovieta troops
be given quarterhad
ofliberated
goods madeEastern Europe
in the but had
Western not of
zone
removed the
Germany; theirNazi
presence; a communist
party was banned;government had been
full participation set up
in the in Poland
League by Stalin;
of Nations thePoland's
and Red Armyfrontier
was thetobiggest
be
in the world and the USA had
moved to the Oder and Neisse rivers.secretly tested a nuclear bomb in the USA. When Truman told Stalin about this he was
furious. The meeting was between Attlee, Truman and Stalin. At Potsdam it was agreed:
Between 1943-45 there were three main peace conferences. The most events that occurred were probably the
ofGermany
creation would
the United be divided
Nations into four
at Tehran zones as
because previously
this became agreed; Germany would
a key institution whenbe demilitarised;
trying to resolve world
democracy
conflicts. Another keywas to bewas
event re-established
the dividinginof
Germany;
Germany Germany hadzones
into four to payatreparations and the
Yalta because thisUSSR would
became anbearea
of mutual given
distrust that led
a quarter of into
goodsthe ColdinWar.
made the Western zone of Germany; the Nazi party was banned; full
participation in the League of Nations and Poland's frontier to be moved to the Oder and Neisse rivers.
Consequence:
Poland in Soviet Sphere of influence
Establishment of United Nations
Germany divided into four zones
Berlin divided into zones of occupation
Lead to increased tension between USA and Soviet Union
Importance:
While Britain, the USA and the Soviet Union were able to work together to defeat Germany, tension was
increasing between the wartime alliances. Differences were beginning to emerge over the future of
Germany and Eastern Europe. Roosevelt’s death had led to Truman becoming president and he was much
more distrustful of the Soviet Union increasing tensions between the USA and the Soviet Union
You might also like
- Igcse History Cold War Notes PDFDocument16 pagesIgcse History Cold War Notes PDFLily Potter100% (2)
- The Third Reich Beginners Strategy GuideDocument4 pagesThe Third Reich Beginners Strategy Guidenemesisuk100% (2)
- Chapter 1 and 2 Fact File: HistoryDocument12 pagesChapter 1 and 2 Fact File: HistoryJemima KaishaNo ratings yet
- 2 Post War Conferences S7his2Document15 pages2 Post War Conferences S7his2louNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER FOUR Who Was To Blame For The Cold War PDFDocument80 pagesCHAPTER FOUR Who Was To Blame For The Cold War PDFMuhammadhNo ratings yet
- Treaty of VersaillesDocument21 pagesTreaty of Versaillesapi-334758672No ratings yet
- Essential Question: - What Were The Terms of The Treaty of Versailles That Ended World War I?Document21 pagesEssential Question: - What Were The Terms of The Treaty of Versailles That Ended World War I?Reshma Dhital Student - PantherCreekHSNo ratings yet
- Cold WarDocument28 pagesCold Warkismut.badeshaNo ratings yet
- History: Treaties Signed During 1900-1980Document2 pagesHistory: Treaties Signed During 1900-1980Jeremy Ang Wei YaoNo ratings yet
- Who Was To Blame For The Cold War NOTESDocument3 pagesWho Was To Blame For The Cold War NOTESM8 GETTHECAMERANo ratings yet
- Berlin BlocadeDocument2 pagesBerlin BlocadeRitik TyagiNo ratings yet
- Cold War Knowledge MapsDocument10 pagesCold War Knowledge MapsWolfwood ManilagNo ratings yet
- Causes of ww2Document3 pagesCauses of ww2rudramohit7No ratings yet
- IGCSE History SummaryDocument5 pagesIGCSE History SummaryMithunSheregar100% (1)
- 3.2 The Grand Alliance - PowerPoint PresentationDocument15 pages3.2 The Grand Alliance - PowerPoint Presentationwon0006.norwood.vic.eduNo ratings yet
- Treaty of VersaillesDocument36 pagesTreaty of VersaillesdickNo ratings yet
- The Inter-War Years Work Book Paris and Post War TreatiesDocument14 pagesThe Inter-War Years Work Book Paris and Post War TreatiesRhea AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 1 Cold War Reading Assignment 1Document7 pages1 Cold War Reading Assignment 1mcurdiaNo ratings yet
- 4 - Who Was To Blame For The Cold WarDocument18 pages4 - Who Was To Blame For The Cold Warlil NemoNo ratings yet
- Cold WarDocument9 pagesCold WarIna NordsethNo ratings yet
