Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 viewsPak Studies Final
Pak Studies Final
Uploaded by
Sajid UsmanThis document discusses the geostrategic importance and foreign policy of Pakistan. It touches on key topics such as Pakistan's location between East and West Asia, its role in regional trade and energy corridors, and its historical pro-West stance balanced with sensitivity to the Muslim world. The document also examines Pakistan's economic challenges including a weak economy, energy crisis, and low foreign investment. It argues that strengthening democracy is important for Pakistan's security and prosperity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Spiritual Secrets of Urine and Ways You Can Use It PT. 2 - Embracing SpiritualityDocument9 pagesSpiritual Secrets of Urine and Ways You Can Use It PT. 2 - Embracing Spiritualityinfo-501699100% (2)
- Saying of Salafs On MarriageDocument5 pagesSaying of Salafs On MarriageMariam Omotoyosi SadeqNo ratings yet
- Ruhi BK 7 Walking Together On A Path of ServiceDocument132 pagesRuhi BK 7 Walking Together On A Path of Servicebeokguk50% (2)
- Folder of Middle East EditedDocument213 pagesFolder of Middle East EditedSaffiNo ratings yet
- Islamiat O Level P 1 Revision Guide 401Document27 pagesIslamiat O Level P 1 Revision Guide 401Azlaan Zareef Khan100% (2)
- Assignment 02 FinalisedDocument11 pagesAssignment 02 FinalisedFaiza GandapurNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy and Pakistan's External RelationsDocument42 pagesForeign Policy and Pakistan's External RelationsManaal tariqNo ratings yet
- Global Powers and Security in South Asia PresentationDocument14 pagesGlobal Powers and Security in South Asia PresentationShaban Gill SbNo ratings yet
- Foreign PolicyDocument48 pagesForeign PolicyA KumarNo ratings yet
- Pak ChinaDocument43 pagesPak Chinaimtiazkhan0234No ratings yet
- Geopoliical Significance of PakistanDocument58 pagesGeopoliical Significance of PakistanYasmin khanNo ratings yet
- To Analyse The Impact of Events in West Asia and Afghanistan On PakistanDocument14 pagesTo Analyse The Impact of Events in West Asia and Afghanistan On PakistanRaman GillNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy of PakistanDocument16 pagesForeign Policy of Pakistani222371 HeerNo ratings yet
- International Business EnvironmentDocument30 pagesInternational Business Environmentaridaman raghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Geo-Strategic Importance of PakistanDocument23 pagesGeo-Strategic Importance of PakistanUzair Maqbool Khan100% (1)
- Why Rajouri-Poonch Belt Is Vulnerable To Terrorist AttacksDocument41 pagesWhy Rajouri-Poonch Belt Is Vulnerable To Terrorist AttacksAnjaneyuluNo ratings yet
- 26 Grid AnswersDocument12 pages26 Grid Answerszeesha tahirNo ratings yet
- Weekly Dawn Deconstruction June 15 To June 22 - by M.usmanDocument139 pagesWeekly Dawn Deconstruction June 15 To June 22 - by M.usmanMuzamil HassanNo ratings yet
- South Asia - An OverviewDocument36 pagesSouth Asia - An Overviewashraf kabirNo ratings yet
- Pak Iran RelationsDocument13 pagesPak Iran RelationsMaryam KamranNo ratings yet
- IR Current NotesDocument7 pagesIR Current NotesAnika BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy of PakistanDocument35 pagesForeign Policy of PakistanEisha NadeemNo ratings yet
- The Asia Pacific RegionDocument35 pagesThe Asia Pacific RegionSureilyValentinEstevezNo ratings yet
- FINALS Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesFINALS Contemporary WorldJairah Faith CammayoNo ratings yet
- Current Situation Current Affairs PRESENTATIONDocument10 pagesCurrent Situation Current Affairs PRESENTATIONcbhavelianNo ratings yet
- Daily News Simplified - DNS NotesDocument9 pagesDaily News Simplified - DNS NotesPriyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Establishment of Pakistan 1947 To 1948Document12 pagesEstablishment of Pakistan 1947 To 1948zobiNo ratings yet
- QuotesDocument6 pagesQuotesGarvit PantNo ratings yet
- India and Pakistan Relations For SSC Banking Exams GK Notes in PDFDocument4 pagesIndia and Pakistan Relations For SSC Banking Exams GK Notes in PDFfaizNo ratings yet
- Rwanda Economic AnalysisDocument21 pagesRwanda Economic AnalysisGery AzhariNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy of India - Evolution, Determinants - EnglishDocument3 pagesForeign Policy of India - Evolution, Determinants - Englisharvsev3103No ratings yet
- Pakistan: By: W Q S RM H O DDocument20 pagesPakistan: By: W Q S RM H O DBharat SethNo ratings yet
- Nepal As A Vibrant BridgeDocument26 pagesNepal As A Vibrant BridgeNiroj GhimireNo ratings yet
- REgional OrganisationDocument14 pagesREgional Organisationkaibalya paridaNo ratings yet
- Indias Security Interest MindmapDocument2 pagesIndias Security Interest MindmapRema RalteNo ratings yet
- SAARC & PakistanDocument35 pagesSAARC & Pakistansaniasiddique802No ratings yet
- Pak Relation With NeighboursDocument32 pagesPak Relation With NeighboursMuhammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Pak StudiesDocument10 pagesPak StudiesFloret UmbelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Domestic Political IssuesDocument28 pagesLecture 2 Domestic Political IssuesUzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- 7 Indo Pacific ConflictsDocument17 pages7 Indo Pacific Conflictsn2974538No ratings yet
- Pak-India Relations June 2020Document45 pagesPak-India Relations June 2020Yasmin khanNo ratings yet
- 6 - Pakistan Relations With The Muslim WorldDocument28 pages6 - Pakistan Relations With The Muslim Worldn2974538No ratings yet
- 3 Regional Geo Political Structure and Role of Pakistan Lecture 3 - Final 04102023 092011pmDocument42 pages3 Regional Geo Political Structure and Role of Pakistan Lecture 3 - Final 04102023 092011pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Geography of PakistanDocument13 pagesGeography of Pakistanwajeehaadeel57No ratings yet
- Classical Geopolitics in The 21st Century: Bangladesh-US Relations India-China RelationsDocument24 pagesClassical Geopolitics in The 21st Century: Bangladesh-US Relations India-China Relationsashraf kabirNo ratings yet
- 8 Political RisksDocument17 pages8 Political RisksvbalodaNo ratings yet
- ChandigarhDocument1 pageChandigarhJaisurya SharmaNo ratings yet
- JEHAN ZEB - Special Css Plan-CompressedDocument1 pageJEHAN ZEB - Special Css Plan-Compressedsafina zahoorNo ratings yet
- Lbs Breakfast Presentation May 2023Document77 pagesLbs Breakfast Presentation May 2023Damie OjoNo ratings yet
- TCWD 111 - Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesTCWD 111 - Midterm ReviewerGDHDFNo ratings yet
- Pakistan-China Strategic RelationsDocument56 pagesPakistan-China Strategic RelationsTSS DTNo ratings yet
- What Are The Roles of Great Power inDocument10 pagesWhat Are The Roles of Great Power inJeffery MillefioreNo ratings yet
