Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 Hours
Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 Hours
Uploaded by
AdrianHedleyCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Math5 COT - Reading and Measuring Temperature Using ThermometerDocument4 pagesMath5 COT - Reading and Measuring Temperature Using ThermometerGlenda Manalo Coching100% (5)
- Ujian Pengesanan T5 2021Document5 pagesUjian Pengesanan T5 2021mahfuzah sobriNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument11 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- ShapesofcomplexionsDocument41 pagesShapesofcomplexions/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 4th Sequence Chemistry BonchouDocument3 pages4th Sequence Chemistry BonchouNgah Lilwaine MNo ratings yet
- Sep 2017Document32 pagesSep 2017Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- VariableoxidationstatesDocument84 pagesVariableoxidationstates/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Week 2 Chemistry Paper 1Document13 pagesWeek 2 Chemistry Paper 19wgd495gqyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KS4 LZ 2.2Document16 pagesChemistry KS4 LZ 2.2hiiamoskalawΛwΛ /-No ratings yet
- Chemistry Yr09 t2 2018Document12 pagesChemistry Yr09 t2 2018imanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysisTeena SheikhNo ratings yet
- 2012 June Exam Y10 Chemistry BDF New CourseDocument6 pages2012 June Exam Y10 Chemistry BDF New CourseLeilaNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangesDocument27 pagesEnergy Changesapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 HacDocument16 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Hacdip-sta-06-22No ratings yet
- Year 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- FinalTestALevel1 2Document12 pagesFinalTestALevel1 2herayatiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Questions 2Document44 pagesChemistry Questions 2Yasmine CaparNo ratings yet
- C6a HW - Electrolysis PrinciplesDocument4 pagesC6a HW - Electrolysis PrinciplesAvaani MalhanNo ratings yet
- Test 2-P2Document8 pagesTest 2-P2Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Transition Metals Formation of Coloured Ions QsDocument27 pages2.4 Transition Metals Formation of Coloured Ions QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam Q ADocument14 pagesChemistry Exam Q AmateialesandraNo ratings yet
- GeneralpropertiesDocument31 pagesGeneralproperties/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- More QuestionsDocument86 pagesMore QuestionssuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysislibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure FDocument15 pagesAtomic Structure FMagical UnicornNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3.5 Shapes of Simple Molecules + IonsDocument89 pages3.1.3.5 Shapes of Simple Molecules + IonsTobiNo ratings yet
- Quantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4Document37 pagesQuantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4KshitijNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicDocument21 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicdissaoctafianellisNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Paper 2Document6 pagesGrade 10 Paper 2romiifreeNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Revision Worksheet SolutionDocument6 pagesTerm 1 Revision Worksheet SolutionIndira SeebachanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.4.3 Applications of Hess's LawDocument103 pages3.1.4.3 Applications of Hess's LawRafi MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2021 SAJC Prelim P2 QnsDocument24 pages2021 SAJC Prelim P2 Qns6fhntwb78dNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesandsaltsDocument26 pagesAcids Basesandsaltsremaselshazly76No ratings yet
- SubstitutionreactionsDocument57 pagesSubstitutionreactions/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 2.2 Bonding and Structure QPDocument42 pages2.2 Bonding and Structure QPabisolafaluyi5No ratings yet
- Autumn Pathway ABDocument42 pagesAutumn Pathway ABH ChowdreyNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Transition Metals Substitution Reactions QsDocument23 pages2.2 Transition Metals Substitution Reactions QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- New Document 1: 162 MinutesDocument40 pagesNew Document 1: 162 MinutesDigola WillsNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Reviewapi-383619824No ratings yet
- New Document 1Document7 pagesNew Document 1James YangNo ratings yet
- C6 Electrolysis QuestionsDocument19 pagesC6 Electrolysis QuestionsParam BhimaniNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Transition Metals Variable Oxidation States QsDocument37 pages2.5 Transition Metals Variable Oxidation States QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisDocument17 pagesIB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisFinn Bruchet100% (1)