- A10: Superpower Relations 1945-1962: Key Events: Causes Key Features ConsequencesDocument15 pagesA10: Superpower Relations 1945-1962: Key Events: Causes Key Features ConsequencesMok 144No ratings yet
- Paper 1, Section B Conflict and Tension, 1918-1939 The Treaty of VersaillesDocument25 pagesPaper 1, Section B Conflict and Tension, 1918-1939 The Treaty of VersaillesKondwani LunguNo ratings yet
- Conflict and Tension Checkist and Revision BookDocument19 pagesConflict and Tension Checkist and Revision Book20sirohiuNo ratings yet
- Treaty of Versailles - History NotesDocument3 pagesTreaty of Versailles - History Noteswaveki6188No ratings yet
- Coursework Final Proposal Sofia MDocument7 pagesCoursework Final Proposal Sofia MHola con SofiNo ratings yet
- International Relations in The 20th Century Treaty of VersaillesDocument17 pagesInternational Relations in The 20th Century Treaty of VersaillesWatuzana Kasengele100% (1)
- IGCSE History - Lucas LehmannDocument135 pagesIGCSE History - Lucas LehmannLucas LehmannNo ratings yet
- E-Book: HOW DID THE COLD WAR DEVELOP? 1943-56 (Origins) (Studyguide - PK) The Widening Gulf Between The AlliesDocument32 pagesE-Book: HOW DID THE COLD WAR DEVELOP? 1943-56 (Origins) (Studyguide - PK) The Widening Gulf Between The AlliesKabeloNo ratings yet
- The Second World WarDocument6 pagesThe Second World WarVINCENT MUHARINo ratings yet
- The Second World WarDocument6 pagesThe Second World WarVINCENT MUHARINo ratings yet
- Unit 6 World War Ii: Causes and Consequences: 6.0 ObjectivesDocument18 pagesUnit 6 World War Ii: Causes and Consequences: 6.0 ObjectivesPrateek BhagatNo ratings yet
- Causes of WWII 2021Document18 pagesCauses of WWII 2021Shajra AkramNo ratings yet
- Were The Peace Treaties of 1919-23 FairDocument13 pagesWere The Peace Treaties of 1919-23 Fairvishrutta5No ratings yet
- Causes of World War TwoDocument2 pagesCauses of World War TwoenyonamampNo ratings yet
- The Big Three During The War Links:: Yalta (Feb 1945)Document3 pagesThe Big Three During The War Links:: Yalta (Feb 1945)Zaina ImamNo ratings yet
- Script: Was Germany Who Chose To Start The War. Thus Why Germany Is Responsible For Causing WorldDocument3 pagesScript: Was Germany Who Chose To Start The War. Thus Why Germany Is Responsible For Causing World5ryng3No ratings yet
- Period 4 - Politics and Power IDocument18 pagesPeriod 4 - Politics and Power IFlounderNo ratings yet
- Causes of WW2Document15 pagesCauses of WW2spade.ace07No ratings yet
- This Is A Transcript of The Podcast From: Terms and Effects of The Treaty of VersaillesDocument4 pagesThis Is A Transcript of The Podcast From: Terms and Effects of The Treaty of VersaillesSoo Ke XinNo ratings yet
- The Treaty of Versaille 1Document4 pagesThe Treaty of Versaille 1api-263356428No ratings yet
- Yalta Conference: Done By: Kritika, Rupadri, Shneha, Shreyoshi, SwagataDocument7 pagesYalta Conference: Done By: Kritika, Rupadri, Shneha, Shreyoshi, SwagataSwagata Bhowmik RoyNo ratings yet
- Yalta vs. PotsdamDocument1 pageYalta vs. PotsdamChris Way50% (2)
- The 1930's Appeasement PolicyDocument3 pagesThe 1930's Appeasement PolicyAnnmar6No ratings yet
- Early Years BackgroundDocument5 pagesEarly Years BackgroundKrishrulesNo ratings yet
- History Notes Chapter 1Document9 pagesHistory Notes Chapter 1BeautifulNo ratings yet
- IGCSE HISTORY REVISION NOTES - Part 1 International Relations 1919 To 2000Document58 pagesIGCSE HISTORY REVISION NOTES - Part 1 International Relations 1919 To 2000Paul AniNo ratings yet
- 14 Outbreak of World War II and Its Impact in ColoniesDocument25 pages14 Outbreak of World War II and Its Impact in Coloniesnishaojha341No ratings yet
- KO4 (Origins of CW) Knowledge OrganiserDocument3 pagesKO4 (Origins of CW) Knowledge OrganiserSamarjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Why Did LoN FailDocument3 pagesWhy Did LoN Failhello.hy123No ratings yet
- HISTORY Revision 2021 Semester 1Document17 pagesHISTORY Revision 2021 Semester 1aplloNo ratings yet
- The Yalta and Potsdam ConferencesDocument1 pageThe Yalta and Potsdam ConferencesOphélie Arnaud-MoineloNo ratings yet
- 9 2 Partition of AfricaDocument19 pages9 2 Partition of AfricaAngelo LagmayNo ratings yet
- Yalta Rough DraftDocument12 pagesYalta Rough Draftapi-314711687No ratings yet
