Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsIntegumentary System
Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Arnie Jean SalazarThis document provides descriptions of common skin diseases and disorders including acne, psoriasis, staph infections, chickenpox, and fungal infections. For each condition, it lists the description, causes and risk factors, symptoms, and typical treatment options. The conditions covered include bacterial, viral, and fungal causes of skin problems. Treatment involves both medical and home care approaches depending on the specific disease or disorder. Maintaining good hygiene practices can help prevent some infectious skin conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Master The Chamber: Dr. Mohammad RaselDocument28 pagesMaster The Chamber: Dr. Mohammad RaselMensa DigiWorldNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Nuts & BoltsDocument42 pagesMicrobiology Nuts & Boltsteena jacobNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of CellulitisDocument8 pagesConcept Map of CellulitisReese Anne100% (1)
- Skin Care For HealthDocument3 pagesSkin Care For HealthGin MananganNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - The SkinDocument5 pagesAnaphy - The SkinGwyn Louise CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Equine Medicine DISEASESDocument14 pagesEquine Medicine DISEASESlowi shooNo ratings yet
- DisordersDocument23 pagesDisordersShelly LazaritoNo ratings yet
- Disease and Cause Manifestation Treatment Prevention Bacteria SignsDocument14 pagesDisease and Cause Manifestation Treatment Prevention Bacteria SignsMc MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Male Genital DermDocument112 pagesMale Genital DermVũ CaoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDocument4 pagesDisorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDylan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Lectures JRRMMCDocument10 pagesDermatology Lectures JRRMMCGi Em100% (1)
- Skin ConditionsDocument3 pagesSkin ConditionsAlyssa AmayaNo ratings yet
- Skin AsthmaDocument7 pagesSkin AsthmaJames Domini Lopez LabianoNo ratings yet
- System Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Document1 pageSystem Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Kassandra MerrillNo ratings yet
- Narsum 1. Acne Treatment 10 Feb 2022Document26 pagesNarsum 1. Acne Treatment 10 Feb 2022Vheny YulandariNo ratings yet
- System Disorder ADDocument1 pageSystem Disorder ADSariahNo ratings yet
- Complication CL OsceDocument6 pagesComplication CL OsceAdam EdzelNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityNeriz Pineda0% (1)
- 11 Realism April Joy TeberioDocument1 page11 Realism April Joy TeberioApril Joy Malinao TeberioNo ratings yet
- Ms 1 Integumentary NursingDocument10 pagesMs 1 Integumentary NursingTrinity Veach100% (1)
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocument4 pagesNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of Childhoo1Document3 pagesCommunicable Diseases of Childhoo1esmirikNo ratings yet
- Hordeolum: Acute Abscess Within An Eyelid Sebaceous Gland: The Clinical PictureDocument3 pagesHordeolum: Acute Abscess Within An Eyelid Sebaceous Gland: The Clinical PictureCamNo ratings yet
- Nursing:: CommunityDocument59 pagesNursing:: CommunityIlyes RaniNo ratings yet
- 0-2873717490134913195Document18 pages0-2873717490134913195michellegin09No ratings yet
- Karanj Oil Research ArticleDocument12 pagesKaranj Oil Research ArticlesahilNo ratings yet
- Community Nursing Wound Care PresentationDocument56 pagesCommunity Nursing Wound Care PresentationkugernnesNo ratings yet
- PHARMA CHAP 12 and 19 UpDocument7 pagesPHARMA CHAP 12 and 19 UpBAUZON, JANINE, C.No ratings yet
- Case Study BurnDocument3 pagesCase Study BurnInday BebeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudydubouzettheresaNo ratings yet
- PBL - IntegumentaryDocument2 pagesPBL - Integumentarygie sarcedaNo ratings yet
- McAlinden Hordeolum PDFDocument3 pagesMcAlinden Hordeolum PDFNur Rakhma AkmaliaNo ratings yet
- PEDIA - Drug Study & NCPDocument24 pagesPEDIA - Drug Study & NCPCzarina Mae Lomboy100% (1)
