Professional Documents
Culture Documents
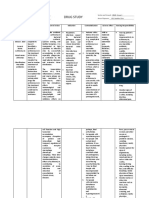
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Jhanna Mae BalbonOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Jhanna Mae BalbonCopyright:
Available Formats
PATIENT VILLE**S
UROSEPSIS- Urosepsis is a severe and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a urinary
tract infection (UTI) progresses to a systemic infection, leading to sepsis. Sepsis is a serious condition
where the body's response to infection can result in widespread inflammation, organ failure, and death if
not treated promptly.
Signs and symptoms of urosepsis may include:
1. Fever and Chills: A high fever, often accompanied by chills, is a common symptom of urosepsis.
2. Increased Heart Rate (Tachycardia): The heart rate may become abnormally fast as the body
tries to respond to the infection.
3. Hypotension (Low Blood Pressure): Urosepsis can lead to a drop in blood pressure, which can
result in dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting.
4. Confusion or Altered Mental State: In severe cases, urosepsis can affect the brain, leading to
confusion or changes in consciousness.
5. Increased Respiratory Rate (Tachypnea): The body may respond to the infection by increasing
the respiratory rate.
6. Pain or Discomfort: There may be pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen, pelvis, or back,
which could be associated with the urinary tract infection.
7. Dysuria: Pain or a burning sensation during urination is a common symptom of a urinary tract
infection.
8. Frequent Urination: An increased urge to urinate may be present.
9. Cloudy or Foul-Smelling Urine: Changes in the appearance or odor of urine can be indicative of a
urinary tract infection.
10. Nausea and Vomiting: Urosepsis can cause gastrointestinal symptoms, including nausea and
vomiting.
DRUG MECHANISM OF INDICATION CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE
NAME ACTION REACTION
Generic Azithromycin • Treatment of respiratory • Hypersensitivity to • Common side
Name: inhibits bacterial tract infections (e.g., azithromycin or effects include:
Azithromycin protein synthesis by pneumonia, bronchitis) other macrolide gastrointestinal
Brand Name: binding to the 50S • Treatment of skin and antibiotics disturbances
Zithromax, ribosomal subunit soft tissue infections • Concomitant use (nausea,
Zmax of susceptible • Sexually transmitted with ergotamine abdominal
Classification: microorganisms, infections (e.g., or pain, diarrhea)
Macrolide thus preventing the chlamydia, gonorrhea) dihydroergotamine • Serious side
Antibiotic formation of effects may
• Prevention and
Actual functional 70S include:
treatment of
dosage, ribosomes. hepatotoxicity
Mycobacterium avium
route, and QT interval
complex (MAC) in certain
frequency: prolongation.
immunocompromised
500 mg/tab
patients • Allergic
1 tab PO, OD reactions,
include: rash
and anaphylaxis
Before During After
1. Conduct a thorough patient 1. Verify prescription. 1. Continuously monitor the patient for
assessment, including Confirm the prescription therapeutic effects and potential adverse
medical history, allergies, details, including the reactions.
and current medications to correct dosage, route, 2. Assess vital signs, including temperature,
identify any and frequency, before heart rate, respiratory rate, and blood
contraindications or preparing the pressure.
potential interactions. medication. 3. Address any discomfort or side effects the
2. Check relevant laboratory 2. Check for allergies to patient may be experiencing, such as nausea
values, such as liver azithromycin or other or gastrointestinal upset.
function tests, as macrolide antibiotics. 4. Educate the patient about the importance of
azithromycin may impact 3. Prepare the medication completing the entire course of antibiotics,
liver function. according to institutional even if the patient feels better before
3. Provide the patient with policies and procedures,
completion.
information about the ensuring accuracy in
5. Educate the patient about potential side
medication, including its dosage and
effects and when to seek medical attention.
purpose, potential side administration route.
