Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15
Uploaded by
JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYThe document discusses several communicable diseases including:
1. Typhoid fever caused by Salmonella typhi bacteria spread through fecal-oral transmission. Symptoms include fever, headache, rose spots on the abdomen. Treatment involves antibiotics and fluid replacement.
2. Leptospirosis caused by Leptospira bacteria spread through contact with infected animals. Symptoms include fever, muscle pain, jaundice and kidney failure. Doxycycline is the antibiotic treatment.
3. Hepatitis which is inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses, alcohol, drugs or chemicals. Viral hepatitis A is referred to as infectious hepatitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 6Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 6JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument10 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingMarisol DizonNo ratings yet
- Dumlao, Michelin H.Document20 pagesDumlao, Michelin H.Mich DumlaoNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals!Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals!Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 3Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 3JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Document4 pagesTop Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- Vector Borne Diseases: Malaria (Ague)Document20 pagesVector Borne Diseases: Malaria (Ague)Nina OaipNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Summarize Notes On ImciDocument6 pagesSummarize Notes On ImciI'm Just A BurgerNo ratings yet
- Wilm's Tumor EtcDocument5 pagesWilm's Tumor EtcDanica BonNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections II IBDDocument8 pagesBacterial Infections II IBDRozeanneNo ratings yet
- Safe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingDocument16 pagesSafe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingJo ckerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Child With Autoimmune Diseases & GI DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Care For Child With Autoimmune Diseases & GI Disordersbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases 2.4-5.22Document9 pagesCommunicable Diseases 2.4-5.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Presented by Abhinay BhugooDocument32 pagesPresented by Abhinay BhugooGideon K. MutaiNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument8 pagesCommunicable DiseasesJamie John EsplanadaNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 17Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 17JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Spondilitis TB AnakDocument36 pagesSpondilitis TB Anaktry intan kartini50% (2)
- AmoebiasisDocument17 pagesAmoebiasisAjay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- GASTRODocument47 pagesGASTROMada mada DaneNo ratings yet
- Step2 - PediatricsDocument18 pagesStep2 - PediatricsKiran Saini100% (1)
- Bacteria-Borne Diseases Handout 2022Document3 pagesBacteria-Borne Diseases Handout 2022Anna CrisNo ratings yet
- HCC Exam 4Document20 pagesHCC Exam 4Sheri BarlingNo ratings yet
- GenitoDocument12 pagesGenitofatima_antonioNo ratings yet
- Week-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-GerryDocument10 pagesWeek-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-Gerryjmmacar19No ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 14 Communicable DiseasesDocument6 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 14 Communicable DiseasesViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- Viral Diseases RuminantDocument34 pagesViral Diseases RuminantNorwood Everett DaduloNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument7 pagesPlacenta Previa Case StudyKing NavsunNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Overview & OutcomesDocument5 pages1.1 Overview & OutcomesShayla HudsonNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFDocument8 pages5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFVince Alvin DaquizNo ratings yet
- (Surgery) Midterms PediatricsDocument5 pages(Surgery) Midterms Pediatricsalmira.s.mercadoNo ratings yet
- Elsie Kho Ap300 Study NotesDocument36 pagesElsie Kho Ap300 Study Noteshanazawa_rui9878030No ratings yet
- Pastel Cute Illustrative Business Report PresentationDocument18 pagesPastel Cute Illustrative Business Report PresentationdocgioreNo ratings yet
