Professional Documents
Culture Documents
KO 1.1 Basic Physics
KO 1.1 Basic Physics
Uploaded by
Abs Mahi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageThe document provides an overview of key concepts in level physics including:
1) The 6 base SI units used to express physical quantities along with some derived units like Newtons.
2) How to add vectors by considering both the magnitude and direction of forces using trigonometry.
3) The definition of torque or moment as a turning effect of a force, calculated as force times perpendicular distance.
4) The principle of moments stating that for equilibrium the net torque must be zero.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of key concepts in level physics including:
1) The 6 base SI units used to express physical quantities along with some derived units like Newtons.
2) How to add vectors by considering both the magnitude and direction of forces using trigonometry.
3) The definition of torque or moment as a turning effect of a force, calculated as force times perpendicular distance.
4) The principle of moments stating that for equilibrium the net torque must be zero.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageKO 1.1 Basic Physics
KO 1.1 Basic Physics
Uploaded by
Abs MahiThe document provides an overview of key concepts in level physics including:
1) The 6 base SI units used to express physical quantities along with some derived units like Newtons.
2) How to add vectors by considering both the magnitude and direction of forces using trigonometry.
3) The definition of torque or moment as a turning effect of a force, calculated as force times perpendicular distance.
4) The principle of moments stating that for equilibrium the net torque must be zero.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
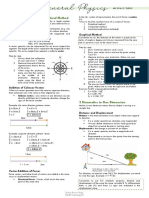
A Level Physics Component 1.
1 Basic Physics
6 essential base units: Adding vectors: Moment/Torque:
Quantities are expressed with a value and a unit. Force is a vector quantity, therefore A moment, or torque, is a turning effect of a force about a
There are 6 base units: when more than one force is acting point. It is calculated using this equation,
on an object you must consider Moment=F×d
Base quantity Unit
the direction and magnitude when
Mass kg calculating the resultant force. Where F is the force and d is the perpendicular distance to
the force. It is expressed in units of N m.
Length m When forces are at right angles to each
Time s other, you can use Pythagoras’ theorem
Principle of moments:
Electrical current A to calculate the magnitude of the resultant
force and trigonometry to calculate its If an object is in equilibrium;
Temperature K
direction. • The resultant force on it must be zero.
Amount of a substance mol
• The resultant moment about any point must be zero.
Other units, such as Newtons, N, and Joules, J, represent (The clockwise and anticlockwise moments must be equal
a combination of these base units. For example, using = 38.9o from the vertical in magnitude.)
the equation for force, F=ma, you can express Newtons
in terms of base units. Remember when making calculations with these conditions,
This method works for all vector quantities.
you may need to use some trigonometry to calculate
components of the force or perpendicular distances from
Resolving vectors: the pivot.
Another important skill is proving that an equation is
Often you will need to calculate the force in a certain direction
homogeneous. This means that the units for both sides
in order to use it in an equation. However, the force will not
of the equation are the same. Centre of gravity:
always be in the direction that you need but at an angle. In this
When using weight of an object in principle of moment
Scalar and vector: situation you must calculate the component of the force in
questions, you must consider where the weight is acting.
Scalar quantities, such as mass, have a magnitude only. the direction you require.
Although gravity acts on the whole object its weight can be
Vector quantities, such as force or acceleration, have a In this example, the weight of considered as acting on one point, the centre of gravity.
magnitude and direction. the object, mg, is acting vertically
For example, the C
downwards but the acceleration
of G for this rod is
Density: is along the slope. You can use
the mid-point.
Density is a measure of how concentrated the mass in a trigonometry to calculate this;
material is. It can be calculated using this equation; Falong the slope = mg cos θ
Remember to give your answer in SI units, kg m-3. Often
information about density is given in g and cm3.
