Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bosch O2 Intro
Bosch O2 Intro
Uploaded by
Taha ShariatiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bosch O2 Intro
Bosch O2 Intro
Uploaded by
Taha ShariatiCopyright:
Available Formats
The first oxygen sensor
developed by Bosch w as
Figure 1. Bosch oxygen sensor. installed in a Volvo 240/260
series vehicle 25 years ago.
B
osch delivered 10 million oxygen sensors to the U.S.
market in 1976 and by 1983 the number had risen to 50 control range (catalyst window)
million. Today, Bosch produces 33 million oxygen
sensors per year. 1
In 1982 Bosch launched the heated oxygen sensor which NOx
reaches full operability in 30 seconds after a cold engine is Engine
started. The sensor is heated to 400 oC and has a service life of emissions
HC
160,000 km, twice as long as the previous unheated sensor. CO
In 1994 Bosch developed an oxygen sensor with a planar
ceramic structure that is fully functioning 10 seconds after the
vehicle is started. 2
CO
Today’s oxygen sensor NOx
Engine
Oxygen sensors (see Figure 1) are required today due to the emissions HC
increasingly tough exhaust emissions and go hand-in-hand
with the catalytic converters. One oxygen sensor is used in the
exhaust branch right before the catalytic converter. Sometimes
a second oxygen sensor is placed in the exhaust system after the 3
catalytic converter of a spark-ignition engine to permit opti-
mum performance of the three-way catalytic converters. -sensor
The information obtained from the sensors indicates how voltage
complete the combustion process is in the combustion cham-
ber. The optimum readings are obtained when the air to fuel
ratio is 14.7 to one. The stoichiometric air/fuel ratio is the mass 0.975 1.0 1.025 1.05
of 14.7 kg of air to 1 kg of gasoline theoretically necessary for rich lean
Excess- air factor
complete combustion. The excess air factor or air ratio ( )
indicates the deviation of the actual air/fuel ratio from the Figure 2. Control range and reductions in exhaust under three
theoretically required ratio. = (actual induced air mass)/ scenarios. Number 1 is without a catalytic converter. Number 2 is with
(theoretical air requirement). a catalytic converter. Number 3 is the oxygen sensor voltage curve.
Service Tech Magazine/May 2001 13
1. Ceramic coating 2. Electrodes 3. Contacts 4. Housing contacts 1. Porous protective layer 2. External electrode
5. Exhaust pipe 6. Ceramic support shield (porous) 3. Sensor laminate 4. Internal electrode 5. Reference air laminate
7. Exhaust gas 8. Ambient air 6. Insulation layer 7. Heater 8. Heater laminate
9. Connection contacts
8 1
7
5
2
4 3
1
4
2 3 5
6 6
V, voltage 6
Figure 3. Oxygen sensor in exhaust pipe. Figure 6. Operational layers in a planar oxygen sensor.
Variations from this optimum ratio result in various levels The three way catalytic converter is able to reduce the HC,
of emissions. Excess fuel results in the formation of hydrocar- CO, and NOx emissions by more than 98% provided the engine
bons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO). Excess air can cause operates within a very narrow scatter range (<1%) centered
increased levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx). The oxygen sensor around the stoichiometric air/fuel ratio (see Figure 2). A closed
or sensors can identify any variations from the ideal air/fuel loop control system that relies on a closed loop control circuit
ratio and send a signal to the engine management system to to maintain the air/fuel mixture consistently within the optimal
adjust the ignition and injection processes. range known as the catalyst window is the best strategy.
Sensor design
1. Sensor housing 2. Ceramic support tube 3. Connection wire 4. Guard tube with slots
5. Active ceramic sensor layer 6. Contact 7. Protective cap 8. Heater element The oxygen sensor (see Figure 3) is a gal-
9. Crimped connections for heater element 10. Spring washer vanic oxygen concentration cell with a
1 2 3 solid state electrolyte. The solid state elec-
trolyte is an impermeable zirconium diox-
ide ceramic unit stabilized with yttrium
oxide. It is open on one end and closed on
the other. Mounted on both the inner and
outer surfaces are gas permeable platinum
electrodes.