- Ncmb312 Lec FinalDocument63 pagesNcmb312 Lec FinalRose Ann CammagayNo ratings yet
- Brosure Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesBrosure Dengue FeverMadvi TadeoNo ratings yet
- Enteric DiseaseDocument2 pagesEnteric DiseaseHazel ZullaNo ratings yet
- Agata Infectious DiseasesDocument34 pagesAgata Infectious DiseasesMartaNo ratings yet
- NP1 BulletsDocument17 pagesNP1 BulletsJea VesagasNo ratings yet
- NP1 BulletsDocument17 pagesNP1 BulletsJea VesagasNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument80 pagesPediatricsmohamed muhsinNo ratings yet
- Module 6.4 ParasitesDocument6 pagesModule 6.4 ParasitesPNo ratings yet
- ENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)Document35 pagesENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)rumman tariqNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NotesDocument13 pagesPediatrics NotesYsa BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Infection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Document109 pagesInfection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Sirawit Namkaeng ChoksuchatNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Tabelle (Examen 6. Jahr)Document34 pagesInfectious Diseases Tabelle (Examen 6. Jahr)Aastha SethNo ratings yet
- Typhidot Is A: Medical Test Elisa Igm Igg Antibodies Outer Membrane Protein Salmonella TyphiDocument5 pagesTyphidot Is A: Medical Test Elisa Igm Igg Antibodies Outer Membrane Protein Salmonella TyphiDecember TwoNo ratings yet
- Parasitic WormsDocument4 pagesParasitic WormsEricNo ratings yet
- Care of NeonatesDocument7 pagesCare of NeonatesJankaruroNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BDocument15 pagesFar Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis: (Amoebic Dysentery)Document32 pagesAmoebiasis: (Amoebic Dysentery)abhinay_1712No ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 4Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 4JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Common Exanthems PDFDocument4 pagesCommon Exanthems PDFKaren Ivy BacsainNo ratings yet
- Sandeep BI YE NotesDocument21 pagesSandeep BI YE NotesPranav ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Human Health and Disease Final PYQs and Exemplar 1Document186 pagesMind Map Human Health and Disease Final PYQs and Exemplar 1Mohit Devraj ParasharNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Sci Chapter 2 8thDocument18 pagesSci Chapter 2 8thAakash ChatakeNo ratings yet
- Final PDFDocument31 pagesFinal PDFHimanshu BishtNo ratings yet
- Pathogens and Pathways, and Small Drinking-Water SuppliesDocument22 pagesPathogens and Pathways, and Small Drinking-Water SuppliesZari Sofia Leviste100% (1)
- Salmonella Infected Model On MiceDocument14 pagesSalmonella Infected Model On MiceAmi FebrizaNo ratings yet
- Department of Haematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument5 pagesDepartment of Haematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodSunil KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Applications of Immunology in DiagnosisDocument5 pagesApplications of Immunology in Diagnosischrist sonNo ratings yet
- Enteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverDocument2 pagesEnteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Godfroy, Marion F. - Kourou and The Struggle For A French AmericaDocument17 pagesGodfroy, Marion F. - Kourou and The Struggle For A French AmericadecioguzNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology - Final Term QuizDocument4 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology - Final Term QuizMary Grace MartinNo ratings yet
- Didier Raoult, Didier Raoult, Michel Drancourt - Paleomicrobiology - Past Human Infections-Springer (2008)Document224 pagesDidier Raoult, Didier Raoult, Michel Drancourt - Paleomicrobiology - Past Human Infections-Springer (2008)Juan Antonio Duque-TardifNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Cocci Gram Positive BacilliDocument103 pagesGram Negative Cocci Gram Positive BacilliMacky IbayNo ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument12 pagesEnterobacteriaceaeFaithNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Epidemiology of Intestinal InfectionsDocument46 pagesLecture 3 Epidemiology of Intestinal InfectionsAli Baker AlgelaneNo ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument11 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAEYormae QuezonNo ratings yet
