Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry (Reviewer)
Biochemistry (Reviewer)
Uploaded by
Jhon Lloyd0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThis document contains information on biochemistry topics including protein digestion in the stomach, vitamin classifications, macrominerals and microminerals, and questions about DNA and RNA, the Krebs cycle, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, ATP production, and protein, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism. Key points covered include protein degradation in the stomach by HCI and the negative nitrogen imbalance, fat soluble and water soluble vitamins, examples of macrominerals like calcium and phosphorus and microminerals like iron and zinc, and differentiating between DNA and RNA.
Original Description:
Original Title
BIOCHEMISTRY (REVIEWER)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains information on biochemistry topics including protein digestion in the stomach, vitamin classifications, macrominerals and microminerals, and questions about DNA and RNA, the Krebs cycle, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, ATP production, and protein, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism. Key points covered include protein degradation in the stomach by HCI and the negative nitrogen imbalance, fat soluble and water soluble vitamins, examples of macrominerals like calcium and phosphorus and microminerals like iron and zinc, and differentiating between DNA and RNA.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageBiochemistry (Reviewer)
Biochemistry (Reviewer)
Uploaded by
Jhon LloydThis document contains information on biochemistry topics including protein digestion in the stomach, vitamin classifications, macrominerals and microminerals, and questions about DNA and RNA, the Krebs cycle, lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, ATP production, and protein, carbohydrate, and lipid metabolism. Key points covered include protein degradation in the stomach by HCI and the negative nitrogen imbalance, fat soluble and water soluble vitamins, examples of macrominerals like calcium and phosphorus and microminerals like iron and zinc, and differentiating between DNA and RNA.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
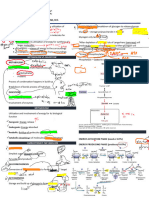
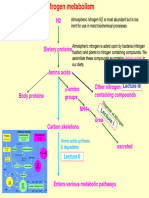
BIOCHEMISTRY -Vitamin D
I. -Vitamin E
STOMACH- protein digestion begins -Vitamin K
HCI- denatures protein WATER SOLUBLE VITAMINS
NEGATIVE NITROGEN IMBALANCE- protein degradation -Non-b complex (VITAMIN C)
exceeds protein synthesis
-B complex
PROTEIN TURNOVER- repetitive process in which body
-vitamin C
proteins are degraded and resynthesized
EXAMPLE OF MACROMINIRALS
DEAMINATION- the removal of amine group as
ammonia -Calcium
GLUTAMATE- this is the most important amino acid -phosphorus
metabolically
EXAMLE OF MICROMINERALS
KETOGENIC- amino acids that form acetoacetate or
acetyl CoA -Iron
LEUCINE AND LYSINE- amino acids that are purely -zinc
ketogenic IV.
UREA- principal end product of protein metabolism 1) differentiate DNA and RNA
UROBILIN- bile pigment that is reddish orange in color 2) Step of krebs cycle
STARVATION- glycogen stores are depleted. Body 3) explain briefly the interrelationship of lipid
protein is broken down into amino acids to synthesize metabolism and carbohydrate metabolism
glucose.
4) total number of ATP production
II.
a. glycolysis – 2
1. LIPASES
2. CHOLESTEROL b. TCA- 2
3. EMULSIFIER c. ETC- 32-34
4. UNSATURATED FATS
5. NUCLEOTIDES 5) importance of protein, carbohydrate, and lipid
6. LEADING STRAND metabolism
7. DNA REPLICATION
8. DNA POLYMERASE
9. UAG
10. GLUCOSE
11. GLYCOGENESIS
12. GLYCOLYSIS
13. GLUCONEOGENESIS
14. GLYCOGEN
III.
FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
-Vitamin A
You might also like
- 18 - Lipid MetabolismDocument26 pages18 - Lipid Metabolismcheckmate100% (1)
- Metabolic Pathways: A. What Is Metabolism?Document3 pagesMetabolic Pathways: A. What Is Metabolism?Amutharasi IndraNo ratings yet
- 5-Amino Acid Catabolism I (12 Oct)Document19 pages5-Amino Acid Catabolism I (12 Oct)api-19824406No ratings yet
- Biochem Rev Chap 8Document3 pagesBiochem Rev Chap 8Jacob PallorinaNo ratings yet
- AA and Nucleotide Metabolism - 1121Document62 pagesAA and Nucleotide Metabolism - 1121ywnrmgp9fxNo ratings yet
- Food Chemistry - Activity 2Document3 pagesFood Chemistry - Activity 2Leda PeñaNo ratings yet
- 1.macronutrients Metabolism, interrelationship-HM 2019Document75 pages1.macronutrients Metabolism, interrelationship-HM 2019Denebo ErsuloNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Introduction To MetabolismDocument7 pagesBiochemistry: Introduction To MetabolismAria ScribeNo ratings yet
- Overview of MetabolismDocument13 pagesOverview of Metabolismgabby chaanNo ratings yet
- Chem 123 - Lect Finals TransesDocument19 pagesChem 123 - Lect Finals TransesSamantha MendozaNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument26 pagesBeta OxidationShivanand MaliNo ratings yet
- Penyusun Molekuler SelDocument22 pagesPenyusun Molekuler SelteclaNo ratings yet
- 2 1 BIOCHEMISTRY Introduction To MetabolismDocument6 pages2 1 BIOCHEMISTRY Introduction To Metabolismcoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsDocument29 pagesLecture 6 - General and Characteristics. Water Soluble VitaminsEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer (Finals)Document16 pagesBiochem Reviewer (Finals)Arabella SelomNo ratings yet
- BiochemLecturecarbohydrate MetabDocument2 pagesBiochemLecturecarbohydrate MetabReginald GironNo ratings yet
- Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism: Chem 454: Biochemistry II University of Wisconsin-Eau ClaireDocument54 pagesProtein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism: Chem 454: Biochemistry II University of Wisconsin-Eau ClaireArif Mc TomsNo ratings yet
- Module 14 MetabolismDocument7 pagesModule 14 MetabolismJeremy GariandoNo ratings yet
- Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapters 23 and 24. Figures in This Document Are FromDocument36 pagesReading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapters 23 and 24. Figures in This Document Are FromAbeer ShalabyNo ratings yet
- Protein MetaboilisamDocument18 pagesProtein MetaboilisamSumit PandyaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Oxidation and The Production PDFDocument34 pagesAmino Acid Oxidation and The Production PDFNini BesiNo ratings yet
- 6.metabolisme Lipid PDFDocument40 pages6.metabolisme Lipid PDFSYITA SHEVIA PRASASTINo ratings yet
- BY: Sunita F1C1 16 064: Chemistry Department Mathematics and Natural Sciences Faculty Halu Oleo University Kendari 2018Document26 pagesBY: Sunita F1C1 16 064: Chemistry Department Mathematics and Natural Sciences Faculty Halu Oleo University Kendari 2018Azka Zaina ArdiningrumNo ratings yet
- 07 Lec Bio024 Biochem Energy ProdDocument10 pages07 Lec Bio024 Biochem Energy ProdMc AllenNo ratings yet
- Materi V - Vitamin B12Document35 pagesMateri V - Vitamin B12Salwa Kamilia100% (1)
- Su5 Cac L1 - 221008 - 103937Document19 pagesSu5 Cac L1 - 221008 - 103937George SchmullingNo ratings yet
- For MatchDocument2 pagesFor MatchesraarabiesalamaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism All LecturesDocument18 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism All Lecturesmizare29gNo ratings yet
- Mls 218 Protein-MetDocument45 pagesMls 218 Protein-MetZainabNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument15 pagesAmino Acid Metabolismshanto.tn98No ratings yet