The platinum electrode on the outside
4 5 6 7 8 9 10 acts as a miniature catalyst to support reac-
tions in the incoming exhaust gases and
Figure 4. Heated oxygen sensor. bring them into a state of stoichiometric
balance. The side that is exposed to the
1. Guard tube 2. Ceramic seal assembly 3. Sensor housing 4. Ceramic support tube exhaust gases also has a porous ceramic
5. Planar sensor element 6. Protective cap 7. Connection wire layer (Spinell coating) to protect against
contamination. A metal tube with numer-
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
ous slots guards the ceramic body against
impacts and thermal shocks. The inner
cavity is open to the atmosphere which
serves as the unit’s reference gas.
The two-state sensor operation is based
in the Nernst Principle. The sensor’s ce-
ramic material conducts oxygen ions at
temperatures 350oC and above. Disparities
in oxygen levels on the respective sides of
Figure 5. Planar oxygen sensor the sensor will result in the generation of
14 Service Tech Magazine/May 2001
electrical voltage between the two surfaces. This voltage
1. Mass airflow sensor 2. Engine 3a. Oxygen sensor 1
serves as the index of how much the oxygen levels vary on the 3b. Oxygen sensor 2 4. Catalytic converter 5. Injectors
two sides of the sensor. The amount of residual oxygen in the 6. Electronic control unit
exhaust fluctuates sharply in response to the variation in the Vv Valve control voltage Vs sensor voltage Qe injection quantity
induction mixture’s air/fuel ratio.
Oxygen sensitive voltage generation ranges from 800 to
1000 millivolts for rich mixtures to as low as 100 millivolts for
lean mixtures. The transition from rich to lean corresponds to Exhaust gas
Air
450 to 500 millivolts.
1 2 4
Heated oxygen sensor
3a 3b
An electric heater element (see Figure 4) is used to warm the
Qe
ceramic material when the engine is operating at low load Fuel
factors. At the higher load factors the sensor’s temperature is 5
determined by the exhaust gas. The heated oxygen sensor helps
Vsa Vsb
ensure low and stable emissions due to the consistent mainte- Vv
nance of optimal operating temperatures.
6
Planar oxygen sensor
The basic operating concept (see Figure 5) is the same as the
heated finger- type sensor in that it generates a response curve
with a characteristic jump at equal to one. The planar sensor
is distinguished from the finger type by:
• the solid body electrolyte consists of ceramic layers Figure 8. Diagram of closed a closed-loop mixture control.
• a solid ceramic sealant retains the sensor element within the
sensor casting chamber (diffusion gap) in the Nernst cell. This configuration
• a dual-wall guard tube protects the sensor element against contrasts with the layout of the two-state sensor by maintaining
excessive thermal and physical stresses a consistently stoichiometric air/fuel ratio in the chamber.
The individual active layers (see Figure 6) are manufactured Electronic circuitry modulates the voltage supply to maintain
using silk-screening techniques. Stacking laminated layers the composition of the gas in the monitoring chamber at a
with various configurations makes it possible to integrate a consistent equals one. The pump cell corresponds to lean
heater within the sensor element. exhaust by discharging oxygen from the diffusion gap to the
outside, but reacts to rich exhaust by pumping oxygen from the
Wide band oxygen sensor surrounding exhaust gas into the diffusion gap, reversing the
This sensor expands on the principle of the Nernst unit (two- direction of the current. Because the pumping current is also
state sensor function) by incorporating a second chamber, the proportional to the oxygen concentration and/or oxygen defi-
pump cell (see Figure 7). It is through this small slot in this ciency, it serves as an index of the excess air-factor of the
pump cell that the exhaust gas enters the actual monitoring exhaust gas. An integral heater unit ensures an operating
temperature of at least 600oC.
The two-state unit uses the voltage at the Nernst cell as a
1. Nernst cell 2. Reference cell 3. Heater 4. Diffusion gap direct measurement signal while the wide band sensor employs
5. Pump cell 6. Exhaust pipe special processing and control circuitry to set the pumping
current. This current is then monitored and measured as an
index of the exhaust gas’s excess-air factor. Because sensor
operation is no longer dependent on the step function response
+
- of the Nernst cell, air factors ranging from 0.7 to 4 can be
monitored as a continuous progression. Thus control of the
engine can proceed on a reference spectrum instead of depend-
ing solely upon a single point.
Closed loop cont rol
3 The oxygen sensor relays a voltage signal to the electronic
engine management unit which then issues a command to the
injection system to enrichen or lean out the mixture as indicated
4
by the oxygen sensor’s signal voltage (see Figure 8). The
system thus counters lean mixtures by increasing the injected
fuel quantity and rich mixtures by reducing it.
5 1 2
Information and illustrations for this article supplied by
6
Bosch.
