Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 16
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 16
Uploaded by
JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 16
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 16
Uploaded by
JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYCopyright:
Available Formats
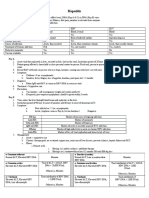
Communicable Diseases
Catarrhal jaundice hepatitis Tea-colored urine
Epidemic hepatitis Acholic stool – clay-colored
CA: Hepatitis A Virus (RNA) Some pre-icteric symptoms may persist but
Feces and blood a lesser degree
MOT: fecal-oral
At risk: Children and food handlers
IP: 2 to 6 weeks Bilirubin
(unconjugated)
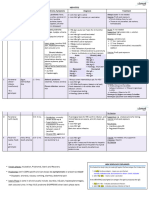
o Hepatitis B – Serum Hepatitis
Homologous Hepatitis
Viral Hepatitis – most fatal
Blood, sputum and other body fluids
MOT:
Bloodstream Kidneys - 2x
Parenteral – BT, sharps and needles
o At risk: Blood recipients, drug
addicts
Oral – oral
Liver Urine
o Kissing
o 6 to 8 gallons
Sexual contact
o Seminal and cervical fluids
Vertical Un/conj
o Mother and child
o Childbirth
IP: 6 wks to 6 months
o Hepatitis C Intestines
Post Transfusion Hepatitis
CA: Hepatitis C virus
MOT: Parenteral
IP: 5 to 12 wks
At risk: Paramedical team, drug addicts, BT Stools
recipients
o Hepatitis D
Dormant type of Hepatitis B
CA: Hepatitis D / Delta virus Acholic
Delta virus cannot multiply by itself – needs
the help of the B virus
MOT: Same as hepatitis B
IP: 3 to 13 wks o Post-icteric
Jaundice disappears
o Hepatitis E Signs and symptoms subsides
CA: Hepatitis E virus Energy level increases
Source: Feces Avoid alcoholic beverages and OTC drugs
MOT: Same as hepatitis A for at least 1 year
IP: 3 to 6 wks o Liver recovers
o Hepatitis G Dx Exam:
CA: Hepatitis G virus o Liver Enzyme Test
MOT: Same as hepatitis C ALT Alanine Aminotransferase
IP: Unknown o 1st to shoot up if liver problem is
present even if asymptomatic
S/sx: AST Aspartate Aminotransferase
o Pre-incteric o Increases upon onset of jaundice
Fever, RUQ pain o Not reliable
Fatigability, weight loss, body malaise ALP Alkaline Phosphatase
o inability to convert glucose to o Obstructive jaundice
glycogen – source of energy GGR Gamma Glutanyl Transferase
Anorexia, nausea and vomiting – o Toxic Hepatitis due to toxic substances
deamination of CHON (e.g. alcohol, drugs, substances)
Anemia - lifespan RBC (60 to 120 days) LDH Lactic Dehydrogenase
o Bilirubin – end product of RBC o Increase = Liver Damage
destruction - accumulates – jaundice o Serum Antigen Antibody Test
o Icteric Med Mgt: Symptomatic
Jaundice, pruritus - accumulation of bile o Hepatic Protection (Liver aid) - ↓ effort of
salts on the skin metabolism, allow liver to relax
University of Santo Tomas – College of Nursing / JSV
You might also like
- TM 11398Document592 pagesTM 11398krill.copco50% (2)
- A Requiem To Mother EarthDocument5 pagesA Requiem To Mother EarthSandra SabuNo ratings yet
- Liver - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFDocument70 pagesLiver - Dr. Allam 2021 PDFMohammedNo ratings yet
- PHA Individual Health Profile & Assessment Form As of Oct.09, 2017Document8 pagesPHA Individual Health Profile & Assessment Form As of Oct.09, 2017Eden VblagasyNo ratings yet
- Vitamins SpreadsheetDocument6 pagesVitamins SpreadsheetB-Rock Daniels100% (1)
- (Alexei Lapkin, David Constable) Green Chemistry Me (B-Ok - CC) PDFDocument337 pages(Alexei Lapkin, David Constable) Green Chemistry Me (B-Ok - CC) PDFAlex Sustaita100% (1)
- What Is RAID Control PDFDocument6 pagesWhat Is RAID Control PDFAhmedNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Hepatitis GDocument9 pagesHepatitis A Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Hepatitis D Hepatitis E Hepatitis Gjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Document5 pagesAcute Viral Hepatitis (Final)Kim LompotNo ratings yet
- Class notes 1Document56 pagesClass notes 1khodja.amina.mf3No ratings yet
- Recall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTDocument4 pagesRecall Questions-February 14, 2018 Wyne Brent M. Corpuz, RMTRafael CayananNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis COLEDocument73 pagesViral Hepatitis COLERuth SanmooganNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis and Hepatic Failure: in ChildrenDocument26 pagesHepatitis and Hepatic Failure: in Childrenchilu20No ratings yet
- Hepatology (Ekanayaka)Document92 pagesHepatology (Ekanayaka)RusiruNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: DR Putra Hendra SPPD UnibaDocument87 pagesHepatitis: DR Putra Hendra SPPD Unibayoga yogafenkanoNo ratings yet