- Alkane and Alkene Review Question MSDocument19 pagesAlkane and Alkene Review Question MSjw wNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Structure and Bonding HDocument14 pages4.2 Structure and Bonding HMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Homework ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesHomework ElectrolysisMithil KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Applicationsof HessslawDocument92 pagesApplicationsof Hessslaw/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NameDocument81 pages3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NamesuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- CCO 2012 Problems EnglishDocument11 pagesCCO 2012 Problems EnglishmarcusmaaaaaNo ratings yet
- HT PAG 1 ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesHT PAG 1 Electrolysisgg gamerNo ratings yet
- Properties of Period 3 Elements and Their Oxides QPDocument11 pagesProperties of Period 3 Elements and Their Oxides QPfatma sNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Chemical Cells and Fuel Cells QPDocument19 pages5.2 Chemical Cells and Fuel Cells QPOllie TruscottNo ratings yet
- Acidsandbases AllDocument95 pagesAcidsandbases AllarindamNo ratings yet
- F3 CHEM 1st Exam - PDF HermesDocument6 pagesF3 CHEM 1st Exam - PDF HermestonghoyeungNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chemistry (Set-1) (Revised Acheivement Test) 2014-15 Time:1.30 Hrs M.M.40Document2 pagesClass Xii Chemistry (Set-1) (Revised Acheivement Test) 2014-15 Time:1.30 Hrs M.M.40rahulNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesPractice Exam QuestionsThy Random UserNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Reactions of Acids QPDocument43 pages4.2 Reactions of Acids QPAysha NaseerNo ratings yet
- Effectofconcpressure PhysicalchemistryDocument61 pagesEffectofconcpressure Physicalchemistry/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- CCC 2015 PTC ENDocument12 pagesCCC 2015 PTC ENmarcusmaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Chem Final Exam Rev Fall 2017Document6 pagesChem Final Exam Rev Fall 2017fdlsdfsNo ratings yet
- Keto Cheeseburger Mini MeatloafDocument2 pagesKeto Cheeseburger Mini MeatloafAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Low Carb Hungarian Stuffed PeppersDocument2 pagesLow Carb Hungarian Stuffed PeppersAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023Document12 pagesYear 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2022Document14 pagesYear 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2022AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Open The Book-Bible Quiz ChildrenDocument4 pagesOpen The Book-Bible Quiz ChildrenradhikaNo ratings yet
- 3rd PE SUMMATIVE1Document2 pages3rd PE SUMMATIVE1NoreL Jan PinedaNo ratings yet
- Elegy Written in A Country Churchyard SummaryDocument5 pagesElegy Written in A Country Churchyard SummarySathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management SPMDocument16 pagesHuman Resource Management SPMsherif_awadNo ratings yet
- Dip One GoroDocument8 pagesDip One GoroanakayamNo ratings yet
- Onshore Utilities and Water Treatment Facilities Package II Saudi Arabia - Profile - 090122Document7 pagesOnshore Utilities and Water Treatment Facilities Package II Saudi Arabia - Profile - 090122salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Parasitology NotesDocument60 pagesMicrobiology Parasitology Notesaramargareth31No ratings yet
- Realistic Pencil Portrait Mastery - TrainerDocument35 pagesRealistic Pencil Portrait Mastery - TrainerBui Nguyen Hoang HaNo ratings yet
- FortiManager Best Practices GuideDocument23 pagesFortiManager Best Practices GuideIzi Rider100% (1)
- Del Rosario-Igtiben V RepublicDocument1 pageDel Rosario-Igtiben V RepublicGel TolentinoNo ratings yet
- What Is Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) - CorzanDocument8 pagesWhat Is Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) - CorzanmrpalmistNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy SourcesDocument12 pagesAlternative Energy SourcesArodis GomezNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument25 pagesIntroductionMina Kumari SinghNo ratings yet
- Lyrics Inta HayatiDocument3 pagesLyrics Inta HayatiFatimah NadiaNo ratings yet
- November 2023Document1 pageNovember 2023innoozokoNo ratings yet
- Kemapoxy 150Document2 pagesKemapoxy 150Mosaad KeshkNo ratings yet
- Feb Cat TT 2022 (1525)Document1 pageFeb Cat TT 2022 (1525)Tise AkinrinmadeNo ratings yet
- 3GPP LTE (Long Term Evolution) : University of Kansas - School of EngineeringDocument39 pages3GPP LTE (Long Term Evolution) : University of Kansas - School of Engineeringخالد ياسر مواسNo ratings yet
- Vijaya Bank ChanchalDocument2 pagesVijaya Bank ChanchalShubham sharmaNo ratings yet
- Eternal Source - HändelDocument2 pagesEternal Source - HändelColégio de Música de FiãesNo ratings yet
