Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effects of Covid in International Trade
Effects of Covid in International Trade
Uploaded by
andreu.oller2002aOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effects of Covid in International Trade
Effects of Covid in International Trade
Uploaded by
andreu.oller2002aCopyright:
Available Formats
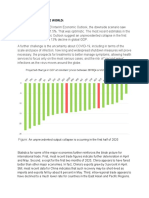
Effects of Covid-19 pandemic on world trade
Fortunately, now that we have some perspective on the Covid-19 pandemic, we can
analyze the impact of this global problem in globalization. If we understand
globalization as a process of communication and interdependence among different
countries, we can see that it has been influenced by the following. In the face of the
coronavirus, the central government did not hesitate to act, blocking tourist
exchanges, trade and closing borders. To analyze the impact of Covid-19 on
globalization, we have divided the report into different points:
Economy: Trade in services fell 20% between 2019 and 2020. The pandemic has not
hit all sectors of the economy equally, for example, sectors such as auto retail have
seen a marked decline, while we have seen significant growth in the pharmaceutical
sector. In addition, due to prolonged quarantines, limited displacement, job losses
and falling incomes have led to a decline in trade, affecting industries such as
catering, hotels and tourism.
Tourism: Tourism has been one of the most affected sectors due to border
restrictions and closures. Globalization was facilitating exchanges between countries
and facilitating tourism, but the pandemic forced it to a standstill, resulting in a 73%
decline in tourism compared to its number one position in 2019.
Culture: Cultural deglobalization of almost 20% is due to a worldwide decline in the
production of commercialized audiovisual services such as films and series, as well as
a lack of activities related to cultural assets.
Important advances in digitization: With the sudden onset of the pandemic, companies
and institutions were forced to find new ways to continue their activities without a
physical presence. In this context, telecommuting and the use of the Internet are
becoming more and more important. Schools and universities must find new ways to
learn online, and organizations must find innovative ways to meet and schedule. As a
result, e-commerce has achieved the most significant boom since its inception, as
society continues to demand basic necessities, office supplies, and leisure products.
The ease of digitization means that these sudden and forced changes will persist even
after the main effects of the pandemic on April 1 have passed.
Implementation of protectionist measures: These measures restrict imports by
erecting legal and economic barriers. This measure increased consumption of
national products and created tension in trade relations between countries.
In conclusion, we can say that post-pandemic globalization will not be the same for
two main reasons, one of which is the weakening of the homogeneous US leadership.
Without such leadership, international cooperation will be difficult. Another reason is
that the pandemic has resurfaced the idea of a large interventionist state and
imposing protectionist measures.
You might also like
- Chapter 1 - Market AspectDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Market AspectPiolen NicaNo ratings yet
- Supplychainman Case 4Document6 pagesSupplychainman Case 4Arman Panopio100% (1)
- The Impact of Covid-19 On International Trade: Evidence From The First ShockDocument5 pagesThe Impact of Covid-19 On International Trade: Evidence From The First ShockMuhammad AsrulNo ratings yet