6. Emphasize the importance of infection
effects, and the importance 4. Administer azithromycin
control practices, including proper hand
of completing the full as prescribed, whether
hygiene, to prevent the spread of infection.
course of treatment. it's an oral tablet, liquid,
4. Obtain informed consent or intravenous
from the patient before formulation.
administering the 5. Administer oral forms
medication, explaining the with or without food,
risks and benefits. depending on the
specific product
instructions.
6. Monitor the patient for
any immediate adverse
reactions during and
after administration.
7. Observe for signs of an
allergic reaction, such as
rash, itching, or difficulty
breathing.
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE REACTION
ACTION
Generic Name: Carvedilol is a non- • Heart Failure: • Known • Dizziness, fatigue,
Carvedilol selective beta- Carvedilol is hypersensitivity hypotension, and
Brand Names: blocker that blocks indicated for to carvedilol. bradycardia.
Coreg, Coreg CR both beta-1 and the treatment • Severe • Serious side effects
Classification: Non- beta-2 receptors. It of heart bradycardia, may include heart
selective beta- also has alpha-1 failure (HF) in heart block failure
blocking activity that patients with greater than first
blocker, alpha-1 reduces the heart reduced left degree, exacerbation,
blocker rate and contractility, ventricular decompensated bronchospasm, and
Actual dosage, leading to a decrease ejection heart failure, liver dysfunction.
route, frequency: in cardiac output. fraction. asthma, and
6.25 mg/ tab Alpha-1 blockade • Hypertension: certain other
1 tab PO, BID causes vasodilation, It is also used conditions.
contributing to its to manage
antihypertensive essential
effects. hypertension.
Before During After
1. Conduct a comprehensive 1. Confirm the correct 1. Document the administration details,
assessment of the patient, medication, dose, and route including the time, dosage, and any
including vital signs, heart rate, before administration. observed patient responses.
blood pressure, and any signs 2. Monitor blood pressure, 2. Reinforce medication instructions,
or symptoms of heart failure. heart rate, and respiratory including the importance of taking
2. Assess the patient's medical rate regularly during and after Carvedilol as prescribed and not
history, especially focusing on administration. skipping doses.
cardiovascular and respiratory 3. Hold the dose and notify the 3. Educate the patient about potential
conditions. healthcare provider if vital side effects, such as dizziness or
3. Confirm the patient's allergy signs indicate a need for fatigue.
status, especially any known dosage adjustment. 4. Provide guidance on managing
allergies to Carvedilol or other 4. Assess the patient's response common side effects and symptoms,
beta-blockers. to the medication, including such as orthostatic hypotension or
4. Educate the patient about the improvements or bradycardia.
purpose of Carvedilol, the exacerbations of heart failure
importance of adherence, and symptoms.
potential side effects. 5. Advise the patient to rise
slowly from a sitting or lying
position to prevent
orthostatic hypotension.
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE REACTION
ACTION
Generic Name: Insulin glargine is Insulin glargine is 1. Hypersensitivity 1. Hypoglycemia:
Insulin Glargine designed to provide a indicated for the to insulin glargine Common adverse
Brand Name: slow, continuous release treatment of or any of its effect, especially if
Lantus of insulin, mimicking the diabetes mellitus components. the dosage is too
Classification: basal insulin secretion in adults and high.
Long-acting insulin that occurs in non- children. 2. Injection Site
analog diabetic individuals. This Reactions: Redness,
Actual dosage, results in a relatively swelling, or itching at
route, frequency: constant level of insulin the injection site.
10 units SQ OD qHS
activity over a 24-hour
period.
Before During After
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE REACTION
ACTION
Generic Name: Rebamipide exerts Gastric Ulcers and • Hypersensitivity • Gastrointestinal
Rebamipide mucoprotective Gastritis: to rebamipide or Disturbances:
Brand Name: effects by increasing • Rebamipide any of its Nausea, diarrhea,
Mucosta the production of is indicated components. abdominal
Classification: mucin, which for the discomfort.