- Cortal V Inaki A Larrazabal EnterprisesDocument11 pagesCortal V Inaki A Larrazabal Enterprisesmarie janNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary & Grammar Test Unit 6 Test ADocument4 pagesVocabulary & Grammar Test Unit 6 Test AStjepan RasicNo ratings yet
- Global AI Governance InitiativeDocument6 pagesGlobal AI Governance InitiativerebvNo ratings yet
- FIP 504 NAA Assignment 1Document2 pagesFIP 504 NAA Assignment 1Srushti RajNo ratings yet
- School Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020Document1 pageSchool Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020CHAPEL JUN PACIENTENo ratings yet
- FINAL TERM P.E.H. 12 Demonstrate Proper Etiquette and Safety in The Use of Facilities and Equipment For Dance ActivitiesDocument3 pagesFINAL TERM P.E.H. 12 Demonstrate Proper Etiquette and Safety in The Use of Facilities and Equipment For Dance Activitiesrandolf wassigNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions - The Dirty DozenDocument5 pagesInterview Questions - The Dirty DozenHimanshu PantNo ratings yet
- Arabic EnglishTranslationinthePalestinian Israeliconflict IdeologyinthewingsDocument18 pagesArabic EnglishTranslationinthePalestinian Israeliconflict IdeologyinthewingsAinaa KhaleesyaNo ratings yet
- Visual Music EbookDocument30 pagesVisual Music EbookAlessandro RatociNo ratings yet
Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 Hours
Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 Hours
Uploaded by
AdrianHedleyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 Hours
Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 Hours
Uploaded by
AdrianHedleyCopyright:
Available Formats
DEPARTMENT FOR CURRICULUM,
LIFELONG LEARNING AND EMPLOYABILITY
Directorate for Learning and Assessment Programmes Track 3
Educational Assessment Unit
Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2023
YEAR 11 CHEMISTRY TIME: 2 hours
Name: _____________________________ Class: _______________
Useful Atomic numbers and relative atomic masses are shown in the Periodic Table printed below.
Data One mole of any gas occupies 22.4 dm3 at standard temperature (0 °C / 273 K) and pressure
(1 atm. / 760 mmHg / 101.3 kPa).
Faraday constant = 96500 C mol-1 Q=It
PERIODIC TABLE
Marks Grid [For Examiner’s use only]
Question Section A Section B
No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Max Theory
10 10 10 10 10 10 20 20 20
Mark Total
Actual
Mark
Theory Paper: 85% Practical: 15% Final Score: 100%
Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 1 of 12
Section A: Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided.
This section carries 60 marks.
1. This question is about solubility and separation techniques.
a. State whether the solubility of a solute in water will increase or decrease with
increasing temperature if the solute is a:
solid: __________________
gas: __________________ (2)
b. The following graph shows the solubility in water of NaCl and KNO3.
Source: https://gradegorilla.com/chemistry/i_EDE/Solubility/IEsolubility1.php
Read the following statements about the solubility of KNO3 and NaCl in water.
Underline the statements that are true. (2)
• At 50 °C NaCl is more soluble than KNO3.
• At 70 °C 160 g of KNO3 would all dissolve in 100 g of water.
• At 5 °C KNO3 is less soluble than NaCl.
• At 40 °C the maximum amount of KNO3 that can be dissolved in 250 g of
water is 150 g.
c. What will happen to a hot saturated solution of copper(II) nitrate as the
solution is cooled down? Underline the correct answer. (1)
• The solvent will evaporate.
• No visible change will occur.
• Crystals will precipitate out of solution.
• The solution will turn from blue to colourless.
Page 2 of 12 Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
d. State which separating technique is suitable to obtain:
i. Iron filings from its mixture with sand.
_________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. Hydrated copper(II) chloride crystals from its solution.
_________________________________________________________ (1)
iii. Lead(II) sulfate produced from the reaction of aqueous lead(II) nitrate and
aqueous sodium sulfate.
_________________________________________________________ (1)
e. Fractional distillation is used to separate a mixture of liquids. Briefly explain how
this technique is used to obtain certain gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, and noble
gases from air.
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 10 marks
2. This question is about the structure of the atom and bonding.
a. Gold (Au) is an important metallic element. Using the Periodic Table provided,
give:
i. the number of protons in a gold atom. __________________________ (1)
ii. the number of neutrons in a gold atom. _________________________ (1)
iii. the number of electrons in the ion formed by gold Au3+. ____________ (1)
b. The table below shows the number of protons in atoms of three elements X, Y,
and Z. These letters are not their chemical symbols.