- NorthCom FEMA Inteoperability! Meet Military Region Commanders Active Duty Army!Document9 pagesNorthCom FEMA Inteoperability! Meet Military Region Commanders Active Duty Army!Guy Razer100% (1)
- Foreign Policy of PakistanDocument2 pagesForeign Policy of PakistanShoaib BalochNo ratings yet
- Geo-Political Importance of The Muslim WorldDocument16 pagesGeo-Political Importance of The Muslim WorldMuqaddas Shehbaz710No ratings yet
- A System of Stories - Leah Zaidi - 2021 1Document1 pageA System of Stories - Leah Zaidi - 2021 1phyo min khantNo ratings yet
- Gujral DoctrineDocument8 pagesGujral DoctrinePritam SahaNo ratings yet
- CPEC by AHUDocument26 pagesCPEC by AHUAbdullah Noor KhanNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 Pakistan Relations With NeighboursDocument69 pagesCHP 10 Pakistan Relations With NeighboursKjsiddiqui Babloo100% (5)
- Wa0005.Document98 pagesWa0005.ahero7820No ratings yet
- South Korea and Argentina: Contributions of Alternative Approaches To DevelopmentDocument9 pagesSouth Korea and Argentina: Contributions of Alternative Approaches To DevelopmentApanjot SahotaNo ratings yet
- AEC - O&T For Hai PhongDocument7 pagesAEC - O&T For Hai PhongHoa TranNo ratings yet
- Internal and External Security Issues + Neighbourhood CAPF IGP 2023Document80 pagesInternal and External Security Issues + Neighbourhood CAPF IGP 2023dubrovnik1857No ratings yet
- Daily Current Affairs - 26 April 2023Document2 pagesDaily Current Affairs - 26 April 2023Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Daily Current Affairs - 1-2 May 2023Document3 pagesDaily Current Affairs - 1-2 May 2023Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Akhuwat ScholarshipDocument1 pageAkhuwat ScholarshipSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Essay OutlineDocument3 pagesEssay OutlineSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- 9-64-BSc (Hons) Agriculture-1st-1Document4 pages9-64-BSc (Hons) Agriculture-1st-1Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Israel War Current AffairsDocument8 pagesIsrael War Current AffairsSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Imec - G20Document8 pagesImec - G20Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Political PhilosophyDocument14 pagesPolitical PhilosophySajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- 6-Scientific Instruments Names PDF Notes For All Competitive ExamsDocument9 pages6-Scientific Instruments Names PDF Notes For All Competitive ExamsSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- BRI - How China's Belt and Road Took Over The World - The DiplomatDocument14 pagesBRI - How China's Belt and Road Took Over The World - The DiplomatSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- B3W Vs BRIDocument16 pagesB3W Vs BRISajid UsmanNo ratings yet
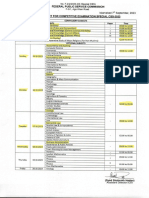
- Date Sheet Competitive Examination Special CSS-2023Document1 pageDate Sheet Competitive Examination Special CSS-2023Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Aniruddha and Usha StoryDocument9 pagesAniruddha and Usha Storysriramnayak100% (1)
- transfigurationlyricshillsong-RechercheGoogle 1677070132193Document4 pagestransfigurationlyricshillsong-RechercheGoogle 1677070132193Zidane Sobtantning TioningNo ratings yet
- American Revolution EssayDocument49 pagesAmerican Revolution Essaym0kih1h0kug3100% (2)
- GMS 691 Week 2Document23 pagesGMS 691 Week 2Mit DaveNo ratings yet
- What Does The Phrase Born of Water and The Spirit Mean? (The New Birth)Document5 pagesWhat Does The Phrase Born of Water and The Spirit Mean? (The New Birth)dlee7067No ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 3Document20 pages08 - Chapter 3Guru DevNo ratings yet
- Surya Namaskar - Searchforlight - Org - Fitness - Suryanamaskar - HTMLDocument4 pagesSurya Namaskar - Searchforlight - Org - Fitness - Suryanamaskar - HTMLmarabunta80No ratings yet
- List of Brahmana SanghasDocument4 pagesList of Brahmana SanghasJayant AgasthyaNo ratings yet
- Artha 26 DefinitionsDocument7 pagesArtha 26 DefinitionsGeo DezicNo ratings yet
- Sawaneh Tajushshariah (Roman Urdu)Document119 pagesSawaneh Tajushshariah (Roman Urdu)Syed Aqib Ali100% (2)
- MarsDocument1 pageMars11ab4611No ratings yet
- Brunstad Christian ChurchDocument6 pagesBrunstad Christian Churchwattssteve21No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Black VenusDocument13 pagesThe Little Book of Black VenusLe On CampbellNo ratings yet
- Surah 25. Al-Furqan, Ayat 63-69 PDFDocument1 pageSurah 25. Al-Furqan, Ayat 63-69 PDFMusaab MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Ibm536 Country Report ChinaDocument22 pagesIbm536 Country Report ChinaNajihah YusoffNo ratings yet
- Dominant CasteDocument8 pagesDominant Castecshrivastava47No ratings yet
- Ganito Kami Noon, Paano Kayo Ngayon: ReflectionDocument2 pagesGanito Kami Noon, Paano Kayo Ngayon: ReflectionJannaRica BeasonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 D TWO ATTRIBUTES OF THE CICM IDENTITYDocument31 pagesLesson 2 D TWO ATTRIBUTES OF THE CICM IDENTITYJamila BullanNo ratings yet
- Greater Sins V 01Document203 pagesGreater Sins V 01mohammad HasnainNo ratings yet
- Philippians Commentaries & Sermons PDFDocument124 pagesPhilippians Commentaries & Sermons PDFAlfonso Escobar Norero100% (2)
- VijayanagarDocument4 pagesVijayanagarpooja.r0829No ratings yet
- Our Swamy16Document4 pagesOur Swamy16api-3758390No ratings yet
- Chapter Xix: Breezing Through The Hexateuch Part 2. Cain and AbelDocument6 pagesChapter Xix: Breezing Through The Hexateuch Part 2. Cain and AbelLegba777No ratings yet
- Gems Cambridge International School-Abu Dhabi Islamic Studies - B, Year 11 Name: - Date: - Islamic DateDocument2 pagesGems Cambridge International School-Abu Dhabi Islamic Studies - B, Year 11 Name: - Date: - Islamic DateKevir ManNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship: Group 4 (12 HUMSS-D)Document17 pagesCommunity Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship: Group 4 (12 HUMSS-D)jeonghan aegiNo ratings yet
- FINAL - Perspectives On Islamic Psychology - Al Raghib Al Isfahani On The Healing of Emotions in The QuranDocument38 pagesFINAL - Perspectives On Islamic Psychology - Al Raghib Al Isfahani On The Healing of Emotions in The QuranArafat FaniNo ratings yet
Pak Studies Final
Pak Studies Final
Uploaded by
Sajid Usman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views9 pagesThis document discusses the geostrategic importance and foreign policy of Pakistan. It touches on key topics such as Pakistan's location between East and West Asia, its role in regional trade and energy corridors, and its historical pro-West stance balanced with sensitivity to the Muslim world. The document also examines Pakistan's economic challenges including a weak economy, energy crisis, and low foreign investment. It argues that strengthening democracy is important for Pakistan's security and prosperity.