- Friends and Family Quiz, Hitler's F PolicyDocument2 pagesFriends and Family Quiz, Hitler's F PolicykatelinzvitaNo ratings yet
- Super Power Relations - Diff StyleDocument11 pagesSuper Power Relations - Diff StylenftsaremyaddictionNo ratings yet
- The Origin of The Cold WarDocument2 pagesThe Origin of The Cold WarzeinabNo ratings yet
- 12Document17 pages12api-3723991No ratings yet
- History Essay - (Causes For WW2 Outbreak)Document3 pagesHistory Essay - (Causes For WW2 Outbreak)SarahNo ratings yet
- DeMarco Text PagesDocument36 pagesDeMarco Text Pagesr ylaplayeNo ratings yet
- What Happened After World War II? History Book for Kids | Children's War & Military BooksFrom EverandWhat Happened After World War II? History Book for Kids | Children's War & Military BooksNo ratings yet
- Owen Connelly, Blundering To Glory (Wilmington: Scholarly Resources, 1987), 1. Ibid. Ibid., 2. Ibid., 80Document7 pagesOwen Connelly, Blundering To Glory (Wilmington: Scholarly Resources, 1987), 1. Ibid. Ibid., 2. Ibid., 80Andrew ZimmermanNo ratings yet
- Source Analysis Origins of NazismDocument2 pagesSource Analysis Origins of NazismEnriqueNo ratings yet
- Why Were Britain and France Willing To Go To War in 1939 and Not 1938Document7 pagesWhy Were Britain and France Willing To Go To War in 1939 and Not 1938Alexander LynskeyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Unit 4 StartcoldwarDocument2 pagesYear 10 Unit 4 Startcoldwarapi-237723807100% (1)
- Teks The Battle of SurabayaDocument1 pageTeks The Battle of SurabayaAdi PutraNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument1 pageBrochureRUDOLF ADRIASNo ratings yet
- D-Day 75th Anniversary: Daily News ArticleDocument9 pagesD-Day 75th Anniversary: Daily News ArticleMK PCNo ratings yet
- History Review - UNIT 6Document9 pagesHistory Review - UNIT 6E.DoolabhNo ratings yet
- The Rise and Fall of Japanese Militarism TimelineDocument1 pageThe Rise and Fall of Japanese Militarism TimelineMikee D. ApaoNo ratings yet
- War and ConflictDocument4 pagesWar and ConflictReggie AguiarNo ratings yet
- Invasion of Poland, Fall 1939 - HolocaustDocument5 pagesInvasion of Poland, Fall 1939 - HolocaustKarolina PopławskaNo ratings yet
- World War IIDocument9 pagesWorld War IITinisha PurohitNo ratings yet
- World War II Timeline Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesWorld War II Timeline Worksheet PDFViviana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- How Had The USSR Gained Control Over Eastern EuropeDocument14 pagesHow Had The USSR Gained Control Over Eastern EuropeTom WatersNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 League of Nations Flash Card & Revision Grid.68037007Document4 pagesPaper 2 League of Nations Flash Card & Revision Grid.68037007Historia UNAB Viña del MarNo ratings yet
- VDC: The Weekly Statistical ReportDocument8 pagesVDC: The Weekly Statistical ReportimpunitywatchNo ratings yet
- WwiDocument3 pagesWwiapi-286829626No ratings yet
- Battle of The Somme RevisionDocument2 pagesBattle of The Somme RevisiontytrNo ratings yet
- Russia's War by Richard Overy - 9780140271690 - PenguinRandomHouse - Com - BooksDocument3 pagesRussia's War by Richard Overy - 9780140271690 - PenguinRandomHouse - Com - BooksMateus SoaresNo ratings yet
- Gold Coast in World War II - WikipediaDocument4 pagesGold Coast in World War II - WikipediaMichael NorteyNo ratings yet
- Post World War 1 and Aims of The Big 3Document19 pagesPost World War 1 and Aims of The Big 3ByeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 NotesDocument35 pagesChapter 16 NotesFawad Hayat MohmandNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 World War I and Its AftermathDocument3 pagesChapter 16 World War I and Its Aftermathapi-264481761No ratings yet
- Apush Unit 7 DBQDocument5 pagesApush Unit 7 DBQfailures12No ratings yet
- Downfall of NapoleonDocument3 pagesDownfall of NapoleonValerie Angel MtemaNo ratings yet
- The Essential World History - All Chapter 25 QuestionsDocument4 pagesThe Essential World History - All Chapter 25 QuestionslegofriesNo ratings yet
- World War 1 - Lesson 2 NotesDocument3 pagesWorld War 1 - Lesson 2 Notesapi-644324581No ratings yet
- 1 SA Infantry Div WW2Document5 pages1 SA Infantry Div WW2pcojediNo ratings yet
- NapoleanDocument28 pagesNapoleanFarhan AhmadNo ratings yet