Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hepatitis
Hepatitis
Uploaded by
luvvemulle0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesHepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses or toxic substances. There are multiple types of hepatitis defined by their causes, which include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses. Symptoms range from mild fatigue and abdominal discomfort to jaundice. Diagnosis involves liver enzyme and bilirubin blood tests, ultrasound imaging, and viral antibody testing. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms for acute cases and antiviral drugs for chronic cases. Complications can include cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer if left untreated. Prevention methods center around vaccination, hand washing, and avoiding sharing personal items that may transmit bodily fluids.
Original Description:
Original Title
Hepatitis (2)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses or toxic substances. There are multiple types of hepatitis defined by their causes, which include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses. Symptoms range from mild fatigue and abdominal discomfort to jaundice. Diagnosis involves liver enzyme and bilirubin blood tests, ultrasound imaging, and viral antibody testing. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms for acute cases and antiviral drugs for chronic cases. Complications can include cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer if left untreated. Prevention methods center around vaccination, hand washing, and avoiding sharing personal items that may transmit bodily fluids.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesHepatitis
Hepatitis
Uploaded by
luvvemulleHepatitis is an inflammation of the liver that can be caused by viruses or toxic substances. There are multiple types of hepatitis defined by their causes, which include hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E viruses. Symptoms range from mild fatigue and abdominal discomfort to jaundice. Diagnosis involves liver enzyme and bilirubin blood tests, ultrasound imaging, and viral antibody testing. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms for acute cases and antiviral drugs for chronic cases. Complications can include cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer if left untreated. Prevention methods center around vaccination, hand washing, and avoiding sharing personal items that may transmit bodily fluids.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as doc, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Hepatitis
Definition is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver.
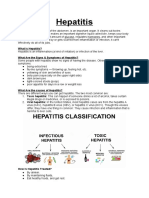
Etiology & Hepatitis can be infectious and non-infectious.
types Non-infectious hepatitis can be caused by toxic drugs, toxins or diseases of immune system (a condition where the immune system attacks and destroys liver cells as foreign bodies).
Infectious hepatitis is caused by viruses A, B, C, D, E (viral) and bacteria (bacterial) and parasites.
Viral hepatitis
Hepatitis A is acquired by consuming materials contaminated with faecal matter of an individual who already has disease. It is usually communicated as a result of poor hygiene or through personal
contact. The virus is able to survive at normal room temperature for hours on a hard surface. The incubation period for hepatitis A lasts about 2-6 weeks. Most patients recover within a few months.
Hepatitis B is spread through infected body fluids like blood, semen, saliva, suppurating sores, breast milk. It doesn’t spread by simple physical contact. The incubation period lasts from 1 to 6 months.
After recovering the infected person will be immune to any later reinfection with this particular virus. Some individuals may fully recover and have no symptoms and yet remain a capable of infecting
others through sexual contact, shared hypodermic needles, food or drinks.
Hepatitis C has no symptoms. Most people become chronically infected. People with strong immune system may recover without treatment. Those with chronic hepatitis C who are not treated or cured
may live normal lives but they remain carriers of the disease and can infect other people. Some patients with hepatitis C develop complications like cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancer. Incubation
period lasts 2weeks-six months.
Hepatitis D attacks only individuals with hepatitis B. A person may get 2 forms at the same time. It is transmitted through the same routs as hepatitis B. Hepatitis D can be suspected when the condition
of someone with hepatitis B suddenly becomes worse. It can be diagnosed with tests that reveal hepatitis D antibodies in the blood.
Hepatitis E (waterborne disease) is similar to hepatitis A and is transmitted contaminated water supplies. Incubation period lasts about 2 or 6 weeks. Most people with hepatitis E recover from it on
their own within a few months. This type of hepatitis is spread in Certain African countries and in Asia.
