Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Photsynthesis
Photsynthesis
Uploaded by
Lady RedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Photsynthesis
Photsynthesis
Uploaded by
Lady RedCopyright:
Available Formats
**Title: Photosynthesis: Nature's Green Alchemy**
**Introduction:**
Photosynthesis, the miraculous process by which plants, algae, and certain bacteria harness light
energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen, serves as the foundation of life
on Earth. Through this intricate biochemical pathway, organisms not only produce their own food but
also generate the oxygen essential for the survival of aerobic life forms. In this essay, we delve into
the fascinating world of photosynthesis, exploring its mechanisms, ecological significance,
adaptations, and its profound impact on the biosphere.
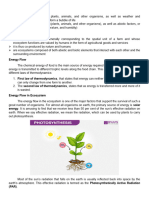
**Mechanisms of Photosynthesis:**
Photosynthesis occurs in specialized organelles called chloroplasts, primarily found in plant leaves.
The process involves two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the light-independent
reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle.
During the light-dependent reactions, chlorophyll molecules within the thylakoid membranes of
chloroplasts absorb light energy. This energy is used to split water molecules into oxygen, protons,
and electrons. The electrons are then transferred through a series of electron carriers, generating ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), which serve as
energy carriers for the subsequent reactions.
In the light-independent reactions, the Calvin cycle, ATP and NADPH produced in the light-
dependent reactions are utilized to fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. This process involves a
series of enzymatic reactions that ultimately produce glucose, a carbohydrate molecule that serves as a
source of energy and carbon for the organism.
**Ecological Significance of Photosynthesis:**
Photosynthesis is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems on Earth. Plants, algae, and
photosynthetic bacteria form the base of the food chain, providing organic compounds that sustain
higher trophic levels. Moreover, photosynthesis is responsible for the oxygenation of the atmosphere,
as plants release oxygen as a byproduct of the process. This oxygen is essential for aerobic respiration
in animals and other organisms, highlighting the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Furthermore, photosynthesis plays a crucial role in the global carbon cycle. By removing carbon
dioxide from the atmosphere and incorporating it into organic molecules, photosynthetic organisms
help regulate Earth's climate and mitigate the effects of anthropogenic carbon emissions.
**Adaptations for Photosynthesis:**
Photosynthetic organisms have evolved a diverse array of adaptations to optimize the efficiency of
photosynthesis in various environmental conditions. For example, plants in arid environments may
possess specialized structures like succulent leaves or CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism)
metabolism, which minimize water loss while maximizing carbon uptake. In aquatic environments,
algae and underwater plants have adaptations to efficiently capture light and nutrients in low-light
conditions.
Additionally, some photosynthetic organisms, such as certain bacteria and algae, are capable of
photosynthesis in the absence of oxygen, known as anoxygenic photosynthesis. These organisms
utilize alternative electron donors and acceptors, allowing them to thrive in anaerobic environments
such as deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
**Impact on Human Life:**
The impact of photosynthesis on human life is profound and multifaceted. Agriculturally,
photosynthesis sustains crop production, providing food, fiber, and biofuels essential for human
consumption and economic development. Furthermore, photosynthetic organisms serve as sources of
pharmaceuticals, biomaterials, and renewable energy, contributing to advancements in medicine,
biotechnology, and sustainable development.
Moreover, the role of photosynthesis in mitigating climate change underscores its significance for
human well-being. Efforts to protect and restore photosynthetic ecosystems, such as forests and
wetlands, are crucial for preserving biodiversity, regulating the climate, and ensuring the long-term
sustainability of Earth's ecosystems.
**Conclusion:**
In conclusion, photosynthesis stands as a marvel of nature, a fundamental process that sustains life on
Earth. From its intricate biochemical mechanisms to its ecological significance and adaptations,
photosynthesis exemplifies the ingenuity and resilience of living organisms. As we continue to
unravel the mysteries of photosynthesis and harness its potential for sustainable development, we
deepen our appreciation for the intricate web of life that depends on this remarkable process. By
fostering stewardship of photosynthetic ecosystems and advancing technologies inspired by nature's
green alchemy, we pave the way for a more sustainable and harmonious relationship between
humanity and the biosphere.
