Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation 1
Presentation 1
Uploaded by
api-7335637700 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views19 pagesThe dental hygienist plays an important role in oral pathology by performing preliminary evaluations of patients' oral cavities. This includes examining the mouth, feeling any areas of concern, and describing any lesions found. Oral pathologies can be variants of normal, such as exostoses and fissured tongue, or more abnormal findings like nevi, cold sores, and squamous cell carcinoma, which may require medical treatment. The hygienist documents any abnormal findings to inform the dentist about the patient's oral health status.
Original Description:
Original Title
presentation 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe dental hygienist plays an important role in oral pathology by performing preliminary evaluations of patients' oral cavities. This includes examining the mouth, feeling any areas of concern, and describing any lesions found. Oral pathologies can be variants of normal, such as exostoses and fissured tongue, or more abnormal findings like nevi, cold sores, and squamous cell carcinoma, which may require medical treatment. The hygienist documents any abnormal findings to inform the dentist about the patient's oral health status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
17 views19 pagesPresentation 1
Presentation 1
Uploaded by
api-733563770The dental hygienist plays an important role in oral pathology by performing preliminary evaluations of patients' oral cavities. This includes examining the mouth, feeling any areas of concern, and describing any lesions found. Oral pathologies can be variants of normal, such as exostoses and fissured tongue, or more abnormal findings like nevi, cold sores, and squamous cell carcinoma, which may require medical treatment. The hygienist documents any abnormal findings to inform the dentist about the patient's oral health status.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 19
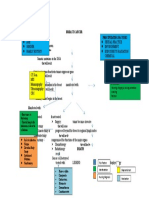
Oral Pathology
What you need to know
By: Vanessa Chamberlin
Oral Pathology
• The specialty of dentistry and discipline that deals with the nature, identification, and management of diseases
affecting the oral and maxillofacial regions.
Biological- There are more than 700 bacteria/microorganisms in the
mouth.
Hormonal- Estrogen, progesterone and even testosterone fluctuations.
Chemical- Tobacco, alcohol & drugs.
Causes of Oral
pathology Nutritional- Diet/certain foods.
Physical- Trauma & heat.
Idiopathic- It just happens and we don't know why.
What role does • The Hygienist performs the preliminary evaluation of the patient's oral cavity.
*Checks with the patient for any health changes.
the dental *Looks in the oral cavity.
hygienist play in
*Palpates the area in question bi-digitally. (Feels it with two fingers)
*Shows the patient the area in question with a hand mirror.
regards to oral *Asks the patient about any symptoms such as pain & duration.
*Measures the lesion with a probe.
pathology? *Describes the lesion with a minimum of 5 descriptors.
Pathologies: Variant of normal
• These are pathologies that are not concerning. They may cause pain & if so, they should be monitored & treated
accordingly by your dentist.
Exostoses
*Hard, bony growths. LOCATIONS
*Called tori or torus. *Roof of the mouth.
*In front of the upper and lower teeth.
CAUSES * Behind the lower teeth.
*Grinding/clenching.
*Can form after a palate expander. TREATMENTS
*Can be common in people 40+ years of age. *Surgical removal.
*Idiopathic.
Geographic tongue
*Looks like moving "spots" on the edge of the tongue.
*Red/white patches. TREATMENTS
*Not typically painful. *Avoidance of acidic, salty
CAUSES or spicy foods.
*Spicy, salty or acidic foods *Can be treated with
may make it worse. steroids or topical numbing.
*Idiopathic.
LOCATIONS
*Typically on the tongue but can be on the gum tissues.
macule
*Spots that are different colors than the rest of the tissue. (freckles)
CAUSES
*Hyperpigmentation of a mucus membrane. One produces more pigment than usual.
LOCATIONS
*Can be anywhere in or around the oral cavity.
TREATMENTS
*Surgical removal.
Lingual Varicosities
*Dilated veins. TREATMENTS
*Purple or red in color. *Sclerotherapy. (Injection into
CAUSES the vein)
*Age
*Stretched veins/veins that have lost elasticity.