Figure 7. Design of a continuous action, wide-band oxygen sensor Interesting? Circle 11
showing the sensor’s installation in the exhaust pipe. Not interesting: Circle 12
Service Tech Magazine/May 2001 15
You might also like
- What Is Decarbonization ?: Main Engine Decarb Preparation, Procedure & Commissioning Sumit NarayanDocument3 pagesWhat Is Decarbonization ?: Main Engine Decarb Preparation, Procedure & Commissioning Sumit NarayanManisha100% (1)
- Lower Fuel Consumption With New Oxygen SensorsDocument4 pagesLower Fuel Consumption With New Oxygen Sensorsddi11100% (1)
- Lambda Sensor PDFDocument3 pagesLambda Sensor PDFManuel João JoãoNo ratings yet
- Zirconium Oxide Oxygen SensorsDocument3 pagesZirconium Oxide Oxygen SensorsBhavin GandhiNo ratings yet
- Oxygen SensorDocument8 pagesOxygen SensormelquicedecNo ratings yet
- Comparison of CyclesDocument32 pagesComparison of CyclesS.Ashwin DanielNo ratings yet
- Assets AMA Conferences AMA Conferences 2017 Proceedings 2017 SENSOR 2017 P5.17Document3 pagesAssets AMA Conferences AMA Conferences 2017 Proceedings 2017 SENSOR 2017 P5.17Visnu SankarNo ratings yet
- City O2Document8 pagesCity O2hocolonkoNo ratings yet
- Automotive ApplicationsDocument10 pagesAutomotive Applicationsrajesh langojuNo ratings yet
- Analizador de Combustion AmbientalDocument8 pagesAnalizador de Combustion AmbientalVendedor VariosNo ratings yet
- Wideband O2 Sensor - Part1Document9 pagesWideband O2 Sensor - Part1RenéNo ratings yet
- Simulation and Design of Ethylene Furnaces Applying Ultra-Low Nox BurnersDocument10 pagesSimulation and Design of Ethylene Furnaces Applying Ultra-Low Nox BurnersLindsey BondNo ratings yet
- Design of A Small SOFC Reactor and Its Heat Exchange System: Conference PaperDocument5 pagesDesign of A Small SOFC Reactor and Its Heat Exchange System: Conference PaperRizky KusumastutiNo ratings yet
- Evaporative Emission Control System Prototype Model-IJAERDV04I0249162Document3 pagesEvaporative Emission Control System Prototype Model-IJAERDV04I0249162Editor IJAERDNo ratings yet
- Project On Gas SensorDocument30 pagesProject On Gas Sensoryoursweetom282815100% (1)
- Increasing Efficiency of Ic Engine by Electrolysis ProcessDocument5 pagesIncreasing Efficiency of Ic Engine by Electrolysis ProcessjishnuNo ratings yet
- Increasing Efficiency of Icengine Using Electrolysis ProcessDocument5 pagesIncreasing Efficiency of Icengine Using Electrolysis ProcessrassNo ratings yet
- Oxygen SensorDocument10 pagesOxygen SensortotoNo ratings yet
- Sensors 10 06773Document15 pagesSensors 10 06773FarzadNo ratings yet
- Autonext Study Material 5 (Exhaust System) PDFDocument8 pagesAutonext Study Material 5 (Exhaust System) PDFspider ManNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical SensorsDocument9 pagesElectrochemical SensorsRsegurasdfNo ratings yet
- IRJET Magnetic FieldDocument8 pagesIRJET Magnetic FieldRithwik pawarNo ratings yet
- Lambda Sensor: 20 Questions & AnswersDocument16 pagesLambda Sensor: 20 Questions & AnswersAntonio NovakovicNo ratings yet
- The 3-Way Catalytic Converter: A) Invention and Introduction Into Commerce - Impacts and Results B) Barriers NegotiatedDocument64 pagesThe 3-Way Catalytic Converter: A) Invention and Introduction Into Commerce - Impacts and Results B) Barriers NegotiatedsikmmmppsNo ratings yet
- CG (Gas Chromatography)Document15 pagesCG (Gas Chromatography)shahebNo ratings yet
- Sensors For Monitoring Environmental Pollution: H - Meixner, J - Gerblinger and M - FleischerDocument10 pagesSensors For Monitoring Environmental Pollution: H - Meixner, J - Gerblinger and M - FleischerNadia F Mohammad Al-RoshdeeNo ratings yet
- NTK O2 Sensor HistoryDocument9 pagesNTK O2 Sensor Historyonukvedat7219No ratings yet