Original Description:
Original Title
Pak studies final
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the geostrategic importance and foreign policy of Pakistan. It touches on key topics such as Pakistan's location between East and West Asia, its role in regional trade and energy corridors, and its historical pro-West stance balanced with sensitivity to the Muslim world. The document also examines Pakistan's economic challenges including a weak economy, energy crisis, and low foreign investment. It argues that strengthening democracy is important for Pakistan's security and prosperity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views9 pagesPak Studies Final
Pak Studies Final
Uploaded by
Sajid UsmanThis document discusses the geostrategic importance and foreign policy of Pakistan. It touches on key topics such as Pakistan's location between East and West Asia, its role in regional trade and energy corridors, and its historical pro-West stance balanced with sensitivity to the Muslim world. The document also examines Pakistan's economic challenges including a weak economy, energy crisis, and low foreign investment. It argues that strengthening democracy is important for Pakistan's security and prosperity.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 9
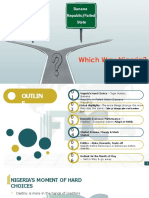
Geo-strategic Importance of Foreign policy of Pakistan ❖ Way forward
Pakistan Decision of authorities based on knowledge • De-hyphenated foreign policy, soft
❖ Introduction and experience to conduct its business with power, ethnic linkages
❖ Geo-strategic: Policies related to rest of the world to realize international goals • Relations with neighbors
military, development, security ❖ Process • Regional cooperation
defined through geo graphical
• Constitution article 90 and 99 • New policy fronts
• Rule of Business article 11 and 13
factors • President, PM and Cabinet
❖ Location of Pakistan • Consultation of other department, Aviation,
• 24 to 36 degree northern latitude
Changing Regional Apparatus
communication,
• ❖ Emergence of new power center
61 to 75 degree eastern longitude ❖ Birdseye view of Pakistan foreign
• North-china 510km policy Before
• North west Afghanistan 2250km • Pak-US
• Pro-west
• East India 1650km • Indo-China
• Security-ridden
• South west Iran 912km • India centric Emerging
❖ Importance • Sensitive to Muslim World • Indo-US
• • Pak-China
It is a junction between eastern and west • Foreign debt dependency
❖ Increasing completion for
Asia ❖ Determinants of Pakistan foreign
• Serve as a transit economy resources
policy
• • South China Sea
It serves as trade and energy corridor • Geo-graphical factors • BRI
• Gateway to central Asian republics • Historical factors • Indian investment in Afghanistan
• Proximity to great powers • Ideological factors • BCIM Trade route
• Junction between Mineral and people • Economic factors • TAPI
rich countries • Provincial ethnic factors ❖ Nuclear proliferation arm race
• Prominent Muslim nuclear state • Technological factors • China-India arms race
• BRI • Internal • Pak-India arm race
• Pivotal Role on war on terror • External factors • Iran nuclear aspiration
• Kashmir issue ❖ 1947 to 1952 • North Korean nuclear threat
❖ Challenges Non-allied policy ❖ Terrorism and militancy threat
➢ Internal • Proxy war
❖ 1952 to 1962 • Middle East Chaos – Yemen, Syria,
• Economy • Pro-West, CENTO, SETO • Kashmir
• Political instability • Good relation US and Europe, bad • ISIS
• Provincial disintegration relation with Russia ❖ Indian Ocean Conflict
• Pashtun nationalism ❖ 1962 to 1969 ❖ Pacific Ocean Conflict
• Baluchistan grievances • Russia, pro-west ❖ Changing dynamics of regional
• Sindhi factionalism ❖ 1971-1977
•
cooperation
Energy crisis • Bhutto’s era ❖ New power nexus
• Environmental degradation • Withdrawal SETO and CENTO • Indo-afghan
Hennery Kiesinger internal strength ❖ 1978-1988 • Indo-Iran
prelude external strength • Zia’s Era • Pak-Russia
➢ External ❖ 1990 to 2000 • Pakistan and CARs
• Pak-Afghan relation • Sanctions • TAPI
• Pak-India Relation • Pressler amendment • CASA
• Pak-Middle relation ❖ 2000-2008 ❖ Aggravated fault line based on
• Pak-Iran • War on terror Sectarian Divide
• Saudi-Iran ❖ 2008-2013 ❖ Saudi-Iran
• US-Iran • Zardari Era
• CPEC- challenges from other • Diversification
perspective ❖ 2013-2018
• US- a global neighbor • Mixed results
❖ 2018 onward
• Russia, Saudi, Middle East, Afghan
peace talk in process
Democratic and political ❖ New power centers • Solution (Land reforms, GMOs,
• Judiciary Microfinancing, Private Sector
evolution of Pakistan • Media Coordination, Sprinkle irrigation)
❖ Political culture – orientation of • Civil society • Industry
society toward politics •
❖ Why Pakistan needs democracy (Mining and quarrying, Manufacturing,
❖ Occurs through socializing agents:
• Prosperity-democracy theory (Robert Construction)
family, educational institution, political • Environmental issues
Petric)
parties, media, civil society- •
• A country having a better ranking in Lack of skills and technology
❖ Political system democratic index will be having a better • Low FDI
A set of institution and practices that define ranking in poverty index also • Energy crisis
government structure – Almond • Democratic peace theory • Low credit
❖ Components of political system • Democracy leads to internal and external • Political instability
• Governmental institutions (parliament, peace • Solutions (microfinance, energy
judiciary, etc.) ❖ Hurdles for democracy in Pakistan solution, investment-friendly regime,
• Organizations (business orgs)
❖ How to strengthen in Pakistan trade, stable polices, technical
• Traditional structures (media, education)
Democracy is security imperative
judiciary, civil society, religions,)
Pakistan • Services
• Anomic phenomenon (protest, riots) • (Finance and insurance, transportation,
A tussle between these components to gain wholesale, communication)
hegemony Economy of Pakistan • Fluctuation currency
❖ Political Culture of Pakistan • Sectors (Overall Growth 3.29%) • FATF
• Overdeveloped states structures Primary • CPEC
• Hamza Alvi’s Marxist Analysis – State Agriculture (growth, .85%, contribution • Oil prices,
vs MBO 19%) • Infrastructure
• Divided opinions Secondary • Low FDI
• Parliamentary vs presidential debates Industry (growth, 1.4%, contribution 21%) • Solution (stable polices, revisiting
• Civilian vs military debates Tertiary CPEC agreements for whole sale, oil
• Secular vs Islamic Services (Services 4.7%, contribution, 60%) prices, modern technology,
❖ Two major components • National economic challenges ❖ Recipe for Economic
• Organizes Structured • Undocumented economy (40%) Development
• Military, bureaucracy, business elites, • Low tax to GDP ratio (11.6%) • Knowledge based economy
politics elites •
• Low HDI (150/189) Business friendly polices
• Unorganized structure components •
• Huge public debt (Rs. 28607 billion) Increased tax base and net