LOCATIONS
*Under the tongue or on the floor of the mouth.
Fordyce granules
*Small, dot like bumps. TREATEMENTS
*Typically white in color. *Micro-punch surgery.
CAUSES *Laser removal.
*Overgrowth of sebaceous (oil) glands. *Topical cream.
LOCATIONS
*Lips
*Inside of the cheeks and lips.
Fissured tongue
*Found in any person of any age/gender.
*Deep grooves.
CAUSES
*Idiopathic. TREATMENTS
*Hormonal changes. *Tongue scrapers to remove
*Sleep habits. (Open mouth) excess bacteria sitting on the
LOCATIONS tongue.
*Top of the tongue.
Pathologies: Abnormal
• These are pathologies that are not normal and can be cause for concern. Can cause pain, odor & obvious enlargement of
tissues in or around the oral cavity, head & neck. These pathologies should be noted & treated as quickly as possible.
Nevus
*Dark colored mole. (Blue or black)
*Vary in sizes. TREATMENTS
*Not painful. *Excision (surgical removal).
CAUSES *Biopsy may be needed to decide
*Clusters of pigment-forming cells. whether or not further
*Excess skin growth. treatment is needed.
LOCATIONS
*Typically on the palate (roof) of the mouth but can be found anywhere in the oral cavity.
Cold Sores
*Blister like sore.
*Causes itching & burning sensations.
*When broken open they weep. TREATMENT
CAUSES *Antiviral medications,
*Herpes Simplex Virus-1. in pill or cream form.
*Due to saliva transfer during an active cold sore.
LOCATIONS
*Any area of the lips.
Candidiasis
*Also referred to as thrush. LOCATIONS
*White coating. Plaque-like. *The entirety of the oral cavity
*Can be a localized or generalized. including lips and tongue.
(Cover a small area or entire mouth) TREATMENTS
CAUSES *Oral or IV antifungal
*The fungus Candida Albicans lines the mouth. meds.
*Medications and health issues such as diabetes.
Black hairy tongue
*Hairy tongue can be brown or black.
*Fuzzy appearance.
*Lengthening of the papillae of the tongue.
CAUSES
*Overgrowth of dead skin cells. TREATMENTS
*Bacteria, yeast, food, tobacco. *Good oral hygiene and
LOCATION avoidance of use of tobacco
*Top of the tongue. products.
Squamous cell carcinoma
*Cancer in the mouth.
*Presents as unhealthy, irritated tissues both red and white.
CAUSES
*Tobacco use. TREATMENTS
*Idiopathic. *Surgical removal of entire lesion
LOCATION and margins.
*Anywhere in the oral cavity. *Radiation therapy.
Hematoma
*Blood blister appearance.
*Typically red or purple in color. TREATMENTS
*Doesn't blanche when pinched. *Applying a warm compress.
CAUSES *Warm salt water rinses.
*Local anesthesia site. *Time.
*Laceration of an artery or vein.
LOCATIONS
*Anywhere in the mouth especially the tongue and lips.
Thanks for reading!