ρ = density in kg m-3 m = mass in kg V = volume in m3 F = force in Newtons (N) d = perpendicular distance in m
You might also like
- Grade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Document23 pagesGrade 11 Physics Study Guide / Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Niki79% (14)
- Grade 11 Physics Study Guide Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Document23 pagesGrade 11 Physics Study Guide Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Kamil GhoshNo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- A Level PPT 1Document56 pagesA Level PPT 1YQ TangNo ratings yet
- 16: Work, Power, and Energy: Key Physics Terms Key ConceptsDocument1 page16: Work, Power, and Energy: Key Physics Terms Key ConceptsBlaine RogalskiNo ratings yet
- StaticsDocument95 pagesStaticsJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Physics AS Notes (2023)Document79 pagesPhysics AS Notes (2023)Nihal TahseenNo ratings yet
- Moments: Turning Effect of A ForceDocument21 pagesMoments: Turning Effect of A ForceAnki AccountNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Basic Mechanics PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 6 Basic Mechanics PDFTarique AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Basic MechanicsDocument22 pagesChapter 6 Basic MechanicsBillyNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument8 pagesRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsNathalie SerafinNo ratings yet
- General Physics Midterm ReviewerDocument10 pagesGeneral Physics Midterm ReviewerDanica RaylaNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 PhysicsReviewerDocument8 pagesChapter8 PhysicsReviewerJuliana UyNo ratings yet
- Ch.4 MomentsDocument1 pageCh.4 MomentsangelinatianranNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Tutorial BB - TaggedDocument18 pagesWeek 3 - Tutorial BB - Taggedlouis parchmentNo ratings yet
- Y12 Mechanics KODocument3 pagesY12 Mechanics KOrebeccaau07No ratings yet
- Topic 2. Scalars, Vectors and Kinematics. (Notes)Document14 pagesTopic 2. Scalars, Vectors and Kinematics. (Notes)M.Burhan TahirNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1-P1.10 - Turning ForcesDocument19 pagesChapter-1-P1.10 - Turning ForcesMicheal XavierNo ratings yet
- 04 Forces, Density and PressureDocument14 pages04 Forces, Density and Pressurefisica2No ratings yet
- Moments Couples Activity OptDocument18 pagesMoments Couples Activity OptShruti GargNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 - Equivalent Vectors Force and Its Characteristics Moment of A Force About A Point Moment of A Force About An Axis PDFDocument55 pagesLecture 7 - Equivalent Vectors Force and Its Characteristics Moment of A Force About A Point Moment of A Force About An Axis PDFMichael Jeawel AlabanNo ratings yet
- Principles of DynamicsDocument7 pagesPrinciples of DynamicsNhezlee AlegreNo ratings yet
- Open ES-1-Handout 2Document61 pagesOpen ES-1-Handout 2JANINA CHRISTELLE ORMITANo ratings yet
- 04 Parallel Forces and RelatedDocument11 pages04 Parallel Forces and Relatedapi-27085921No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Fundamental Concepts in Mechanics, Forces and MomentsDocument44 pagesLecture 1 - Fundamental Concepts in Mechanics, Forces and MomentsMonica B. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Ch.5 Forces and FrictionDocument1 pageCh.5 Forces and FrictiondqtkgqvpwcNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Mechanics - LectureDocument48 pagesFundamental Mechanics - LectureAhmed SamiraNo ratings yet
- ΙΒ PHYSICS CHAPTER 6 and 10 Circular Motion and Gravitation HLDocument19 pagesΙΒ PHYSICS CHAPTER 6 and 10 Circular Motion and Gravitation HLAnastasia VergouNo ratings yet