Element Number of protons
X 12
Y 6
Z 16
i. Using the letters Y and Z, give the formula of a compound that contains the
elements Y and Z. _____________ (1)
ii. Name the type of bonding in the compound formed by Y and Z.
______________ (1)
iii. Using the letters X and Z, give the formula of a compound that is formed
between elements X and Z. _____________ (1)
Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 3 of 12
iv. Draw a dot and cross diagram showing all electron shells, to show the bonding
in the compound formed between X and Z. State the type of bonding in this
compound.
(4)
Total: 10 marks
3. This question is about group 7 elements and their reactivity.
a. Using the Periodic Table provided, arrange the group 7 elements according to
their increasing reactivity, starting with the least reactive element. Use their
chemical symbols in your answer.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
b. Explain why the reactivity in group 7 changes in the order you gave in part (a).
_______________________________________________________________
_______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
c. Oxygen (atomic number 8) is in group 6 of the Periodic Table. Is it more or less
reactive than fluorine (atomic number 9)? Give a reason for your answer.
_______________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________ (2)
d. There are two naturally occurring isotopes of chlorine: Cl-35 and Cl-37.
i. Explain the difference between the two isotopes by referring to the
subatomic particles.
_________________________________________________________ (1)
ii. The relative atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5. Which of the two isotopes is
least abundant in nature?
_________________________________________________________ (1)
Page 4 of 12 Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
e. Chlorine gas is able to turn wet blue litmus paper to red and then bleaches it
white.
i. Complete the following chemical equation for the reaction of chlorine with
water. (1)
Cl2(g) + H2O(l) → _______(aq) + HOCl(aq)
ii. By referring to the above equation, explain the changes caused by chlorine
on a wet blue litmus paper.
____________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 10 marks
4. The following question is about qualitative analysis.
a. The table below shows a number of tests which were carried out on ionic
compounds A to C. All observations made from these tests are included in the
table. (NB: “n/a” means test not carried out.)
Addition of
NaOH(aq)
Effect of Addition of Addition
Flame &
Appearance heat on aqueous of
test aluminium
substance acid NaOH(aq)
turnings +
heat
Gives a Gives a
pungent gas pungent gas
White that turns that turns No visible Lilac
A powder orange orange change colouration
n/a
dichromate dichromate
green green
Gives a gas
Gives a gas Blue
that turns
Bluish-green that turns precipitate, Blue-green
B powder
lime water
lime water insoluble in colouration
n/a
milky and a
milky excess
black solid
Gives a
White pungent gas
White Liberates a
No visible precipitate, No visible that turns
C crystalline brown, toxic
change insoluble in change damp red
solid gas
excess litmus paper
to blue
Write the name or formula of:
Compound A: _____________________________ (2)
Compound B: _____________________________ (2)
Compound C: _____________________________ (2)
Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 5 of 12
b. When sodium hydroxide solution is added dropwise to a solution of iron(III)
chloride, a coloured precipitate is obtained.
i. Write a balanced equation for the reaction of sodium hydroxide solution
(NaOH) with iron(III) chloride (FeCl3) solution.
_________________________________________________________ (2)
ii. What is the colour of the precipitate obtained?
_________________________________________________________ (1)
c. Solution X is added to another solution containing dissolved sodium sulfate
(Na2SO4). The reaction produces a white precipitate which does not react with
dilute acid. Give the chemical formula of solution X.
____________________________________________________________ (1)
Total: 10 marks
5. This question is about rates of reaction.
a. Solid zinc carbonate reacts with dilute sulfuric acid to give a solution of zinc
sulfate, water, and carbon dioxide gas.
i. Write a chemical equation for the reaction.
_________________________________________________________ (2)
ii. The reaction is done twice, once with a 5 g solid block and then using 5
blocks of 1 g each of zinc carbonate. The same volume and concentration of
acid are used in both experiments. Will the rate of the two reactions be the
same? Explain.
____________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________ (2)
b. The reaction between dilute hydrochloric acid and sodium thiosulfate produces
sulfur which is insoluble. The rate of reaction can be followed by monitoring the
cloudiness of the solution with time.