- Case-Scenario-Oxygen Therapy-BuenconsejoDocument6 pagesCase-Scenario-Oxygen Therapy-BuenconsejoCarna BuenconsejoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: EliminationDocument2 pagesPharmacokinetics Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: EliminationChrislyn LangegNo ratings yet
- Drug Study With NCPDocument4 pagesDrug Study With NCPJoanne Kathleen SantolicesNo ratings yet
- DAY 2 Mahesa Burn Rehabilitation PresentasiDocument16 pagesDAY 2 Mahesa Burn Rehabilitation Presentasichristin megaNo ratings yet
- Acne NetterDocument2 pagesAcne NetterSELLULARNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Lec. Activity 1 (Repaired)Document1 pageNCM 114 Lec. Activity 1 (Repaired)Juan Miguel Caspe MangayaNo ratings yet
- Permethrin 5% Cream: Medication MOA Instruction CommentsDocument1 pagePermethrin 5% Cream: Medication MOA Instruction CommentsChron MedNo ratings yet
- Skin AbnormalsDocument2 pagesSkin AbnormalsJp CasperNo ratings yet
- Causative Agent Characteristic Symptom 1 Management: Surgery Is The Most Important Modality For MalignantDocument2 pagesCausative Agent Characteristic Symptom 1 Management: Surgery Is The Most Important Modality For MalignantJp CasperNo ratings yet
- Moisture Associated Skin Damage MASD Pathway Aug 22Document1 pageMoisture Associated Skin Damage MASD Pathway Aug 22rodolfo opidoNo ratings yet
- PsoriasisDocument27 pagesPsoriasisNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Ncma Course Task 11 PDFDocument4 pagesNcma Course Task 11 PDFJaja ManezNo ratings yet
- 7 Active Ingredients For Special Products: 7.1 Definition of Special CreamsDocument43 pages7 Active Ingredients For Special Products: 7.1 Definition of Special CreamsElizabeth TovittoNo ratings yet
- BURNSDocument26 pagesBURNSGaurav pareekNo ratings yet
- ImportantDocument21 pagesImportantGaurav pareekNo ratings yet
- Allergies Hives Rashes Handout 509kDocument2 pagesAllergies Hives Rashes Handout 509kIndu SinghNo ratings yet
- 56-Topical Drugs Used in The Treatment of Skin DisordersDocument13 pages56-Topical Drugs Used in The Treatment of Skin DisordersMujeebNo ratings yet
- Derma Quiz 3 NotesDocument11 pagesDerma Quiz 3 NotesJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Insect Bites StingsDocument1 pageInsect Bites StingsnamibadiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology NG CandidiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology NG CandidiasisJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- EczemaDocument13 pagesEczemaCollective123No ratings yet
- Dry Eye DiseaseDocument8 pagesDry Eye DiseaseaNo ratings yet
- Rash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: EmergencyDocument1 pageRash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: Emergencykdlsfk kajjksolsNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan RabiesDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan RabiesYanis Emmanuelle LimNo ratings yet
- Client Bed BathDocument6 pagesClient Bed BathLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Skin DiseasesDocument4 pagesSkin DiseaseschellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- Sarcoptes Scabei Var. HumanusDocument2 pagesSarcoptes Scabei Var. HumanusZai Ra DianaNo ratings yet
- Natural Products for Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue DisordersFrom EverandNatural Products for Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue DisordersNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System QuizDocument1 pageReproductive System QuizArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document14 pagesLesson 1Arnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Dietary AssignmentDocument2 pagesDietary AssignmentArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- MalnutritionDocument1 pageMalnutritionArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document24 pagesLesson 2Arnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Self From Psychological PerspectiveDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Self From Psychological PerspectiveArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Philosophical PerspectivesDocument20 pagesLesson 1 Philosophical PerspectivesArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 SOCIETY AND THE SELFDocument17 pagesLesson 2 SOCIETY AND THE SELFArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Thromboembolic Complications in Chronic Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument6 pagesThromboembolic Complications in Chronic Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY F - ChloramphericolDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY F - ChloramphericolJane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Formal Examination Period: Session 1, June 2019Document18 pagesFormal Examination Period: Session 1, June 2019Lynstel NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Epididymitis PDFDocument4 pagesChronic Epididymitis PDFDereck HowseNo ratings yet