You might also like
- Breast CA Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast CA Concept MapDianne Kate CadioganNo ratings yet
- Term 3 Rationale Pharmacology and MCNDocument35 pagesTerm 3 Rationale Pharmacology and MCNKing KongNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDocument89 pagesPhysical Assessment Mouth Throat NoseDeeeee100% (3)
- REVISED CITIZENS CHARTER-NWRB Dec 10 2013 PDFDocument41 pagesREVISED CITIZENS CHARTER-NWRB Dec 10 2013 PDFJecky Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Variasi Normal Lesi Rongga MulutDocument34 pagesVariasi Normal Lesi Rongga MulutAfaf MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 - Oral PathologyDocument50 pagesChapter 17 - Oral PathologyShoyo HinataNo ratings yet
- Salcedo HA CU 9 ASSESSMENT of MOUTH THROAT 24 RDocument26 pagesSalcedo HA CU 9 ASSESSMENT of MOUTH THROAT 24 RshaimonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Oral Cavity FinalDocument117 pagesDiseases of Oral Cavity FinalRamanujam SridharNo ratings yet
- Xerostomia BrochureDocument2 pagesXerostomia Brochureapi-312451539No ratings yet
- 4 Cold Sores and Mouth UlcersDocument41 pages4 Cold Sores and Mouth UlcersLQYNo ratings yet
- DD of TeethDocument53 pagesDD of TeethRanjit DanielNo ratings yet
- Variants of NormalDocument9 pagesVariants of NormalFaizah HannyNo ratings yet
- Oral Path Flipchart 1233Document11 pagesOral Path Flipchart 1233api-397871513No ratings yet
- SodaPDF Merged Merging Result 1Document203 pagesSodaPDF Merged Merging Result 1nonelNo ratings yet
- תוכנית רבעונית q1 נראם גדבאןDocument84 pagesתוכנית רבעונית q1 נראם גדבאןIoana DănilăNo ratings yet
- Good Morning: by Ibrahim GBRDocument34 pagesGood Morning: by Ibrahim GBRDento - PhilicNo ratings yet
- CANDIDIASISDocument32 pagesCANDIDIASISShraddha SuchakNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Oral Cavity and Common DisordersDocument24 pagesAnatomy of Oral Cavity and Common DisordersMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Flipchart - Carissa WachendorfDocument18 pagesOral Pathology Flipchart - Carissa Wachendorfapi-499223511No ratings yet
- Perio Case HistoryDocument90 pagesPerio Case HistoryMoola Bharath Reddy100% (1)
- Lecture No 1Document36 pagesLecture No 1Pawan balesara PkNo ratings yet
- Mouth and Teeth NotesDocument9 pagesMouth and Teeth NotesChananNo ratings yet
- 1.1a The Normal Oral Mucosa PDF-2Document18 pages1.1a The Normal Oral Mucosa PDF-2marianaffernandes10No ratings yet
- Cm2 Cu9 Assessment of Mouth Throat Nose Sinuses 2Document14 pagesCm2 Cu9 Assessment of Mouth Throat Nose Sinuses 2Eli LopezNo ratings yet
- Mouth Disorder For Teaching Angkor UniversityDocument23 pagesMouth Disorder For Teaching Angkor UniversityMey KeangNo ratings yet
- Deviated Nose..... Ear Nose and ThroatDocument83 pagesDeviated Nose..... Ear Nose and ThroatBinita ShakyaNo ratings yet
- 10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatDocument25 pages10 - Nose, Mouth, and ThroatArka Ogeh100% (1)
- Physical and Chemical Injuries: Oral Complications of H and N Radiation TherapyDocument5 pagesPhysical and Chemical Injuries: Oral Complications of H and N Radiation TherapynewmexicoomfsNo ratings yet
- Checklist EBP - Nose, Throat and MouthDocument6 pagesChecklist EBP - Nose, Throat and Mouths138140No ratings yet
- Leukoplakia: Farida Ulfa 15-057Document9 pagesLeukoplakia: Farida Ulfa 15-057farida ulfaNo ratings yet
- Oral Diagnosis and Treatment Planning IIDocument19 pagesOral Diagnosis and Treatment Planning IIAIME WILFRIED BEASSO FOZOCKNo ratings yet
- GIT Conditions - StudentsDocument57 pagesGIT Conditions - StudentsShamal KoyeNo ratings yet
- Oral Path Flip ChartDocument22 pagesOral Path Flip Chartapi-742616973No ratings yet