• Media, civil society, religions elites •
• Poor governance Reforming FBR
❖ Democratic Evolution • Vicious Cycle of Poverty • Overcoming energy crisis
• Fifties saw control controlled • Current account deficit ($ 11.58 billion • Reaping demographic dividends
democracy dollar) • Good governance
• Sixties saw basic democracies • Trade deficit ($ 5.72 billion) • Green Economy
• Seventies saw social democracy • High cost of production • Blue Economy
• Eighties saw guided democracy • Energy crisis • Exploitation of Exclusive economic
• Nineties saw sham democracy • Burgeoning population Zones
• Dawn of 21st century saw quasi- • Structural unemployment • Encouraging Entrepreneurship
democracy •
• Consumption based economy Diversification of economy(tourism)
❖ Rise of oligarchies between 1947 to • Massive public sector subsides( 400
2008 billion/year)
• Military, bureaucracy, religious elites,
• Sector wise challenges
political elites and business elites
• Agriculture
❖ Politics from 2008 onward
• (Crops, Livestock’s, fishing, Forestry)
• Revival of democracy • Substance level farming
• Charter of democracy • Outdated technology
• Transition of three democratic • Lack of markets
governments
• Lack of financing
Education in Pakistan Health issues in Pakistan Afghan War, its impact,
• Literacy rate, 62% ❖ Issues emergence of non-state
• Male literacy rate 72% • Food insecurity
• Female literacy rate, 51% • Child mortality (62/1000)
actors, its impact on Pakistan
• School enrollment rate 5.3% • Maternal mortality (178/100,000) ❖ Retrospect
❖ Educational issues in Pakistan ❖ Political crisis in Afghanistan
• Undernutrition (43%)
• People Democratic Party’s division
• Low budget allocation, 2.4 % of GDP • Stunted Children (38% UNICEF)
into Parcham and Khalq after the
(recent budget reduced by 20%), • Water sanitation and hygiene
coup
• According to UNESCO report, if • Privatization of health sector
• Parcham wrote USSR for invasion
Pakistan wants to educate 36miilion • No Family planning
• USSR invasion in 1979
people 2015 to 20 it needs 1788 million • Low immunization
• UN result ion for USSR withdrawal
rupees. • Lack of trainings of doctors and staff
• • Afghan Mujahideen paid by USA
Quality of education (teacher training, ❖ Solutions and Saudi and train by Pakistan
large number of students, lack of • Universal coverage of essential
resources,) ❖ Impact on Pakistan
interventions
• High dropout ratio (76%, reason: • Revival of US-Pak relation
• Reducing inequities
poverty, social barrier, malnutrition • Nuclear proliferation of Pakistan
• Increased budget
(43%),) • US military support
• Integration of stakeholders
• Out-of-School Children (23million, • Afghan refugees burden on Pakistan
• Monitoring and accountability (over 4m)
poverty, distant schools, punishment
• Food security and clean water • Drug trafficking (8200 metric tons
culture,)
• Implementation of SDGs
• Problems of Female Education smuggled in 2007)
(cultural barriers, lack of school for • Rise of violent non-state actors
girls, lack female teachers) Pakistan’s National Culture • Sectarianism
• Parallel systems of education reflects unity • Kalashnikov culture
• Dr. Tariq Rehman’s five-tier model ❖ Introduction • Terrorism
• Elite schools • Multi-cultural society • Economist cost (Approx. $121b)
• Military schools • National culture • Transit route for illegal trade of
• Private schools weapon and drugs
❖ Definition
• Governmental schools
A set of norms behaviors, beliefs and
❖ Non-traditional Security Threats
• Deeni Madrasah customs that exist within entire nations • Refugees crisis
• Issues of Education inequalities • Diversity in national culture • Sectarianism
• Zubaida Mustafa’s two-tier model • Economic lagging
• Language: Punjabi, Sindhi, Balochi,
• State of the education for privileges • Drug culture
Pashto, etc.
• Decaying system of Underprivileged • Extremism
• Tourism
• Flawed curriculum (no national • Ethnic conflicts
curriculum, outdated syllabi and • Poetry ❖ Rise of non-state actors
teaching method) • Music and dance • Extremist organizations
• Neglect toward technical education • Religion • INGOs
(low industry-academic linkages, lack of • National events
technological universities, • National dress
• Flawed examination and evaluation • Food
methods (annual vs semester, private vs ❖ How national culture promotes
regular, leakage papers)
unity
• Lack of research culture
• It incorporates all national culture
• Lack of institutionalization of
educational practices • Mutual co-existence
• Poor implementation of education • Common goals
policies • Shared ideology
❖ Solutions
“Peace in not unity in similarity but unity in
diversity –Mikhail Garbachov)
Ideology of Pakistan • The Orthodox Ulema (Shah, Sirhindi) • International efforts
• Ideology ideos (ideas) logos(study) • Muslim Modernists (Jinna, Iqbal, Sir • Negotiation (PLO and Israel
❖ Definition Syed) government)
• Cluster of ideas, beliefs, and concepts ❖ Factors that led to Muslim • Mediator (US, Russia, UN, EU)
that are deeply ingrained in social Nationalism • Camp David Accord 1978
conscience of people over period of time • Ideological conflicts (Monotheism • Oslo Accord 1993 (Area ABC, not
(Shareef ul Mujahid ) (Muslims), Hindu believes in different implemented)
❖ Significance of ideology Gods) • Camp David Summit 2000
• Weltanschauung (worldview) • Hinduism was absorptive • Taba summit 2001
• People binding force • Islam withstood the thirst of other • Roadmap for peace 2002
• Helps in legitimization or de- religions • Arab peace initiative
legitimization • Impact of revivalist movements • Recent Developments
• Manifest the ends that a society is • Muslim (Faraizi, Algarh, Deoband) • Israeli settlement
pursuing • Hindu Brahumu, Ary, Deyo Samaj, • Gaza blockade
❖ Ideology and Nationhood • Impact of British rules • Wall inside West Bank
• Earnst Rena • Muslim subjugation, education, German • Imprisonment
• Nationalism is a dynamic expression of and Italian nationalism) • Humanitarian crisis
desires to live together as nations • Implementation of Westminster Model • Home demolition
• It the two component (parliamentary democracy, majority • Human Rights Violation
rule) •
• Past (Rich heritage of memory) US recognition Jerusalem as capital of
• Indian National Congress Policies
• Present (Desires to live together and Israel, December 2017
(711/1858) • $3.1billion aid by US to Israel and
preserve the heritage)
• Muslim nationalism converts into
• Ideology is abstract, but when it $362million to Palestine
separatist
manifests itself, it requires three thing • Solutions
✓ State (provides grounds) • Hindu extremist organization
• Two-state solutions
✓ Leadership (interprets and • Cultural Factors (language (Urdu/Hindi),
• One-state solution (not viable)
Cow slaughter, Vande Mahtram, Tri-
implement the ideology • Modus vivendi (maintains peace)
✓ Follower (follow and strengthens it) color flag)
• Is there a military solution?