- Calcarea CarbonicumDocument10 pagesCalcarea CarbonicumVictor CironeNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Trait TheoriesDocument8 pagesContemporary Trait TheoriesMuhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Types of Personality DisorderDocument2 pagesTypes of Personality DisorderWinnie Salazar AriolaNo ratings yet
- HIV Stigma IndexDocument36 pagesHIV Stigma Indexjohn mwambuNo ratings yet
- EuthanasiaDocument22 pagesEuthanasiaSANA SAFDARNo ratings yet
- ECG LictureDocument25 pagesECG LictureALi NursingNo ratings yet
- The Challenges and Perspectives of The Integration Between Virtual and Augmented Reality and Manual TherapiesDocument18 pagesThe Challenges and Perspectives of The Integration Between Virtual and Augmented Reality and Manual Therapiesradhianie djanNo ratings yet
- Fastidious Gram Negative RodsDocument74 pagesFastidious Gram Negative RodsMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Fulltext Schizophrenia v3 Id1026!12!2Document8 pagesFulltext Schizophrenia v3 Id1026!12!2Saskia MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Nov AIIMS 2018 Pathology Questions and Explanations by Dr. SUSHANT SONIDocument9 pagesNov AIIMS 2018 Pathology Questions and Explanations by Dr. SUSHANT SONIZahidha BegumNo ratings yet
- Care of Adults 28 Hematological and Oncological ManagementDocument40 pagesCare of Adults 28 Hematological and Oncological ManagementGaras AnnaBerniceNo ratings yet
- Aphasia and DysphasiaDocument8 pagesAphasia and Dysphasiamoizghani37No ratings yet
- Olivia Tween COGS Aphantasia Thesis Final Version PDFDocument23 pagesOlivia Tween COGS Aphantasia Thesis Final Version PDFJORGE ENRIQUE CAICEDO GONZ�LES100% (1)
- Neurologic ExaminationDocument67 pagesNeurologic Examinationሀይደር ዶ.ር100% (1)
- Physical Disability by FabricationDocument25 pagesPhysical Disability by FabricationALYELA PETERNo ratings yet
- ARISE QRP All 19 High YieldDocument267 pagesARISE QRP All 19 High YieldAnjali TamrakarNo ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument21 pagesBirth AsphyxiaAntonyNo ratings yet
- Sinus and FistulaDocument3 pagesSinus and FistulaAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder in Adults: Diagnosis & Management: ScopeDocument19 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder in Adults: Diagnosis & Management: ScopeBadii AmamouNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUdy & Postpartum NCPDocument3 pagesDRUG STUdy & Postpartum NCPireneNo ratings yet
- Carpel Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)Document16 pagesCarpel Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)heerNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox What Is Chickenpox?Document19 pagesChickenpox What Is Chickenpox?s.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Structure and Function of The Human Skin MicrobiomeDocument20 pagesHHS Public Access: Structure and Function of The Human Skin MicrobiomeEugeniaNo ratings yet
- Rabbit ProductionDocument19 pagesRabbit ProductionPASKAL GWALTUNo ratings yet
Integumentary System
Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Arnie Jean Salazar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesThis document provides descriptions of common skin diseases and disorders including acne, psoriasis, staph infections, chickenpox, and fungal infections. For each condition, it lists the description, causes and risk factors, symptoms, and typical treatment options. The conditions covered include bacterial, viral, and fungal causes of skin problems. Treatment involves both medical and home care approaches depending on the specific disease or disorder. Maintaining good hygiene practices can help prevent some infectious skin conditions.