- Riaz Gul AHN Unit 1Document106 pagesRiaz Gul AHN Unit 1Riaz Gul RindNo ratings yet
- StomatitisDocument39 pagesStomatitisNyakie MotlalaneNo ratings yet
- Causes of Bad Breath (Halitosis)Document13 pagesCauses of Bad Breath (Halitosis)Steven KauNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances - Dr. Nermine El BaheyDocument11 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances - Dr. Nermine El BaheyMOHAMED AMINNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner: Red and Pigmented LesionsDocument7 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental Practitioner: Red and Pigmented LesionsKaty LunaNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Cancer: Section B-Group 1Document6 pagesHead and Neck Cancer: Section B-Group 1Mari FeNo ratings yet
- Disease of The Oral CavityDocument86 pagesDisease of The Oral CavityAnonymous wqnuimNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examination 2022-2023Document39 pagesClinical Examination 2022-2023نورالهدى حسام عليNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis and Ludwigu2019s AnginaDocument21 pagesCellulitis and Ludwigu2019s AnginaLawrence WanderiNo ratings yet
- Premalignant Conditions of Oral CavityDocument18 pagesPremalignant Conditions of Oral CavityHaneen Masarwa AtamnaNo ratings yet
- Syphilis in Ent DiseaseDocument19 pagesSyphilis in Ent DiseaseMohamad YusriNo ratings yet
- 2 Normal Oral Cavity Findings and Variants of NormalDocument6 pages2 Normal Oral Cavity Findings and Variants of NormalalbaablyNo ratings yet
- Developmental Anomalies of TongueDocument23 pagesDevelopmental Anomalies of TonguePriyaNo ratings yet
- 7mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus AssessmentDocument27 pages7mouth, Throat, Nose & Sinus AssessmentFerocious WitNo ratings yet
- Tonguedisorders 150616104030 Lva1 App6892Document34 pagesTonguedisorders 150616104030 Lva1 App6892Mohan VeerabomalaNo ratings yet
- Oral Ulcers: DR Vadish Bhat Professor, ENT KshemaDocument33 pagesOral Ulcers: DR Vadish Bhat Professor, ENT KshemaAkhil RajeevNo ratings yet
- 2.ent EmergenciesDocument54 pages2.ent Emergenciesmesay zelekeNo ratings yet
- Folliate PappilaeDocument9 pagesFolliate PappilaeEga Muhamad YusufNo ratings yet
- Oral Medicine - Update For The Dental PractitionerDocument8 pagesOral Medicine - Update For The Dental PractitionernavyaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Mouth & PharynxDocument79 pagesAssessment of Mouth & PharynxMUHAMMAD SALMANNo ratings yet
- Developmental Disturbances of The Oral Mucosa, Gingiva and TongueDocument51 pagesDevelopmental Disturbances of The Oral Mucosa, Gingiva and Tonguekavin_sandhu100% (1)
- Lichen Planus: DR Hira BashirDocument37 pagesLichen Planus: DR Hira BashirSaroash SadruddinNo ratings yet
- Patology of LinguaDocument37 pagesPatology of LinguaVlad ScutelnicNo ratings yet
- Tips Intra Oral ExaminationDocument47 pagesTips Intra Oral ExaminationferdyNo ratings yet
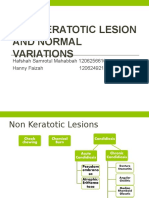
- Non Keratotic Lesion and Normal VariationsDocument35 pagesNon Keratotic Lesion and Normal VariationshannyfaizahNo ratings yet
- 2 Diseases of Tongue Lips PDFDocument17 pages2 Diseases of Tongue Lips PDFmarianaffernandes10No ratings yet
- CA Tongue EntDocument18 pagesCA Tongue EntNoor Ul AminNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Tongue LesionDocument26 pagesOral Pathology - Tongue Lesionneji_murniNo ratings yet
- Lesions of Oral CavityDocument43 pagesLesions of Oral CavityDawood NasserNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Bad Breath and Mouth DiseasesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Final ReflectionDocument2 pagesFinal Reflectionapi-733563770No ratings yet