• Formation spiritual aspect of nationalism • Pan-Islamic Movements
• Military solution is not a solution
• Shah Wali Ullah and Shiekh Ahmed • Jihad Movement
• Khilafat movement • Suggestion
Sirhindi (Developed the concept of
• Role of Muslim leaders • US neutral role
TNT)
• • Security and economic assistance
• Sir Syed Ahmed Khan (Interpretation of Role of Muslim press
• Engage Hamas
TNT)
• AL Fatah Reforms
• M.A. Jinnah ( Operationalize) Palestine Issue • Realistic ease fire
❖ Derivation of ideology ❖ Retrospect • Implementation of UN resolution
• Culture • Balfour Declaration 1917 • Role of regional players
• Social practices ❖ UN Resolution -181, 194, 242
• Religions ❖ War
• Historical experiences • 1948
• Intellectual exercise • 1967 (six days war)
• Example of secular Democracy in West, • 1973 (ended 1978 Camp David Accord)
which developed due to conflict with ❖ Core Issues
religion • Jerusalem (East and West)
• Muslim’s ideology- Quran and Sunnah • Refugees
❖ Ideology of Pakistan • Illegal Settlement
• IOP = IOI + TNT • West bank
• Islamic ideology • Security and airspace
• Quran and Sunnah (refer to Islamiat • Border issue
Capsule) • Resources issue
❖ Evolution of Muslim Nationalism • Occupied and disputed
in subcontinent • Mutual recognition
• Two set of forces
Role of Judiciary in Political System of Pakistan
Constitutional Development ❖ Definition of system Pakistan Foreign policy post
❖ Definition of political system 9/11
of Pakistan ❖ Pakistan political system under
❖ Introduction • Decision of governing bodies to
constitution of 1973
realized international goals
❖ State organ (3) • Parliamentary system
• Pro-west, security ridden, Indian-
❖ Judicial Review • Bicameral centric, foreign debt dependency,
❖ Role of Judiciary in constitutional • Executive (PM the head of govt.) sensitive to Muslim world
Development • Legislative (NA and Senate) • Determinants
❖ Maulvi Tameezudin case • Judiciary (3 tiers)
• Geographical factors, historical
• Dissolution of Assembly Jinnah favored parliamentary system
factors, ideological factors, economic
• Decision in favor G.G ❖ 1956 constitutions (parliamentary)
factors, Ethno-provincial factors
• Doctrine of necessity ❖ 1962 (presidential)
,technological factors, external and
• Negative role of judiciary ❖ 1973 (parliamentary)
Internal factors
❖ Usif Patel case ❖ Zia’s 8th amendment (strong
president) • Post 9/11 Foreign Policy
• Consent of G.G was necessary for • Retrospect of 9/11
every bill ❖ N. Sharif’s 13 amendment (strong
PM) • Pakistan foreign policy from
• Retrospective effects were given to
laws ❖ Musharraf 17th amendment (strong 2001 to 2008
• Limited G.G to form constituent president) • Frontline ally in WoT
assembly for legislation ❖ Presidential system • Dependence on Foreign aid
• Both positive and negative role • Certain and stable • Warm relation with USA
❖ State vs. Dosso case • Long-term polices • Support for US backed Afghan
• Validation of Martial Law by declaring • Separation of power government
that declaring that successful coup is an • Vindication of opponent • Improvement with bilateral ties with
internationally recognized method • Weak provincial autonomy India
❖ Asma Jilani vs. Govt. of Punjab • More prone to corruption • 2008 to 2013
• Imposition of martial law as invalidated ❖ Parliamentary system • Diversification
• Doctrine of state necessity was Merits • Moscow, Beijing, Ankara, Tehran
condemned martial was lifted • Power to elected representatives • CPEC, TAPI and IPGP
❖ Begum Nusrat Bhutto vs. C.O.A.S • Strong political parties • Good relation with India
• Appeal against martial law imposition • Accountability of executive • 2013 to 2018
• State necessity was invoked Demerits • Neutral role in Yemen war
❖ Zafar Ali Shah vs Pervez Musharaf • Consensus building issues • Worsening of ties with India –
• State necessity was invoked again • Weak and unstable government Kulbashan Jhadav, Pathan Kot, Uri
❖ Judicial activism after 2009 • Short-term polices attack
❖ Attack of Lawyers on Doctors • Issues during emergency • Membership of SCO
❖ Role of Judiciary • 2018 onward
• Rule of Law • Strengthening ties with China and
• Implementation of Judicial decision Russia
• Continuing of political process • Issue with India,
• Supremacy of constitution • Good relation with Malaysia and
Turkey
• Kashmir policy
• Afghan peace talk
• Pakistan Role in regional and
global politics
• Afghan peace process
• Kashmir Conflict resolution (UN talk)
• Saudi-Iran Conflict
• CPEC
• US-China Trade War
• Great Game Politics
Qatar crisis SCO • SCO and Pakistan
❖ Major players • Shanghai five (1996) Opportunities
• Saudi Arabia, Egypt, UAE, Bahrain vs. • Build for CBM and border resolution • Inclusion is Diplomatic cum
Qatar • SCO (2001) substantial breakthrough for
Islamabad
• US base in Qatar (Al-Udeid) important ❖ Now 8 Members
• Positive International Image
for US in ME • Russia
• Political and economic dividends
❖ Causes of Conflict • China
• Geographical location makes Pakistan
• Doha support for violent Islamist • Tajikistan
a transit economy for SCO
groups like Muslim Brotherhood • Kyrgyzstan
• Influence in Regional Security
• Role of Al Jazeera • Kazakhstan
architecture
• • Uzbekistan (2001)
Support for Iran • SCO serves for border resolution
• India (2017)
• Impact of Arab Spring • Fight Against Three evils is in
• Pakistan (2017) alignment with Pakistan’s Foreign
• President Trump visit to SA, Egypt,
❖ Objectives Policy
Saudi, UAE but not Qatar
• Mutual Trust • CPEC and SCO
❖ Current scenario • Pol, soc, eco, cultural, energy,
• Diplomatic crisis • Iran and Afghan inclusion can help
education cooperation resolve the issues with both neighbors
• Qatar is not going back on its stance • Regional peace and security • New Great Game perspective
• Economically independent • New international political and • Counter balance to Indo-US nexus
• US will do no harm because of Al- economic order
• Challenges for Pakistan
Udied ❖ Achievements • Balance b/w US and China relation
• Nor will other party go back • International partnerships
• Indian strengthened relations in the
❖ Impacts • Trade between members region
• Split in Sunnis camp • Border resolutions • Not to become a proxy again
• • Fight against three evils: Terrorism,
Tendency of Qatar, Turkey and Iran • US and SCO
Extremism, Separatism
(this nexus can further exacerbate • Indifference to doubt to attention
• Fight against money laundering and
situation in ME) • 2005 onward US has engaged with
terror financing
• Impact on price of oil SCO to prevent it from becoming a
• Inter-bank Union
• Can change security and power Sino-Russian instrument for New
❖ Challenges Great Game
structure in Middle East
• Nascent organization •
• Diplomatic economic and military • Ideological differences with NATO
To contain Iran from Inclusion
escalation • US policies to contain SCO
• Traditional security ventures can curb • Integration strategy to unite CARS
❖ Solution internal turmoil of Kyrgyzstan with South Asia