Gastrointestinal enhances the treatment • Allergic Reactions:
mucoprotective protective barrier of of gastric Rash, itching,
agent the gastric mucosa. It ulcers and swelling.
Actual dosage, also has anti- gastritis.
route, frequency: inflammatory and
100 mg/tab antioxidant
1 tab PO, TID properties.
Before During After
DRUG NAME MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS CONTRAINDICATION ADVERSE REACTION
ACTION
Generic Name: The exact • Management • Hypersensitivity • Hepatotoxicity:
Paracetamol mechanism is not of mild to to paracetamol Overdose can lead
Brand Name: fully understood, moderate or any of its to severe liver
Acetaminophen but paracetamol is pain (such as components. damage.
Classification: believed to inhibit headache, • Severe liver • Allergic reactions
• Classification: the synthesis of muscle disease. (rare).
Analgesic (pain prostaglandins in aches, and
reliever) the central nervous toothache)
• Antipyretic system, leading to • Reduction of
(fever reducer) its analgesic and fever
Actual dosage, route, antipyretic effects.
frequency: 300 mg
IVTT
Q4 PRN for fever with
T >38 °C
Before During After
You might also like
- NCLEX SimpleNursing PediatricsDocument120 pagesNCLEX SimpleNursing PediatricsOlrac Agairdam100% (5)
- Grabovoi NumbersDocument25 pagesGrabovoi Numberssorin6186% (14)
- An Individual Case Study Entitled PYELONEPHRITISDocument12 pagesAn Individual Case Study Entitled PYELONEPHRITISShane JacobNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY DoxycyclineDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY DoxycyclineAMIN BARINo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For ThyroidectomyDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For ThyroidectomyHARVEY SELIM100% (2)
- Generic Name: Classification: IndicationDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Classification: IndicationKristine YoungNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAndrea Isabel U. O'DellNo ratings yet
- Post Test - CasesDocument5 pagesPost Test - CasesChristian Angelo LeonorNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAzithromycin Drug StudySHEILA MAE SACLOTNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument29 pagesAntimicrobial AgentsGwyneth Maehram Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Prescriber - 2010 - Fallon - Recommended Drug Options for Nausea and VomitingDocument8 pagesPrescriber - 2010 - Fallon - Recommended Drug Options for Nausea and VomitingI CbergNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJavie Bryant RedilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument10 pagesDrug Study FinalJashine DajayNo ratings yet
- EthambutolDocument1 pageEthambutolSibel ErtuğrulNo ratings yet
- Druggggggg StudyDocument8 pagesDruggggggg StudyAcob, Jean LykaNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document6 pagesModule 3richelleambrocio054No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial AgentsDocument14 pagesAntimicrobial AgentsMay Chelle ErazoNo ratings yet
- Anti InfectivesDocument126 pagesAnti Infectiveseunice lachicaNo ratings yet
- 5 Drug Study SampleDocument5 pages5 Drug Study SampleMarianne Angela CortezNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial DrugsDocument20 pagesAntimicrobial Drugsnadar shahNo ratings yet
- Albacio Eddiva Dapli-An Magwilang MaspilDocument138 pagesAlbacio Eddiva Dapli-An Magwilang MaspilJustineNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument5 pagesDocumentPRECIOUS LOVE LAGRIMASNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide DrugDocument1 pageMetoclopramide DrugMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyCris SolisNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime ZoltaxDocument2 pagesCefuroxime ZoltaxMJformorejokes minecraftNo ratings yet