- Special Needs Treatment Plan 1Document5 pagesSpecial Needs Treatment Plan 1api-733563770No ratings yet
- Perio Paper 1Document9 pagesPerio Paper 1api-733563770No ratings yet
- Presentation1 2Document12 pagesPresentation1 2api-733563770No ratings yet
- Vanessa Chamberlin-ResumeDocument2 pagesVanessa Chamberlin-Resumeapi-733563770No ratings yet
- Pre-Setting Manual Balancing Valves CIM 788: Technical InformationDocument7 pagesPre-Setting Manual Balancing Valves CIM 788: Technical InformationblindjaxxNo ratings yet
- Muscle Energy Techniquesto Correct Postural DysfunctionsDocument3 pagesMuscle Energy Techniquesto Correct Postural DysfunctionsdasaNo ratings yet
- Carlos Morzan - Hoja de VidaDocument2 pagesCarlos Morzan - Hoja de Vidarosa monteza valquiNo ratings yet
- ASI4517 R3 V 06Document2 pagesASI4517 R3 V 06Дмитрий СпиридоновNo ratings yet
- Test Bank Linux For Programmers and Users SolutionDocument4 pagesTest Bank Linux For Programmers and Users SolutionRichard1LauritsenNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure MCQDocument6 pagesForce and Pressure MCQnitikaNo ratings yet
- Information About Uterine Fibroids From The Royal Free Hospital, London, UKDocument151 pagesInformation About Uterine Fibroids From The Royal Free Hospital, London, UKHarith NaharNo ratings yet
- July 12, 2019 Strathmore TimesDocument20 pagesJuly 12, 2019 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- Neatecha 1Document20 pagesNeatecha 1cram retselNo ratings yet
- 3 PDFDocument16 pages3 PDFzahidNo ratings yet
- EMM-Important Questions PDFDocument26 pagesEMM-Important Questions PDFsyed abdul rahamanNo ratings yet
- Case Study - : The Chubb CorporationDocument6 pagesCase Study - : The Chubb Corporationtiko bakashviliNo ratings yet
- Trends in The Use of Marine Ingredients in Anti-Aging CosmeticsDocument11 pagesTrends in The Use of Marine Ingredients in Anti-Aging CosmeticsANGIE TATIANA RUIZ LADINONo ratings yet
- CE 394K.2 Hydrology - Lecture 1: Some Slides in This Presentation Were Prepared by Venkatesh MerwadeDocument16 pagesCE 394K.2 Hydrology - Lecture 1: Some Slides in This Presentation Were Prepared by Venkatesh MerwadeJayson PagalNo ratings yet
- 02-Citizens-Charter (1) EODocument3 pages02-Citizens-Charter (1) EOAgustin MharieNo ratings yet
- Structure of A ChloroplastDocument2 pagesStructure of A ChloroplastsreenitthiNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Effectiveness of The Adapted Adversity Quotient Program in A Special Education SchoolDocument11 pagesAssessing The Effectiveness of The Adapted Adversity Quotient Program in A Special Education Schoolelly putriNo ratings yet
- CyclamenDocument50 pagesCyclamenLAUM1No ratings yet
- Soil Science: Classification of PedologyDocument24 pagesSoil Science: Classification of Pedologyekush amar100% (1)
- Career Portfolio Juguilon Marjorie T. BSHM 702Document9 pagesCareer Portfolio Juguilon Marjorie T. BSHM 702Ivy Nicole SisonNo ratings yet
- Is 1391 2 2018Document20 pagesIs 1391 2 2018EME HPCNo ratings yet
- P2 Ped 030 ReviewerDocument6 pagesP2 Ped 030 ReviewerFrancis DeocaresNo ratings yet
- 415 V System Stage-1Document18 pages415 V System Stage-1raghavendran raghuNo ratings yet
- Goodhormonehealth News Jan16 PDFDocument10 pagesGoodhormonehealth News Jan16 PDFBrian CoxNo ratings yet
- 3A2988C - XM PFP Mix Manifold, Instructions - Parts, EnglishDocument22 pages3A2988C - XM PFP Mix Manifold, Instructions - Parts, Englishjorge ChavezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Connective Tissue NotesDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Connective Tissue NotesBinadi JayNo ratings yet
- Effective Parent Consultation in Play TherapyDocument14 pagesEffective Parent Consultation in Play TherapyMich García Villa100% (1)