- Hepatologi 1 (CMP)Document61 pagesHepatologi 1 (CMP)Yun ZhaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis TableDocument2 pagesViral Hepatitis TableJohnNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis - An Overview: Dr. JayalakshmiDocument77 pagesHepatitis - An Overview: Dr. JayalakshmiNithin SundarNo ratings yet
- LIVERDISEASEDocument82 pagesLIVERDISEASEHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Dr. A. MowafyDocument222 pagesRevision Notes Dr. A. MowafyMohammed RisqNo ratings yet
- Module 7Document8 pagesModule 7soriano2214989No ratings yet
- Alcoholism and HepatitisDocument15 pagesAlcoholism and HepatitisTom MallinsonNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Handouts Spring 2019Document27 pagesGastroenterology Handouts Spring 2019Sasoo EmadNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Hepatic/Biliary Dysfunction: Hepatitis Cirrhosis Gall Bladder DiseaseDocument70 pagesManagement of Patients With Hepatic/Biliary Dysfunction: Hepatitis Cirrhosis Gall Bladder DiseaseRCNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument8 pagesHepatitisGilankNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B Kronik Pada Kehamilan - Dr. Dr. Anita Rachmawati, SpOG (K)Document92 pagesHepatitis B Kronik Pada Kehamilan - Dr. Dr. Anita Rachmawati, SpOG (K)Rustan VickyNo ratings yet
- JaundiceDocument17 pagesJaundiceDarwithaNo ratings yet
- Acute Hepatitis DR NjokuDocument43 pagesAcute Hepatitis DR Njokufrankozed1No ratings yet
- Abses PerianalDocument110 pagesAbses PerianalHanni HaeraniNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis D SirosisDocument103 pagesHepatitis D SirosisTri AyatiNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument3 pagesHepatitisapi-648401824No ratings yet
- Jaundice and Hepatitis in Children: Dr. MwendwaDocument46 pagesJaundice and Hepatitis in Children: Dr. MwendwaAlvin OmondiNo ratings yet
- HEPATITISDocument4 pagesHEPATITISYalin AbouhassiraNo ratings yet
- Med Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyDocument1 pageMed Surg: GI - Gastrointestinal: PathophysiologyTori RolandNo ratings yet
- هیپاتایتیس - bDocument28 pagesهیپاتایتیس - bitsanoshjanNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyDocument44 pagesHepatitis: Dr. Amany A. GhazyJosé Luis García GarcíaNo ratings yet
- CD Learning Material 4 Blood Borne DiseaseDocument22 pagesCD Learning Material 4 Blood Borne Disease2C1 - YABES, JenniferNo ratings yet
- Pathologi Klinik Edited by MememeDocument11 pagesPathologi Klinik Edited by MememeReynaldi FernandesNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A, B and C VirusDocument46 pagesHepatitis A, B and C VirusChyzhi SylviaNo ratings yet
- Prolonged Cholestasis Due To Hepatitis A Virus Infection in A Young Adolescent Male With A Known Case of Hemoglobin E Disease: Early Response To Steroid TherapyDocument4 pagesProlonged Cholestasis Due To Hepatitis A Virus Infection in A Young Adolescent Male With A Known Case of Hemoglobin E Disease: Early Response To Steroid TherapyBOHR International Journal on GastroenterologyNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Hepatitis-2Document21 pagesAcute Viral Hepatitis-2Jasselia Fei100% (1)
- Viral Hepatitis VirusDocument8 pagesViral Hepatitis VirusJFNo ratings yet
- CD Hepatitis - Dr. Yapendon 2014Document13 pagesCD Hepatitis - Dr. Yapendon 2014jeccomNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis D SirosisDocument103 pagesHepatitis D SirosisMuhammadKhasanFadlyNo ratings yet
- Acute Upper GI BleedingDocument31 pagesAcute Upper GI BleedingEusebius01No ratings yet
- CCE090 Liver and Biliary TractDocument21 pagesCCE090 Liver and Biliary TractBharathi ManiyanNo ratings yet
- Acute VH Definition:: Diffuse Liver Inflammation Lasting Less Than 6 MonthsDocument22 pagesAcute VH Definition:: Diffuse Liver Inflammation Lasting Less Than 6 Monthsnanda ashriNo ratings yet
- Viral HepatitisDocument30 pagesViral HepatitisAliya DawoodNo ratings yet
- Slides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Document47 pagesSlides DR Ashgar Approach To LFTs 12.12.2021Maryam OmarNo ratings yet
- DM HT CRF Study CaseDocument31 pagesDM HT CRF Study CaseErlina KusumastutiNo ratings yet
- Osce Metab Topics CompleteDocument10 pagesOsce Metab Topics Completerossbee jordasNo ratings yet
- CLD FinalDocument17 pagesCLD FinalHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis (Pediatrics)Document82 pagesHepatitis (Pediatrics)Hazel AsperaNo ratings yet