You might also like
- Written Report Topic: Introduction of Photosynthesis Sub. To: Prof. Ruthela Payawal Sub. By: Platero, Emily SDocument4 pagesWritten Report Topic: Introduction of Photosynthesis Sub. To: Prof. Ruthela Payawal Sub. By: Platero, Emily Sgtalite100% (1)
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisjellyngan1022No ratings yet
- The Marvels of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Marvels of PhotosynthesisDwight KintanarNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesismachitidzenanikoNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesishurainsahar21No ratings yet
- Session - 7 Unit - III Material Cycles: Dr. H.S. RameshDocument8 pagesSession - 7 Unit - III Material Cycles: Dr. H.S. RameshPraful KakdeNo ratings yet
- En Sci Lec 2ADocument25 pagesEn Sci Lec 2AJk DumpNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems: A Description: The Raw Materials of An EcosystemDocument8 pagesEcosystems: A Description: The Raw Materials of An EcosystemMonasterio Tan KennethNo ratings yet
- Nabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Document11 pagesNabila Tisa Lathifah - Week 2Nabila LathifahNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisAlexie AlmohallasNo ratings yet
- The Wonders of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesThe Wonders of Photosynthesisarvinraghubar9No ratings yet
- Illuminating The Miracle of Photosynthesis - Nature's Green AlchemyDocument4 pagesIlluminating The Miracle of Photosynthesis - Nature's Green Alchemymr.kupiduoNo ratings yet
- Essay On PhotosynthesisDocument1 pageEssay On PhotosynthesisRameesha MalikNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument23 pagesECOSYSTEMVenkatesh KumarNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 8..Q4..W6 7..ecosystemDocument4 pagesSCIENCE 8..Q4..W6 7..ecosystemMaam LC CamosaNo ratings yet
- Biological ProductivityDocument27 pagesBiological ProductivityKaz YuanNo ratings yet
- Nutrient CycleDocument5 pagesNutrient CycleKhadijah HabeebahNo ratings yet
- Session - 7 Unit - III Material Cycles: Dr. H.S. RameshDocument48 pagesSession - 7 Unit - III Material Cycles: Dr. H.S. Rameshadithya700No ratings yet
- Civ 4204: Environmental Quality Management: Ntroduction and DefinitionsDocument8 pagesCiv 4204: Environmental Quality Management: Ntroduction and Definitionsmulabbi brianNo ratings yet
- Ecosystems: 3.1 Types of Ecosystems There Are Essentially Two Kinds of Ecosystems Aquatic and Terrestrial. AnyDocument6 pagesEcosystems: 3.1 Types of Ecosystems There Are Essentially Two Kinds of Ecosystems Aquatic and Terrestrial. AnyMariia RivasNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesisHans ZacariasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Earth SystemsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Earth SystemsTwix ChweNo ratings yet
- 14 EcosystemDocument17 pages14 EcosystemshashiwiproNo ratings yet
- Module1 ExploreDocument20 pagesModule1 ExploreQueen May OmandamNo ratings yet
- Environmental Sciences and Practices - 03 - EcosystemDocument23 pagesEnvironmental Sciences and Practices - 03 - EcosystemSayan MedyaNo ratings yet
- Indranil - Karunit 22020-05-16envs Unit 2 Ecology and EcosystemsDocument12 pagesIndranil - Karunit 22020-05-16envs Unit 2 Ecology and EcosystemsBs JanNo ratings yet
- Energy Flow Through Ecosystems: Group 4Document42 pagesEnergy Flow Through Ecosystems: Group 4Febe AnneNo ratings yet
- Agri NotesDocument7 pagesAgri NotesMikaella GarciaNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY NOTES On Biodiversity & PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesSUMMARY NOTES On Biodiversity & PhotosynthesisBonachita YamNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem EssayDocument3 pagesEcosystem Essaymichelle_14100% (1)