Methods of Methods of diagnostics are Liver tests include measurements of specific enzymes that seep into the blood. The bilirubin test measures the amount of this pigment in the blood. (A level above 3mg/dl
diagnostics indicates a liver disorder) Liver biopsy, Ultrasound, Viral antibody testing
Clinical Hepatitis can be acute (short-term) and chronic (symptoms last more than a few months).
picture At first, chronic hepatitis often does not cause any symptoms. People with symptoms most commonly complain of fatigue. Fatigue worsens throughout the day .Other common symptoms include:
Mild upper abdomen discomfort
Loss of appetite
Nausea
Vomiting
Low-grade fever
Jaundiced skin colouring, yellowing of the whites of the eyes
Dark urine
If chronic hepatitis becomes more severe, people may experience additional symptoms, including: Abdominal swelling, Weight loss, Muscle weakness
Treatment In patients with acute viral hepatitis, the initial treatment consists of relieving the symptoms of nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Only those medications that are considered necessary should be administered since the impaired liver is not able to eliminate drugs normally. Moreover, sedatives and "tranquilizers" are avoided
because they may accentuate the effects of liver failure on the brain and cause lethargy and coma.
The patient must avoid drinking alcohol, since alcohol is toxic to the liver.
It is necessary to provide intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration caused by vomiting. Patients with severe nausea and/or vomiting may need to be hospitalized for treatment and intravenous fluids.
Treatment of chronic viral hepatitis include
Antiviral drugs
avoiding further liver damage from alcohol or NSADs (Tylenol).
A well-balanced diet
Regular exercises
Cessation of smoking
Avoiding salty food if there is a tendency to accumulate fluids
Corticosteroids are used to suppress the immune system are the main treatment of autoimmune chronic hepatitis. These drugs usually decrease symptoms, reduce liver inflammation and prolong
survival.
Complications Cirrhosis, liver failure, liver cancer
Prevention Vaccination
Washing hands.
Avoiding tap water when traveling to certain countries or regions, sharing drug needles and
Avoiding sharing personal items—such as toothbrushes, razors and nail clippers—with an infected person.
You might also like
- UVA Family Medicine QbankDocument32 pagesUVA Family Medicine QbankjamesmgangNo ratings yet
- What Is Life A Guide To Biology 3rd Edition Phelan Test Bank DownloadDocument29 pagesWhat Is Life A Guide To Biology 3rd Edition Phelan Test Bank DownloadClara Rodas100% (20)
- BIOCHEMISTRY ExamDocument4 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY Examchristinejoan100% (2)
- Case Study For Hepatitis BDocument24 pagesCase Study For Hepatitis BEmma Mariz Bernas Garcia67% (6)
- Experiment 8 and 9 PDFDocument17 pagesExperiment 8 and 9 PDFKrizzi Dizon GarciaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: HepatitisDocument12 pagesAssignment On: HepatitisAbdallah KisswaniNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Joan M Pino-Tablot RN MSN Apn Cs FALL 2005Document44 pagesHepatitis: Joan M Pino-Tablot RN MSN Apn Cs FALL 2005dharmin_joshiNo ratings yet
- What Is The HepatitisDocument14 pagesWhat Is The HepatitisBlack Hack HakerNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument6 pagesHepatitisMOHIT KUMARNo ratings yet
- Science Hepatitis Group 2Document12 pagesScience Hepatitis Group 2Joy VillafloresNo ratings yet
- A. What Is Hepatitis B?Document8 pagesA. What Is Hepatitis B?Raditya PrayogaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Viral HepatitisDocument6 pagesLesson 9 Viral Hepatitisgimel tenorioNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument10 pagesHepatitisBheru LalNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hepatitis ADocument7 pagesJurnal Hepatitis AarifNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis: Ms. Whelhelmina Montefrio, BSN, R.NDocument49 pagesViral Hepatitis: Ms. Whelhelmina Montefrio, BSN, R.NAhmad BaolayyanNo ratings yet
- Your Liver Is The Largest Organ Inside Your Bod1Document14 pagesYour Liver Is The Largest Organ Inside Your Bod1Rrhandy Mae dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B OverviewDocument8 pagesHepatitis B OverviewAnnieElizabethNo ratings yet