Original Description:
Original Title
Integumentary-system
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides descriptions of common skin diseases and disorders including acne, psoriasis, staph infections, chickenpox, and fungal infections. For each condition, it lists the description, causes and risk factors, symptoms, and typical treatment options. The conditions covered include bacterial, viral, and fungal causes of skin problems. Treatment involves both medical and home care approaches depending on the specific disease or disorder. Maintaining good hygiene practices can help prevent some infectious skin conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesIntegumentary System
Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Arnie Jean SalazarThis document provides descriptions of common skin diseases and disorders including acne, psoriasis, staph infections, chickenpox, and fungal infections. For each condition, it lists the description, causes and risk factors, symptoms, and typical treatment options. The conditions covered include bacterial, viral, and fungal causes of skin problems. Treatment involves both medical and home care approaches depending on the specific disease or disorder. Maintaining good hygiene practices can help prevent some infectious skin conditions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
ARNIE JEAN E.
SALAZAR – Caregiver Batch 50
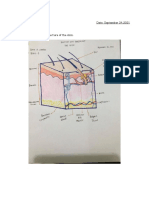
1. What is skin disease or disorder?
a. A skin disease or disorder refers to any abnormal condition or ailment that affects the skin's
health, appearance, or functioning. These conditions can affect the skin's appearance, texture,
or functioning and may cause discomfort, pain, or other health problems. Skin diseases or
disorders can be caused by various factors, including genetics, infections, allergies,
autoimmune reactions, environmental factors, or underlying health conditions.
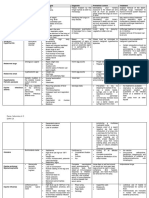
2. Look for the description, causes or risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options for
each disease below.
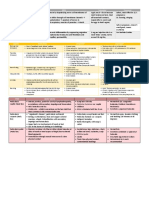
Items Description Causes Or Risk Symptoms Treatment Options
Factors
ACNE Acne, also known Excess Oil Production Pimples Topical Treatments
as acne vulgaris, is Hair Follicle Clogging Blackheads (Benzoyl Peroxide,
a common skin Bacteria Whiteheads Salicylic Acid, Retinoids)
condition that Hormonal Changes Nodules Oral Medications
occurs when hair Certain Medications Cysts (Antibiotics, Birth Control
follicles become Diet
Pills, Isotretinoin)
clogged with oil
and dead skin Laser Therapy
cells. It often Chemical Pills
results in the Extraction
formation of Gentle Cleansing
pimples, Non-Comedogenic
blackheads, Products
whiteheads, and, in Healthy Diet
more severe cases,
cysts or nodules. It's important to consult a
Acne can appear dermatologist for a
on the face, neck, personalized treatment
chest, back, and plan, especially for
shoulders. moderate to severe acne.
PSORIASIS Psoriasis is a Genetics Red, raised patches Topical Treatments
chronic Immune System Itching (Topical Steroids
autoimmune skin Environmental Thickened, pitted, or Topical Vitamin D
disorder Triggers discolored nails Analogs
characterized by Joints Topical Retinoids
the rapid buildup of
Coal tar preparations)
skin cells. This
buildup results in Light Therapy (UVB
scaling on the Phototherapy, Psoralen
skin's surface, plus ultraviolet A
causing red, itchy, Therapy)
and sometimes Oral or Injectable
painful patches or Medications (Oral
plaques. Psoriasis Retinoids,
can occur on any Immunosuppressant
part of the body Medications, Biologics)
and ranges in Lifestyle and Self-care
severity from mild (Moisturizers, Avoid
to severe. Triggers, Stress
Management)
STAPH Staphylococcus Skin contact Skin Infections Antibiotics
aureus, commonly Wounds or Cuts Systemic Infections: Drainage (the pus to aid
known as Staph, is Weakened Immune Toxic Shock the healing)
a type of bacteria System Syndrome (TSS) Wound Care
that can cause a Hospital Settings Pneumonia Intravenous (IV) Therapy
wide range of
Poor Hygiene Supportive Care
infections in
humans.