- Meningitis 1Document533 pagesMeningitis 1Bhan Panom GatdietNo ratings yet
- BoookDocument131 pagesBoookDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Summative Test ScienceDocument5 pagesSummative Test ScienceElmalyn Bernarte100% (2)
- Water Borne DiseasesDocument15 pagesWater Borne DiseasesDeepak BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing 2020Document421 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing 2020Kenneth Myro GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Diseases Are Commonly Caused by Wastewater?Document7 pagesWhat Diseases Are Commonly Caused by Wastewater?RimaQuitainNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Disease: Group 4Document57 pagesTyphoid Disease: Group 4ajeng astiaNo ratings yet
- Dengue TitersDocument4 pagesDengue TitersPeter Francis RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Enterics 15 ShortlyDocument82 pagesLecture 1 - Enterics 15 ShortlyIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Calixtro, LJ Bacterial Infections Narrative PathophysiologyDocument14 pagesCalixtro, LJ Bacterial Infections Narrative PathophysiologyKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaaminzaghiNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever,-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesTyphoid Fever,-WPS OfficeElvisNo ratings yet
- PREDICTIVEHOMOEOPATHYDocument46 pagesPREDICTIVEHOMOEOPATHYHomeopathy Torrents85% (34)
- First Quiz Q1 With Tos All SubjectsDocument34 pagesFirst Quiz Q1 With Tos All SubjectsJohn Erroll GesmundoNo ratings yet
- Widal Test - Introduction, Principle, Procedure, Interpretation and LimitationDocument13 pagesWidal Test - Introduction, Principle, Procedure, Interpretation and LimitationAshik ThapaNo ratings yet
- PGuidelines Enteric. FeverDocument4 pagesPGuidelines Enteric. FeverSara Ilyas KhanNo ratings yet
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15
Uploaded by
JULIUS CEZAR QUINAY0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageThe document discusses several communicable diseases including:
1. Typhoid fever caused by Salmonella typhi bacteria spread through fecal-oral transmission. Symptoms include fever, headache, rose spots on the abdomen. Treatment involves antibiotics and fluid replacement.
2. Leptospirosis caused by Leptospira bacteria spread through contact with infected animals. Symptoms include fever, muscle pain, jaundice and kidney failure. Doxycycline is the antibiotic treatment.
3. Hepatitis which is inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses, alcohol, drugs or chemicals. Viral hepatitis A is referred to as infectious hepatitis.
Original Description:
Original Title
tinywow_Communicable-Diseases_48897647_15
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses several communicable diseases including:
1. Typhoid fever caused by Salmonella typhi bacteria spread through fecal-oral transmission. Symptoms include fever, headache, rose spots on the abdomen. Treatment involves antibiotics and fluid replacement.
2. Leptospirosis caused by Leptospira bacteria spread through contact with infected animals. Symptoms include fever, muscle pain, jaundice and kidney failure. Doxycycline is the antibiotic treatment.
3. Hepatitis which is inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses, alcohol, drugs or chemicals. Viral hepatitis A is referred to as infectious hepatitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15
Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 15
Uploaded by
JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYThe document discusses several communicable diseases including:
1. Typhoid fever caused by Salmonella typhi bacteria spread through fecal-oral transmission. Symptoms include fever, headache, rose spots on the abdomen. Treatment involves antibiotics and fluid replacement.
2. Leptospirosis caused by Leptospira bacteria spread through contact with infected animals. Symptoms include fever, muscle pain, jaundice and kidney failure. Doxycycline is the antibiotic treatment.
3. Hepatitis which is inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses, alcohol, drugs or chemicals. Viral hepatitis A is referred to as infectious hepatitis.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
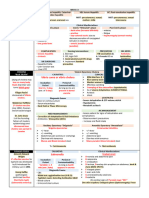
Communicable Diseases