- BSC III SEC MEDICAL DIGNOSDocument28 pagesBSC III SEC MEDICAL DIGNOSDipak PawarNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument4 pagesHepatitis- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Optionssusanajala3No ratings yet
- Hepatitis- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument4 pagesHepatitis- Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Optionssusanajala3No ratings yet
- Hepatitis and How To Treat ThemDocument3 pagesHepatitis and How To Treat ThemLit Central DreamsNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Institute of Medicine (IOM), 2010Document18 pagesHepatitis Institute of Medicine (IOM), 2010cedricNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A: Presented By: Aurora LumbresDocument10 pagesHepatitis A: Presented By: Aurora LumbresElkissa Joy Lumbres YutucNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Hepa ADocument5 pagesCase Study For Hepa AGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument53 pagesHepatitisBinish Chughtai JunaidNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument69 pagesHepatitisPrakash BudhaNo ratings yet
- Liver DiseaseDocument69 pagesLiver DiseaseNathan CruzNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument9 pagesHepatitisDelliora DemonNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A BDocument5 pagesHepatitis A BLouise OpinaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis:: Bilirubin From The BloodDocument2 pagesHepatitis:: Bilirubin From The BloodansyNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment: Submitted By: Maham Ahmed (01-171182-013) Class: BS Psychology Date: 23 Submitted To: Sir Kashif AliDocument6 pagesBiology Assignment: Submitted By: Maham Ahmed (01-171182-013) Class: BS Psychology Date: 23 Submitted To: Sir Kashif Alihurricane2010No ratings yet
- Reporting Draft For PPT InputsDocument2 pagesReporting Draft For PPT InputsPhaestus ReverseNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument7 pagesHepatitisPriyaNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument2 pagesHepatitisBenazir SheikhNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis: Aashi Rajput 20PHPH010030 MicrobiologyDocument18 pagesHepatitis: Aashi Rajput 20PHPH010030 MicrobiologyManjunath ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Chronic Viral HepatitisDocument8 pagesPharmacotherapeutic Management of Chronic Viral HepatitisAishwarya ANo ratings yet
- Hepatitis ADocument13 pagesHepatitis AEbrahim El-sayedNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B OverviewDocument12 pagesHepatitis B OverviewJunita Jeanne PalimanNo ratings yet
- Haepatitis - EDocument5 pagesHaepatitis - ERatnaPrasadNalamNo ratings yet
- What Is HepatitisDocument8 pagesWhat Is HepatitisAnoop KumarNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document25 pagesWa0003.Aamnaa 639No ratings yet
- Etiologic Agent Means A Disease-Causing Agent. Hepatitis A - o - o o - o - oDocument5 pagesEtiologic Agent Means A Disease-Causing Agent. Hepatitis A - o - o o - o - ojin0meNo ratings yet
- Etiologic Agent Means A Disease-Causing Agent. Hepatitis A - o - o o - o - oDocument5 pagesEtiologic Agent Means A Disease-Causing Agent. Hepatitis A - o - o o - o - ojin0meNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Hepatitis ADocument5 pagesJurnal Hepatitis ANurul Amaliah LestariNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Tract Diarrhea Nausea Viral Infection BacteriaDocument60 pagesGastrointestinal Tract Diarrhea Nausea Viral Infection BacteriawakuyllibNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Hepa BDocument5 pagesCase Study For Hepa BGabbii CincoNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis, Viral: Type A (HAV) Type B (HBV) Type C (HCV)Document17 pagesHepatitis, Viral: Type A (HAV) Type B (HBV) Type C (HCV)herlindaNo ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument25 pagesHepatitisAamnaa 639No ratings yet
- Causes, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Hepatitis A Hepatitis C Hepatitis DDocument41 pagesCauses, Incidence, and Risk Factors: Hepatitis A Hepatitis C Hepatitis DAmber ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of HepatitisDocument3 pagesTreatment of HepatitisPirasan Traditional Medicine CenterNo ratings yet