- Antifungals 2Document2 pagesAntifungals 2Aldrin Francis TacangNo ratings yet
- CDU Care Plan. UTIDocument7 pagesCDU Care Plan. UTImutiso mutieNo ratings yet
- Copydrugstudy 03Document61 pagesCopydrugstudy 03Ishtar LovernNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Losartan DRUG STUDYDocument7 pagesCefuroxime Losartan DRUG STUDYKiela Therese LabroNo ratings yet
- SURGERYDocument13 pagesSURGERYSVPSNo ratings yet
- Risk Factor PneumoniaDocument6 pagesRisk Factor Pneumoniaali subchanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Guidelines For Adults 2018 PDFDocument58 pagesAntibiotic Guidelines For Adults 2018 PDFAhmad RizqiNo ratings yet
- Chf-Drug StudyDocument6 pagesChf-Drug StudySophia Kaye AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- NCM 106 AntibacterialDocument11 pagesNCM 106 AntibacterialBruno, Kurt Andrei V.No ratings yet
- Week 4 Chemotherapeutic AgentsDocument339 pagesWeek 4 Chemotherapeutic AgentsLassie AbusadoNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Agents 2021Document82 pagesAntimicrobial Agents 2021Aprilene Angel Balaque ZunegaNo ratings yet
- Anti InfectivesDocument40 pagesAnti InfectivesIconMaicoNo ratings yet
- D. Antiviral Antiprotozoal AntihilmenticsDocument31 pagesD. Antiviral Antiprotozoal AntihilmenticsKim Shyen BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic PolicyDocument38 pagesAntibiotic Policysapphiresalem9No ratings yet
- AminoglycosidesDocument5 pagesAminoglycosidesFerreze AnnNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument2 pagesMetoclopramidehoneyNo ratings yet
- DrugStudy SedinioDocument4 pagesDrugStudy Sediniociela00034No ratings yet
- Celecoxib OSDocument2 pagesCelecoxib OSCrissah LacernaNo ratings yet
- Piddig. Yuan Marcos - Dela Cruz Angela Corine, UDocument15 pagesPiddig. Yuan Marcos - Dela Cruz Angela Corine, UAngela CorineNo ratings yet
- Refamonte Ceftriaxone DexamethasoneDocument4 pagesRefamonte Ceftriaxone DexamethasoneMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Anti Tuberculars Fungals ViralsDocument51 pagesAnti Tuberculars Fungals ViralsTito, Stephen Gabriel, A.No ratings yet
- Drug Data Generic Name: 0.5% Sodium Chloride Brand Name: Plain Natural Saline SolutionDocument10 pagesDrug Data Generic Name: 0.5% Sodium Chloride Brand Name: Plain Natural Saline SolutionHayashi Breads MaaNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)Document1 pagePiperacillin Tazobactam (Zosynpiperacillin)ENo ratings yet
- K6. Penggunaan Antibiotik RasionalDocument32 pagesK6. Penggunaan Antibiotik RasionalAfdaliaNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin TazobactamDocument5 pagesPiperacillin TazobactamJoshua GonzalesNo ratings yet
- 01 Chapter Anti InfectiveDocument90 pages01 Chapter Anti InfectiveMSKCNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chapter - Anti-Infectives EditedDocument102 pages1 - Chapter - Anti-Infectives EditedleonNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LactuloseDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LactuloseBRYCE WILLIAM GONo ratings yet
- Contin. Pharma NotesDocument37 pagesContin. Pharma Notesdelie joy dacdacNo ratings yet
- Respi Sas 26Document3 pagesRespi Sas 26Yuji TanakaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Anticancer and PNSDocument6 pagesAssignment Anticancer and PNSSheky GeriosaaaNo ratings yet
- Azithromycin Medication PDFDocument1 pageAzithromycin Medication PDFmp1757No ratings yet
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (Aids) : DescriptionDocument10 pagesAcquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (Aids) : DescriptiongoyaNo ratings yet
- ClarithromycinDocument3 pagesClarithromycinJoshua GonzalesNo ratings yet