Staphylococcal Preventing Staph infections
infections can vary involves good hygiene
from minor skin practices, regular
infections to handwashing, proper
severe, life- wound care, and avoiding
threatening contact with infected
conditions. individuals or contaminated
Staphylococcus surfaces.
aureus is a
bacterium that
normally resides on
the skin and in the
nasal passages
without causing
any harm.
However, when it
enters the body
through a cut,
wound, or other
opening, it can
cause infections.
Staph infections
can manifest as
skin infections,
pneumonia,
bloodstream
infections, or more
serious conditions
like toxic shock
syndrome.
CHICKENPOX Chickenpox, also Varicella-Zoster Virus Rash Home Care (Keeping the
known as varicella, (VZV) Fever skin clean and cool, using
is a highly Not Previously Infected Fatigue over-the-counter anti-itch
contagious viral Close Contact Itching creams, keeping nails
infection primarily Weakened Immune Loss of Appetite trimmed and wearing
affecting children. It System mittens to prevent
is caused by the scratching, encouraging
varicella-zoster fluids to prevent
virus, which leads dehydration, resting to aid
to an itchy rash and in recovery)
flu-like symptoms. Antiviral Medications
Chickenpox is Vaccination
typically a mild and Immune Globulin (IG)
self-limiting
disease, but it can
be more severe in
certain populations.
FUNGAL Fungal infections, Weak Immune System Athlete's Foot Antifungal Medications
INFECTIONS also known as Warm and Moist Ringworm Topical Treatments
mycoses, are Environments Yeast Infections Oral Medications
caused by fungi Diabetes Nail Infections Nail Removal
and can affect Skin Breaks or Cuts Oral Thrush Home Remedies
various parts of the Poor Hygiene Systemic Infections Preventive Measures
body, including the
skin, nails, genitals,
throat, and internal
organs. Fungi are
present
everywhere in our
environment and
can cause
infections when
they enter the body
and multiply
excessively.
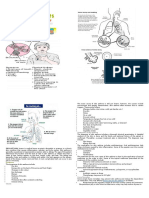
3. What is burn? - In the context of injuries, a "burn" refers to damage or injury to the skin or other
tissues caused by various factors such as heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation.
4. What are the kinds of burn? - First-Degree Burns, Second-Degree Burns, Third-Degree Burns,
Fourth-Degree Burns, Chemical Burns, Electrical Burns
5. Identify the 3 levels or degree of burns. Explain each.
First-Degree Burns (Superficial Burns):
- These burns affect only the top layer of the skin, the epidermis.
- They typically result in redness, pain, and mild swelling.
- Sunburn is a common example of a first-degree burn.
- Healing usually occurs within a few days without scarring.
Second-Degree Burns (Partial-Thickness Burns):
- These burns affect both the epidermis and the layer beneath it, the dermis.
- They are characterized by red, blistered skin, severe pain, and swelling.
- Healing can take several weeks, and scarring may occur.
Third-Degree Burns (Full-Thickness Burns):
- These burns destroy the entire thickness of the skin, including the dermis.
- The skin may appear white, charred, or leathery.
- Nerve endings are often destroyed, so the affected area may be numb.
- Third-degree burns require medical attention and often surgical intervention for treatment.