- Brochure GC Nexis 2030Document20 pagesBrochure GC Nexis 2030LABSSSSSNo ratings yet
- WPL 2 Low Dynamic PressureDocument10 pagesWPL 2 Low Dynamic Pressuretw2skgfcmhwtgh2pw04No ratings yet
- Oxygen Sensors Trade BrochureDocument8 pagesOxygen Sensors Trade Brochurehd.gholipourNo ratings yet
- Wartsila Ship EngineDocument5 pagesWartsila Ship EngineDorin SavaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Sensors: Table of ContentDocument9 pagesOxygen Sensors: Table of ContentNicolas MonroyNo ratings yet
- FAQ On Hydrocarbons in Compressed Air SystemsDocument3 pagesFAQ On Hydrocarbons in Compressed Air Systemshadi.pgdNo ratings yet
- Thydzik Conf Hydrogen Concentration Sensor Selection For The Renewable Energy VehicleDocument4 pagesThydzik Conf Hydrogen Concentration Sensor Selection For The Renewable Energy VehiclethydzikNo ratings yet
- How Does The Lambda Sensor WorkDocument24 pagesHow Does The Lambda Sensor WorkMoon boonbon100% (1)
- Investigations On LPG Sensing of Nanostructured Zinc Oxide Synthesized Via Mechanochemical MethodDocument6 pagesInvestigations On LPG Sensing of Nanostructured Zinc Oxide Synthesized Via Mechanochemical MethodAJER JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Ethylene OxideDocument12 pagesEthylene Oxideapi-3838921100% (1)
- Design and Dynamic Characteristics of A Liquid-Propellant Thrust Chamber Avandelino Santana JuniorDocument8 pagesDesign and Dynamic Characteristics of A Liquid-Propellant Thrust Chamber Avandelino Santana JuniorMûkêsh Kàñnâñ AJNo ratings yet
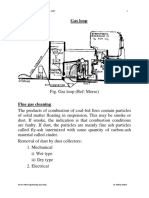
- ME413 (Gas Loop) (161117)Document31 pagesME413 (Gas Loop) (161117)md mahdiNo ratings yet
- Nap 505 ManualDocument30 pagesNap 505 ManualAngelNo ratings yet
- Design of Gasifier System For Diesel Engine PPT FinaleDocument28 pagesDesign of Gasifier System For Diesel Engine PPT FinaleNitu ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Sensor 2Document2 pagesOxygen Sensor 2Kevin Strong100% (1)
- Technical Note 180 SPE 5BSolid Polymer Electrolyte5D Oxygen Sensor 11 05Document2 pagesTechnical Note 180 SPE 5BSolid Polymer Electrolyte5D Oxygen Sensor 11 05Yahya BachtiarNo ratings yet
- Autothermal Reforming of Methane Design and PerforDocument7 pagesAutothermal Reforming of Methane Design and Perforromi moriNo ratings yet
- Helicopter GearboxDocument9 pagesHelicopter GearboxlvrevathiNo ratings yet
- Analizador O2Document23 pagesAnalizador O2joselin gijonNo ratings yet
- Wa0007.Document7 pagesWa0007.aapkistory2021No ratings yet
- Oxygen Transport Membranes For Ultra-Clean Fuel Production: E.T. RobinsonDocument3 pagesOxygen Transport Membranes For Ultra-Clean Fuel Production: E.T. RobinsonAnonymous v9cXHdjNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon DetectionDocument17 pagesHydrocarbon DetectionNovember RainNo ratings yet
- Isuzu EGR Euro4 & 5Document12 pagesIsuzu EGR Euro4 & 5dmit789100% (2)
- Explain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelDocument15 pagesExplain Function of Mass Air Flow Sensor.: The Leaner FuelAbubaker MuzayinNo ratings yet
- Non-Dispersive Infra-Red Absorption (Ndir)Document9 pagesNon-Dispersive Infra-Red Absorption (Ndir)thilip-kumar-6622No ratings yet
- 10 AECS Newsletter - O2 Sensor DiagnosticsDocument6 pages10 AECS Newsletter - O2 Sensor DiagnosticsJordan DechevNo ratings yet
- E406Document4 pagesE406diego100% (1)
- General Engg - IJGET - New Ieee4Document6 pagesGeneral Engg - IJGET - New Ieee4iaset123No ratings yet
- Physico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentFrom EverandPhysico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Biofilms in Bioelectrochemical Systems: From Laboratory Practice to Data InterpretationFrom EverandBiofilms in Bioelectrochemical Systems: From Laboratory Practice to Data InterpretationNo ratings yet