• Both parties should deescalate • Conflict of Interest • Bilateral relation with SCO member
• USA as a mediator • China wants Economic and political states
influence • Increased communication with SCO
• Russia aims at Influence in CARS • Using NATO and EU to improve
• Indo-Pak conflict cooperation with SCO
• CPEC as an opportunity as well as
threat
• Weak industries of CARS member
states
❖ Expansion of SCO
• Now it has 45 % of global Population,
19% of global GDP, 4 nuclear states, 2
UNSC chairs
• Iran and Afghan aspirations for
inclusion
SAARC Sir Syed Ahmad Khan ❖ Impact of AGM
South Asian Association for Regional • Political Impact
1817 to 1898 • British reaction / relation changed
Cooperation (1985)
21% of global population, 3% world area
❖ Introduction. • Muslim rights reserved
• British atrocities, great reformer, 1857 • National unity
Countries
❖ Members
Served as panacea for Muslim • Created leaders
• His services are known as Ali Garah • AGM is forerunner of Pakistan
Pakistan, India, Bangladesh, Maldives. Movement, started in Ali Garah. Movement
Nepal, Bhutan. Sri Lanka, Afghanistan ❖ Conditions of Muslim • Educational Impacts
❖ Objective • Decline in moral life • Muslim learned English
• Welfare • Mughal rule ended • Urdu language was protected
• Economic, social, cultural • Heavy hand of British on Muslim
Development • Social Impacts
• Deprive of jobs • Transformed social outlook of Muslim
• Collective Self-reliance • Ban on Persia, Arabic by British
• Mutual trust • Muslim society was introduced to
• Jumma prayer banned
• Active collaboration at international • British promoted Christianty
West
level
❖ Role of Sir Syed Iqbal’s concept of Muslim
❖ Achievements Emphasis on education, separatism
• Track 2 diplomacy To educate, educate, and educate, • Introduction
• SAFTA according to his biographers • Separate recognition of the Muslims
• SAPTA ❖ Objective of AGM (different religion ad nations in sub-
• Visa exemptions • AGM was meant to remove continent)
• Cultural Exchanges misunderstanding movement b/t British • Condemnation of Western Democratic
❖ Failure and Muslim
Concept (Westminster system)
• Less than five percent of global trade • To educate Muslim
• • Concept of Separate Muslim state
No implementation of SAFTA and • To protect Muslim rights
• Acclamation of idea of single nation
SAPTA ❖ Political services
• Strained relations among members • Rapprochement between Muslim and • Concept of TNT
• Cancellation of 11 summits British - Causes of revolt (book) • Eradication of racial and regional
• Poor Populations • Keep Muslim away from agitational prejudices
❖ Reasons for Failure politics • Explanation of relation of Islam and
• Inter-state disputes • TNT, 1967 Urdu- Hindi controversy politics
• Fear of Indian domination ❖ Educational Services • Islam complete code of life
• Clash of civilizations • Madrassah Muradabad 1959 • Islam is a lively power
• Unstable financial positions of • Madrassah Ghazipur 1962 • Islam is the way of success
members • Ali Garh School 1975 • Opposition to nationalism
• Low mutual trade Ghazipur scientific society • Foundation of Pakistan
• Lack of trust among members • Translated over 700 books from eng to
• Exclusion of contentious issue urdu
resolution from the charter • Muhamaddan Educational Conference
• Different political systems to discuss Muslim issues, it led to
• Lack of people-to-people contact formation of Muslim League.
❖ Suggestions • Tehzeb ul Ikhlaq (book) Muslim daily
• CBM life
• People to people contact • Israr ul sanadeed (book) History of
• Joint Counter terrorism strategy Dehli
• Joint media and cultural exchanges • Anjuman e tahreek e urdu
• China should become a member ❖ Religious Services
• Increased relations with CARS • Adopted rational approach to religion
William More wrote a book on life
Muhammad , Syed wrote in response
'Khutbat e Ahmadia
• Tried reduce the gap between Shia Sunni
Sheikh Ahmad Sirhindi Islamic Military Alliance Brexit
15 December, 2015, Pakistan joined Jan, 1975 membership of EU
1564- 1624 2016
❖ Education Britain Concerns regarding EU
• 41 states membership
• Holy Quran • Iran, Syria, Libya, Iraq excluded
• Hadith, Tafsir (commentary) and National sovereignty
❖ Reasons for formation
Ma‟qual (philosophy). National security (immigrants)
• US military retrenchment
• Isbat-un-Nabuwwat (affirmation of • Rise of ISIS
Compromising Economic Security
prophet hood) • Saudi-Iran relations
Increase in European immigrants in
❖ Religious And Social Services • Declining Saudi influence in Middle Britain
• Opposition of Din-i-Ilahi East Loss decrease as compare to benefits
• Social Reforms • Criticism of West for not acting against Inefficiency of EU - large bureaucracy
• Reforms in Tasawaf(Spirituality) terrorism
• Tried to purify Muslim society • Arab Spring David Cameron concern - 2013
• True image of Islam. ❖ Issues of IMA (Muslim Ummmmah) No refugee admission from ME
• Emphasis on (Ittibat-i-Sunnah) ❖ Opportunities for Pakistan Separate currency
• Emphasized on the concept of Tauheed • Nuclear leader June 2016 referendum
• Exposed the fallacy of Din-i-Illahi • Appreciation of Anti-terrorism resolve 52 vs 48
• Principles of Islam • Strategic relation with Saudi Cameron resigned
• Reformation of Nobles • Increased influence in Middle East Theresa may
• Emphasis on Islamic Values • Improved space for Pakistani diaspora Article 50 - notice before leaving EU -
• Strictly adhere to Namaz • Diplomatic support from GCC Deal Brexits.
• Two Nation Theory • Leverage to bring Iran on Table Transient period of two years - term and
• Firmly believed in Two-Nation Theory • Bulwark against India efforts to isolate condition for relation with EU members
• Differences between Hindus and Pakistan
after Brexit.
Muslims ❖ Challenges for Pakistan
• Wahdat-ul-Wajud and Wahdat-ul- • Impact on Pak-Iran relation
No-deal brexit.
Shahud • Backlash of ISIS
No support from EU. No condition
• Wahdat-ul-Wajud means there is no • Potential for domestic sectarian divide
living difference between the Man and ❖ Way forward Brexist a prospect for Britain
his creator • Reconciliation of Saudi and Iran Referendum led Boom in
• Every particle of the universe • Pak-Iran relation manufacturing sector
represented the presence of God and, No finance to EU from Britain
therefore, the worship of God’s Political sovereignty
creature amounted to the worship of
God Threats
• Negated this philosophy
• Wahdat-ul-Shahud, which meant that
80 % of Britian economy is on services
the creator and creatures were two
different and separate, entitles.
sectors
• The Influence of Sheikh Ahmad’s Access to EU countries. No tariff
Efforts Financial investment in EU countries -
• Indelible impact on the history of can lead to unemployment
Muslim India US-Britain one to one deal
• Allama Iqbal considers him as the Threat to Britain economy
spiritual guardian of the Muslims of
India
• Gave new life to the Muslims
• Impact in religious and practical fields.