o DOTS – program to encourage drug o Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance
compliance Monitor I and O
Assess for signs of DHN - # 1 sign within 24 hrs
Prevention – weight loss
o Same as pneumonia Fluids per orem
o BCG – at birth Regulate IVF
o 0.05/ ID o Provide adequate nutrition
o Deltoid Small but frequent feeding
o Abscess formation heal scar (within 2 Pedia – NPO 4 to 8 hrs – rest the GI tract
to 3 months) Clear liquid diet soft diet DFA
o Indolent Abscess – Koch’s o Provide comfort measures
Phenomenon Prevention: TEMPORARY IMMUNITY
Wrong technique by the nurse o Immunization – CDT – Cholera, Dysentery, Typhoid
o Child had exposure to a patient with o Avoid the 5 Fs
active TB – usually asymptomatic Feces – proper disposal
o Bring back child to health center – I & Fingers – hand washing
D Food – preparation, handling, storage
o Give prophylaxis – INH Flies – environmental sanitation
Effect: Fomites – Avoid putting anything to our
o Children - 6 mos to 8 mos mouths – ballpen
Immunocompromised – 12 mos
o No booster 2. LEPTOSPIROSIS
AKA: Mud Fever, Canicola Fever, Swamp Fever,
GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT Pre-tibial Fever, Ictero-hemorrhagica
Bacteria Disease, Weil’s Disease, Swineherd’s Disease
o Typhoid CA: Leptospira (Spirochete)
o Leptospirosis Source: Rats
o Bacillary MOT: Skin penetration
o Cholera IP: 2 days to 4 weeks
Protozoa – Amebiasis Affects striated muscles, Liver, Kidneys
Virus – Hepatitis o Cause of death: Kidney failure
Helminths – Parasitism
S/sx:
o Fever, headache, vomiting
1. TYPHOID FEVER o Muscle tenderness, pain (calf)
CA: Salmonella typhosa Patient does not stand up or walk
MOT: Fecal-oral o Jaundice with hemorrhage
o 5 Fs o Orange eyes/ skin
Food o Oliguria/ Anuria – Kidney failure
Fingers
Flies Dx Exam:
Feces o Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
Fomites Med Mgt:
Target organ: Peyer's patches o Antibiotic – Doxycycline
Prophylaxis - 200 mg twice a day for 3 days
S/sx: Nrsg Care:
o Fever, dull headache, abdominal pain o Supportive
o Vomiting, diarrhea/ constipation o UO – consistency, frequency and amount
o Clinical features: Refer if with changes
Ladderlike fever
Rose spots – Abdomen Prevention: TEMPORARY IMMUNITY
Spleenomegaly o Eradicate the source of infection (rats)
Dx Exam: o Use of protective barrier when walking in flood
o Blood culture
o Widal Test – Antigen left by the microorganism 3. DYSENTERY
AgO – Somatic – Presently infected * see table
AgH – Flagellar – Exposed/ Had an
immunization 4. HEPATITIS
o Thyphidot – Antibody Inflammation of the liver
IgM – presently infected Causes:
IgG – some form of immunity/ recovering o Alcoholism
o Drug intoxication
Med Mgt: o Chemical intoxication – Arsenic
o Antibiotic o Microorganism
Chloramphenicol – drug of choice
o Fluid and electrolyte replacement Viral Hepatitis
o Hepatitis A
Nrsg Care: Infectious hepatitis
University of Santo Tomas – College of Nursing / JSV
You might also like
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 6Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 6JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease NursingDocument10 pagesCommunicable Disease NursingMarisol DizonNo ratings yet
- Dumlao, Michelin H.Document20 pagesDumlao, Michelin H.Mich DumlaoNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals!Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals!Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 3Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 3JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Top Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Document4 pagesTop Communicable Diseases in The Philippines 2019Nicole cuencosNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseVinceNo ratings yet
- Vector Borne Diseases: Malaria (Ague)Document20 pagesVector Borne Diseases: Malaria (Ague)Nina OaipNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- NCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Document25 pagesNCMB 312 Finals! (2.0)Justine Dinice MunozNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 18JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Summarize Notes On ImciDocument6 pagesSummarize Notes On ImciI'm Just A BurgerNo ratings yet
- Wilm's Tumor EtcDocument5 pagesWilm's Tumor EtcDanica BonNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Infections II IBDDocument8 pagesBacterial Infections II IBDRozeanneNo ratings yet