- Natural HistoryDocument1 pageNatural HistoryRocel LomedaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis - Types, Symptoms, and PreventionDocument14 pagesViral Hepatitis - Types, Symptoms, and PreventionMustafa AlmasoudiNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Basic InformationDocument3 pagesViral Hepatitis Basic Informationberuangmadu777No ratings yet
- ABCs of Hepatitis.Document13 pagesABCs of Hepatitis.Ali AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument28 pagesHepatitis BLex DgtNo ratings yet
- ELLANA, Jelaine C. Bsn-Iv Hepatitis C Key Facts: BloodDocument8 pagesELLANA, Jelaine C. Bsn-Iv Hepatitis C Key Facts: BloodJelaine EllanaNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Nursing Care Plan and Management: DescriptionDocument128 pagesViral Hepatitis Nursing Care Plan and Management: DescriptionnatalieshirleyNo ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument11 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggrisgita nadaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Knowing You Have Hepatitis CDocument9 pagesThe Importance of Knowing You Have Hepatitis Capi-237657970No ratings yet
- 2014 - 08 - (August) HepatitisDocument1 page2014 - 08 - (August) HepatitisEkwoh Okwuchukwu ENo ratings yet
- GastritisDocument4 pagesGastritisRegina Claudette GarciaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis BDocument6 pagesHepatitis BHazel Anne FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument6 pagesChapter 10 BloodSymonette OcturaNo ratings yet
- FERMENTATION OF SORGHUM USING YEAST (Saccharomyces Cerevisiae) AS A STARTER CULTURE FOR BURUKUTU PRODUCTIONDocument12 pagesFERMENTATION OF SORGHUM USING YEAST (Saccharomyces Cerevisiae) AS A STARTER CULTURE FOR BURUKUTU PRODUCTIONwilolud2059100% (3)
- Veterinary Virology PDFDocument275 pagesVeterinary Virology PDFSam Bot100% (5)
- Test 10Document23 pagesTest 10antlarrNo ratings yet
- Reading Comprehension Handout: (Speed Enhancement & Eye Span Devpt.)Document5 pagesReading Comprehension Handout: (Speed Enhancement & Eye Span Devpt.)Khushi VermaNo ratings yet
- ANTIMETDocument49 pagesANTIMETWAHYU NOFANDARI HERDIYANTINo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument82 pagesEnzyme KineticsjacobNo ratings yet
- Fallone 2019Document10 pagesFallone 2019Noel Saúl Argüello SánchezNo ratings yet
- Genital Tract Infections - GynecologyDocument17 pagesGenital Tract Infections - GynecologyKC Dela RosaNo ratings yet
- Anti Microbial ActivityDocument10 pagesAnti Microbial ActivitydevendraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PathologyDocument59 pagesIntroduction To PathologyRyan ColeNo ratings yet
- QUALITY MANUAL v008 FinalDocument22 pagesQUALITY MANUAL v008 FinalPERICODELOSPALOTESNo ratings yet
- EUCAST Reading Guide For Broth Microdilution: January 2019Document16 pagesEUCAST Reading Guide For Broth Microdilution: January 2019Trọng TínNo ratings yet
- Tumours and Inflammatory Lesions of The Anal Dawson2015Document12 pagesTumours and Inflammatory Lesions of The Anal Dawson2015DannyNo ratings yet
- CDC - Malaria - About Malaria - BiologyDocument11 pagesCDC - Malaria - About Malaria - Biologyselimamira018No ratings yet
- B.Sc. (Ug) Zoology Syllabus: Tumkur University TumakuruDocument40 pagesB.Sc. (Ug) Zoology Syllabus: Tumkur University TumakuruPraveen NekkantiNo ratings yet
- Congenital SyphilisDocument1 pageCongenital SyphilisAparna Devi100% (1)
- CE1 (T2) Presentation Molecular BiologyDocument11 pagesCE1 (T2) Presentation Molecular BiologyRohit MaliNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Alum and Its Bhasma (Sphatika Bhasma)Document12 pagesIn Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Alum and Its Bhasma (Sphatika Bhasma)IJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Important Additional Notes-Other Major Blood GroupsDocument1 pageImportant Additional Notes-Other Major Blood GroupsJohanna MarieNo ratings yet
- 337d PDFDocument8 pages337d PDFEka MeylianaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PhysiologyDocument7 pagesDigestive System Physiologyaminqasm111No ratings yet
- Mook 2004Document21 pagesMook 2004BerryEkaPardaBancinNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument13 pagesBio ProjectASAD RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Loilo ST., Zone 5, Bulan, Sorsogon S.Y. 2020-2021Document3 pagesLoilo ST., Zone 5, Bulan, Sorsogon S.Y. 2020-2021Cristina Gillego GalosNo ratings yet
- MT1 HSCI LEC L7 HematopoiesisDocument10 pagesMT1 HSCI LEC L7 HematopoiesisSEBASTIEN ANDREI BUENAFENo ratings yet