You might also like
- Spiritual Secrets of Urine and Ways You Can Use It PT. 2 - Embracing SpiritualityDocument9 pagesSpiritual Secrets of Urine and Ways You Can Use It PT. 2 - Embracing Spiritualityinfo-501699100% (2)
- Saying of Salafs On MarriageDocument5 pagesSaying of Salafs On MarriageMariam Omotoyosi SadeqNo ratings yet
- Ruhi BK 7 Walking Together On A Path of ServiceDocument132 pagesRuhi BK 7 Walking Together On A Path of Servicebeokguk50% (2)
- Folder of Middle East EditedDocument213 pagesFolder of Middle East EditedSaffiNo ratings yet
- Islamiat O Level P 1 Revision Guide 401Document27 pagesIslamiat O Level P 1 Revision Guide 401Azlaan Zareef Khan100% (2)
- Assignment 02 FinalisedDocument11 pagesAssignment 02 FinalisedFaiza GandapurNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy and Pakistan's External RelationsDocument42 pagesForeign Policy and Pakistan's External RelationsManaal tariqNo ratings yet
- Global Powers and Security in South Asia PresentationDocument14 pagesGlobal Powers and Security in South Asia PresentationShaban Gill SbNo ratings yet
- Foreign PolicyDocument48 pagesForeign PolicyA KumarNo ratings yet
- Pak ChinaDocument43 pagesPak Chinaimtiazkhan0234No ratings yet
- Geopoliical Significance of PakistanDocument58 pagesGeopoliical Significance of PakistanYasmin khanNo ratings yet
- To Analyse The Impact of Events in West Asia and Afghanistan On PakistanDocument14 pagesTo Analyse The Impact of Events in West Asia and Afghanistan On PakistanRaman GillNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy of PakistanDocument16 pagesForeign Policy of Pakistani222371 HeerNo ratings yet
- International Business EnvironmentDocument30 pagesInternational Business Environmentaridaman raghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Geo-Strategic Importance of PakistanDocument23 pagesGeo-Strategic Importance of PakistanUzair Maqbool Khan100% (1)
- Why Rajouri-Poonch Belt Is Vulnerable To Terrorist AttacksDocument41 pagesWhy Rajouri-Poonch Belt Is Vulnerable To Terrorist AttacksAnjaneyuluNo ratings yet
- 26 Grid AnswersDocument12 pages26 Grid Answerszeesha tahirNo ratings yet
- Weekly Dawn Deconstruction June 15 To June 22 - by M.usmanDocument139 pagesWeekly Dawn Deconstruction June 15 To June 22 - by M.usmanMuzamil HassanNo ratings yet
- South Asia - An OverviewDocument36 pagesSouth Asia - An Overviewashraf kabirNo ratings yet
- Pak Iran RelationsDocument13 pagesPak Iran RelationsMaryam KamranNo ratings yet
- IR Current NotesDocument7 pagesIR Current NotesAnika BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy of PakistanDocument35 pagesForeign Policy of PakistanEisha NadeemNo ratings yet
- The Asia Pacific RegionDocument35 pagesThe Asia Pacific RegionSureilyValentinEstevezNo ratings yet
- FINALS Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesFINALS Contemporary WorldJairah Faith CammayoNo ratings yet
- Current Situation Current Affairs PRESENTATIONDocument10 pagesCurrent Situation Current Affairs PRESENTATIONcbhavelianNo ratings yet
- Daily News Simplified - DNS NotesDocument9 pagesDaily News Simplified - DNS NotesPriyanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Establishment of Pakistan 1947 To 1948Document12 pagesEstablishment of Pakistan 1947 To 1948zobiNo ratings yet
- QuotesDocument6 pagesQuotesGarvit PantNo ratings yet
- India and Pakistan Relations For SSC Banking Exams GK Notes in PDFDocument4 pagesIndia and Pakistan Relations For SSC Banking Exams GK Notes in PDFfaizNo ratings yet
- Rwanda Economic AnalysisDocument21 pagesRwanda Economic AnalysisGery AzhariNo ratings yet
- Foreign Policy of India - Evolution, Determinants - EnglishDocument3 pagesForeign Policy of India - Evolution, Determinants - Englisharvsev3103No ratings yet
- Pakistan: By: W Q S RM H O DDocument20 pagesPakistan: By: W Q S RM H O DBharat SethNo ratings yet
- Nepal As A Vibrant BridgeDocument26 pagesNepal As A Vibrant BridgeNiroj GhimireNo ratings yet
- REgional OrganisationDocument14 pagesREgional Organisationkaibalya paridaNo ratings yet
- Indias Security Interest MindmapDocument2 pagesIndias Security Interest MindmapRema RalteNo ratings yet
- SAARC & PakistanDocument35 pagesSAARC & Pakistansaniasiddique802No ratings yet
- Pak Relation With NeighboursDocument32 pagesPak Relation With NeighboursMuhammad RehanNo ratings yet
- Pak StudiesDocument10 pagesPak StudiesFloret UmbelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Domestic Political IssuesDocument28 pagesLecture 2 Domestic Political IssuesUzair SoomroNo ratings yet
- 7 Indo Pacific ConflictsDocument17 pages7 Indo Pacific Conflictsn2974538No ratings yet
- Pak-India Relations June 2020Document45 pagesPak-India Relations June 2020Yasmin khanNo ratings yet
- 6 - Pakistan Relations With The Muslim WorldDocument28 pages6 - Pakistan Relations With The Muslim Worldn2974538No ratings yet
- 3 Regional Geo Political Structure and Role of Pakistan Lecture 3 - Final 04102023 092011pmDocument42 pages3 Regional Geo Political Structure and Role of Pakistan Lecture 3 - Final 04102023 092011pmMuhammad SarmadNo ratings yet
- Geography of PakistanDocument13 pagesGeography of Pakistanwajeehaadeel57No ratings yet
- Classical Geopolitics in The 21st Century: Bangladesh-US Relations India-China RelationsDocument24 pagesClassical Geopolitics in The 21st Century: Bangladesh-US Relations India-China Relationsashraf kabirNo ratings yet
- 8 Political RisksDocument17 pages8 Political RisksvbalodaNo ratings yet
- ChandigarhDocument1 pageChandigarhJaisurya SharmaNo ratings yet
- JEHAN ZEB - Special Css Plan-CompressedDocument1 pageJEHAN ZEB - Special Css Plan-Compressedsafina zahoorNo ratings yet
- Lbs Breakfast Presentation May 2023Document77 pagesLbs Breakfast Presentation May 2023Damie OjoNo ratings yet
- TCWD 111 - Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesTCWD 111 - Midterm ReviewerGDHDFNo ratings yet
- Pakistan-China Strategic RelationsDocument56 pagesPakistan-China Strategic RelationsTSS DTNo ratings yet
- What Are The Roles of Great Power inDocument10 pagesWhat Are The Roles of Great Power inJeffery MillefioreNo ratings yet