- Group 5Document18 pagesGroup 5Mark Niño DelosoNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WPS OfficeDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis WPS OfficeObaro AjekeNo ratings yet
- Environment and Ecology: Environmental Studies, I/Ii Sem B.E.-Vtu Unit 1 & 2Document15 pagesEnvironment and Ecology: Environmental Studies, I/Ii Sem B.E.-Vtu Unit 1 & 2Praful KakdeNo ratings yet
- EcologyDocument13 pagesEcologyFatimah KhanNo ratings yet
- SBTA1304Document123 pagesSBTA1304Suchitra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Structural ComponentsDocument10 pagesEcosystem Structural ComponentsPogi AkoNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument7 pagesEcosystemHamza Khan100% (1)
- 0 Environmental Systems, EcosystemDocument21 pages0 Environmental Systems, EcosystemitzmeabeerNo ratings yet
- Cycles and FlowsDocument28 pagesCycles and FlowsRogers Talemwa WakefieldNo ratings yet
- FYBMS Environmental Management NotesDocument43 pagesFYBMS Environmental Management NotesAshu Salian100% (5)
- Topic One888Document22 pagesTopic One888BabaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerTristan BaceraNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Environmental Systems, EcosystemDocument18 pages2.2 Environmental Systems, EcosystemSadi Mohammad HridoyNo ratings yet
- Nov, 02 Last Out Put On Tuesdaydifferentiate Between Photosynthesis andDocument2 pagesNov, 02 Last Out Put On Tuesdaydifferentiate Between Photosynthesis andJosua SaysonNo ratings yet
- CBSE - Class9 - Science - Capter 9 - PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesCBSE - Class9 - Science - Capter 9 - PhotosynthesismukeshNo ratings yet
- Material Cycles and Life Processes Lesson 2Document9 pagesMaterial Cycles and Life Processes Lesson 2Pamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- Bio SHHWDocument15 pagesBio SHHWrishika000162No ratings yet
- Escosystem Biodiversity Modul 3Document19 pagesEscosystem Biodiversity Modul 3sujeetNo ratings yet
- ECOLOGYDocument6 pagesECOLOGYAllan DeGuzman Dela VegaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Photosynthesis On Earth S Life: Project Made By: Mostafa Hany Grade:8EDocument3 pagesEffect of Photosynthesis On Earth S Life: Project Made By: Mostafa Hany Grade:8EMezo7272No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis #1Document1 pagePhotosynthesis #1Wally WestNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument1 pagePhotosynthesisdellavajames192000No ratings yet
- Module 4 & 5Document17 pagesModule 4 & 5Divine Grace CincoNo ratings yet
- Environment 06 - Daily Class Notes - (Sankalp (UPSC 2024) )Document6 pagesEnvironment 06 - Daily Class Notes - (Sankalp (UPSC 2024) )WHITE SHADOWNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem PDFDocument17 pagesEcosystem PDFRamachandranPerumalNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution ControlFrom EverandWater Pollution ControlSuresh T. NesaratnamNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Biogeochemistry: The Ecophysiology of Mineral CyclingFrom EverandBacterial Biogeochemistry: The Ecophysiology of Mineral CyclingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Web of Life: Understanding Ecology and Our Place in ItFrom EverandThe Web of Life: Understanding Ecology and Our Place in ItNo ratings yet
- Exicutive MBADocument10 pagesExicutive MBALady RedNo ratings yet
- 2Document2 pages2Lady RedNo ratings yet
- AfricaDocument2 pagesAfricaLady RedNo ratings yet
- Rain Forest - AmazonDocument2 pagesRain Forest - AmazonLady RedNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument2 pagesAtomsLady RedNo ratings yet