Page 6 of 12 Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
Two experiments are done as follows:
Volume of Vol. of Total
Volume of
0.1 mol dm-3 0.1 mol dm-3 Volume of
Experiment water
Na2S2O3(aq) HCl(aq) mixture
(cm3)
(cm3) (cm3) (cm3)
1 20 30 5 55
2 40 10 5 55
The equation of the reaction is as follows:
2HCl(aq) + Na2S2O3(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) + SO2(g) + S(s) + H2O(l)
i. Explain how and why the rate of the two experiments will differ.
____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________ (2)
ii. Calculate the number of moles of Na2S2O3 in 40 cm3 of 0.1 mol dm-3 Na2S2O3
solution as used in experiment 2.
____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________ (2)
iii. Convert the number of moles of Na2S2O3 calculated in part (b) (ii) to mass
in grams.
____________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 10 marks
6. Hydrocarbons are organic compounds containing hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
a. Name TWO different homologous series which contain only hydrocarbons.
___________________________________________________________ (2)
b. Draw the molecule of ethene and explain why it is known as an unsaturated
compound.
(2)
___________________________________________________________ (1)
Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 7 of 12
c. Name the polymer formed when ethene undergoes polymerisation.
___________________________________________________________ (1)
d. Draw the repeating unit of the polymer mentioned in part (c).
(2)
e. This polymer is not biodegradable. Explain what this statement means and
state what should be done to reduce its negative effects on the environment.
______________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________ (2)
Total: 10 marks
Section B: Answer any TWO questions only on the foolscaps provided. This
section carries 40 marks.
7. Electrolysis is a very important process which is used on a large scale to obtain
important materials.
a. Molten aluminium oxide is electrolysed using inert electrodes in industry.
i. Name the main ore of aluminium. (1)
ii. What are inert electrodes? (1)
iii. Write an ionic half equation for the reaction taking place at the cathode. State
whether it is an oxidation or a reduction. (3)
iv. A current of 25000 A is used to obtain aluminium from its ore in industry.
Calculate the mass of aluminium obtained in 1 hour. (3)
b. Metals can be extracted from their ores using various methods. For example,
iron is obtained from haematite by reduction with carbon monoxide in the Blast
Furnace. However, reactive metals such as aluminium can only be extracted
from their ores by electrolysis. Briefly explain why. (2)
c. Concentrated sodium chloride solution (brine) is also electrolysed in industry on
a large scale. This process yields chlorine gas and hydrogen gas at the
electrodes.
Page 8 of 12 Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
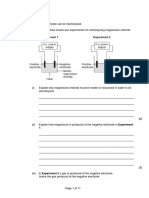
i. Draw a labelled diagram of a suitable setup that can be used to electrolyse a
concentrated solution of sodium chloride in the laboratory, with the aim of
collecting both gases released at the electrodes. (5)
ii. Write an ionic half equation for the reaction taking place at the anode to
produce chlorine. State whether it is an oxidation or a reduction. (3)
iii. During this process, apart from chlorine and hydrogen, another important
substance is produced in the electrolytic cell. Name this substance. (1)
iv. If instead of a concentrated solution, very dilute sodium chloride is
electrolysed, a different product will be formed at the anode. Name this
substance. (1)
Total: 20 marks
8. A student wanted to produce potassium chloride from a neutralisation reaction.
a. Name an alkali and an acid which could be used for this reaction. (2)
b. Write a balanced equation for this reaction including state symbols. (3)
c. Potassium chloride is a soluble salt, so the reaction was carried out in two steps.
First, a titration with an indicator was done and the volumes of acid and alkali
were noted.
In the second part of the experiment the volumes of acid and alkali, as noted
from the first experiment, were mixed in a beaker without the indicator. The
solution was then crystallised to obtain the potassium chloride salt.
i. Name an indicator which could be used in this titration. (1)
ii. Given that 25 cm of 1.5 mol dm acid were used, what volume of
3 -3
2 mol dm-3 alkali was required for complete neutralisation? (3)
iii. Describe how a titration should be carried out. (5)
iv. Draw a diagram of the burette which should be used during the
experiment. (1)
d. In part (c) it was stated that: “In the second part of the experiment the volumes
of acid and alkali, as noted from the first experiment, were mixed in a beaker
without the indicator.” Explain why this is necessary. (2)
e. Calculate the mass of salt which one should expect to collect after
crystallisation. (2)
f. The mass of salt collected was in fact 2.25 g. Give ONE reason which could
explain why this happened. (1)
Total: 20 marks
Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 9 of 12
9. Liquid hydrazine (N2H4) is a very unstable material. It is one of the ingredients used
in rocket fuel. In the presence of oxygen it burns rapidly to form nitrogen and water
vapour.