- Physics Cheat SheetDocument21 pagesPhysics Cheat SheetDinu PereraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 (Ch.5) : y MG PEDocument3 pagesQuiz 3 (Ch.5) : y MG PEbat.laughNo ratings yet
- Y7 Science ForcesDocument2 pagesY7 Science ForcesshaneagcaintNo ratings yet
- L3 Force SystemsDocument23 pagesL3 Force SystemsKISAKYE MOSESNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Year 11 First Term Slides 2023-2024Document167 pagesPHYSICS Year 11 First Term Slides 2023-2024adedoyindasilva26No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Statics: Universiti Teknologi MalaysiaDocument40 pagesChapter 1 - Statics: Universiti Teknologi Malaysiacaps lockNo ratings yet
- Moment and CoupleDocument42 pagesMoment and CoupleClifford Ryan GalenzogaNo ratings yet
- CH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsDocument4 pagesCH 3 & 5 & 6 Vectors, Newton's Laws, & Applications of Newton's LawsMelindaNo ratings yet
- ME 555 Stress Analysis Unit 4Document57 pagesME 555 Stress Analysis Unit 4TheoNo ratings yet
- Moments & Equilibrium PDFDocument4 pagesMoments & Equilibrium PDFaspNo ratings yet
- E1 - Vector AlgebraDocument9 pagesE1 - Vector AlgebraMiguel ApiladoNo ratings yet
- - - محصلة القوى - ويكيبيديا - .ar.enDocument13 pages - - محصلة القوى - ويكيبيديا - .ar.enyr44grf94kNo ratings yet
- Lecture 10, 11, 12 - Chapter 5 Distributed ForcesDocument43 pagesLecture 10, 11, 12 - Chapter 5 Distributed Forcesrobel metikuNo ratings yet
- PHY201 Final TopicsDocument5 pagesPHY201 Final TopicsBeaner0_0No ratings yet
- Eng Mech. - Statics LectureDocument68 pagesEng Mech. - Statics Lecturemwendwakelvin842No ratings yet
- Mechanics Final For Equtaion SgeetDocument4 pagesMechanics Final For Equtaion SgeetAlex SutherlandNo ratings yet
- AS Units Revision Notes IAL EdexcelDocument10 pagesAS Units Revision Notes IAL EdexcelMahbub KhanNo ratings yet
- Mechanics II: Statics: 1 Balancing ForcesDocument23 pagesMechanics II: Statics: 1 Balancing ForcesEmuNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument49 pagesRotational Equilibrium and Rotational Dynamicsmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Further Maths - Work, Energy and PowerDocument1 pageFurther Maths - Work, Energy and PowerLola SmithNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Science Principles Lecture Notes Guide Ldsm04Document92 pagesMechanical Science Principles Lecture Notes Guide Ldsm04mokuaisaiah769No ratings yet
- WorkDocument5 pagesWorkUmer KhalidNo ratings yet
- AQA Physics Topic 5 Forces Knowledge OrganiserDocument7 pagesAQA Physics Topic 5 Forces Knowledge OrganiserNaveen ChebroluNo ratings yet
- 2024 PHYSICAL Sciences StrategyDocument18 pages2024 PHYSICAL Sciences Strategydarrenstanford3No ratings yet
- Mechanics: PhysicsDocument24 pagesMechanics: PhysicsAziz KarimNo ratings yet
- Y13 MechanicsDocument5 pagesY13 MechanicsphanhNo ratings yet
- Physics Gce o Level Syllabus 2010 2Document44 pagesPhysics Gce o Level Syllabus 2010 2abi_5dec94100% (3)
- Physics NotesDocument38 pagesPhysics NotesAlexNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumDocument3 pages2.3 Work Energy Power and MomentumEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- LN005 MN116 Centre of GravityDocument61 pagesLN005 MN116 Centre of Gravityjordangeorge.66jNo ratings yet
- Understanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsFrom EverandUnderstanding Vector Calculus: Practical Development and Solved ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Container LiquidsDocument202 pagesContainer Liquidsanon_484117881No ratings yet