- 19bce0696 VL2021220701671 Ast04Document9 pages19bce0696 VL2021220701671 Ast04Parijat NiyogyNo ratings yet
- World EconomyDocument4 pagesWorld EconomyArman HossainNo ratings yet
- MBA Business Administration Statistics and Research Methodology (Bus 637) Summarize Two Articles Eman Osama Khalil 1195027Document4 pagesMBA Business Administration Statistics and Research Methodology (Bus 637) Summarize Two Articles Eman Osama Khalil 1195027Eman KhalilNo ratings yet
- NeliaDocument4 pagesNeliaMiguelOriellNo ratings yet
- Hoekstra Leeflang2020 Article MarketingInTheEraOfCOVID 19Document12 pagesHoekstra Leeflang2020 Article MarketingInTheEraOfCOVID 19ghzaoui chaimaeNo ratings yet
- Marketing in The Era of COVID 19: Janny C. Hoekstra Peter S. H. LeeflangDocument12 pagesMarketing in The Era of COVID 19: Janny C. Hoekstra Peter S. H. LeeflangEnglish ClassNo ratings yet
- Coronavirus: The Economic ImpactDocument19 pagesCoronavirus: The Economic ImpactEkansh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- How Coronavirus Pandemic Will Impact The EconomyDocument3 pagesHow Coronavirus Pandemic Will Impact The EconomyIshanNo ratings yet
- The Impact of COVID19 On Global EconomyDocument9 pagesThe Impact of COVID19 On Global Economyمحمود عليمىNo ratings yet
- Concept PaperDocument7 pagesConcept PaperCatherine HirangNo ratings yet
- Development Status and Countermeasures of Tmall During The Covid-19 EpidemicDocument6 pagesDevelopment Status and Countermeasures of Tmall During The Covid-19 EpidemicAJHSSR JournalNo ratings yet
- Course: Intermediate Macroeconomics (INE 2102E)Document19 pagesCourse: Intermediate Macroeconomics (INE 2102E)Duy Hùng ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Molney Banking ProjectDocument10 pagesMolney Banking ProjectAnurag KarnNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Final AssignmentDocument13 pagesGroup 2 Final AssignmentdostonNo ratings yet
- Executive SummaryDocument7 pagesExecutive SummaryFahad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Covid-19's Impact On Bangladesh's EconomyDocument6 pagesCovid-19's Impact On Bangladesh's EconomyMayaz Al MahinNo ratings yet
- Artikel DimasDocument1 pageArtikel DimasDimas SyahputraNo ratings yet
- Covid 19Document12 pagesCovid 19musa imanNo ratings yet
- WPIR EssayDocument11 pagesWPIR Essaybartiercardi21savageNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment 3Document8 pagesIndividual Assignment 3Amran Abd HamidNo ratings yet
- Financial Nationalism Vs International Financial LawDocument3 pagesFinancial Nationalism Vs International Financial LawMarc SyapzeNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic On International MarketingDocument8 pagesImpact of Covid-19 Pandemic On International Marketingramya penmatsaNo ratings yet
- Name: Rohit Purohit Submitted To: DR - Sumedh Lokhande. Subject: Political Science Assignment: Research Paper Om Covid-19 and It's EffectsDocument4 pagesName: Rohit Purohit Submitted To: DR - Sumedh Lokhande. Subject: Political Science Assignment: Research Paper Om Covid-19 and It's EffectsmarshmelloNo ratings yet
- Impact of Covid-19 On International Trade Law: Rijuka Naresh JainDocument4 pagesImpact of Covid-19 On International Trade Law: Rijuka Naresh JainJinal ShahNo ratings yet
- Assesment 2Document13 pagesAssesment 2Marian ValentinNo ratings yet
- Sample IR 1A+Document9 pagesSample IR 1A+Christel ROLLINSNo ratings yet
- Canuto, Kimberly Anne V. Iv-BmaDocument2 pagesCanuto, Kimberly Anne V. Iv-BmaLayca Clarice Germino BrimbuelaNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument6 pagesIntroductionArnab SenNo ratings yet