- Vitamin B12Document31 pagesVitamin B12DR JIJIN J UNo ratings yet
- Vitamin: Mikrobiologi IndustriDocument66 pagesVitamin: Mikrobiologi IndustriZefryoktaNo ratings yet
- Lipid Metobolism B Pharm-1Document67 pagesLipid Metobolism B Pharm-1Dhaval TelangNo ratings yet
- Degradasi Karbohidrat 1Document32 pagesDegradasi Karbohidrat 1Bryan AswNo ratings yet
- NScELEC3 WEEK 14 LESSONDocument6 pagesNScELEC3 WEEK 14 LESSONAlyssa Jane AbellonNo ratings yet
- Thiamine and The Cellular Energy Cycles: A Novel Perspective On Type 2 Diabetes TreatmentDocument34 pagesThiamine and The Cellular Energy Cycles: A Novel Perspective On Type 2 Diabetes Treatmentthariq mubarakNo ratings yet
- Week10 Ch9Document35 pagesWeek10 Ch9jkz8zpbpvbNo ratings yet
- Concept Map - Biology - 2018 - JulyDocument1 pageConcept Map - Biology - 2018 - JulyRahique ShuaibNo ratings yet
- L15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and KetogenesisDocument50 pagesL15 Oxidation of Fatty Acids and Ketogenesisyebadem228No ratings yet
- Lesson 7 FA-HZDocument28 pagesLesson 7 FA-HZliaorNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics. Tricarboxylic Acids CycleDocument60 pagesBioenergetics. Tricarboxylic Acids CyclePurwa RaneNo ratings yet
- The Metabolic Map Proteins AtfDocument3 pagesThe Metabolic Map Proteins AtfJoax Wayne SanchezNo ratings yet
- BACTERIOLOGY - Bacterial MetabolismDocument7 pagesBACTERIOLOGY - Bacterial MetabolismRobie LeañoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical PathwaysDocument38 pagesBiochemical PathwaysMarja Shania Galido RañolaNo ratings yet
- Biomolecule-Short Cut TipsDocument2 pagesBiomolecule-Short Cut TipsEbe JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Energy+metabolismDocument12 pagesEnergy+metabolismAdib ANzainNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid Metabolism 2Document29 pagesAmino Acid Metabolism 2Francis GacheruNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Quiz - Enzymes and Vitamins - Answer KeyDocument8 pagesBiochemistry Quiz - Enzymes and Vitamins - Answer KeyKennethNo ratings yet
- Food Nutrient: Protein and Health EffectsDocument34 pagesFood Nutrient: Protein and Health EffectsMoeurng SreylakNo ratings yet
- Beta OxidationDocument41 pagesBeta Oxidationguna sundariNo ratings yet
- Revision BioDocument9 pagesRevision BioyoussefbeniameenNo ratings yet
- Gandham RajeevDocument41 pagesGandham RajeevAlok PatraNo ratings yet
- Englec 29 Fa Odd 2021Document3 pagesEnglec 29 Fa Odd 2021Yannick fokaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Amino Acid Degradation and SynthesisDocument33 pagesChapter 6 Amino Acid Degradation and Synthesischono090196No ratings yet
- Glycerol Metabolism Fatty Acid Metabolism Interrelationship of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism Ketosis, Acidosis, and DehydrationDocument32 pagesGlycerol Metabolism Fatty Acid Metabolism Interrelationship of Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism Ketosis, Acidosis, and DehydrationJanella Marie EspinoNo ratings yet
- Protein FinalsDocument5 pagesProtein Finalssaculala0291pamNo ratings yet
- Lec 9 Protein Metabolism - No Voice 1Document31 pagesLec 9 Protein Metabolism - No Voice 1staenley estacioNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Energy ProductionDocument15 pagesBiochemical Energy ProductionBeatrice ChenNo ratings yet
- Biochemstry Ii: Metabolism of ProteinDocument9 pagesBiochemstry Ii: Metabolism of ProteinGrace MadaoNo ratings yet
- (Reviewer) MICROSDocument8 pages(Reviewer) MICROSJhon LloydNo ratings yet
- Basic Foods ReviewerDocument9 pagesBasic Foods ReviewerJhon LloydNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY (Review)Document2 pagesANAPHY (Review)Jhon LloydNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Finalreviewer 2)Document3 pagesAnaphy (Finalreviewer 2)Jhon LloydNo ratings yet