- Frequency of Free Damped Vibrations (Viscous Damping)Document8 pagesFrequency of Free Damped Vibrations (Viscous Damping)ذوالفقار علي حسينNo ratings yet
- Aerial Robotics Lecture 1B - 1 Basic MechanicsDocument4 pagesAerial Robotics Lecture 1B - 1 Basic MechanicsIain McCulloch100% (3)
- Double-Jet Ejection of Cooling Air For Improved Film-CoolingDocument11 pagesDouble-Jet Ejection of Cooling Air For Improved Film-CoolingAlexandros DerkNo ratings yet
- Return Date Instructor: Dr. Alizadeh Spring SemesterDocument5 pagesReturn Date Instructor: Dr. Alizadeh Spring SemesterANH DoNo ratings yet
- UBC97 Seismic Design PresentationDocument55 pagesUBC97 Seismic Design Presentationmario_gNo ratings yet
- Pool Foundation DesignDocument91 pagesPool Foundation Designradespino1No ratings yet
- Final Project For Advanced Fluid MechanicsDocument15 pagesFinal Project For Advanced Fluid MechanicsMohammed SulemanNo ratings yet
- January 2011 MS - Unit 1 WJEC Physics A-LevelDocument4 pagesJanuary 2011 MS - Unit 1 WJEC Physics A-Levelfadi baqainNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample TestDocument3 pagesPhysics Sample Testumaima rizwanNo ratings yet
- Motion 5Document5 pagesMotion 5gobinda prasad barmanNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice ProblemDocument2 pagesPhysics Practice ProblemnurulalomadorNo ratings yet
- 05 RCC - MDocument46 pages05 RCC - MSafikul HossainNo ratings yet
- Buoyancy Problem SetDocument5 pagesBuoyancy Problem Setjohn harold lopez cabuquitNo ratings yet
- ME2112 - (Part 1) - Shear Stress in Beams-L1 PDFDocument4 pagesME2112 - (Part 1) - Shear Stress in Beams-L1 PDFShang PingNo ratings yet
- Definition 1: Definition 2:: Work Is A Transfer of EnergyDocument3 pagesDefinition 1: Definition 2:: Work Is A Transfer of EnergyS M DineshNo ratings yet
- AQA As Unit 2 Sample PageDocument34 pagesAQA As Unit 2 Sample Pagenchauhan2120% (1)
- Catalog ART 2021Document593 pagesCatalog ART 2021Rubens PetrisNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids 5Th Edition Potter Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument64 pagesMechanics of Fluids 5Th Edition Potter Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFJacobFloresxbpcn100% (14)
- Chapter 3 Lecture 1Document19 pagesChapter 3 Lecture 1Yonatan TesfayeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Intro To Structural Steel DesignDocument10 pagesMODULE 1 - Intro To Structural Steel DesignGail Nathalie LiraNo ratings yet
- Propped Cantilever With UdlDocument5 pagesPropped Cantilever With UdlIqbal Hossain50% (4)
- CFD Analysis of Heat Transfer in A Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Using FluentDocument48 pagesCFD Analysis of Heat Transfer in A Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Using FluentManishSharma90% (10)
- Tutorial (Annotated) 1.2 MotionDocument8 pagesTutorial (Annotated) 1.2 Motionliming chenNo ratings yet
- 2 - 1 - Ejercicios Comportamiento ElastoplasticoDocument7 pages2 - 1 - Ejercicios Comportamiento ElastoplasticoConstanza de la FuenteNo ratings yet
- Mitchell 2014Document13 pagesMitchell 2014Kingshuk MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Machine Fault Simulator (MFS) For Fault DiagnosisDocument8 pagesDesign and Development of Machine Fault Simulator (MFS) For Fault DiagnosisAnonymous pKuPK3zUNo ratings yet
- Discussion and Conclusion (Flat Boundary Layer)Document2 pagesDiscussion and Conclusion (Flat Boundary Layer)Falcon Ford100% (1)
- Chapter 3. Reversibility and Entropy: Initial State Final StateDocument25 pagesChapter 3. Reversibility and Entropy: Initial State Final Stateanand singhNo ratings yet