a. Write a balanced equation for the combustion of hydrazine. (2)
b. Calculate the volume of nitrogen produced at STP from the combustion of 50 g
of hydrazine. (3)
c. Calculate the volume the nitrogen produced in part (b) would occupy, when it
is compressed to a pressure of 203200 Pa. Assume that no temperature changes
occur during compression.
(Standard atmospheric pressure = 101300 Pa) (2)
d. The following table shows the pressure of nitrogen in a closed container at
different temperatures.
Temperature (K) Pressure (kPa)
173 36.00
223 46.40
273 56.70
323 67.10
373 77.50
423 88.00
i. Plot a graph on page 11 of pressure (y-axis) against temperature (x-axis).
Start your y-axis at 35 and the x-axis at 170. (5)
ii. From the graph state what can be concluded about the relationship
between temperature and pressure. (1)
e. Explain, by means of the kinetic theory, why nitrogen can be compressed. (1)
f. Nitrogen can be used in the Haber process to produce ammonia.
i. State the temperature and catalyst used in this reaction. (2)
ii. A pressure of 200 atmospheres is usually employed in this reaction. Write
a balanced equation including state symbols for this reaction and use it to
explain why such a high pressure is required. (4)
Total: 20 marks
Page 10 of 12 Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023 Page 11 of 12
Blank Page
Page 12 of 12 Chemistry – Year 11 – Track 3 – 2023
You might also like
- Math5 COT - Reading and Measuring Temperature Using ThermometerDocument4 pagesMath5 COT - Reading and Measuring Temperature Using ThermometerGlenda Manalo Coching100% (5)
- Ujian Pengesanan T5 2021Document5 pagesUjian Pengesanan T5 2021mahfuzah sobriNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument11 pagesYear 11 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- ShapesofcomplexionsDocument41 pagesShapesofcomplexions/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 4th Sequence Chemistry BonchouDocument3 pages4th Sequence Chemistry BonchouNgah Lilwaine MNo ratings yet
- Sep 2017Document32 pagesSep 2017Dylan EllulNo ratings yet
- VariableoxidationstatesDocument84 pagesVariableoxidationstates/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Week 2 Chemistry Paper 1Document13 pagesWeek 2 Chemistry Paper 19wgd495gqyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry KS4 LZ 2.2Document16 pagesChemistry KS4 LZ 2.2hiiamoskalawΛwΛ /-No ratings yet
- Chemistry Yr09 t2 2018Document12 pagesChemistry Yr09 t2 2018imanNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysisTeena SheikhNo ratings yet
- 2012 June Exam Y10 Chemistry BDF New CourseDocument6 pages2012 June Exam Y10 Chemistry BDF New CourseLeilaNo ratings yet
- Energy ChangesDocument27 pagesEnergy Changesapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Chemistry Paper 1 HacDocument16 pagesChemistry Paper 1 Hacdip-sta-06-22No ratings yet
- Year 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 10 Chemistry Time: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- FinalTestALevel1 2Document12 pagesFinalTestALevel1 2herayatiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Questions 2Document44 pagesChemistry Questions 2Yasmine CaparNo ratings yet
- C6a HW - Electrolysis PrinciplesDocument4 pagesC6a HW - Electrolysis PrinciplesAvaani MalhanNo ratings yet
- Test 2-P2Document8 pagesTest 2-P2Salman Ul MoazzamNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Transition Metals Formation of Coloured Ions QsDocument27 pages2.4 Transition Metals Formation of Coloured Ions QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam Q ADocument14 pagesChemistry Exam Q AmateialesandraNo ratings yet
- GeneralpropertiesDocument31 pagesGeneralproperties/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- More QuestionsDocument86 pagesMore QuestionssuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysislibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure FDocument15 pagesAtomic Structure FMagical UnicornNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3.5 Shapes of Simple Molecules + IonsDocument89 pages3.1.3.5 Shapes of Simple Molecules + IonsTobiNo ratings yet
- Quantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4Document37 pagesQuantititive Chemistry - Paper 1 TES - 4KshitijNo ratings yet