You might also like
- Master The Chamber: Dr. Mohammad RaselDocument28 pagesMaster The Chamber: Dr. Mohammad RaselMensa DigiWorldNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Nuts & BoltsDocument42 pagesMicrobiology Nuts & Boltsteena jacobNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of CellulitisDocument8 pagesConcept Map of CellulitisReese Anne100% (1)
- Skin Care For HealthDocument3 pagesSkin Care For HealthGin MananganNo ratings yet
- Anaphy - The SkinDocument5 pagesAnaphy - The SkinGwyn Louise CarolinoNo ratings yet
- Equine Medicine DISEASESDocument14 pagesEquine Medicine DISEASESlowi shooNo ratings yet
- DisordersDocument23 pagesDisordersShelly LazaritoNo ratings yet
- Disease and Cause Manifestation Treatment Prevention Bacteria SignsDocument14 pagesDisease and Cause Manifestation Treatment Prevention Bacteria SignsMc MagtibayNo ratings yet
- Male Genital DermDocument112 pagesMale Genital DermVũ CaoNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDocument4 pagesDisorders of The Integumentary System: Internet ResourcesDylan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Lectures JRRMMCDocument10 pagesDermatology Lectures JRRMMCGi Em100% (1)
- Skin ConditionsDocument3 pagesSkin ConditionsAlyssa AmayaNo ratings yet
- Skin AsthmaDocument7 pagesSkin AsthmaJames Domini Lopez LabianoNo ratings yet
- System Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Document1 pageSystem Disorder: Dermatitis and Acne: Atopic Dermatitis 57Kassandra MerrillNo ratings yet
- Narsum 1. Acne Treatment 10 Feb 2022Document26 pagesNarsum 1. Acne Treatment 10 Feb 2022Vheny YulandariNo ratings yet
- System Disorder ADDocument1 pageSystem Disorder ADSariahNo ratings yet
- Complication CL OsceDocument6 pagesComplication CL OsceAdam EdzelNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocument3 pagesImpaired Skin IntegrityNeriz Pineda0% (1)
- 11 Realism April Joy TeberioDocument1 page11 Realism April Joy TeberioApril Joy Malinao TeberioNo ratings yet
- Ms 1 Integumentary NursingDocument10 pagesMs 1 Integumentary NursingTrinity Veach100% (1)
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocument4 pagesNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases of Childhoo1Document3 pagesCommunicable Diseases of Childhoo1esmirikNo ratings yet
- Hordeolum: Acute Abscess Within An Eyelid Sebaceous Gland: The Clinical PictureDocument3 pagesHordeolum: Acute Abscess Within An Eyelid Sebaceous Gland: The Clinical PictureCamNo ratings yet
- Nursing:: CommunityDocument59 pagesNursing:: CommunityIlyes RaniNo ratings yet
- 0-2873717490134913195Document18 pages0-2873717490134913195michellegin09No ratings yet
- Karanj Oil Research ArticleDocument12 pagesKaranj Oil Research ArticlesahilNo ratings yet
- Community Nursing Wound Care PresentationDocument56 pagesCommunity Nursing Wound Care PresentationkugernnesNo ratings yet
- PHARMA CHAP 12 and 19 UpDocument7 pagesPHARMA CHAP 12 and 19 UpBAUZON, JANINE, C.No ratings yet
- Case Study BurnDocument3 pagesCase Study BurnInday BebeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudydubouzettheresaNo ratings yet
- PBL - IntegumentaryDocument2 pagesPBL - Integumentarygie sarcedaNo ratings yet
- McAlinden Hordeolum PDFDocument3 pagesMcAlinden Hordeolum PDFNur Rakhma AkmaliaNo ratings yet
- PEDIA - Drug Study & NCPDocument24 pagesPEDIA - Drug Study & NCPCzarina Mae Lomboy100% (1)
- Case-Scenario-Oxygen Therapy-BuenconsejoDocument6 pagesCase-Scenario-Oxygen Therapy-BuenconsejoCarna BuenconsejoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetics Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: EliminationDocument2 pagesPharmacokinetics Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: EliminationChrislyn LangegNo ratings yet