- Safe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingDocument16 pagesSafe Drugs During Pregnancy & Lactation: Category Pregnancy Breast-FeedingJo ckerNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Child With Autoimmune Diseases & GI DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Care For Child With Autoimmune Diseases & GI Disordersbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases 2.4-5.22Document9 pagesCommunicable Diseases 2.4-5.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Presented by Abhinay BhugooDocument32 pagesPresented by Abhinay BhugooGideon K. MutaiNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseasesDocument8 pagesCommunicable DiseasesJamie John EsplanadaNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 17Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 17JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Spondilitis TB AnakDocument36 pagesSpondilitis TB Anaktry intan kartini50% (2)
- AmoebiasisDocument17 pagesAmoebiasisAjay AgrawalNo ratings yet
- GASTRODocument47 pagesGASTROMada mada DaneNo ratings yet
- Step2 - PediatricsDocument18 pagesStep2 - PediatricsKiran Saini100% (1)
- Bacteria-Borne Diseases Handout 2022Document3 pagesBacteria-Borne Diseases Handout 2022Anna CrisNo ratings yet
- HCC Exam 4Document20 pagesHCC Exam 4Sheri BarlingNo ratings yet
- GenitoDocument12 pagesGenitofatima_antonioNo ratings yet
- Week-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-GerryDocument10 pagesWeek-13 Cd-Vid-Lec-1-3-Sir-Gerryjmmacar19No ratings yet
- NCM 112 LEC Topic 14 Communicable DiseasesDocument6 pagesNCM 112 LEC Topic 14 Communicable DiseasesViviene Faye FombuenaNo ratings yet
- Viral Diseases RuminantDocument34 pagesViral Diseases RuminantNorwood Everett DaduloNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument7 pagesPlacenta Previa Case StudyKing NavsunNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Overview & OutcomesDocument5 pages1.1 Overview & OutcomesShayla HudsonNo ratings yet
- 5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFDocument8 pages5.1 - Infectious Diseases PDFVince Alvin DaquizNo ratings yet
- (Surgery) Midterms PediatricsDocument5 pages(Surgery) Midterms Pediatricsalmira.s.mercadoNo ratings yet
- Elsie Kho Ap300 Study NotesDocument36 pagesElsie Kho Ap300 Study Noteshanazawa_rui9878030No ratings yet
- Pastel Cute Illustrative Business Report PresentationDocument18 pagesPastel Cute Illustrative Business Report PresentationdocgioreNo ratings yet
- Ncmb312 Lec FinalDocument63 pagesNcmb312 Lec FinalRose Ann CammagayNo ratings yet
- Brosure Dengue FeverDocument3 pagesBrosure Dengue FeverMadvi TadeoNo ratings yet
- Enteric DiseaseDocument2 pagesEnteric DiseaseHazel ZullaNo ratings yet
- Agata Infectious DiseasesDocument34 pagesAgata Infectious DiseasesMartaNo ratings yet
- NP1 BulletsDocument17 pagesNP1 BulletsJea VesagasNo ratings yet
- NP1 BulletsDocument17 pagesNP1 BulletsJea VesagasNo ratings yet
- PediatricsDocument80 pagesPediatricsmohamed muhsinNo ratings yet
- Module 6.4 ParasitesDocument6 pagesModule 6.4 ParasitesPNo ratings yet
- ENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)Document35 pagesENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)rumman tariqNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NotesDocument13 pagesPediatrics NotesYsa BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Infection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Document109 pagesInfection of The Urinary Tract: Campbell-Walsh 11th ED, CH12Sirawit Namkaeng ChoksuchatNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases Tabelle (Examen 6. Jahr)Document34 pagesInfectious Diseases Tabelle (Examen 6. Jahr)Aastha SethNo ratings yet
- Typhidot Is A: Medical Test Elisa Igm Igg Antibodies Outer Membrane Protein Salmonella TyphiDocument5 pagesTyphidot Is A: Medical Test Elisa Igm Igg Antibodies Outer Membrane Protein Salmonella TyphiDecember TwoNo ratings yet
- Parasitic WormsDocument4 pagesParasitic WormsEricNo ratings yet
- Care of NeonatesDocument7 pagesCare of NeonatesJankaruroNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BDocument15 pagesFar Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BHarlyn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Amoebiasis: (Amoebic Dysentery)Document32 pagesAmoebiasis: (Amoebic Dysentery)abhinay_1712No ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 4Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 4JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Common Exanthems PDFDocument4 pagesCommon Exanthems PDFKaren Ivy BacsainNo ratings yet