- IronDocument2 pagesIronLady RedNo ratings yet
- Hearing AidDocument2 pagesHearing AidLady RedNo ratings yet
- PacemakerDocument2 pagesPacemakerLady RedNo ratings yet
- NUS Power Quality Temp-2BDocument19 pagesNUS Power Quality Temp-2Brajiv kundalaNo ratings yet
- Evc 04 Ac 7Document46 pagesEvc 04 Ac 7Bala DhandapaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument4 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat Nosourabh patil100% (1)
- Aeroshell Specification GuideDocument2 pagesAeroshell Specification GuideAdrian PintilieNo ratings yet
- Carbon Film / Metal Film Resistors: ResistorDocument5 pagesCarbon Film / Metal Film Resistors: ResistorSanjay BoregowdaNo ratings yet
- Dryers: Proven Design and Competitive SolutionsDocument5 pagesDryers: Proven Design and Competitive SolutionsJuan Fernando Pineda GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 3RD PT Science 6Document7 pages3RD PT Science 6CHARMAINE MONTESNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram of Centrifugal Compressor: Euler's Equation For Energy TransferDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagram of Centrifugal Compressor: Euler's Equation For Energy TransferMallepalli YadaiahNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Readiness and Reduction Module 9 - The Elements of Fire Triangle What'S inDocument4 pagesDisaster Risk Readiness and Reduction Module 9 - The Elements of Fire Triangle What'S inKimchiiNo ratings yet
- Tools Ko TotDocument11 pagesTools Ko TotElaica Joy PuadaNo ratings yet
- PVT LabDocument98 pagesPVT LabMansoorNo ratings yet
- Procedures To Start & Stop The KNG's ModelsDocument3 pagesProcedures To Start & Stop The KNG's ModelsMarcelo MesoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Bolted Joint DesignDocument15 pages3.1 Bolted Joint Designssn MLNo ratings yet
- Riciclo Batterie LitioDocument57 pagesRiciclo Batterie LitiomattiaNo ratings yet
- BALLISTICSDocument18 pagesBALLISTICSvan vanNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2021-02-04 at 21.37.09Document3 pagesScreenshot 2021-02-04 at 21.37.09DoriNo ratings yet
- TDI Injection and Glow Plug System 4-Cyl 2 0 LTR 4-Valve Common RailDocument77 pagesTDI Injection and Glow Plug System 4-Cyl 2 0 LTR 4-Valve Common RailergdegNo ratings yet
- AlcochemILTbrochure Unimar2018Document12 pagesAlcochemILTbrochure Unimar2018milton rebelloNo ratings yet
- Hyster 3 TONDocument738 pagesHyster 3 TONahmedaljamel433No ratings yet
- Atomic McQs 4-2Document13 pagesAtomic McQs 4-2Muhammed FaheemNo ratings yet
- DBM DPR Babji SirDocument2 pagesDBM DPR Babji Sirdevshakti swainNo ratings yet
- What Is Process Flow DiagramDocument6 pagesWhat Is Process Flow DiagramDanh DothanhNo ratings yet
- BASICS OF AN INSTRUMENT AIR SUPPLY SYSTEM - Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDocument4 pagesBASICS OF AN INSTRUMENT AIR SUPPLY SYSTEM - Instrumentation and Control EngineeringAhmadTaufikMuradNo ratings yet
- Bom-R K e MCC PanelDocument2 pagesBom-R K e MCC PanelNitesh KhamariNo ratings yet
- Desalination of Water Using Solar Stills: Ahmed Abdullah HassanDocument22 pagesDesalination of Water Using Solar Stills: Ahmed Abdullah Hassanالزهور لخدمات الانترنيتNo ratings yet
- ENGGEN 140 2023 S1 - Mock Test 2 SolutionsDocument24 pagesENGGEN 140 2023 S1 - Mock Test 2 SolutionsKingstanIINo ratings yet
- 03) Overvoltage and Travelling WavesDocument35 pages03) Overvoltage and Travelling WavesshafquatNo ratings yet
- Accelerator Pedal Position SensorDocument4 pagesAccelerator Pedal Position SensorRicka AndriamadyNo ratings yet
- Experimental SkillsDocument76 pagesExperimental SkillsDeepak PandeyNo ratings yet
- BQTs 466 - 2+NB-1253Document7 pagesBQTs 466 - 2+NB-1253Respect Your Own WorkNo ratings yet