- Drug Study With NCPDocument4 pagesDrug Study With NCPJoanne Kathleen SantolicesNo ratings yet
- DAY 2 Mahesa Burn Rehabilitation PresentasiDocument16 pagesDAY 2 Mahesa Burn Rehabilitation Presentasichristin megaNo ratings yet
- Acne NetterDocument2 pagesAcne NetterSELLULARNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Lec. Activity 1 (Repaired)Document1 pageNCM 114 Lec. Activity 1 (Repaired)Juan Miguel Caspe MangayaNo ratings yet
- Permethrin 5% Cream: Medication MOA Instruction CommentsDocument1 pagePermethrin 5% Cream: Medication MOA Instruction CommentsChron MedNo ratings yet
- Skin AbnormalsDocument2 pagesSkin AbnormalsJp CasperNo ratings yet
- Causative Agent Characteristic Symptom 1 Management: Surgery Is The Most Important Modality For MalignantDocument2 pagesCausative Agent Characteristic Symptom 1 Management: Surgery Is The Most Important Modality For MalignantJp CasperNo ratings yet
- Moisture Associated Skin Damage MASD Pathway Aug 22Document1 pageMoisture Associated Skin Damage MASD Pathway Aug 22rodolfo opidoNo ratings yet
- PsoriasisDocument27 pagesPsoriasisNikkaDablioNo ratings yet
- Ncma Course Task 11 PDFDocument4 pagesNcma Course Task 11 PDFJaja ManezNo ratings yet
- 7 Active Ingredients For Special Products: 7.1 Definition of Special CreamsDocument43 pages7 Active Ingredients For Special Products: 7.1 Definition of Special CreamsElizabeth TovittoNo ratings yet
- BURNSDocument26 pagesBURNSGaurav pareekNo ratings yet
- ImportantDocument21 pagesImportantGaurav pareekNo ratings yet
- Allergies Hives Rashes Handout 509kDocument2 pagesAllergies Hives Rashes Handout 509kIndu SinghNo ratings yet
- 56-Topical Drugs Used in The Treatment of Skin DisordersDocument13 pages56-Topical Drugs Used in The Treatment of Skin DisordersMujeebNo ratings yet
- Derma Quiz 3 NotesDocument11 pagesDerma Quiz 3 NotesJolaine ValloNo ratings yet
- Insect Bites StingsDocument1 pageInsect Bites StingsnamibadiNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology NG CandidiasisDocument2 pagesPathophysiology NG CandidiasisJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- EczemaDocument13 pagesEczemaCollective123No ratings yet
- Dry Eye DiseaseDocument8 pagesDry Eye DiseaseaNo ratings yet
- Rash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: EmergencyDocument1 pageRash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: Emergencykdlsfk kajjksolsNo ratings yet
- Student Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan RabiesDocument2 pagesStudent Nurses' Community: Nursing Care Plan RabiesYanis Emmanuelle LimNo ratings yet
- Client Bed BathDocument6 pagesClient Bed BathLorenz Jude CańeteNo ratings yet
- Skin DiseasesDocument4 pagesSkin DiseaseschellesuguitanNo ratings yet
- Sarcoptes Scabei Var. HumanusDocument2 pagesSarcoptes Scabei Var. HumanusZai Ra DianaNo ratings yet
- Natural Products for Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue DisordersFrom EverandNatural Products for Treatment of Skin and Soft Tissue DisordersNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System QuizDocument1 pageReproductive System QuizArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument1 pageSkeletal SystemArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document14 pagesLesson 1Arnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Dietary AssignmentDocument2 pagesDietary AssignmentArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- MalnutritionDocument1 pageMalnutritionArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document24 pagesLesson 2Arnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Self From Psychological PerspectiveDocument21 pagesLesson 3 Self From Psychological PerspectiveArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Philosophical PerspectivesDocument20 pagesLesson 1 Philosophical PerspectivesArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 SOCIETY AND THE SELFDocument17 pagesLesson 2 SOCIETY AND THE SELFArnie Jean SalazarNo ratings yet