- Sandeep BI YE NotesDocument21 pagesSandeep BI YE NotesPranav ThakoreNo ratings yet
- Mind Map Human Health and Disease Final PYQs and Exemplar 1Document186 pagesMind Map Human Health and Disease Final PYQs and Exemplar 1Mohit Devraj ParasharNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 11JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 7JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 8JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 10JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 19JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYNo ratings yet
- Sci Chapter 2 8thDocument18 pagesSci Chapter 2 8thAakash ChatakeNo ratings yet
- Final PDFDocument31 pagesFinal PDFHimanshu BishtNo ratings yet
- Pathogens and Pathways, and Small Drinking-Water SuppliesDocument22 pagesPathogens and Pathways, and Small Drinking-Water SuppliesZari Sofia Leviste100% (1)
- Salmonella Infected Model On MiceDocument14 pagesSalmonella Infected Model On MiceAmi FebrizaNo ratings yet
- Department of Haematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDocument5 pagesDepartment of Haematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodSunil KhandekarNo ratings yet
- Applications of Immunology in DiagnosisDocument5 pagesApplications of Immunology in Diagnosischrist sonNo ratings yet
- Enteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverDocument2 pagesEnteric Fever and Dysentery (Typhoid FeverAlaa BahjatNo ratings yet
- Godfroy, Marion F. - Kourou and The Struggle For A French AmericaDocument17 pagesGodfroy, Marion F. - Kourou and The Struggle For A French AmericadecioguzNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology - Final Term QuizDocument4 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology - Final Term QuizMary Grace MartinNo ratings yet
- Didier Raoult, Didier Raoult, Michel Drancourt - Paleomicrobiology - Past Human Infections-Springer (2008)Document224 pagesDidier Raoult, Didier Raoult, Michel Drancourt - Paleomicrobiology - Past Human Infections-Springer (2008)Juan Antonio Duque-TardifNo ratings yet
- Gram Negative Cocci Gram Positive BacilliDocument103 pagesGram Negative Cocci Gram Positive BacilliMacky IbayNo ratings yet
- EnterobacteriaceaeDocument12 pagesEnterobacteriaceaeFaithNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Epidemiology of Intestinal InfectionsDocument46 pagesLecture 3 Epidemiology of Intestinal InfectionsAli Baker AlgelaneNo ratings yet
- ENTEROBACTERIACEAEDocument11 pagesENTEROBACTERIACEAEYormae QuezonNo ratings yet
- Meningitis 1Document533 pagesMeningitis 1Bhan Panom GatdietNo ratings yet
- BoookDocument131 pagesBoookDeepak SinghNo ratings yet
- Summative Test ScienceDocument5 pagesSummative Test ScienceElmalyn Bernarte100% (2)
- Water Borne DiseasesDocument15 pagesWater Borne DiseasesDeepak BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Nursing 2020Document421 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing 2020Kenneth Myro GarciaNo ratings yet
- What Diseases Are Commonly Caused by Wastewater?Document7 pagesWhat Diseases Are Commonly Caused by Wastewater?RimaQuitainNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Disease: Group 4Document57 pagesTyphoid Disease: Group 4ajeng astiaNo ratings yet
- Dengue TitersDocument4 pagesDengue TitersPeter Francis RaguindinNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Enterics 15 ShortlyDocument82 pagesLecture 1 - Enterics 15 ShortlyIsak Isak IsakNo ratings yet
- Calixtro, LJ Bacterial Infections Narrative PathophysiologyDocument14 pagesCalixtro, LJ Bacterial Infections Narrative PathophysiologyKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaaminzaghiNo ratings yet
- Typhoid Fever,-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesTyphoid Fever,-WPS OfficeElvisNo ratings yet
- PREDICTIVEHOMOEOPATHYDocument46 pagesPREDICTIVEHOMOEOPATHYHomeopathy Torrents85% (34)
- First Quiz Q1 With Tos All SubjectsDocument34 pagesFirst Quiz Q1 With Tos All SubjectsJohn Erroll GesmundoNo ratings yet
- Widal Test - Introduction, Principle, Procedure, Interpretation and LimitationDocument13 pagesWidal Test - Introduction, Principle, Procedure, Interpretation and LimitationAshik ThapaNo ratings yet
- PGuidelines Enteric. FeverDocument4 pagesPGuidelines Enteric. FeverSara Ilyas KhanNo ratings yet