- Topic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicDocument21 pagesTopic Test Oxfordaqa Int A Level Chemistry As Level InorganicdissaoctafianellisNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Paper 2Document6 pagesGrade 10 Paper 2romiifreeNo ratings yet
- Term 1 Revision Worksheet SolutionDocument6 pagesTerm 1 Revision Worksheet SolutionIndira SeebachanNo ratings yet
- 3.1.4.3 Applications of Hess's LawDocument103 pages3.1.4.3 Applications of Hess's LawRafi MohammedNo ratings yet
- 2021 SAJC Prelim P2 QnsDocument24 pages2021 SAJC Prelim P2 Qns6fhntwb78dNo ratings yet
- Acids BasesandsaltsDocument26 pagesAcids Basesandsaltsremaselshazly76No ratings yet
- SubstitutionreactionsDocument57 pagesSubstitutionreactions/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 2.2 Bonding and Structure QPDocument42 pages2.2 Bonding and Structure QPabisolafaluyi5No ratings yet
- Autumn Pathway ABDocument42 pagesAutumn Pathway ABH ChowdreyNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Transition Metals Substitution Reactions QsDocument23 pages2.2 Transition Metals Substitution Reactions QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- New Document 1: 162 MinutesDocument40 pagesNew Document 1: 162 MinutesDigola WillsNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 ReviewDocument5 pagesTopic 2 Reviewapi-383619824No ratings yet
- New Document 1Document7 pagesNew Document 1James YangNo ratings yet
- C6 Electrolysis QuestionsDocument19 pagesC6 Electrolysis QuestionsParam BhimaniNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Transition Metals Variable Oxidation States QsDocument37 pages2.5 Transition Metals Variable Oxidation States QsJesulayomi BolajiNo ratings yet
- IB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisDocument17 pagesIB Chemistry Worksheet 1: Significant Figures and Dimensional AnalysisFinn Bruchet100% (1)
- Alkane and Alkene Review Question MSDocument19 pagesAlkane and Alkene Review Question MSjw wNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Structure and Bonding HDocument14 pages4.2 Structure and Bonding HMagd OsamaNo ratings yet
- Homework ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesHomework ElectrolysisMithil KanojiaNo ratings yet
- Applicationsof HessslawDocument92 pagesApplicationsof Hessslaw/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- 3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NameDocument81 pages3.1.1.3 Electron Configuration: NamesuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- CCO 2012 Problems EnglishDocument11 pagesCCO 2012 Problems EnglishmarcusmaaaaaNo ratings yet
- HT PAG 1 ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesHT PAG 1 Electrolysisgg gamerNo ratings yet
- Properties of Period 3 Elements and Their Oxides QPDocument11 pagesProperties of Period 3 Elements and Their Oxides QPfatma sNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Chemical Cells and Fuel Cells QPDocument19 pages5.2 Chemical Cells and Fuel Cells QPOllie TruscottNo ratings yet
- Acidsandbases AllDocument95 pagesAcidsandbases AllarindamNo ratings yet
- F3 CHEM 1st Exam - PDF HermesDocument6 pagesF3 CHEM 1st Exam - PDF HermestonghoyeungNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Chemistry (Set-1) (Revised Acheivement Test) 2014-15 Time:1.30 Hrs M.M.40Document2 pagesClass Xii Chemistry (Set-1) (Revised Acheivement Test) 2014-15 Time:1.30 Hrs M.M.40rahulNo ratings yet
- Practice Exam QuestionsDocument11 pagesPractice Exam QuestionsThy Random UserNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Reactions of Acids QPDocument43 pages4.2 Reactions of Acids QPAysha NaseerNo ratings yet
- Effectofconcpressure PhysicalchemistryDocument61 pagesEffectofconcpressure Physicalchemistry/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- CCC 2015 PTC ENDocument12 pagesCCC 2015 PTC ENmarcusmaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Chem Final Exam Rev Fall 2017Document6 pagesChem Final Exam Rev Fall 2017fdlsdfsNo ratings yet