- Liver Pathology PDFDocument7 pagesLiver Pathology PDFjohn smithNo ratings yet
- MLSP: Nature of The Clinical LaboratoryDocument4 pagesMLSP: Nature of The Clinical LaboratorythisbusinesstobusyNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hepatitis B InfectionDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Hepatitis B InfectionSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Group 2 HepatitisDocument27 pagesGroup 2 HepatitisMaica LectanaNo ratings yet
- HBV Si HCV Studenti 201 PDFDocument117 pagesHBV Si HCV Studenti 201 PDFDianaTricoracheNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis - KBKDocument53 pagesVirus Hepatitis - KBKfifi anggraeniNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument23 pagesHepatitis BMarty Asis100% (1)
- Farmakoterapi SirosisDocument27 pagesFarmakoterapi SirosisfizaNo ratings yet
- DR Moh AbdalgaderDocument27 pagesDR Moh AbdalgaderAlex SamNo ratings yet
- Discrepant Urinalysis Results 2012 PDFDocument1 pageDiscrepant Urinalysis Results 2012 PDFTrang HuynhNo ratings yet
- DR Moh AbdalgaderDocument27 pagesDR Moh AbdalgaderAlex SamNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Material Balance PDFDocument31 pagesMaterial Balance PDFApril Joy HaroNo ratings yet
- Drawing Details: Cie 332 Quantity Surveying and Estimation Lecture Two Lecturer: Eng. Goodson MashekaDocument23 pagesDrawing Details: Cie 332 Quantity Surveying and Estimation Lecture Two Lecturer: Eng. Goodson MashekaPerpetual hubbyNo ratings yet
- Cibse Solar AcDocument11 pagesCibse Solar Acdhananjay176No ratings yet
- CD Dye RD0005Document7 pagesCD Dye RD0005Juan CarlosNo ratings yet
- Rakit Lampu LedDocument11 pagesRakit Lampu LedIbnusyam UtihNo ratings yet
- Technical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosDocument4 pagesTechnical Specification: 1) Filter Feed Pump With Motor 1 NosKamatchi NathanNo ratings yet
- Regulator InfoDocument6 pagesRegulator InfoAguilar AlexNo ratings yet
- Ciarrochi Fisher and Lane Link Between Values and Well-Being Among People With Cancer 2010 Psycho OncologyDocument9 pagesCiarrochi Fisher and Lane Link Between Values and Well-Being Among People With Cancer 2010 Psycho OncologyJuan C. VargasNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Engineering Lab 1 (PGE313) Experiment 2 Determination of PorosityDocument13 pagesPetroleum Engineering Lab 1 (PGE313) Experiment 2 Determination of PorosityAli AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Surveillance, Torture and Contr - Rosanne Marie SchneiderDocument135 pagesSurveillance, Torture and Contr - Rosanne Marie SchneiderMagic MikeNo ratings yet
- Kohima Nagaland LBDocument1 pageKohima Nagaland LBIndia TreadingNo ratings yet
- Yuxi CatalogueDocument16 pagesYuxi CatalogueSoltani AliNo ratings yet
- How To Keep Your Brain HealthyDocument3 pagesHow To Keep Your Brain HealthySyahidah IzzatiNo ratings yet
- HEI Tech Sheet 110Document15 pagesHEI Tech Sheet 110Suganya LokeshNo ratings yet
- Autonomous University of Baja California: Faculty of Engineering Aerospace EngineeringDocument18 pagesAutonomous University of Baja California: Faculty of Engineering Aerospace EngineeringOscar Oreste Salvador CarlosNo ratings yet
- Coal Ash Dewatering SolutionDocument23 pagesCoal Ash Dewatering Solution류태하No ratings yet
- Gds Manual Flo2d ProDocument182 pagesGds Manual Flo2d ProbycmNo ratings yet
- Vacon Nxs Robust Drive For Heavy UseDocument11 pagesVacon Nxs Robust Drive For Heavy UseLuis PinedaNo ratings yet
- Flotrac Algorithm White PaperDocument4 pagesFlotrac Algorithm White PaperAnestesia 2017 UDECNo ratings yet
- Anjana Seminar SlideshareDocument38 pagesAnjana Seminar SlideshareAnjana kpNo ratings yet
- Research Progress of The Arti Ficial Intelligence Application in Wastewater Treatment During 2012 - 2022: A Bibliometric AnalysisDocument17 pagesResearch Progress of The Arti Ficial Intelligence Application in Wastewater Treatment During 2012 - 2022: A Bibliometric AnalysisjinxiaohuibabaNo ratings yet
- T2T 32T BTC Master Manual enDocument10 pagesT2T 32T BTC Master Manual enRAMON RUIZNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Cancer Case StudyDocument3 pagesBronchial Cancer Case StudyericaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Document12 pagesCarbon Capture Corrosion Current Practice 2023Wayne MonneryNo ratings yet
- 02 - D03 - Basic Funtion of SIPROTEC 5Document7 pages02 - D03 - Basic Funtion of SIPROTEC 5DianaNo ratings yet