- NorthCom FEMA Inteoperability! Meet Military Region Commanders Active Duty Army!Document9 pagesNorthCom FEMA Inteoperability! Meet Military Region Commanders Active Duty Army!Guy Razer100% (1)
- Foreign Policy of PakistanDocument2 pagesForeign Policy of PakistanShoaib BalochNo ratings yet
- Geo-Political Importance of The Muslim WorldDocument16 pagesGeo-Political Importance of The Muslim WorldMuqaddas Shehbaz710No ratings yet
- A System of Stories - Leah Zaidi - 2021 1Document1 pageA System of Stories - Leah Zaidi - 2021 1phyo min khantNo ratings yet
- Gujral DoctrineDocument8 pagesGujral DoctrinePritam SahaNo ratings yet
- CPEC by AHUDocument26 pagesCPEC by AHUAbdullah Noor KhanNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 Pakistan Relations With NeighboursDocument69 pagesCHP 10 Pakistan Relations With NeighboursKjsiddiqui Babloo100% (5)
- Wa0005.Document98 pagesWa0005.ahero7820No ratings yet
- South Korea and Argentina: Contributions of Alternative Approaches To DevelopmentDocument9 pagesSouth Korea and Argentina: Contributions of Alternative Approaches To DevelopmentApanjot SahotaNo ratings yet
- AEC - O&T For Hai PhongDocument7 pagesAEC - O&T For Hai PhongHoa TranNo ratings yet
- Internal and External Security Issues + Neighbourhood CAPF IGP 2023Document80 pagesInternal and External Security Issues + Neighbourhood CAPF IGP 2023dubrovnik1857No ratings yet
- Daily Current Affairs - 26 April 2023Document2 pagesDaily Current Affairs - 26 April 2023Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Daily Current Affairs - 1-2 May 2023Document3 pagesDaily Current Affairs - 1-2 May 2023Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Akhuwat ScholarshipDocument1 pageAkhuwat ScholarshipSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Essay OutlineDocument3 pagesEssay OutlineSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- 9-64-BSc (Hons) Agriculture-1st-1Document4 pages9-64-BSc (Hons) Agriculture-1st-1Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Israel War Current AffairsDocument8 pagesIsrael War Current AffairsSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Imec - G20Document8 pagesImec - G20Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Political PhilosophyDocument14 pagesPolitical PhilosophySajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- 6-Scientific Instruments Names PDF Notes For All Competitive ExamsDocument9 pages6-Scientific Instruments Names PDF Notes For All Competitive ExamsSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- BRI - How China's Belt and Road Took Over The World - The DiplomatDocument14 pagesBRI - How China's Belt and Road Took Over The World - The DiplomatSajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- B3W Vs BRIDocument16 pagesB3W Vs BRISajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Date Sheet Competitive Examination Special CSS-2023Document1 pageDate Sheet Competitive Examination Special CSS-2023Sajid UsmanNo ratings yet
- Aniruddha and Usha StoryDocument9 pagesAniruddha and Usha Storysriramnayak100% (1)
- transfigurationlyricshillsong-RechercheGoogle 1677070132193Document4 pagestransfigurationlyricshillsong-RechercheGoogle 1677070132193Zidane Sobtantning TioningNo ratings yet
- American Revolution EssayDocument49 pagesAmerican Revolution Essaym0kih1h0kug3100% (2)
- GMS 691 Week 2Document23 pagesGMS 691 Week 2Mit DaveNo ratings yet
- What Does The Phrase Born of Water and The Spirit Mean? (The New Birth)Document5 pagesWhat Does The Phrase Born of Water and The Spirit Mean? (The New Birth)dlee7067No ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 3Document20 pages08 - Chapter 3Guru DevNo ratings yet
- Surya Namaskar - Searchforlight - Org - Fitness - Suryanamaskar - HTMLDocument4 pagesSurya Namaskar - Searchforlight - Org - Fitness - Suryanamaskar - HTMLmarabunta80No ratings yet
- List of Brahmana SanghasDocument4 pagesList of Brahmana SanghasJayant AgasthyaNo ratings yet
- Artha 26 DefinitionsDocument7 pagesArtha 26 DefinitionsGeo DezicNo ratings yet
- Sawaneh Tajushshariah (Roman Urdu)Document119 pagesSawaneh Tajushshariah (Roman Urdu)Syed Aqib Ali100% (2)
- MarsDocument1 pageMars11ab4611No ratings yet
- Brunstad Christian ChurchDocument6 pagesBrunstad Christian Churchwattssteve21No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Black VenusDocument13 pagesThe Little Book of Black VenusLe On CampbellNo ratings yet
- Surah 25. Al-Furqan, Ayat 63-69 PDFDocument1 pageSurah 25. Al-Furqan, Ayat 63-69 PDFMusaab MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Ibm536 Country Report ChinaDocument22 pagesIbm536 Country Report ChinaNajihah YusoffNo ratings yet
- Dominant CasteDocument8 pagesDominant Castecshrivastava47No ratings yet
- Ganito Kami Noon, Paano Kayo Ngayon: ReflectionDocument2 pagesGanito Kami Noon, Paano Kayo Ngayon: ReflectionJannaRica BeasonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 D TWO ATTRIBUTES OF THE CICM IDENTITYDocument31 pagesLesson 2 D TWO ATTRIBUTES OF THE CICM IDENTITYJamila BullanNo ratings yet
- Greater Sins V 01Document203 pagesGreater Sins V 01mohammad HasnainNo ratings yet
- Philippians Commentaries & Sermons PDFDocument124 pagesPhilippians Commentaries & Sermons PDFAlfonso Escobar Norero100% (2)
- VijayanagarDocument4 pagesVijayanagarpooja.r0829No ratings yet
- Our Swamy16Document4 pagesOur Swamy16api-3758390No ratings yet
- Chapter Xix: Breezing Through The Hexateuch Part 2. Cain and AbelDocument6 pagesChapter Xix: Breezing Through The Hexateuch Part 2. Cain and AbelLegba777No ratings yet
- Gems Cambridge International School-Abu Dhabi Islamic Studies - B, Year 11 Name: - Date: - Islamic DateDocument2 pagesGems Cambridge International School-Abu Dhabi Islamic Studies - B, Year 11 Name: - Date: - Islamic DateKevir ManNo ratings yet
- Community Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship: Group 4 (12 HUMSS-D)Document17 pagesCommunity Engagement, Solidarity and Citizenship: Group 4 (12 HUMSS-D)jeonghan aegiNo ratings yet
- FINAL - Perspectives On Islamic Psychology - Al Raghib Al Isfahani On The Healing of Emotions in The QuranDocument38 pagesFINAL - Perspectives On Islamic Psychology - Al Raghib Al Isfahani On The Healing of Emotions in The QuranArafat FaniNo ratings yet