- Keto Cheeseburger Mini MeatloafDocument2 pagesKeto Cheeseburger Mini MeatloafAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Low Carb Hungarian Stuffed PeppersDocument2 pagesLow Carb Hungarian Stuffed PeppersAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023Document12 pagesYear 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursDocument12 pagesYear 11 Biology TIME: 2 HoursAdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Year 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2022Document14 pagesYear 10 Biology TIME: 2 Hours: Annual Examinations For Secondary Schools 2022AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- B F3 Annual 2023Document18 pagesB F3 Annual 2023AdrianHedleyNo ratings yet
- Open The Book-Bible Quiz ChildrenDocument4 pagesOpen The Book-Bible Quiz ChildrenradhikaNo ratings yet
- 3rd PE SUMMATIVE1Document2 pages3rd PE SUMMATIVE1NoreL Jan PinedaNo ratings yet
- Elegy Written in A Country Churchyard SummaryDocument5 pagesElegy Written in A Country Churchyard SummarySathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management SPMDocument16 pagesHuman Resource Management SPMsherif_awadNo ratings yet
- Dip One GoroDocument8 pagesDip One GoroanakayamNo ratings yet
- Onshore Utilities and Water Treatment Facilities Package II Saudi Arabia - Profile - 090122Document7 pagesOnshore Utilities and Water Treatment Facilities Package II Saudi Arabia - Profile - 090122salman KhanNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Parasitology NotesDocument60 pagesMicrobiology Parasitology Notesaramargareth31No ratings yet
- Realistic Pencil Portrait Mastery - TrainerDocument35 pagesRealistic Pencil Portrait Mastery - TrainerBui Nguyen Hoang HaNo ratings yet
- FortiManager Best Practices GuideDocument23 pagesFortiManager Best Practices GuideIzi Rider100% (1)
- Del Rosario-Igtiben V RepublicDocument1 pageDel Rosario-Igtiben V RepublicGel TolentinoNo ratings yet
- What Is Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) - CorzanDocument8 pagesWhat Is Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride (CPVC) - CorzanmrpalmistNo ratings yet
- Alternative Energy SourcesDocument12 pagesAlternative Energy SourcesArodis GomezNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument25 pagesIntroductionMina Kumari SinghNo ratings yet
- Lyrics Inta HayatiDocument3 pagesLyrics Inta HayatiFatimah NadiaNo ratings yet
- November 2023Document1 pageNovember 2023innoozokoNo ratings yet
- Kemapoxy 150Document2 pagesKemapoxy 150Mosaad KeshkNo ratings yet
- Feb Cat TT 2022 (1525)Document1 pageFeb Cat TT 2022 (1525)Tise AkinrinmadeNo ratings yet
- 3GPP LTE (Long Term Evolution) : University of Kansas - School of EngineeringDocument39 pages3GPP LTE (Long Term Evolution) : University of Kansas - School of Engineeringخالد ياسر مواسNo ratings yet
- Vijaya Bank ChanchalDocument2 pagesVijaya Bank ChanchalShubham sharmaNo ratings yet
- Eternal Source - HändelDocument2 pagesEternal Source - HändelColégio de Música de FiãesNo ratings yet
- Cortal V Inaki A Larrazabal EnterprisesDocument11 pagesCortal V Inaki A Larrazabal Enterprisesmarie janNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary & Grammar Test Unit 6 Test ADocument4 pagesVocabulary & Grammar Test Unit 6 Test AStjepan RasicNo ratings yet
- Global AI Governance InitiativeDocument6 pagesGlobal AI Governance InitiativerebvNo ratings yet
- FIP 504 NAA Assignment 1Document2 pagesFIP 504 NAA Assignment 1Srushti RajNo ratings yet
- School Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020Document1 pageSchool Action Plan in NDEP 2019 2020CHAPEL JUN PACIENTENo ratings yet
- FINAL TERM P.E.H. 12 Demonstrate Proper Etiquette and Safety in The Use of Facilities and Equipment For Dance ActivitiesDocument3 pagesFINAL TERM P.E.H. 12 Demonstrate Proper Etiquette and Safety in The Use of Facilities and Equipment For Dance Activitiesrandolf wassigNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions - The Dirty DozenDocument5 pagesInterview Questions - The Dirty DozenHimanshu PantNo ratings yet
- Arabic EnglishTranslationinthePalestinian Israeliconflict IdeologyinthewingsDocument18 pagesArabic EnglishTranslationinthePalestinian Israeliconflict IdeologyinthewingsAinaa KhaleesyaNo ratings yet
- Visual Music EbookDocument30 pagesVisual Music EbookAlessandro RatociNo ratings yet