- HTP HemoptysisDocument10 pagesHTP HemoptysisみずNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionFrom EverandHandbook of Drug Interaction and the Mechanism of InteractionRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Pathophysiology of Pyelonephritis: How It HappensDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Pyelonephritis: How It HappensReno Jun NagasanNo ratings yet
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument4 pagesNCP Nursing Care Plan For Urinary Tract InfectionsRaveen mayi89% (9)
- Renal or Urinary Tract DisorderDocument6 pagesRenal or Urinary Tract DisorderMarcel Quario OrinaNo ratings yet
- Philippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFDocument82 pagesPhilippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFVirginia AbalosNo ratings yet
- Vivivian PyelonephritisDocument73 pagesVivivian PyelonephritisGideon Owusu AttaNo ratings yet
- Section 1 Functional Disturbances and Diseases of Kidneys: DR - Damodar SedaiDocument82 pagesSection 1 Functional Disturbances and Diseases of Kidneys: DR - Damodar SedaiShreeya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Jardiance Us PiDocument50 pagesJardiance Us PiWertonNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury Kidney Infection: ClasificationDocument1 pageAcute Kidney Injury Kidney Infection: ClasificationSiti RuchjayaniNo ratings yet
- Basic Microbiology and Infection Control For Midwives-4Document207 pagesBasic Microbiology and Infection Control For Midwives-4rehanaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihDocument29 pagesAntibiotik Dan Antiseptik Saluran KemihPutri Sari SeptirianiNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection: Prof DR DR Jazanul Anwar SPFKDocument32 pagesUrinary Tract Infection: Prof DR DR Jazanul Anwar SPFKdouce3No ratings yet
- Effect of 5 Day Nitrofurantoin Vs Single Dose Fosfomycin On Clinical Resolution of Uncomplicated LUTI in WomenDocument9 pagesEffect of 5 Day Nitrofurantoin Vs Single Dose Fosfomycin On Clinical Resolution of Uncomplicated LUTI in WomenMr. LNo ratings yet
- Urosepsis 1Document7 pagesUrosepsis 1Anonymous Xajh4w100% (1)
- Bacteriuria Asintomática & Embarazo - Smaill 2007Document12 pagesBacteriuria Asintomática & Embarazo - Smaill 2007Rolando LaraNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection in ChildrenDocument74 pagesUrinary Tract Infection in ChildrenNadya Magfira100% (1)
- EAU Guidelines On Urological Infections 2023Document84 pagesEAU Guidelines On Urological Infections 2023AntonisNo ratings yet
- IVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesDocument151 pagesIVMS-Gross Pathology, Histopathology, Microbiology and Radiography High Yield Image PlatesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (2)
- Case Presentation and Discussion: Internal Medicine DepartmentDocument8 pagesCase Presentation and Discussion: Internal Medicine DepartmentCalingalan Hussin CaluangNo ratings yet
- Campbell 12 TH CH 56 Inflammatory and Pain Conditions of The MaleDocument22 pagesCampbell 12 TH CH 56 Inflammatory and Pain Conditions of The MaleIkramIzatNo ratings yet
- Activity 12 MicrolabDocument3 pagesActivity 12 MicrolabDarius June Nolasco SacupasoNo ratings yet
- Infeksionet e Traktit Urinar 4Document23 pagesInfeksionet e Traktit Urinar 4Lindrit AliuNo ratings yet
- K - 9 Urinary Tract Infection (Ilmu Penyakit Dalam)Document24 pagesK - 9 Urinary Tract Infection (Ilmu Penyakit Dalam)Ruthra Devi NarayanasamyNo ratings yet
- Renal Disease in PregnancyDocument32 pagesRenal Disease in PregnancyHannahKarizaNo ratings yet
- Renal FailureDocument56 pagesRenal FailureKoRnflakes100% (2)
- Modul UrologyDocument49 pagesModul UrologysonyNo ratings yet
- UTI TreatmentDocument3 pagesUTI TreatmentMaria RezitadinaNo ratings yet
- MsgenitourinaryDocument7 pagesMsgenitourinarybekbekk cabahugNo ratings yet