- Thromboembolic Complications in Chronic Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument6 pagesThromboembolic Complications in Chronic Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY F - ChloramphericolDocument7 pagesDRUG STUDY F - ChloramphericolJane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Formal Examination Period: Session 1, June 2019Document18 pagesFormal Examination Period: Session 1, June 2019Lynstel NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Epididymitis PDFDocument4 pagesChronic Epididymitis PDFDereck HowseNo ratings yet
- Calcarea CarbonicumDocument10 pagesCalcarea CarbonicumVictor CironeNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Trait TheoriesDocument8 pagesContemporary Trait TheoriesMuhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- Types of Personality DisorderDocument2 pagesTypes of Personality DisorderWinnie Salazar AriolaNo ratings yet
- HIV Stigma IndexDocument36 pagesHIV Stigma Indexjohn mwambuNo ratings yet
- EuthanasiaDocument22 pagesEuthanasiaSANA SAFDARNo ratings yet
- ECG LictureDocument25 pagesECG LictureALi NursingNo ratings yet
- The Challenges and Perspectives of The Integration Between Virtual and Augmented Reality and Manual TherapiesDocument18 pagesThe Challenges and Perspectives of The Integration Between Virtual and Augmented Reality and Manual Therapiesradhianie djanNo ratings yet
- Fastidious Gram Negative RodsDocument74 pagesFastidious Gram Negative RodsMaria ClaraNo ratings yet
- Fulltext Schizophrenia v3 Id1026!12!2Document8 pagesFulltext Schizophrenia v3 Id1026!12!2Saskia MonalisaNo ratings yet
- Nov AIIMS 2018 Pathology Questions and Explanations by Dr. SUSHANT SONIDocument9 pagesNov AIIMS 2018 Pathology Questions and Explanations by Dr. SUSHANT SONIZahidha BegumNo ratings yet
- Care of Adults 28 Hematological and Oncological ManagementDocument40 pagesCare of Adults 28 Hematological and Oncological ManagementGaras AnnaBerniceNo ratings yet
- Aphasia and DysphasiaDocument8 pagesAphasia and Dysphasiamoizghani37No ratings yet
- Olivia Tween COGS Aphantasia Thesis Final Version PDFDocument23 pagesOlivia Tween COGS Aphantasia Thesis Final Version PDFJORGE ENRIQUE CAICEDO GONZ�LES100% (1)
- Neurologic ExaminationDocument67 pagesNeurologic Examinationሀይደር ዶ.ር100% (1)
- Physical Disability by FabricationDocument25 pagesPhysical Disability by FabricationALYELA PETERNo ratings yet
- ARISE QRP All 19 High YieldDocument267 pagesARISE QRP All 19 High YieldAnjali TamrakarNo ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument21 pagesBirth AsphyxiaAntonyNo ratings yet
- Sinus and FistulaDocument3 pagesSinus and FistulaAndrew BonusNo ratings yet
- Major Depressive Disorder in Adults: Diagnosis & Management: ScopeDocument19 pagesMajor Depressive Disorder in Adults: Diagnosis & Management: ScopeBadii AmamouNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUdy & Postpartum NCPDocument3 pagesDRUG STUdy & Postpartum NCPireneNo ratings yet
- Carpel Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)Document16 pagesCarpel Tunnel Syndrome (CTS)heerNo ratings yet
- Chickenpox What Is Chickenpox?Document19 pagesChickenpox What Is Chickenpox?s.khan9211rediffmail.comNo ratings yet
- HHS Public Access: Structure and Function of The Human Skin MicrobiomeDocument20 pagesHHS Public Access: Structure and Function of The Human Skin MicrobiomeEugeniaNo ratings yet
- Rabbit ProductionDocument19 pagesRabbit ProductionPASKAL GWALTUNo ratings yet