- Opportunities and Challenges of Current Pandemic DiseaseDocument18 pagesOpportunities and Challenges of Current Pandemic DiseaseSolomon AberaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Covid 19 To International TradeDocument4 pagesEffects of Covid 19 To International TradeWilliam Jefferson HomyaoNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 Impact On World Economy PDFDocument15 pagesCOVID 19 Impact On World Economy PDFChowdhury Shakawat Hossan100% (1)
- ECO Group Assignment 1Document9 pagesECO Group Assignment 1NanthaNo ratings yet
- The Need For Change and Shaping The Post-COVID Business Environment in RomaniaDocument12 pagesThe Need For Change and Shaping The Post-COVID Business Environment in RomaniaLucia Morosan-DanilaNo ratings yet
- A Covid-19.01Document6 pagesA Covid-19.01Nida AbbasNo ratings yet
- Eng - Summary Group 1&2Document2 pagesEng - Summary Group 1&2jeisel keziaNo ratings yet
- Research On The Effects COVID19 in Nigeria.Document4 pagesResearch On The Effects COVID19 in Nigeria.Marvellous WilhelmNo ratings yet
- Freight Transportation Individual Project - U1911052Document6 pagesFreight Transportation Individual Project - U1911052Aziza 191x118No ratings yet
- IvanDocument1 pageIvanFrancis PeraltaNo ratings yet
- The World Economy The Peril and The Promise: Special ReportDocument5 pagesThe World Economy The Peril and The Promise: Special ReportViruu DiazNo ratings yet
- Impact of COVID 19 On Global Economy and Ways To Minimize Its ImpactDocument4 pagesImpact of COVID 19 On Global Economy and Ways To Minimize Its ImpactNarayan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Vietnam's International Trade Is Showing Signs of Recovery After The Covid-19 PandemicDocument18 pagesVietnam's International Trade Is Showing Signs of Recovery After The Covid-19 PandemicBích Ngọc Ngô ThịNo ratings yet
- L2.Pressrelease KOFGI 2021Document2 pagesL2.Pressrelease KOFGI 2021Gino PinoNo ratings yet
- Parcor ResearchDocument9 pagesParcor ResearchJessa MontonNo ratings yet
- GA.ibi Tham KhảoDocument13 pagesGA.ibi Tham KhảoHoàng TriềuNo ratings yet
- Effect of COVID 19 Global Pandemic To International Business and TradeDocument3 pagesEffect of COVID 19 Global Pandemic To International Business and TradeJade Maertella C. BarcenasNo ratings yet
- IT ReportDocument26 pagesIT ReportWrite EnglishNo ratings yet
- International BusinessDocument23 pagesInternational BusinessMohammed MujahidNo ratings yet
- Impact of COVID-19 On BusinessDocument3 pagesImpact of COVID-19 On BusinessHasan Rabbi100% (4)
- Assignment 1 International BusinessDocument6 pagesAssignment 1 International BusinessJoaquin Navarro TrisanoNo ratings yet
- Manuscript PDFDocument16 pagesManuscript PDFMpilo MaqhashalalaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Covid-19 On World Economy: AssignmentDocument3 pagesEffect of Covid-19 On World Economy: AssignmentShubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- Review PaperDocument7 pagesReview PaperTenzin LhundupNo ratings yet
- The Impact of The Covid-19 Pandemic To The Globalization and The Contemporary WorldDocument3 pagesThe Impact of The Covid-19 Pandemic To The Globalization and The Contemporary WorldLiameNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Global Impact and Industrial Organization Catch-Up PlanDocument12 pagesCOVID-19 Global Impact and Industrial Organization Catch-Up PlanAlaine Danica Dimaandal100% (4)
- Global Business: Name Institution Course DateDocument15 pagesGlobal Business: Name Institution Course DateRichardNo ratings yet
- Impact of The Whole WorldDocument4 pagesImpact of The Whole Worldوسيم أكرمNo ratings yet
- T1 Business Faculty "Commercial Economic Reality of Peru, Considering Trends and Cultural Changes"Document6 pagesT1 Business Faculty "Commercial Economic Reality of Peru, Considering Trends and Cultural Changes"mario joseNo ratings yet