- Braintree 15Document6 pagesBraintree 15paypaltrexNo ratings yet
- A Note On Ethics and StrategyDocument3 pagesA Note On Ethics and StrategyLaura RamonaNo ratings yet
- 2021 YISS - INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS - Hyunjung KimDocument3 pages2021 YISS - INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER GRAPHICS - Hyunjung KimFung AlexNo ratings yet
- 03 Product SpecificationDocument10 pages03 Product Specificationxor_45No ratings yet
- Irctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Document1 pageIrctcs E-Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Jay ParkheNo ratings yet
- CNS-Classifications by Dr-Islahkhan (Humble Pharmacist)Document24 pagesCNS-Classifications by Dr-Islahkhan (Humble Pharmacist)M Ils Meteor Pharmacist0% (1)
- Human Resources Management in 2020.Document11 pagesHuman Resources Management in 2020.DheerajNo ratings yet
- ABLRFD v1403 Summary RevisionsDocument2 pagesABLRFD v1403 Summary RevisionsMiguel AngelNo ratings yet
- LG 29FG1RL 12950 Chassis CW-62C Manual de ServicioDocument34 pagesLG 29FG1RL 12950 Chassis CW-62C Manual de Serviciopepe sanchezNo ratings yet
- Wordlist Unit 3 PDFDocument3 pagesWordlist Unit 3 PDFYea boyNo ratings yet
- Primary Worksheets: Frog Life CycleDocument6 pagesPrimary Worksheets: Frog Life CycleMylene Delantar AtregenioNo ratings yet
- Absolute C 6th Edition Savitch Test BankDocument36 pagesAbsolute C 6th Edition Savitch Test Bankproteosemolehill.g1n1h100% (25)
- Onkyo Repair-Tips (ET)Document34 pagesOnkyo Repair-Tips (ET)perico1962100% (1)
- Documents That Need To Be Submitted During TCSDocument4 pagesDocuments That Need To Be Submitted During TCSAnkur AgrawalNo ratings yet
- User ConsentDocument3 pagesUser ConsentvikuvishnuvikuNo ratings yet
- Price ScheduleDocument10 pagesPrice ScheduleRen SalazarNo ratings yet
- Track ListDocument1 pageTrack ListTiago LopesNo ratings yet
- Procedure: Administering An Intradermal Injection For Skin TestDocument3 pagesProcedure: Administering An Intradermal Injection For Skin TestSofia AmistosoNo ratings yet
- Victoria Resume 2Document2 pagesVictoria Resume 2api-549232785No ratings yet
- ToyotaCare Plus CalculationDocument2 pagesToyotaCare Plus CalculationShao MaNo ratings yet
- Pre Board POL - SCI Paper 2Document6 pagesPre Board POL - SCI Paper 2harsh jatNo ratings yet
- Buying Vs Renting: Net Gain by Buying A HomeDocument2 pagesBuying Vs Renting: Net Gain by Buying A HomeAnonymous 2TgTjATtNo ratings yet
- HTWL Service Manual: Failure ListDocument2 pagesHTWL Service Manual: Failure ListClaudio Valencia MarínNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Temporal Hydrological Variations Due To Land Use Changes Using Remote Sensing/GISDocument38 pagesAssessment of Temporal Hydrological Variations Due To Land Use Changes Using Remote Sensing/GISWubieNo ratings yet
- Kärcher K7 Compact Pressure Washer - 2600 PSI Supercheap AutoDocument1 pageKärcher K7 Compact Pressure Washer - 2600 PSI Supercheap Autobrock.retschlagNo ratings yet
- MIT Insight Report On (Chemistry) Industry DigitalizationDocument21 pagesMIT Insight Report On (Chemistry) Industry DigitalizationEllezah Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- GATES Industrial ManualDocument59 pagesGATES Industrial ManualMartinez Valladares OscarNo ratings yet
- 0399 PDFDocument243 pages0399 PDFOnCo TallaNo ratings yet
- Talent Acquisition 2008 - Survey and Analysis of The Changing Recruiting Landscape PDFDocument20 pagesTalent Acquisition 2008 - Survey and Analysis of The Changing Recruiting Landscape PDFVaishnavi SivaNo ratings yet