- WP 373.tsutomu Watanabe - The Responses of Consumption and Prices in Japan...Document17 pagesWP 373.tsutomu Watanabe - The Responses of Consumption and Prices in Japan...Justin BelieberNo ratings yet
- Stocks Only Go Up: What role did apps like Robinhood, influencers like David Portnoy and government stimulus checks play in the emergence of Millennials in the stock market?From EverandStocks Only Go Up: What role did apps like Robinhood, influencers like David Portnoy and government stimulus checks play in the emergence of Millennials in the stock market?No ratings yet
- Minutes of Opening of BidsDocument4 pagesMinutes of Opening of BidsEleonor LuarcaNo ratings yet
- Cahs Flow StatementDocument18 pagesCahs Flow Statementtaniya17No ratings yet
- Lesson 7Document20 pagesLesson 7Tin NguyenNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document45 pagesCH 12Pulkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Aca Labor Digests MidtermsDocument195 pagesAca Labor Digests MidtermsPaul Tisoy100% (2)
- Mcqs On Index NumbersDocument17 pagesMcqs On Index NumbersAnnapoorna Avula100% (1)
- Ebook Ebook PDF International Marketing 6Th Edition by Dana Nicoleta All Chapter PDF Docx KindleDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF International Marketing 6Th Edition by Dana Nicoleta All Chapter PDF Docx Kindlemonique.simmerman868100% (32)
- Problem StatementDocument6 pagesProblem StatementSyed Bilal AliNo ratings yet
- Cefic FactsAnd Figures 2018 Industrial BROCHURE TRADE PDFDocument79 pagesCefic FactsAnd Figures 2018 Industrial BROCHURE TRADE PDFRehan RaufNo ratings yet
- Icai Capital BudgetingDocument72 pagesIcai Capital BudgetingMwenda MongweNo ratings yet
- Doing Business in Mexico Understanding CDocument18 pagesDoing Business in Mexico Understanding CmarcoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Public Finance and Taxation - 2022-ExtensionDocument3 pagesAssignment Public Finance and Taxation - 2022-ExtensionMesfin YohannesNo ratings yet
- Basic Accounting Final ExamDocument7 pagesBasic Accounting Final ExamCharmae Agan Caroro75% (4)
- Project On Tata Finance PDF FreeDocument113 pagesProject On Tata Finance PDF FreeOmkar Kawade100% (1)
- Management of Business: Teacher: Miss. GardnerDocument33 pagesManagement of Business: Teacher: Miss. GardnerOckouri BarnesNo ratings yet
- 12.T24 Money Market - R15Document68 pages12.T24 Money Market - R15Jagadeesh JNo ratings yet
- Master Your FinancesDocument15 pagesMaster Your FinancesBrendan GirdwoodNo ratings yet
- Starbucks Value Chain Analysis PDFDocument4 pagesStarbucks Value Chain Analysis PDFAnonymous 31fa2FAPhNo ratings yet
- Proposed Resolution - Magna Carta For Agriculturist (AutoRecovered)Document2 pagesProposed Resolution - Magna Carta For Agriculturist (AutoRecovered)Eszikeil Luah ArthasNo ratings yet
- Challenges Faced by Indian Banking IndustryDocument5 pagesChallenges Faced by Indian Banking IndustryPooja Sakru100% (1)
- ACC100.101 Analyzing Transactions - Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesACC100.101 Analyzing Transactions - Practice QuestionsZACARIAS, Marc Nickson DG.No ratings yet
- Femi UWL MSMEDocument12 pagesFemi UWL MSMEAkash SahaNo ratings yet
- 9410 - Job Order CostingDocument7 pages9410 - Job Order CostingMarshmallowNo ratings yet
- Kinerja Keuangan HipotesisDocument14 pagesKinerja Keuangan HipotesisYustika MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Finmar)Document25 pagesChapter 1 (Finmar)Ashley Nicole AguilarNo ratings yet
- Total Financial RatiosDocument2 pagesTotal Financial RatioshoangsubaxdNo ratings yet
- Palma Company Had 90Document2 pagesPalma Company Had 90Melody Domingo BangayanNo ratings yet
- Differences Between PSAK and IFRSDocument3 pagesDifferences Between PSAK and IFRSInney SildalatifaNo ratings yet